Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) Business - 1 - Business activity and influences on business
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Financial aims and objectives
Are linked to money. Their goal is to either make sure the business can afford to keep running or help it to make a profit.
Survival
Is a very common objective for a small business. Business survival refers to keeping the business operating for a certain amount of time. Most businesses initially aim to survive their first year.
Profit
Refers to any money left over after all costs have been taken away from any revenue made by a business. Businesses usually aim to make a profit within the first two years.
Sales
Refer to an amount of a product or service sold by a business. A business will set a target for how much it wants to sell each month and year. This gives the business a target to aim for and a purpose to what its employees do each day.
Market share
Refers to the percentage of the market that a business occupies. The market is the industry that a business operates in, for example the fast food industry. An example of an objective for market share might be 'to have 5% share of the fast food market within a 100-mile radius in the first 12 months'.
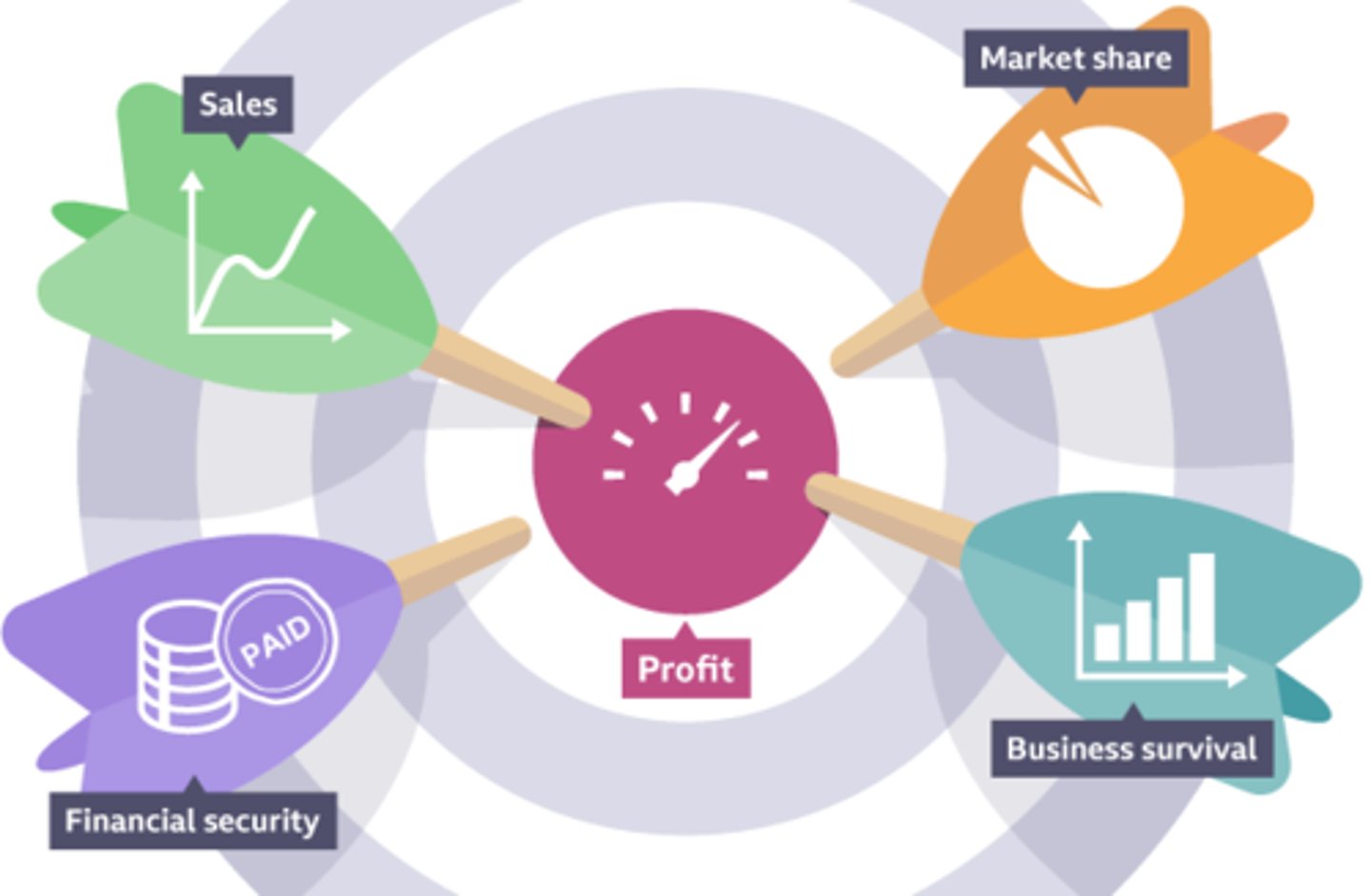
Financial security
Relates to a business being able to afford to pay off all its costs and have enough cash left to survive. It also relates to an entrepreneur achieving a level of income that will allow them to keep the business operating.
Non-financial aims and objectives
Are linked to anything other than making money for the business. These are usually linked to personal reasons behind an entrepreneur setting up a business.
Social objectives
Are linked to doing things in an ethical or environmentally friendly manner, or having a business whose sole purpose is to meet a social need. For example, an entrepreneur may aim to provide only products that are sustainably sourced or use only solar energy to power their business.

