YEAR 11 ATAR ECONOMICS CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS- SEMESTER 1 EXAM REVISION
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Economics
The study of how people allocated limited resources to satisfy their unlimited wants.
Three Economic Questions
What to produce? How to produce? How much to produce?
Mico Economics
Understand how consumers and producers make decisions.
Macro Economics
Concerned with the performance of the whole economy.
Positive Statements
Are objective and testable, describing facts about the world.
Normative Statements
Are opinionative and express opinions or value judgements about what should happen.
Opportunity Cost
The value on the best alternative that you give up when making a decision.
Marginal Cost
Extra production costs at one or more units of a good.
Economic Model
Simplified representation of economic reality. Have assumptions and are simplified representations.
PPF: Production Possibility Frontier
Shows the services/goods produced by an economy given the availability of resources and level of technology.
Outward shift
Caused by increase in the factors of production.
Economic Growth
Expansion of an economy's productive potential, the economy can produce more of goods and services across all sectors.
Technological Advancments
Makes it possible to produce more goods with the same factors of production.
Inward Shift
Decreased factors of production.
Market Economy
Type of economic system where price system or systems allocate recourses.
Consumer Goods
Goods that have no future productive use.
Capital Goods
Any good that may be used to help increase future production.
Consumer Sovereignty
Consumers hold the power to influence production decisions based on what goods or services they purchase.
What to produce? (Question)
There is consumer sovereignty, consumers can decide what goods and services will be produced.
How much? (Question)
Level of consumer demand dictates how much of each product should be produced.
How to produce? (Question)
The profit motive of sellers encourages them to produce goods and services as efficiently as possible.
Buyers
Who create market demand.
Sellers
Who create market supply.
Commodity
Something that is being bought or sold.
Voluntary Exchange
People can chose weather or not to participate.
Process
Mechanism or arrangement through which buyers and sellers "meet."
Price
Set by market demand and supply.
Product Markets
Deal with buying and selling of goods and services.
Factor Markets
Deal in buying and selling of factors of production and resources.
Competitive Markets
Large number of buyers and sellers, firm are price takers, very similar (homogenous) products, easy entry into the market (no barriers of entry.)
Non Competitive Markets
Small number of firms, product differentiation, firms are price setters- they have market power, entry into the market is restricted.
Demand
The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy of a particular price and a particular point of time.
Law of Supply
Increase in the price of goods or services results in an increase producers supply. Positive Relationship.
Law of Demand
When the price of a product goes up, the quantity demanded will go down. Inverse relationship.
The Income Effect
When the price of a good rises consumers are not willing to buy as much of the good as their real income or purchasing power has decreased,
The Substitution Effect.
When the price of one good rises other goods become more attractive.
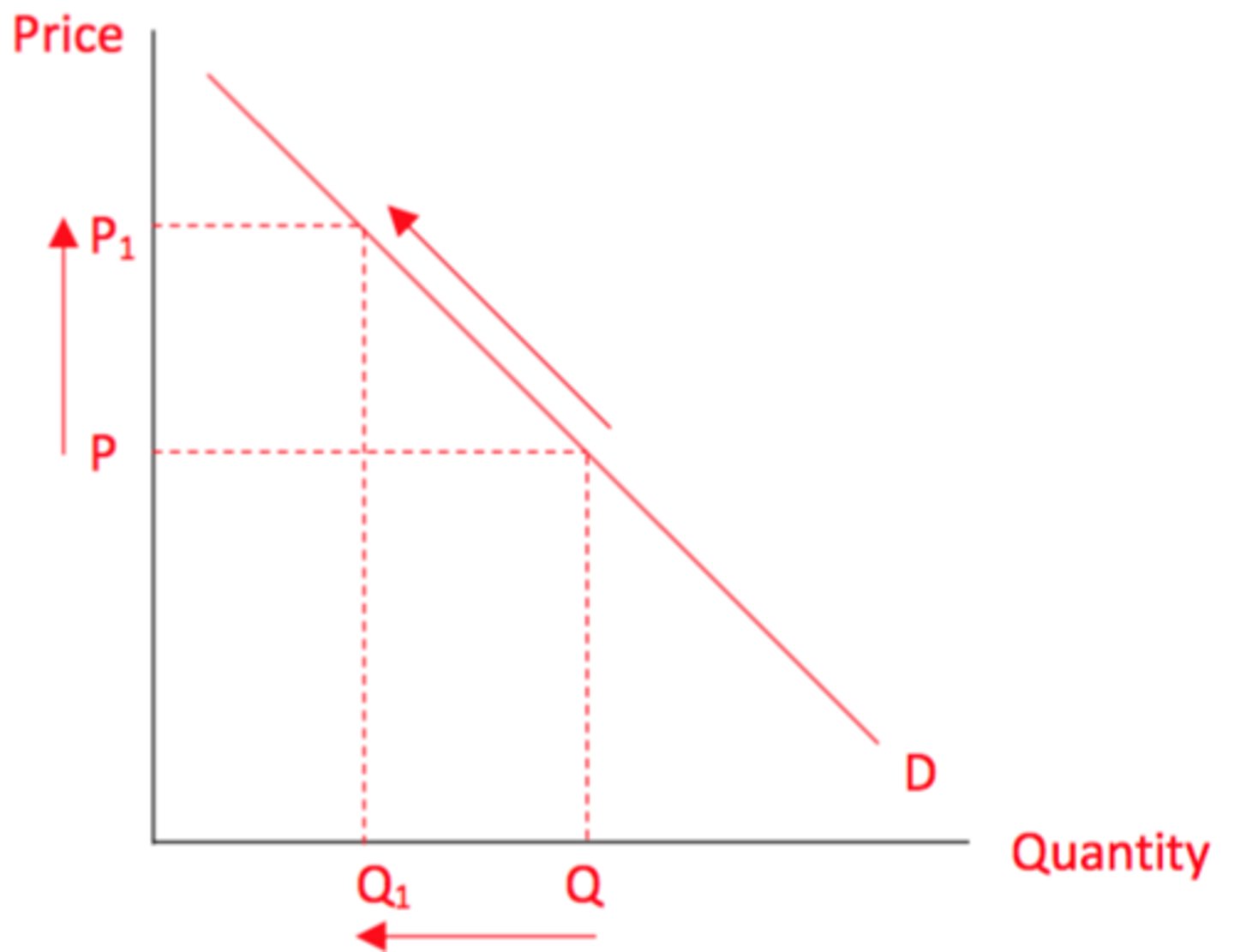
Contraction In Demand
Equals an increase in price, a rising movement along the demand curve.
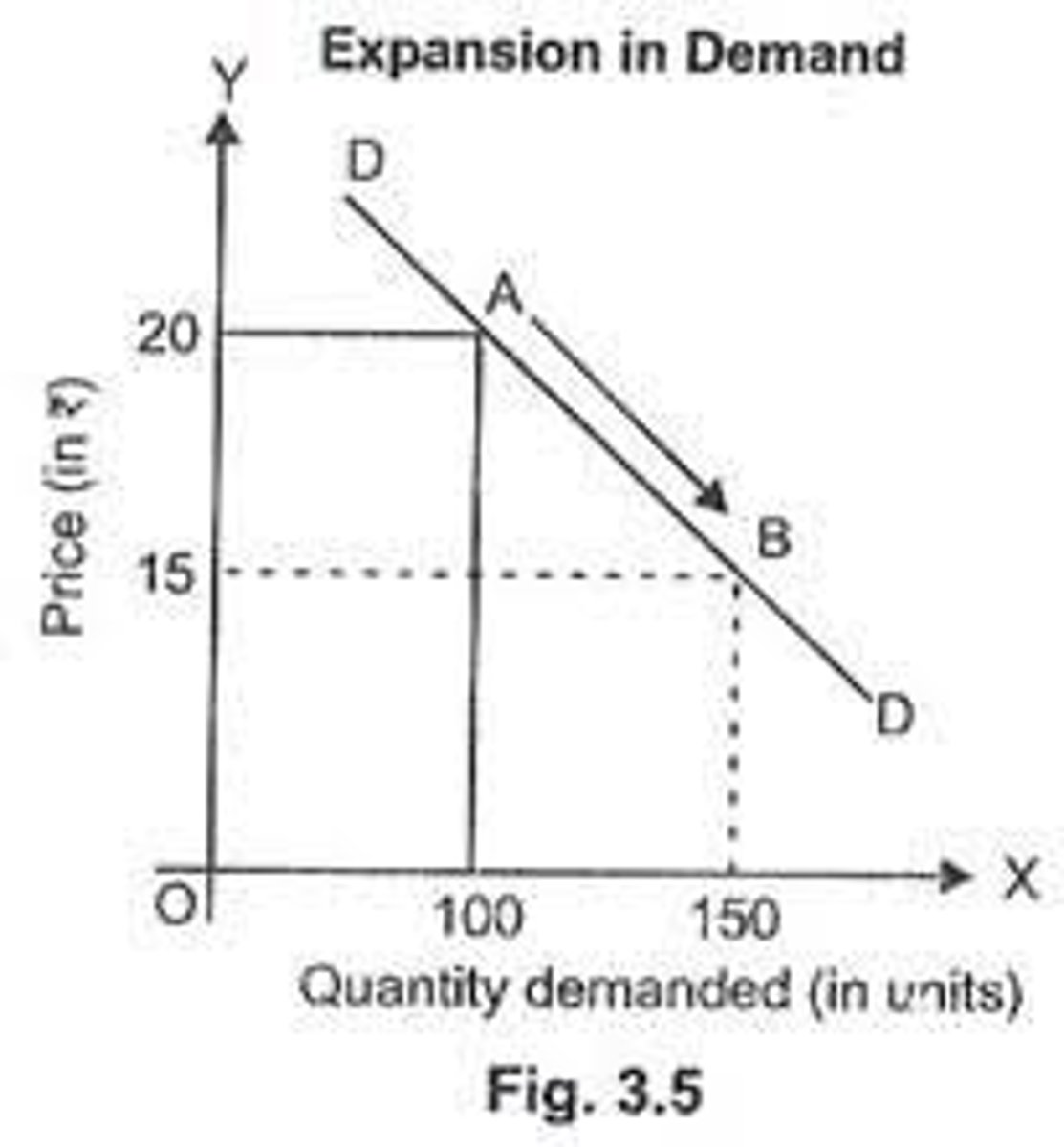
Expansion In Demand
Equals to a decrease in price, a downwards movement along the demand curve.
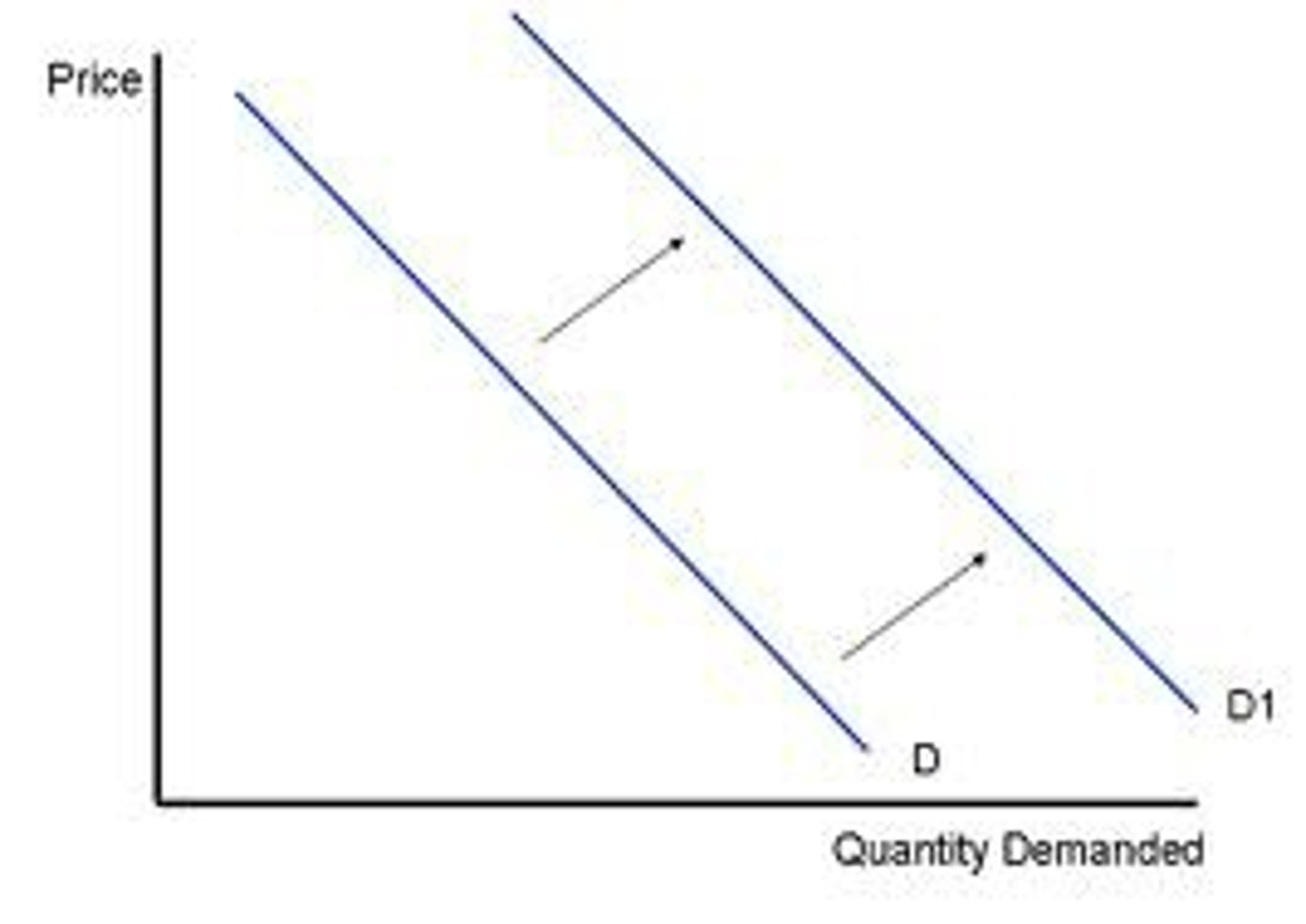
Increase In Demand
A shift to the right is an increase in demand.
Decrease In Demand
A shift to the left is an decrease in demand.

Causes of Shift in the Demand Curve
Levels of disposable, Price of related/substitutional goods, Tastes and preferences, Expectations of consumers, Demographic Factors.
Complementary Goods
Products that align in conjunction with one another e.g. Butter and Toast.
Normal Good
Demand is increased as income rises
Interior Good
Good where demand decreases as income increases.
Supply
The quantity of goods and services producers are willing and able to sell at a particular point in time.
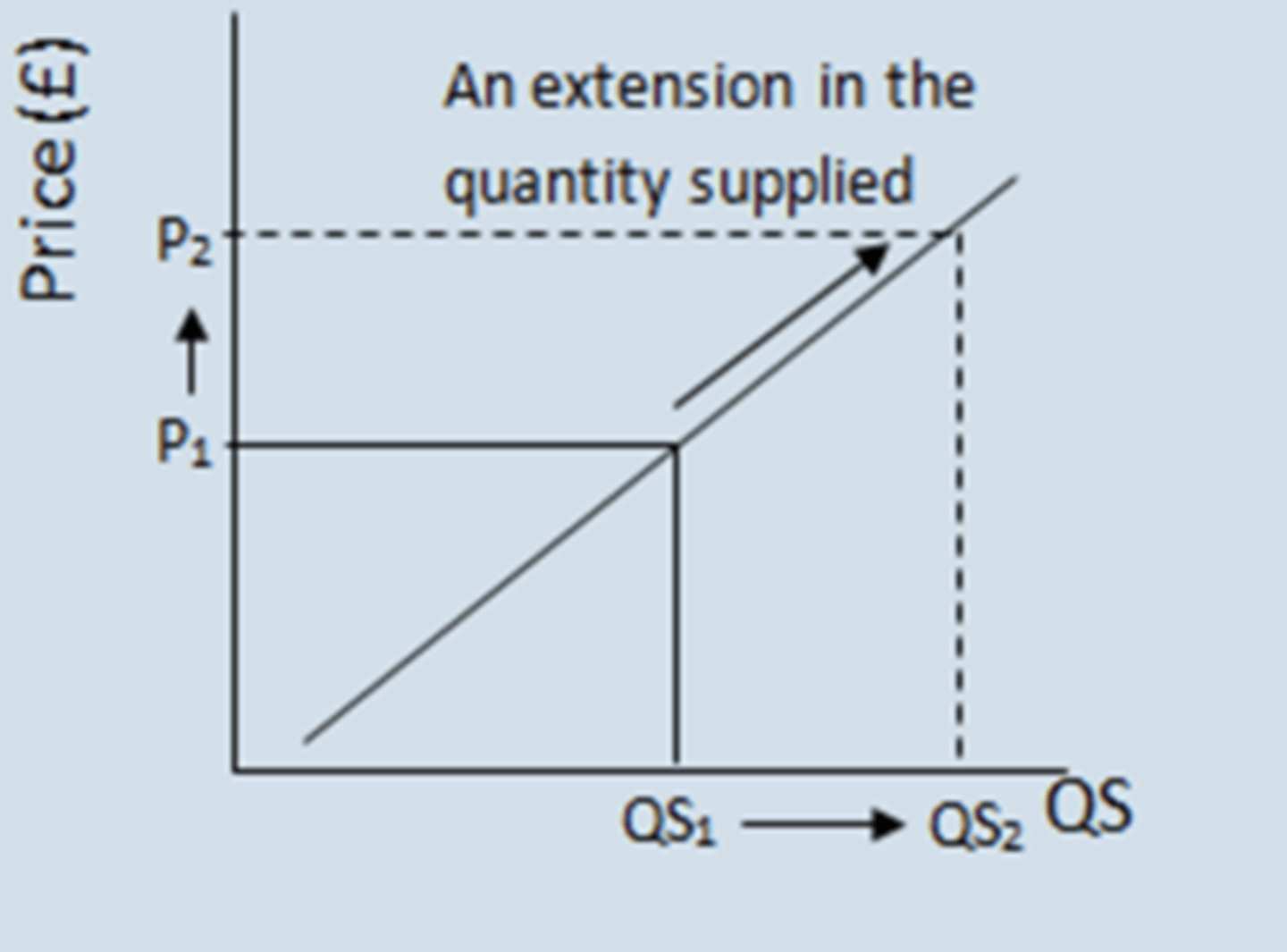
Expansion in Supply
As price rises, amount supplied rises. Directly relative with quantity.
Contraction in Supply
As price decreases, amount supplied decreases. Directly relative with quantity.
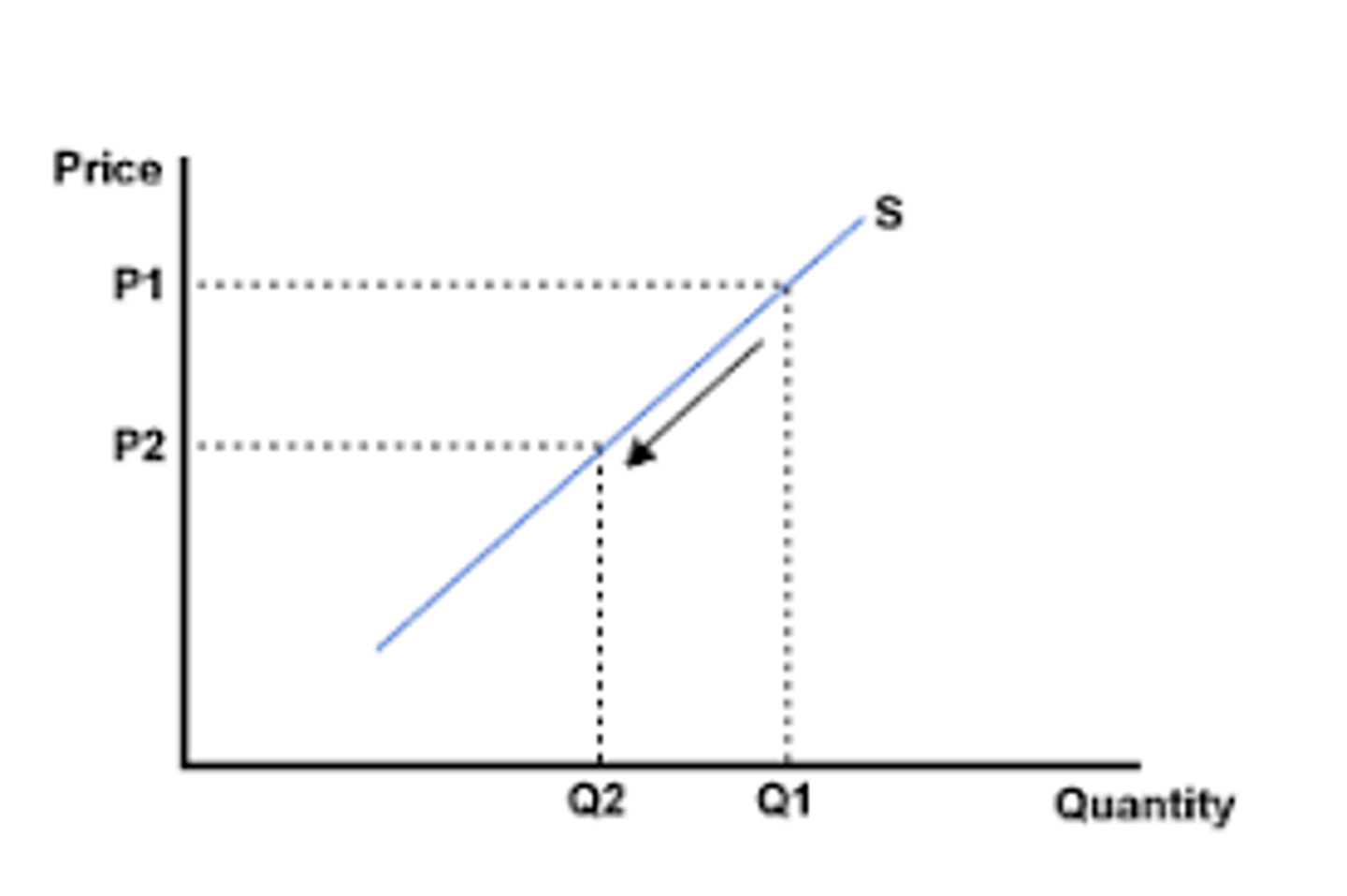
Costs of Production
Expected future prices, Number of suppliers, Technology, Events affecting the availability of resources and the supply chain.