Personal satisfaction
Relates to an entrepreneur feeling satisfaction that they have created a successful business. It may be that an entrepreneur is able to make a business out of a hobby or personal interest.

Challenge
Relates to an entrepreneur setting up a business with the intention that making it successful will challenge them or take them out of their comfort zone.

Control
Relates to an entrepreneur's goal of being able to control the business and make decisions about how it is run. These aims and objectives may relate to decisions around what the business sells, where it buys raw materials from, and how much its product or service is sold for.

Independence
Relates to an entrepreneur working for themselves and running their own business. It is also to do with them making their own key business decisions. A desire for independence is a common reason for an entrepreneur to set up a business.
Why business aims and objectives change: market conditions
The introduction of new products from competitors is an example of how the competitive environment changes. Therefore a business in this situation may focus on protecting its market share.
Why business aims and objectives change technology
Development in technology/new technology from competitors might change existing product designs. Therefore a business may improve their own product range. Failing to do this could affect the business’s ability to achieve its sales and profits aims and objectives.
Why business aims and objectives change performance
A business may have suffered from diseconomies of scale due to poor communication and low levels of staff morale. Therefore it opts to focus on survival whilst it attempts to increase productivity and sales revenue.
Why business aims and objectives change: legislation
Legislation changes such as the need to put in place new COVID 19 health and safety measures will increase set up and running costs. This in turn will impact the extent to which a business will attain its profit maximisation aims and objectives.
Why business aims and objectives change internal reasons
A prolonged loss of focus and poor co-ordination may have contributed to a lack of management/business owners control over the employee performance. Therefore the business owners/managers may introduce new methods of monitoring and control over the day to day supervision of employee performance.
Sole trader
Individual who runs an unincorporated business on his/her own.
PROS – makes all the final decisions and keeps all the profits
CONS – personally liable (unlimited liability) for the debts of the business and has the stress of making all the final decisions

Partnership
An association of two or more people formed for the purpose of setting up and running a business.
PROS – the workload is shared and ability to raise larger amounts of startup capital
CONS – all partners are personally liable (unlimited liability) for the debts of the business and profits have to be shared

Private Limited Company (Ltd)
A private limited company (LTD) and in fact also a public limited company (PLC) have a separate legal identify from its shareholders
PROS – can raise more startup capital by selling shares privately and have limited liability – meaning that if the LTD fails the shareholders are not liable for debts of the company they are limited to lose only what they invested in the company.
CONS – cannot sell shares publically on the stock market and it takes longer to set up due to increased governmental processes to complete

Public limited company (plc)
Like LTDs has a separate legal identity but also the company's shares may be offered for sale to members of the general public.
PROS – can raise more startup capital by selling shares publicly and have limited liability.
CONS – risk of takeovers and have to publish their accounts so competitors can view their financial information.

Public corporations
Public corporations have a separate legal existence. Their assets are owned by the government but on behalf of the public. Their objectives emphasise social aspects. Examples would be the BBC or Royal Mail. However even such corporations are influenced by commercial considerations like generating profits.
PROS – Services are not duplicated by multiple competitors and therefore resources are not wasted. The profits made by the public corporation can be reinvested in the economy by the government.
CONS – The running of the public corporation can be politically motivated by governments wanting to win elections. Often tax payers have to pay higher taxes to cover any losses made by the public corporation.

Stakeholder
A stakeholder is any individual or organisation who has an interest in the activities and decision making of a particular business.
Shareholder
Is a part owner of a company.

Franchises
When a franchisor grants a license (franchise) to another business (franchisee) to allow it trade using the brand / business format.
Advantage to franchisor much quicker geographical growth and source of profits for the franchisor.
Disadvantage to franchisor hard to manage levels of quality of product/service and therefore a huge risk to reputation of the business.
Advantage to franchisee benefits of national advertising and support and training from the franchisor.
Disadvantage to franchisee costs to buy a franchised is expensive and often have to pay a percentage of profit and sometimes also sales revenue to the franchisor.

Social enterprise
Businesses whose profits are reinvested to achieve specific social purpose.
Advantage of tax breaks and higher success rate in raising finance through crowd funding websites.
Disadvantage in that it is harder to raise finance from banks and attract investors as profit making is not the main aim.

Multinational company (MNC)
A multinational company (MNC) is a business organisation that has its operations in more than one country.
PROS – MNC’s can be a source of foreign investment to a host country, and can create employment opportunities for citozens in the host country.
CONS – The jobs created by MNE's are often low skilled which allows MNCs to exploit the availability of cheap labour. Workers in such MNCs work long hours for low wages. MNCs also add to the environmental degradation in developing countries by over mining for raw materials.

limited liability
the liability of a firm's owners for no more than the capital they have invested in the business.
unlimited liability
requirement that an owner is personally and fully responsible for all losses and debts of a business
privatisation
The sale of public sector organisations i.e. public corporations to the private sector
nationalisation
The sale of private sector businesses to the government. The sale may be voluntary, forced, coerced or the assets simply expropriated (taken over)
Primary sector
The part of the economy that draws raw materials from the natural environment

Secondary sector
The part of the economy that transforms raw materials into manufactured goods

Tertiary sector
The part of the economy that involves the sale of goods and services.

Proximity to market
Businesses that serve their customers directly must be located close to those customers.

Labour
The physical and mental human effort used in the production process

Business activity
The process of producing goods and services to satisfy consumer needs and wants

E-commerce
The buying and selling of goods over the internet

Globalisation
The increasing integration of economies and societies around the world particularly through international trade.

Exchange rate
The value of a currency in one country compared with the value in another

Currency appreciation
For example, if the value of the pound changes from £1 = US $1.20 to £1 = US $1.25 then £100 would now convert to US $125 ($1.25x£100)instead of US $120. This is known as an appreciation in the value of the pound.

Currency depreciation
A depreciation in the value of the pound, eg from £1.00 = US $1.20 to £1.00 = US $1.10, would mean that less foreign currency can be obtained for the same amount of domestic currency. So, the pound has become weaker.

Public spending
How the government spends the money it makes on public services (through taxes, for example).

Public Services
Services provided by a government such as education

Taxation
Money raised by the government to provide services for the common good of the community/country

Infrastructure
Fundamental facilities and systems serving a country, city, or area, as transportation and communication systems, power plants, and schools

Legislation
A law or set of laws made by a government that can act as a constraint or an enabler of opportunties for businesses.