Substitutes for Production
If the price of productive substitutes increases then the supply of goods your producing decreases.
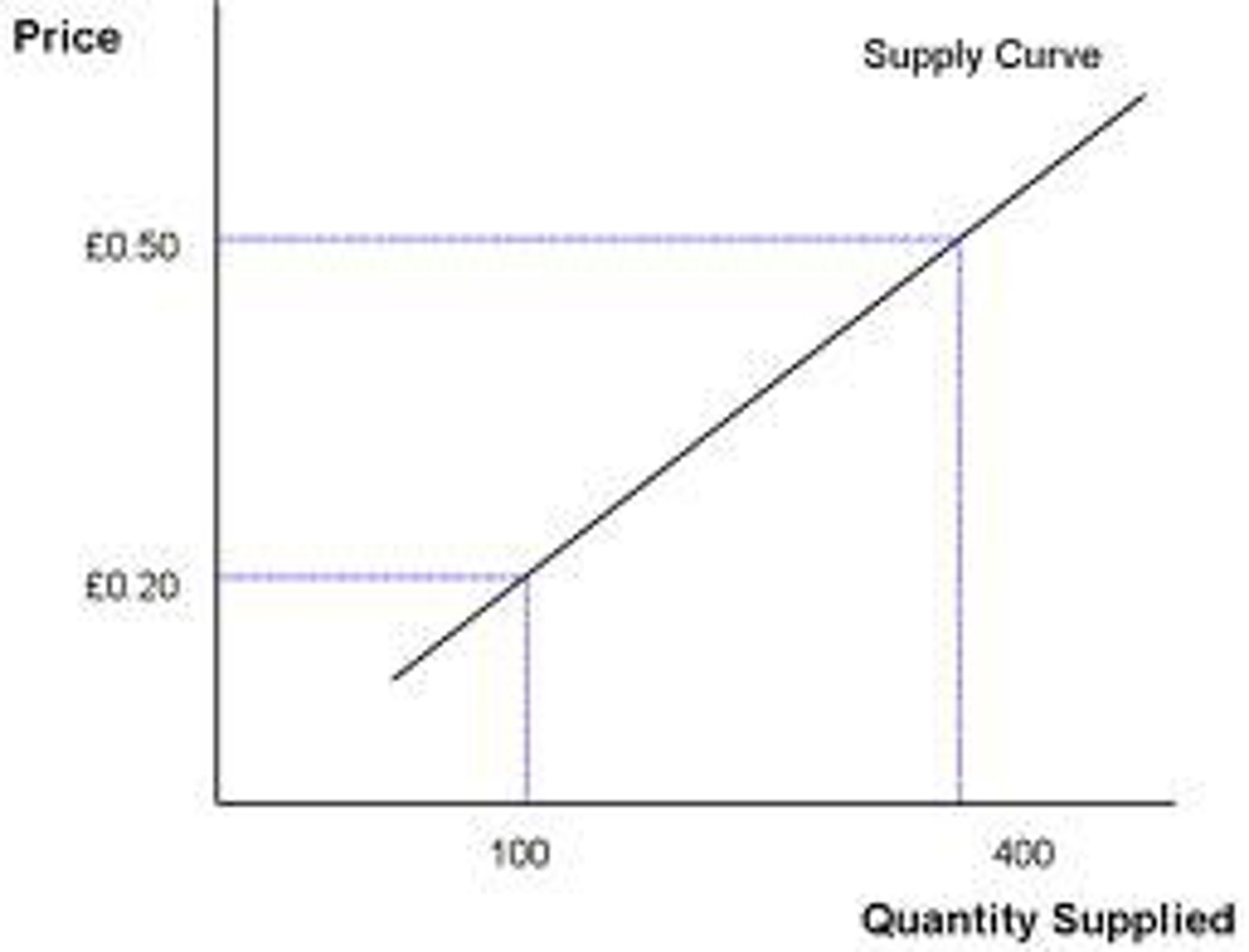
Supply Curve
Linear line that directly represents the relationship between quantity supplied and prices.
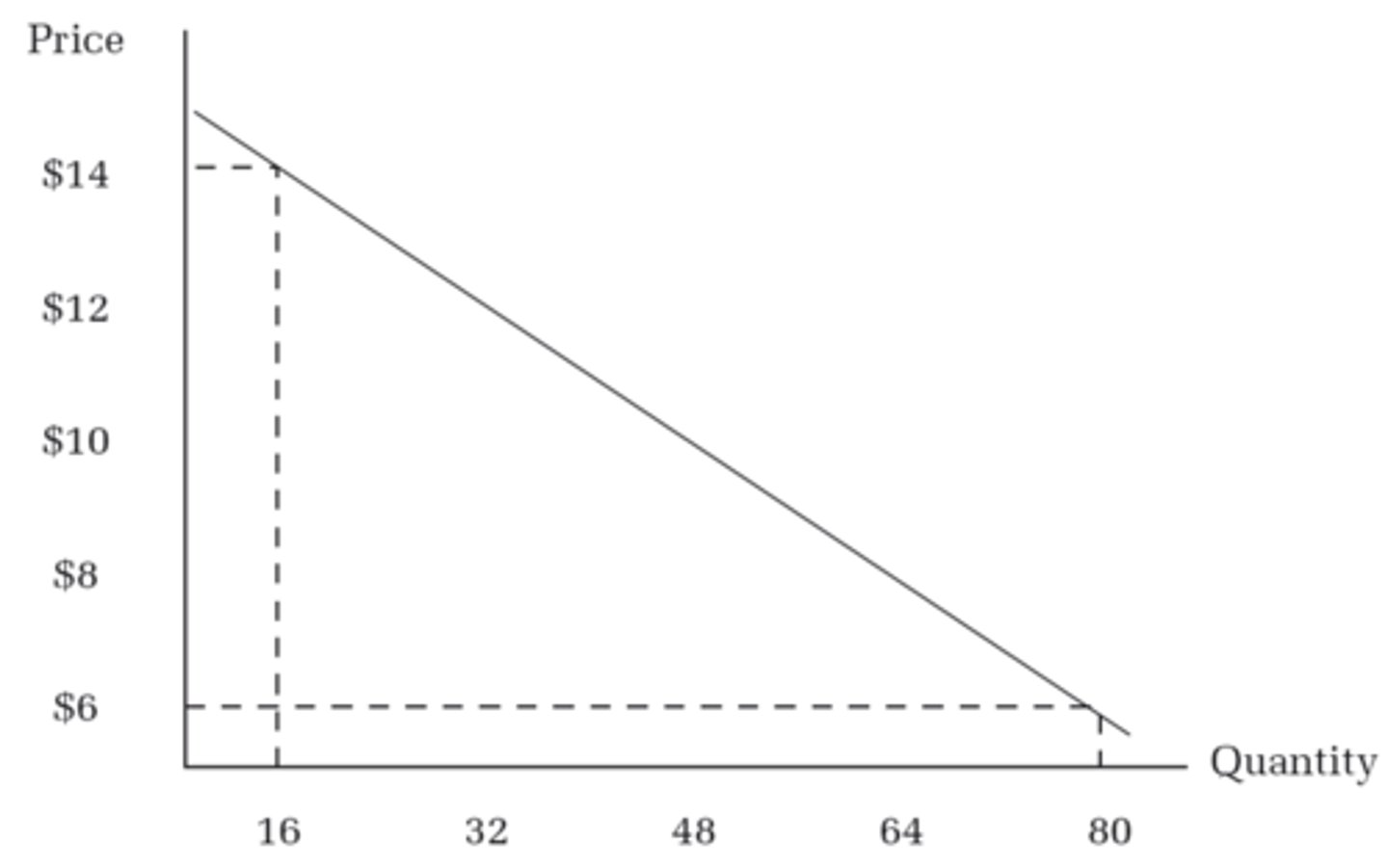
Demand Curve
Linear line that reflects the relationship between the prices of goods and services and the quantity demanded.
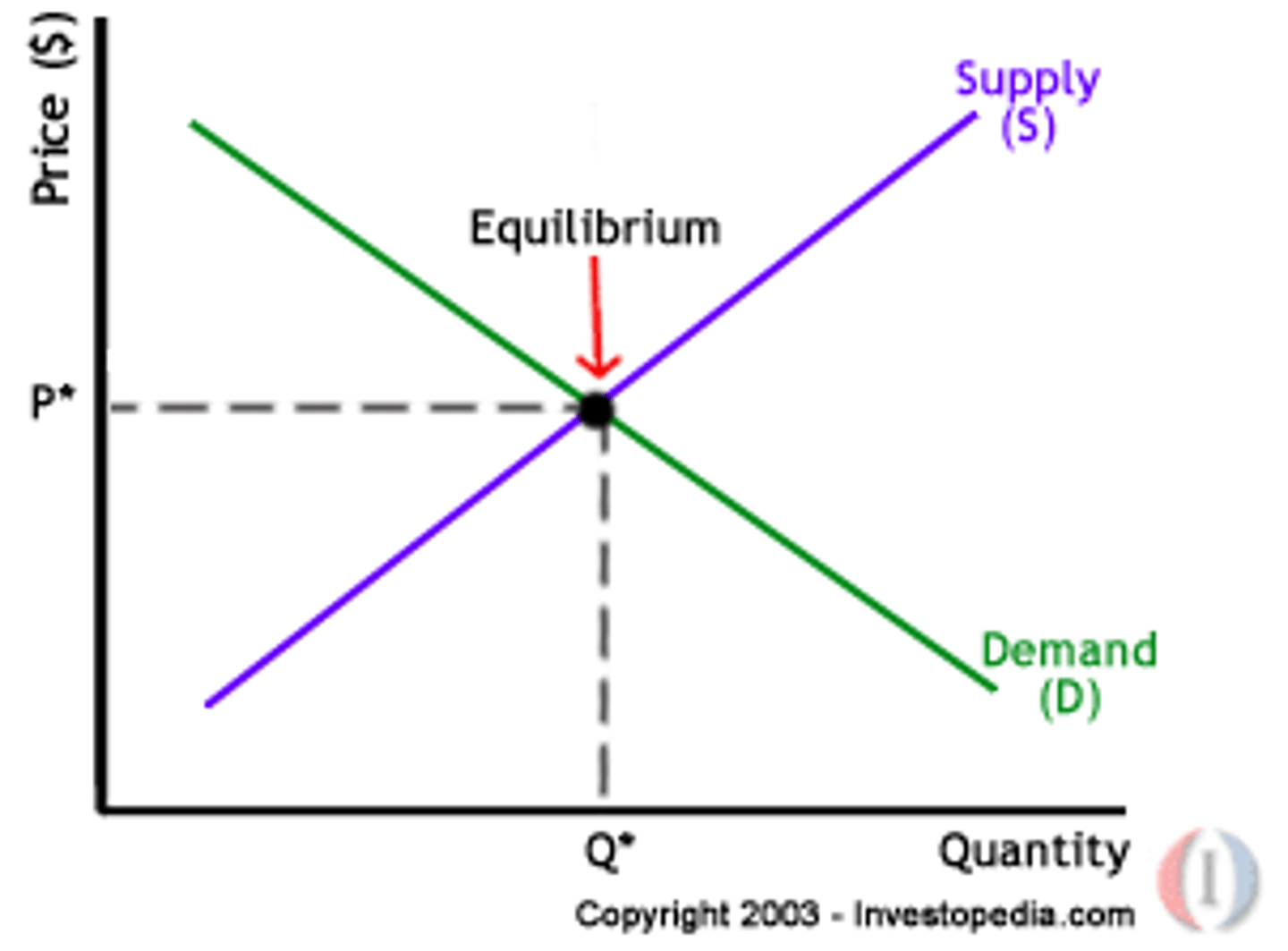
Equilibrium Price
Where the quantity of goods supplied meets the quantity of goods demanded at an intersection.