Trade policy
A government policy that directly influences the quantity of goods and services that a country imports or exports

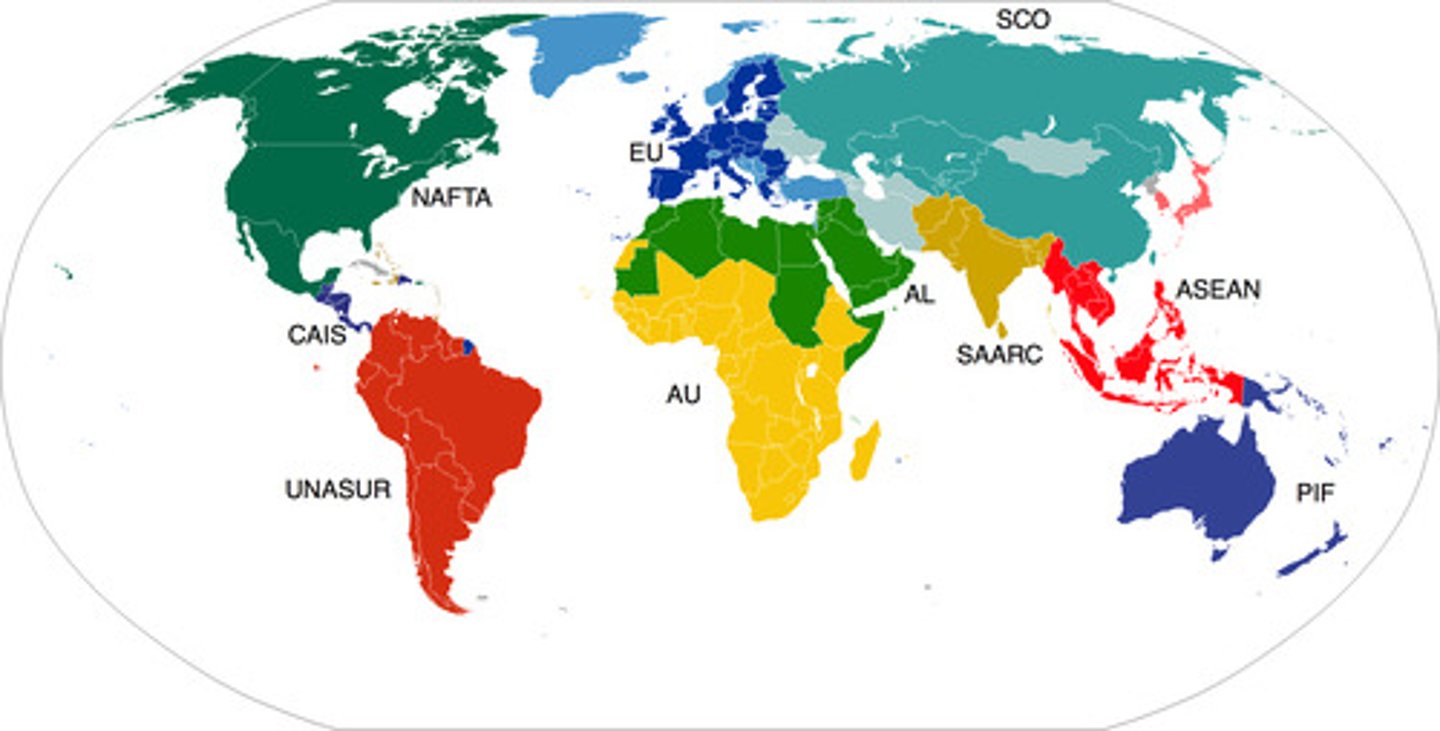
Trade block
A trading bloc is a group of countries that work together to provide special deals for trading. This promotes trade between specific countries within the bloc
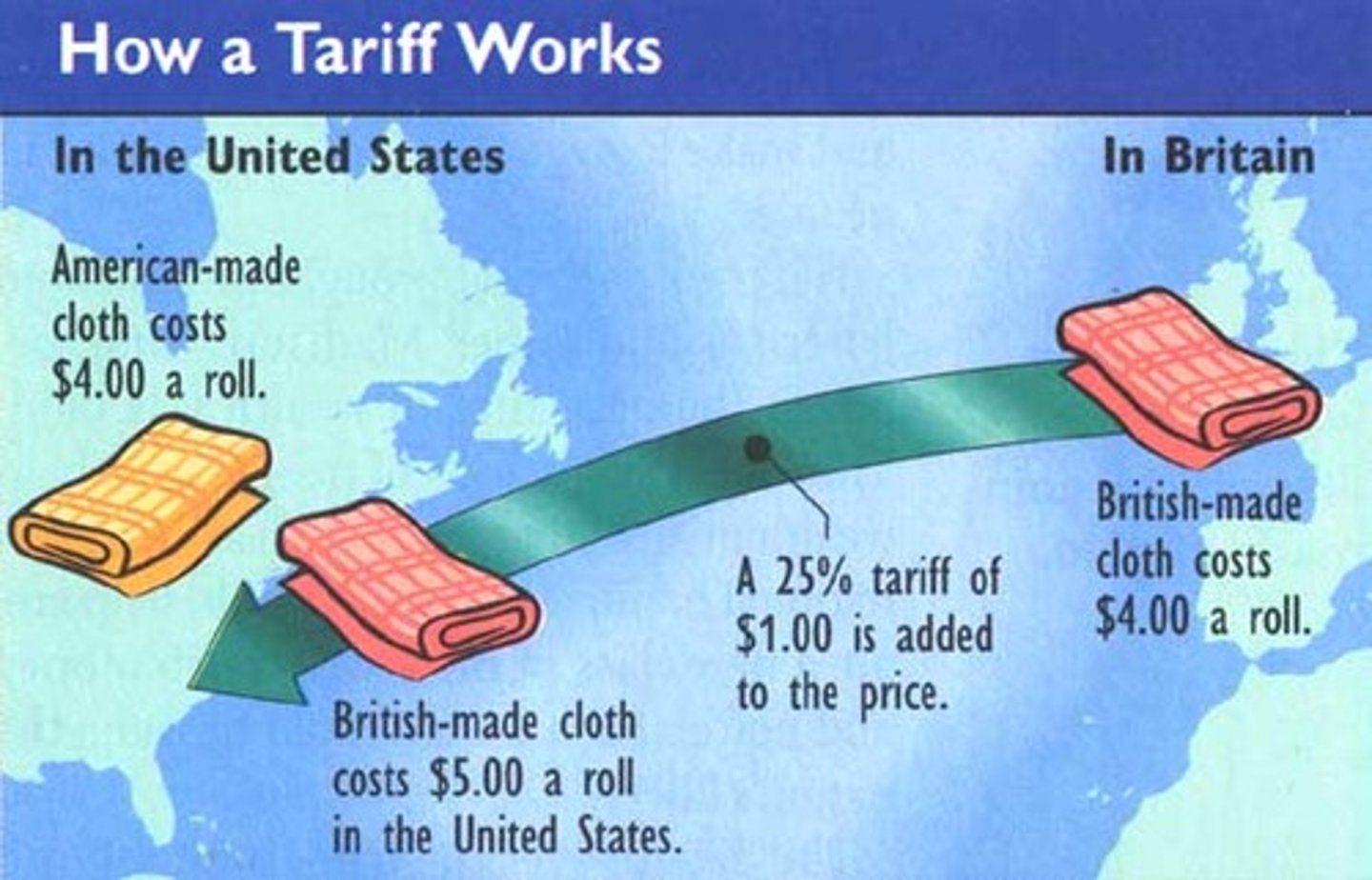
Tariff
A tax on imported goods
Interest rates
The interest rate is the price of borrowing money from a lender or the return on saving money with a bank or an amount loaned out to a borrower.