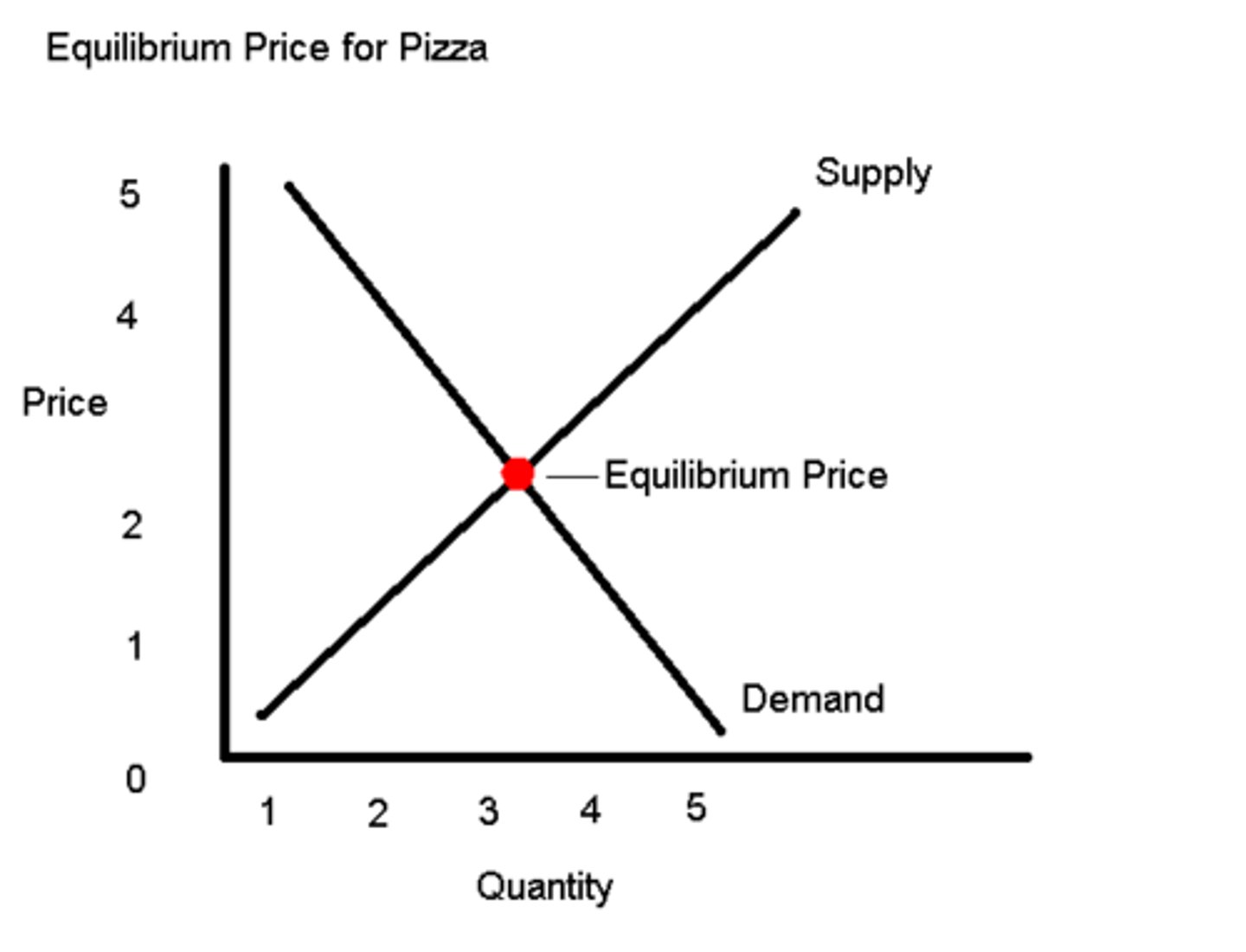
Equilibrium Quantity
When there is no shortage or surplus of a product in the market. Met at the same intersect as Equilibrium Price.
Shortage
When the demand outweighs the supply.
Surplus
When the supply outweighs the demand.
Price Elasticity of Demand
Responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a change in the price of a good or service.
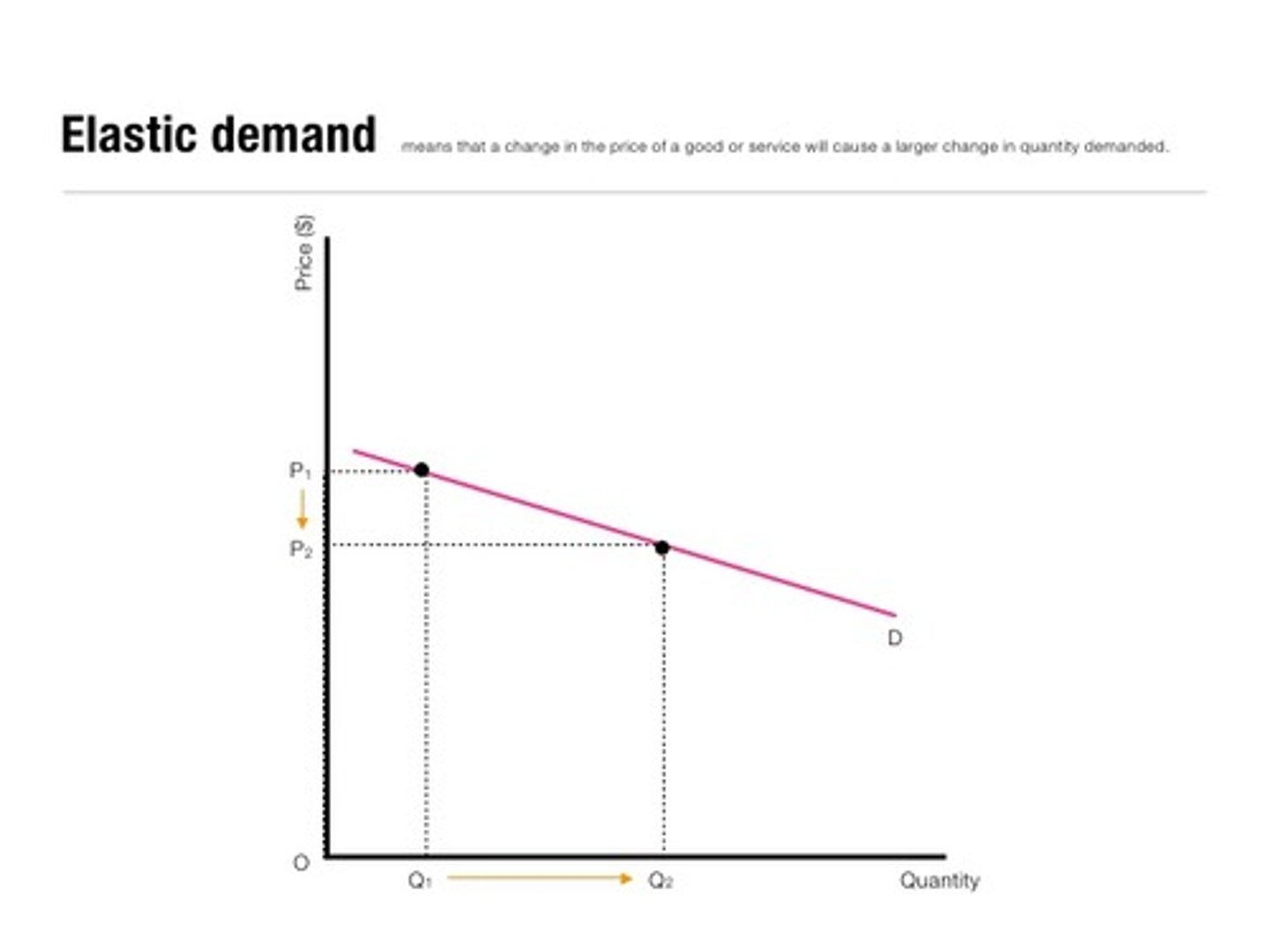
Elastic Demand
Demanded is said to be elastic when a change in price leads to a larger than proportional change in quantity demanded.
Elastic Demand Curve
Smaller change in price leading to a larger change in quantity demanded.
Inelastic Demand Curve
Demand is said to be ________when a change in price leads to a smaller than proportional change in quantity demanded.
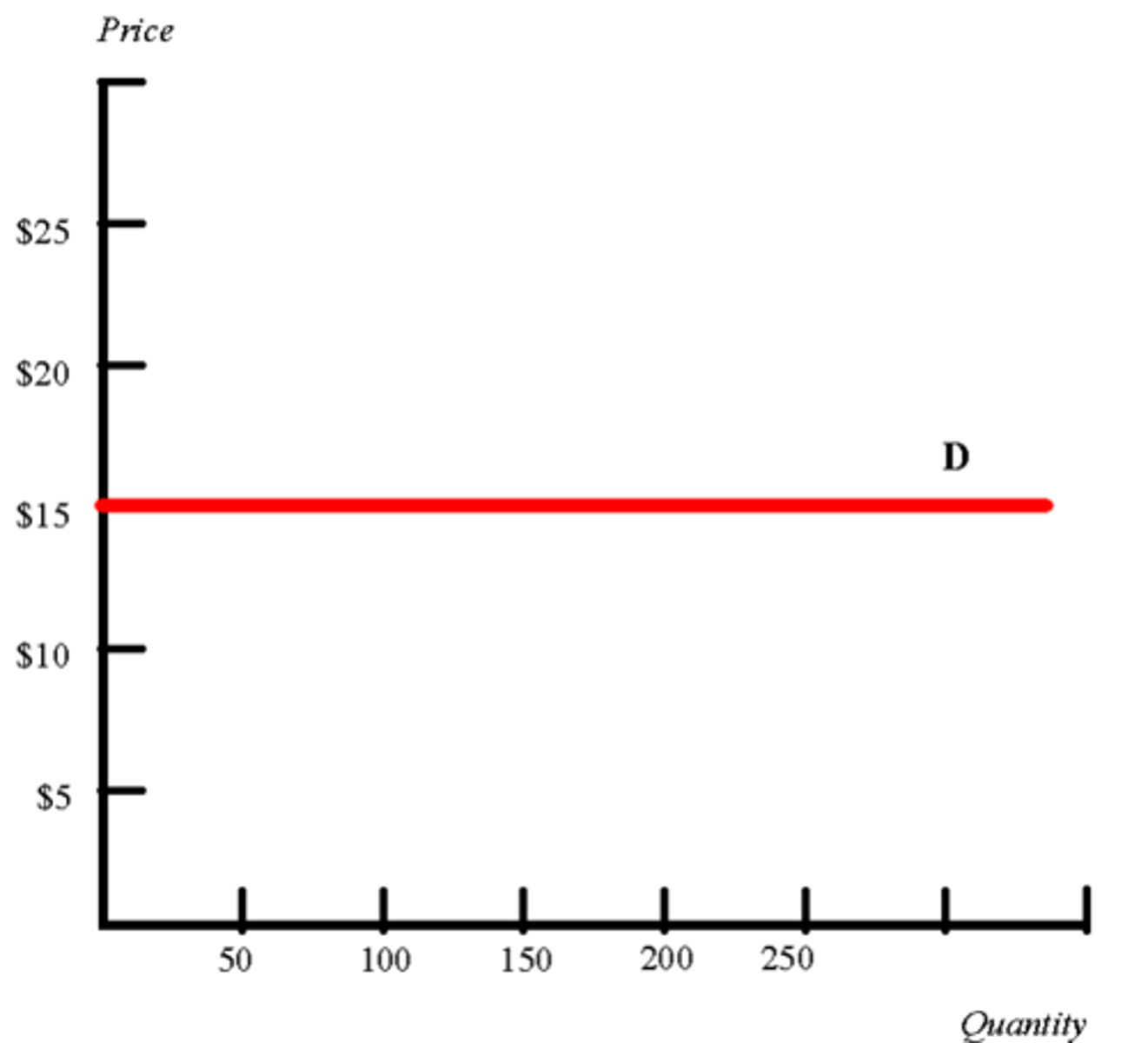
Perfect Elasticity
Any change in price leads to all changes in consumption.
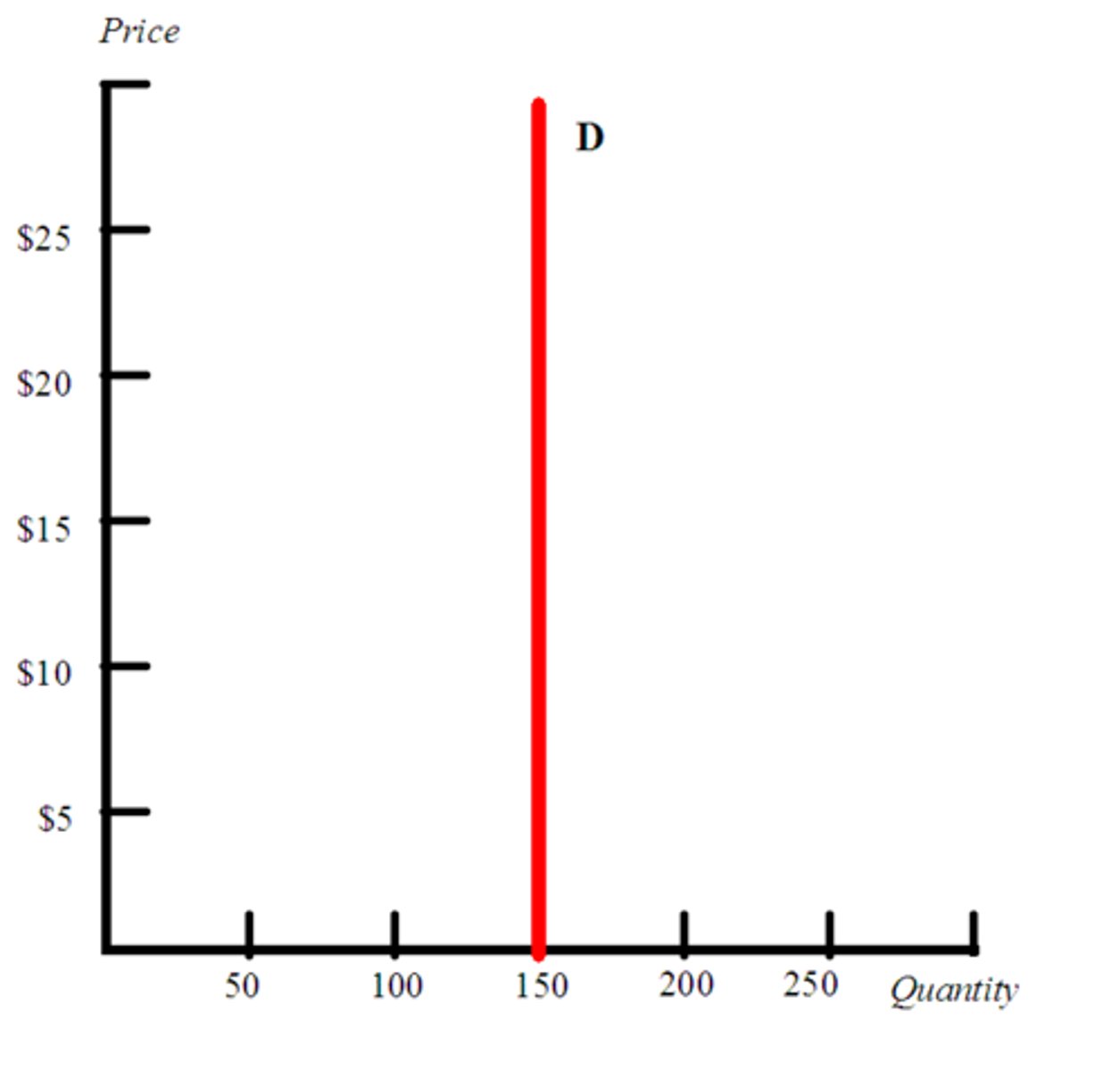
Perfect Inelasticity
Any change in price leads to no change in quantity.
Factors Affecting Price Elasticity of Demand
Availability of substitutes, weather a good is a necessity or a luxury, proportion of income spent, time, definition of market.
Total Revenue Method
Total revenue = price x quantity
Elasticity Coefficient- Point Method
% change in quantity / % change in price = Elasticity Demand Coefficient
Elasticity of Supply
Price elasticity of measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price.
Price Discrimination
Refers to firms adjusting their pricing to different consumer groups to boost their total revenue. Firms base their pricing on the different prices elasticity of demand of each consumer groups.
Market Efficiency
A competitive market results from thousands of buyers abd sellers with one another. Producing the goods that society wants at the lowest possible costs.
Marginal Benefit
Additional benefits a consumer gets from each additional good.