Political (PEST Analysis)
How changes in government policies might affect businesses.
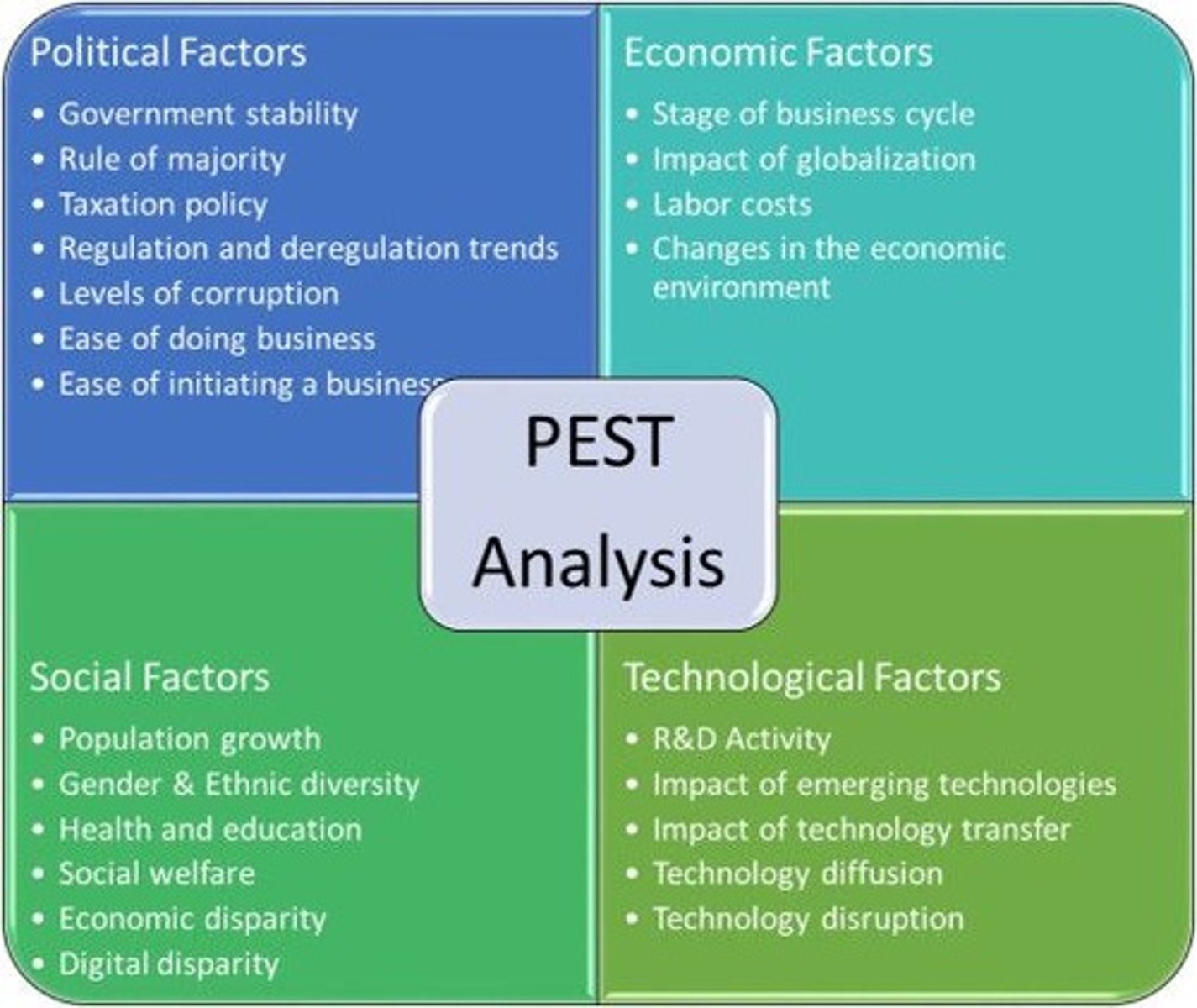
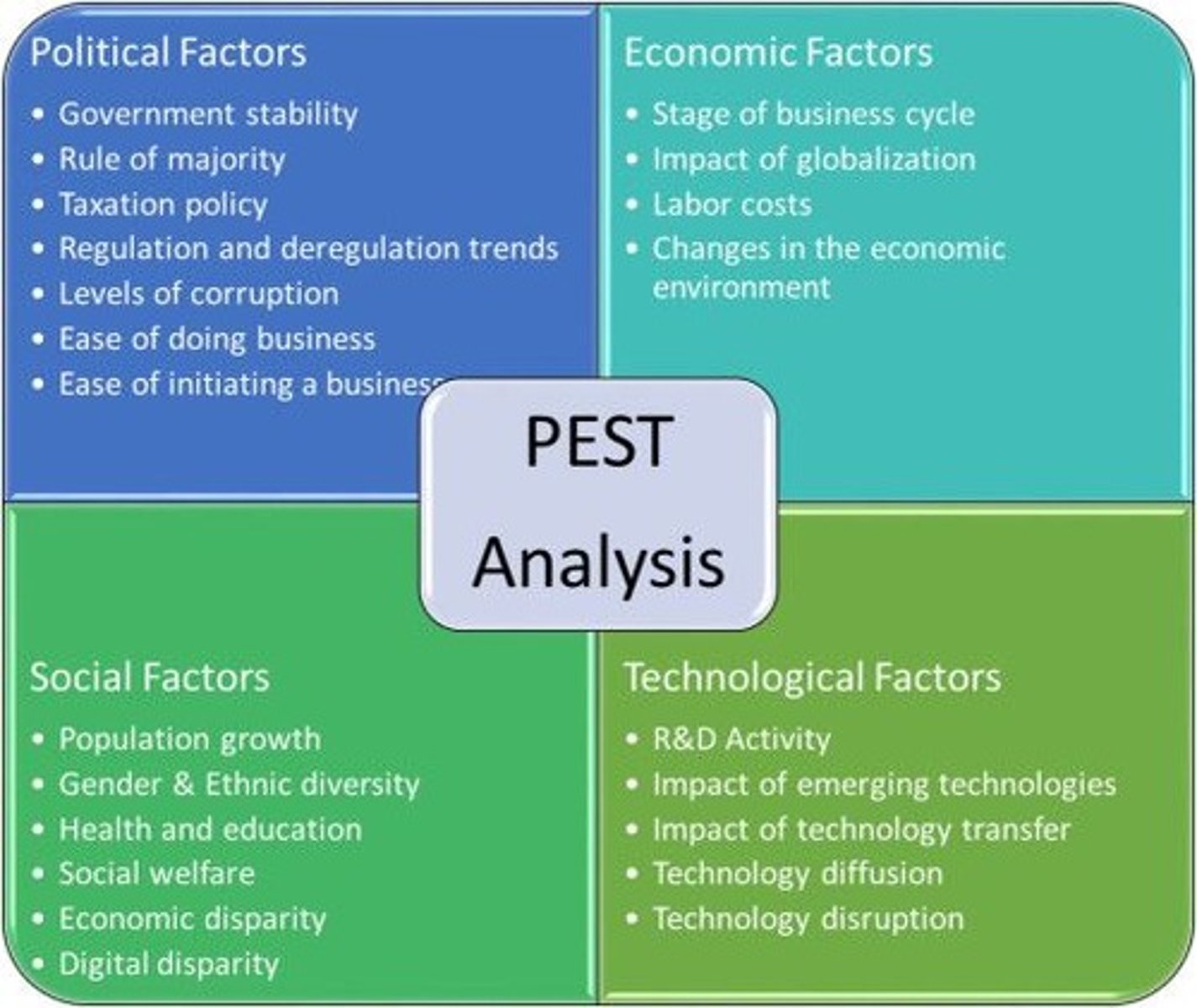
Enviromental (PEST Analysis)
The effects of changes in ecological and environmental aspects such as climate change.
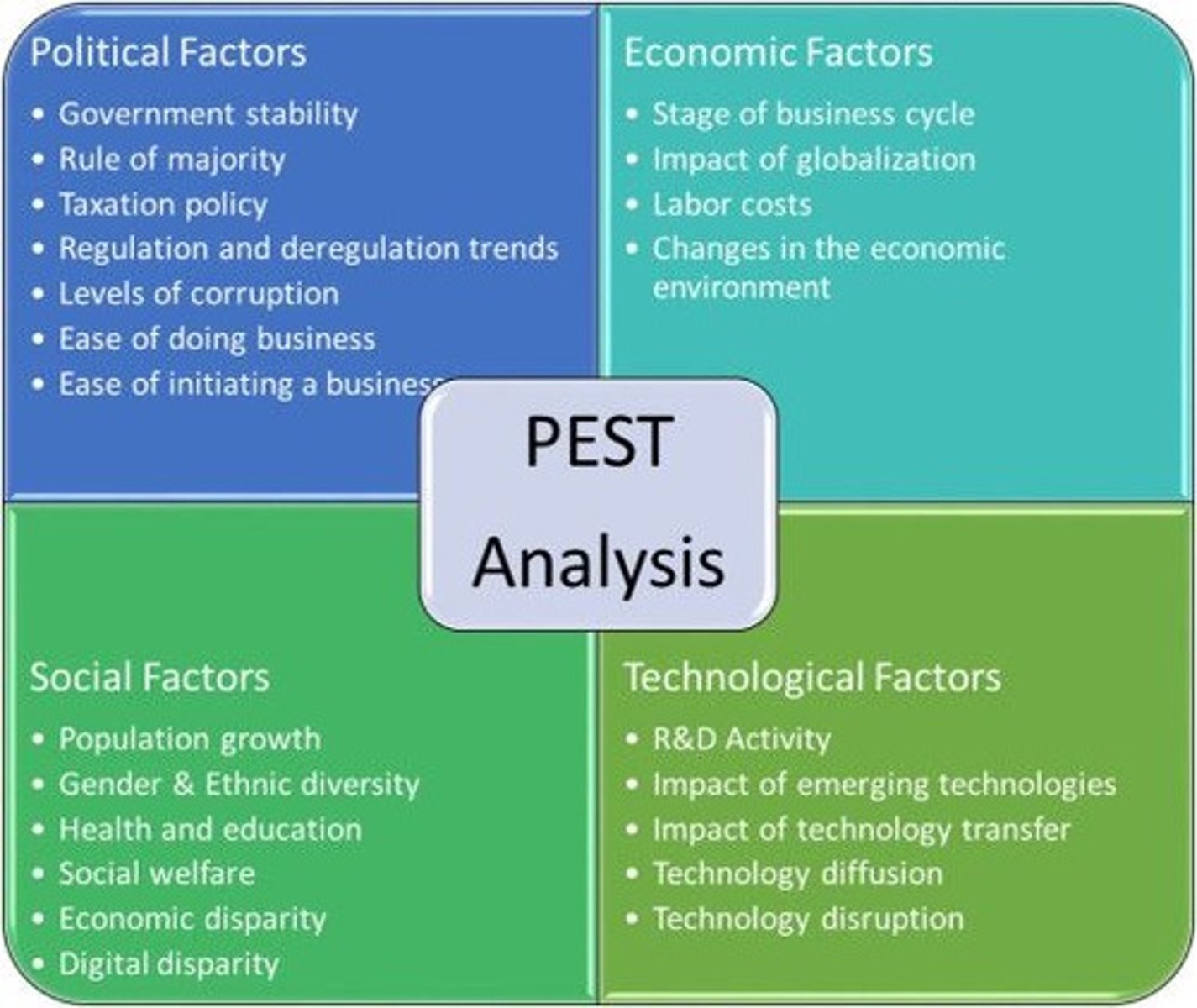
Social (PEST Analysis)
How consumers, households and communities behave according to their own set of norms and values.
Technological (PEST Anlaysis)
How the quick pace of change in production processes and innovation affects businesses.
Shareholder satisfaction
The extent to which shareholders are happy or content with the financial performance of the business they own shares in.
Employee satisfaction
The extent to which employees are happy or content with their employment in a business

Cashflow problems
Having problems with the amount of money coming in and out of a business