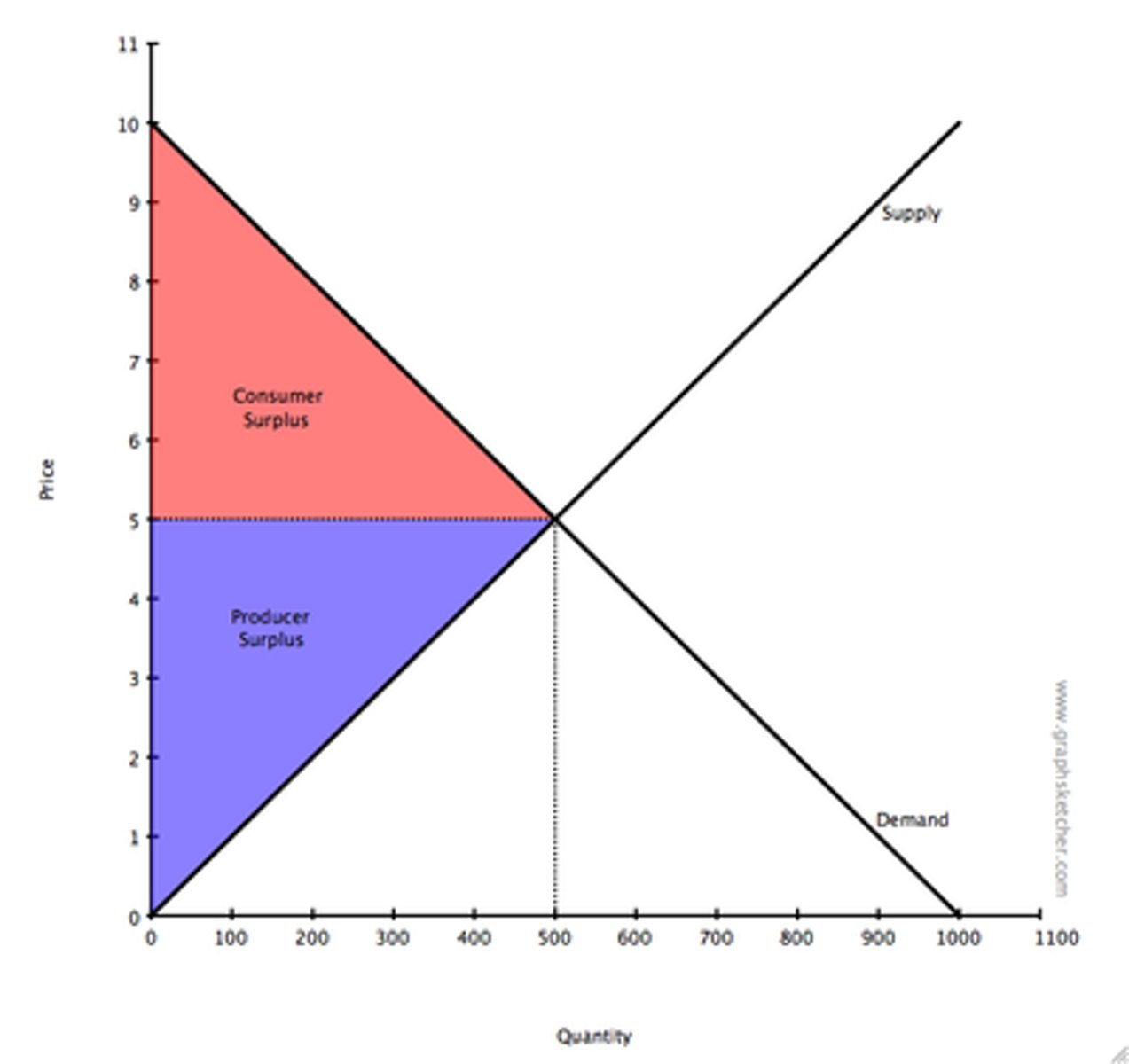
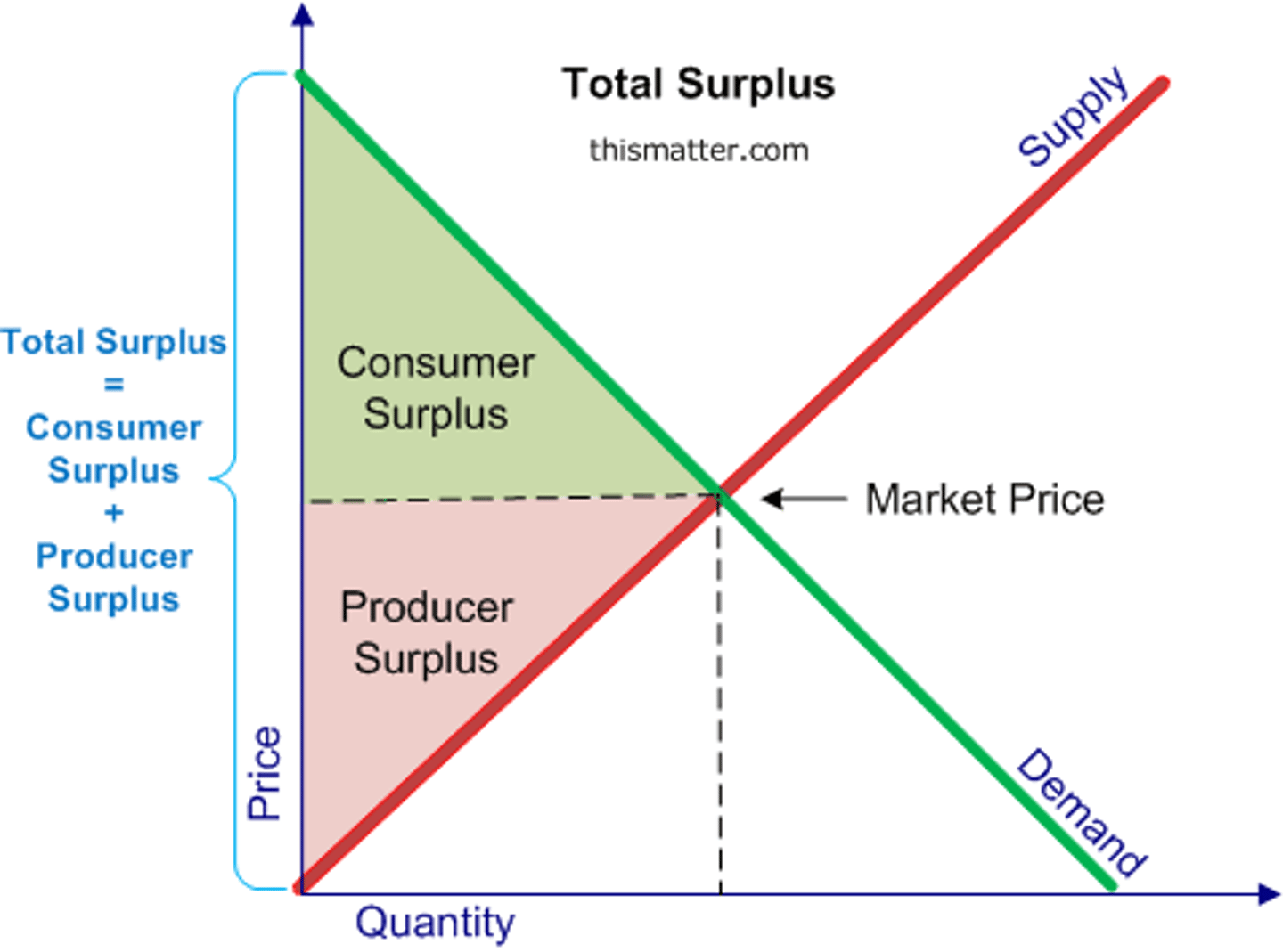
Consumer Surplus
Difference between what a consumer is prepared to pay and what they actually pay in a market.
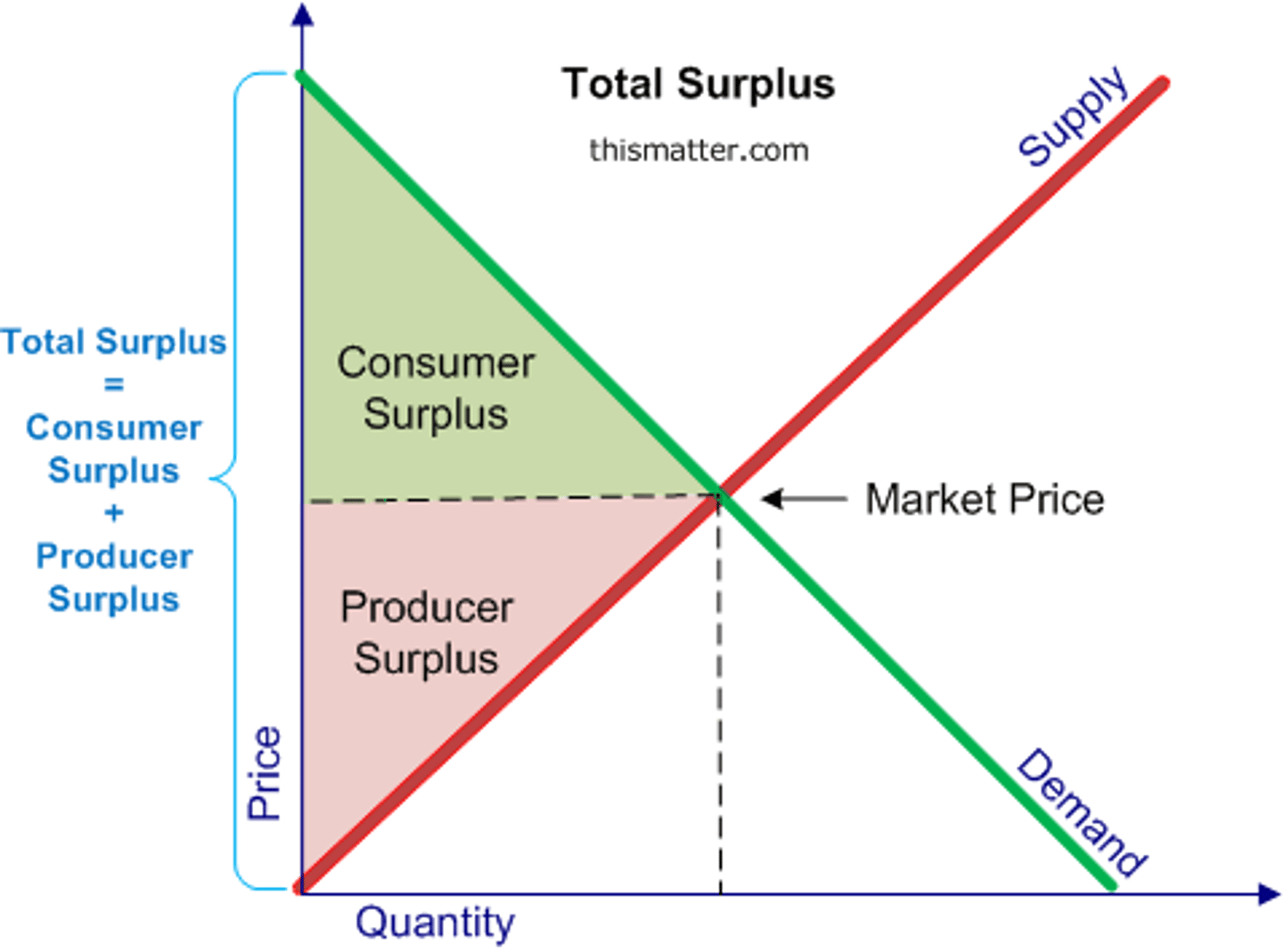
Producer Surplus
Difference between what a producer is prepared to sell a product for compared to what they sell it for.
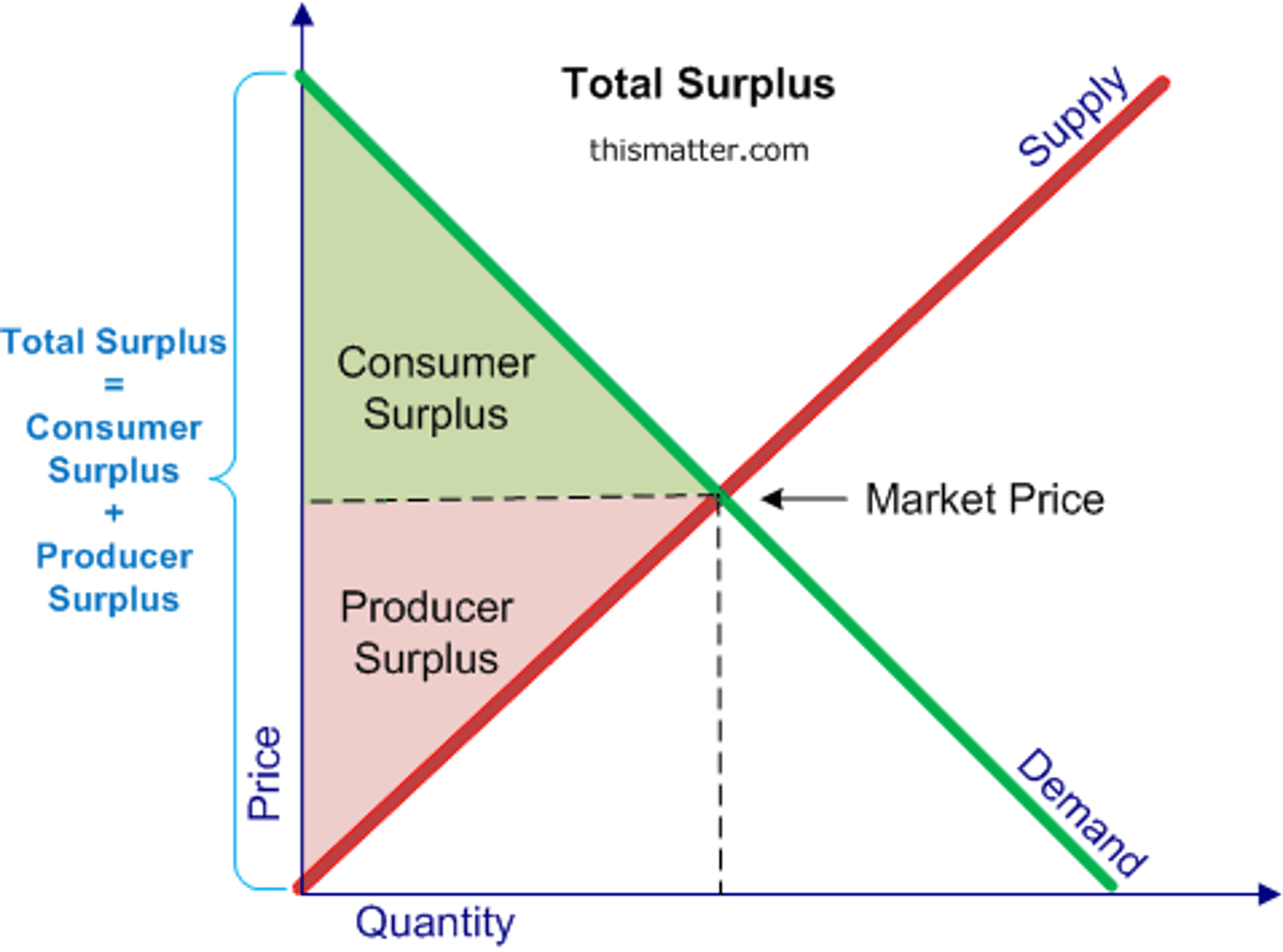
Total Surplus
Is the consumer and producer surplus combined.
Deadweight Loss
When total surplus is reduced because of either under or over production.

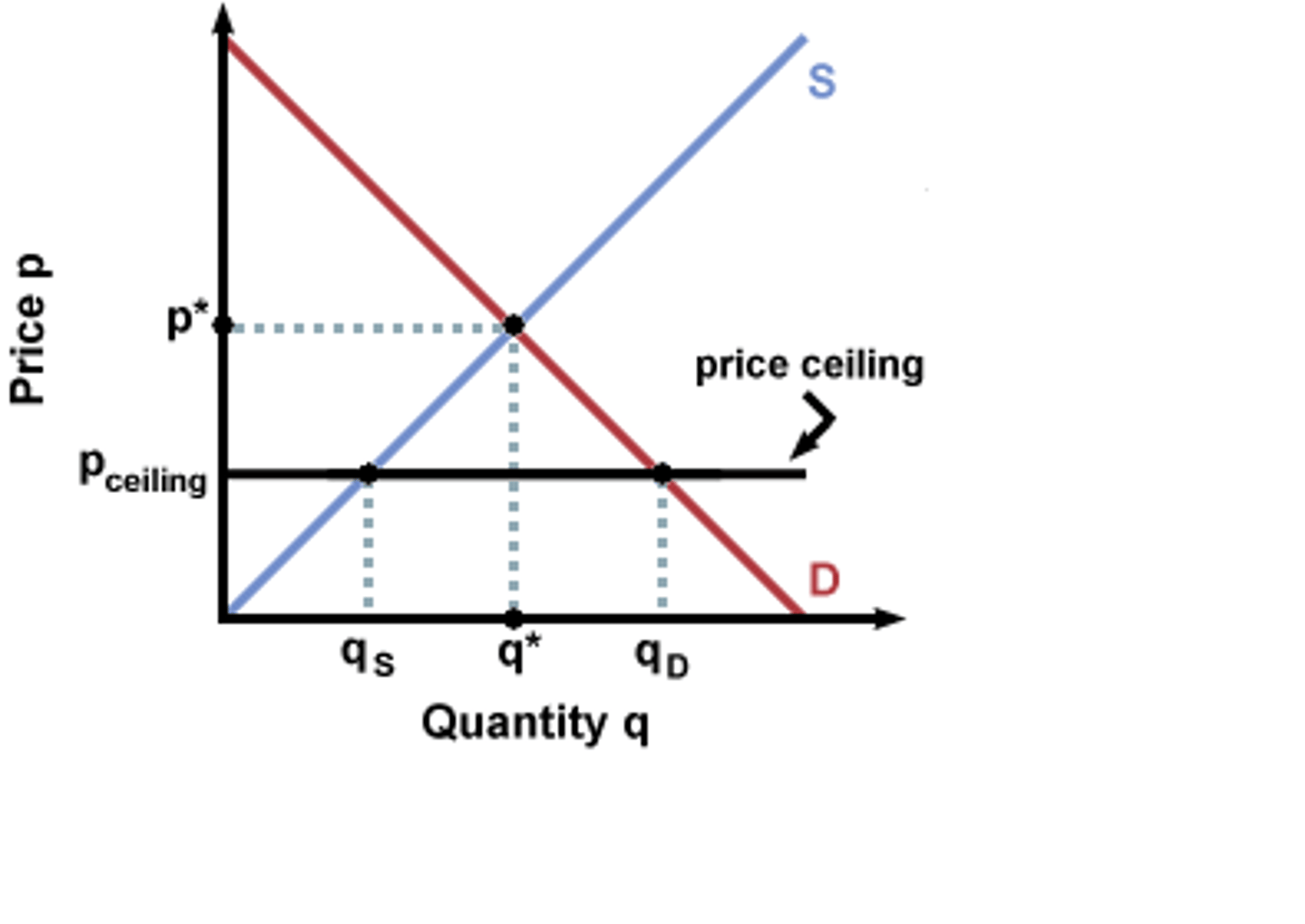
Price Ceiling
Legislated maximum price that sellers are allowed to charge in a market. BELOW equilibrium price.
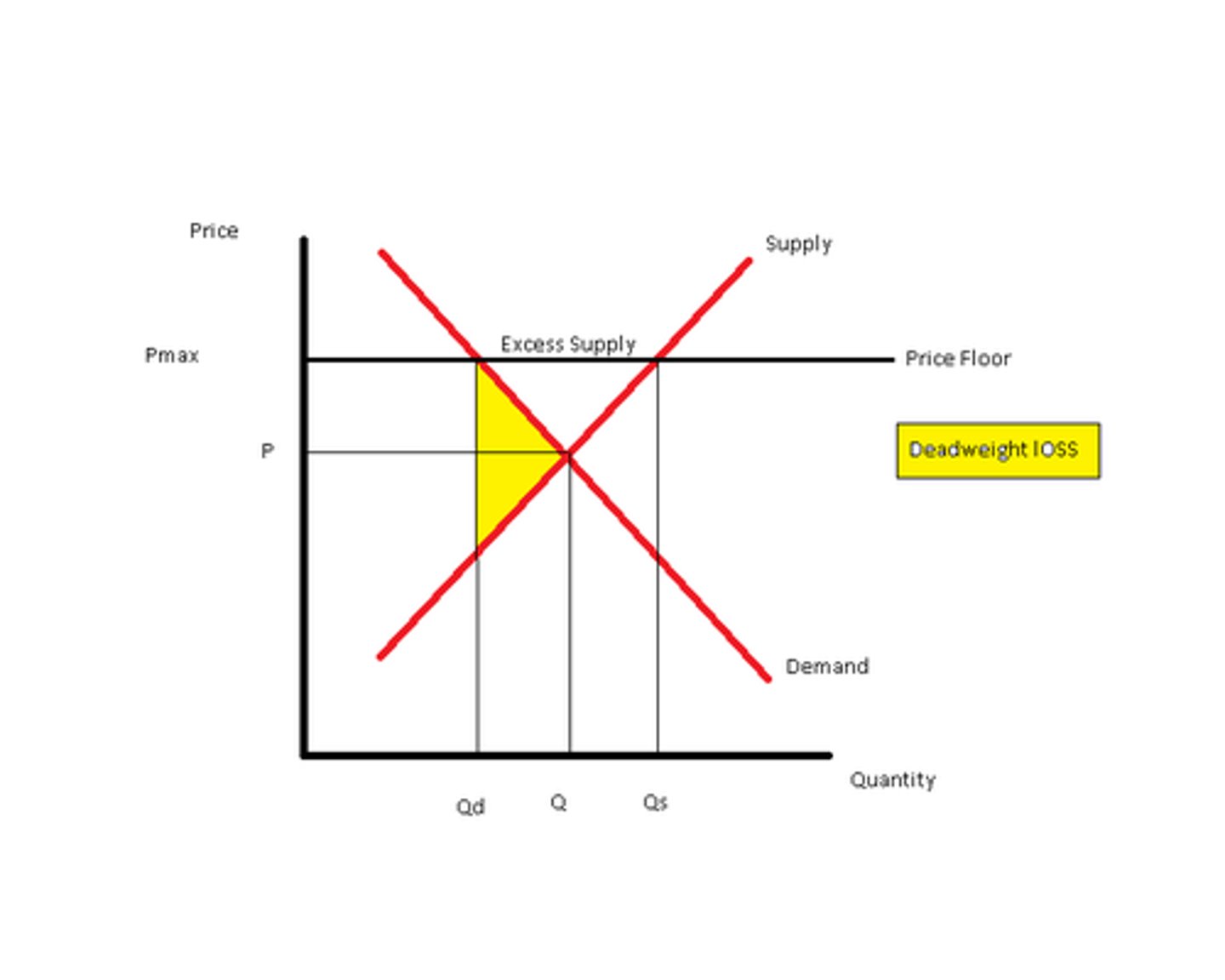
Price Floor
Legislated minimum price that sellers are allowed to charge in a market. ABOVE equilibrium price.
Taxes (Indirect)
Governments can levy taxes to raise revenue so that they can spend on worthwhile projects that improve efficiency of the economy.
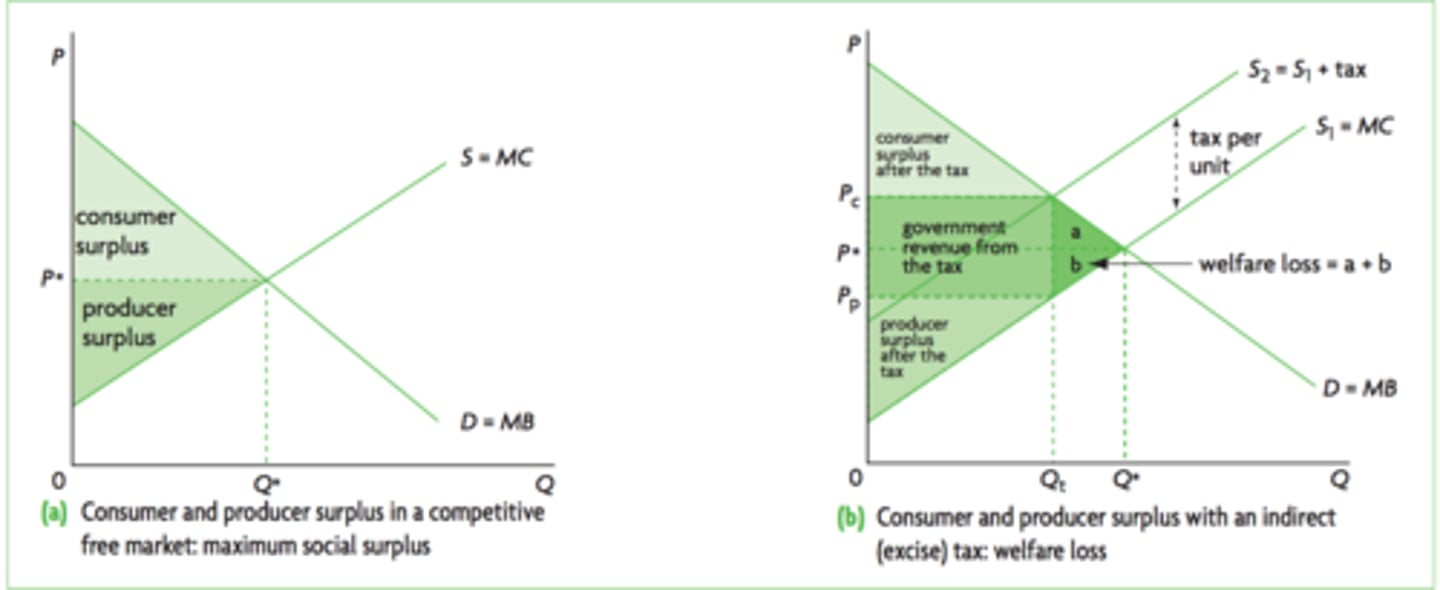
Elasticity Impact on a Tax
More inelastic demand is, the greater the tax revenue.
Subsidy
A payment by the government to a film in order to increase output.
Market Share
A firms sales expressed as a proportion of total sales in the market.
Concentration Ratio
Market share of the biggest firm.
Price Gauging
When a firm excessively increases price unfairly, taking advantage of demand.
Market Failure
When resources are not allocated efficiently- total surplus not maximised.
Monopoly
Extreme type of imperfect market with just one dominant firm.
Duopoly
A market with two dominant firms.
Olipology
A market with a few dominant firms.
Market Power
When a buyer or seller in a market has the ability to exert significant influence over the quantity of goods and services or price.
Positive Externality
External benefits to society from either production or consumption.
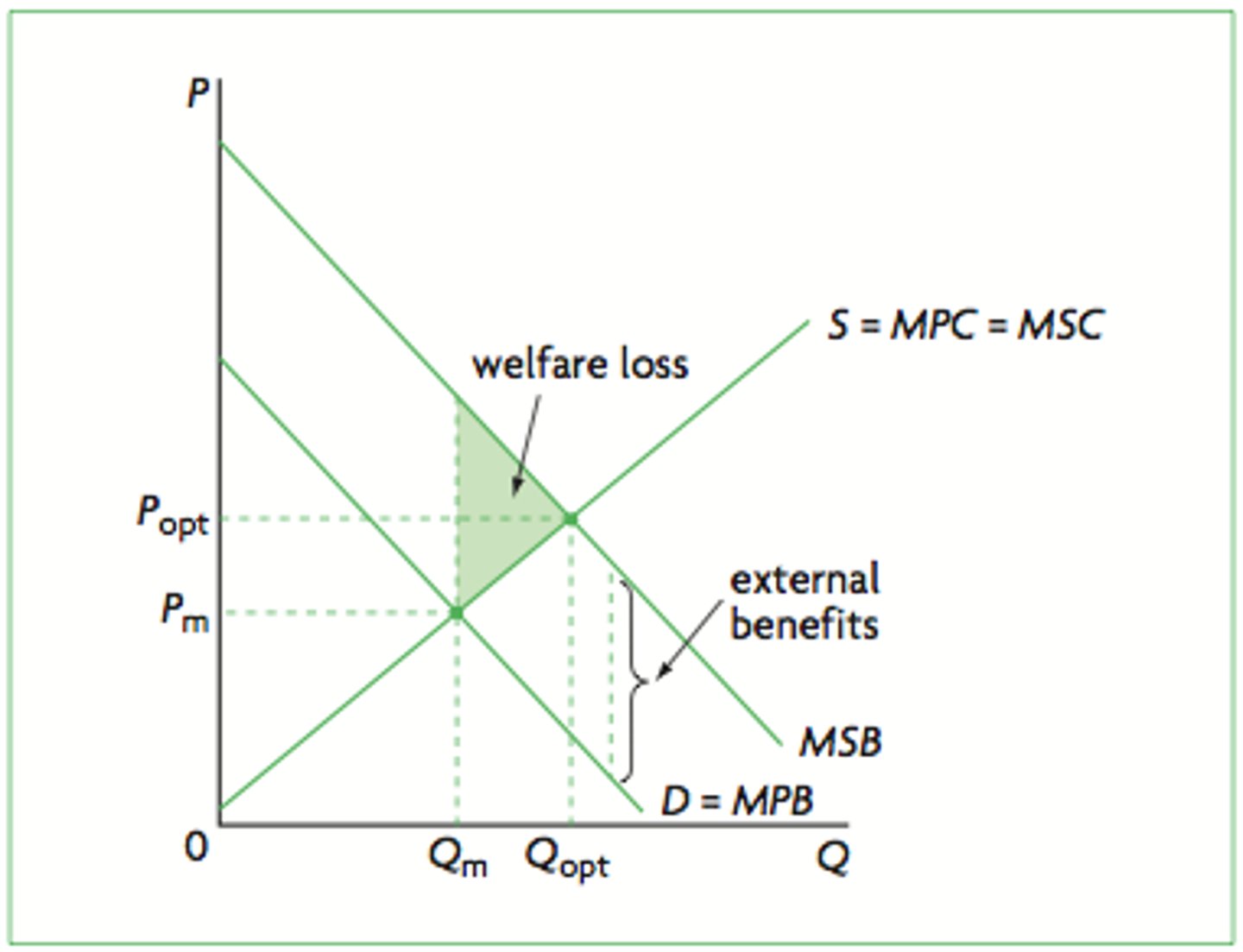
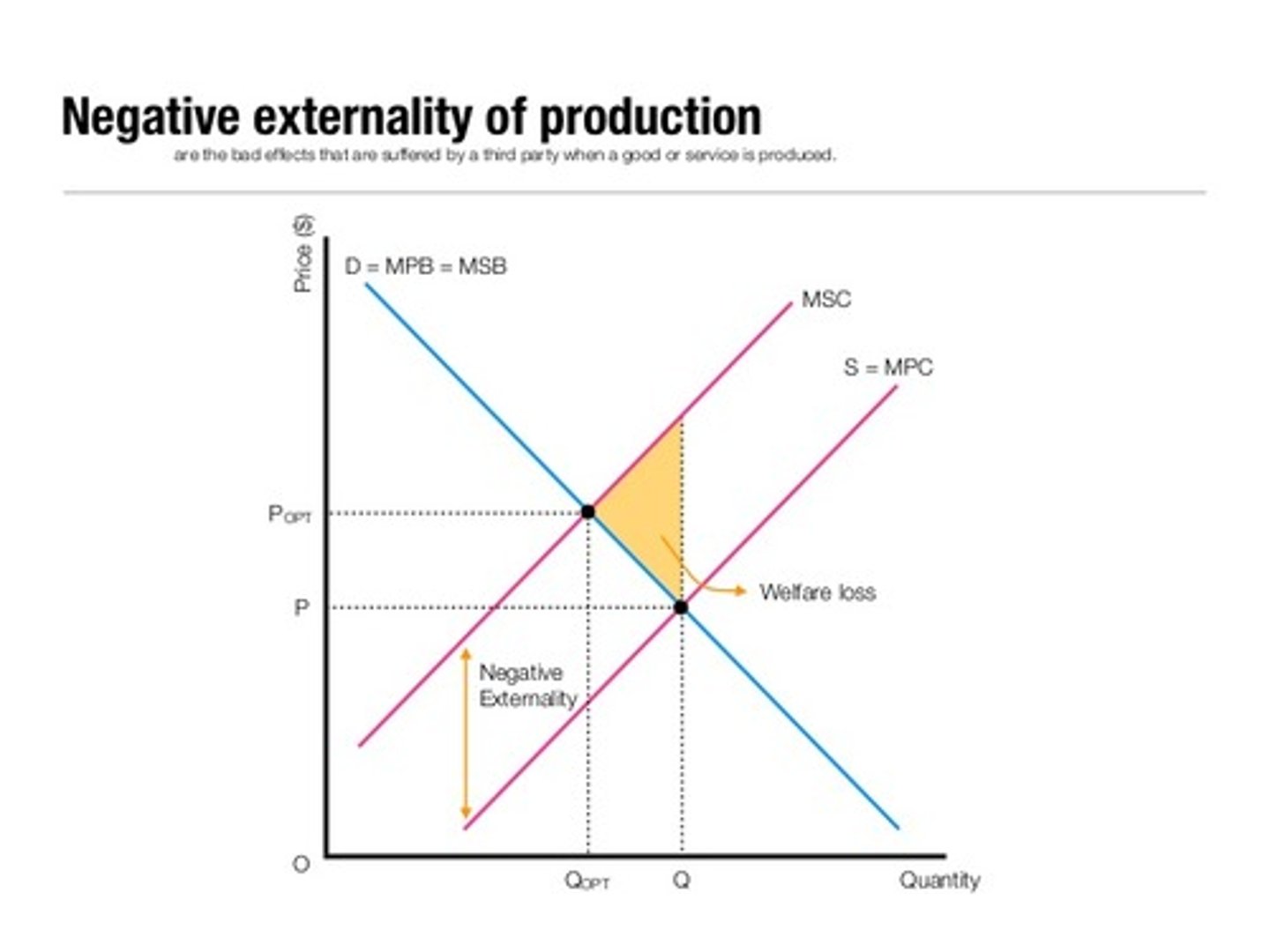
Negative Externality
External costs to society from either production or consumption.
Externalities
External side affect of all economic activity in an economy.
Private cost/benefit
cost/benefit to buyers + sellers.
External cost/benefit
cost/benefit to third parties.
Imperfect Market
When equilibrium is not being met and deadweight loss is being present. Represented mostly by monopoly, duopoly markets.
Rival Goods
A good where one consumer can prevent the simultaneous consumption for other consumers. E.g. drinks and food
Excludable Good
When a good or service can be limited to customers that only pay for it. E.g. Clothes and Shoes
Club Good
A good or service that is excludable but non-rival. When individuals can be prevented from consuming them however, their consumption does not reduce their availability to others. E.g. Netflix
Private Goods
A good where the ownership is restricted to a group, or an individual that has purchased the good for their own consumption. E.g. Computer
Negative Production Externality
When the production of a good or service causes harm to a third party.
Positive Production Externality
When the production of a good or service causes benefit to a third party.