CSCS
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
173 Terms
1
New cards
Glycemic Index
Ranks carbohydrates according to how quickly they are digested and absorbed
2
New cards
Glycemic Load
Takes amount of food into account affecting blood sugar levels
3
New cards
Protein Recommendation for Endurance Athlete
1.0-1.6 g/kg
4
New cards
Protein Recommendation for Strength Athlete
1\.4-1.7 g/kg
5
New cards
Carbohydrate recommendation for endurance athlete
8-10 g/kg
6
New cards
Carbohydrate Recommendation for Strength/Speed Athlete
5-6 g/kg
7
New cards
Amount of Glycogen stored in body
about 15g per kg
8
New cards
Carbohydrate Recommendation 1 Hour before Competition
.5 g/kg
9
New cards
Carbohydrate Recommendation 2 Hour before competition
1 g/kg
10
New cards
Carbohydrate Recommendation 4 Hour Before Competition
1-4 g/kg
11
New cards
Protein Recommendation 4 Hour Before Competition
.15 - .25 g/kg
12
New cards
Optimal % of carbohydrates in Sports Drinks
6-8%
13
New cards
10% or greater of carbohydrates in sports drinks leads to
Delayed gastric emptying, which can lead to upset stomach
14
New cards
Force =
Mass \* Acceleration
15
New cards
Work =
Force \* Displacement
16
New cards
Power =
Work / Time
17
New cards
Cardiac Output =
Stroke Volume \* Heart Rate
18
New cards
Fick Equation
V02 = Q \* a-V02 Difference
19
New cards
MAP =
((Systolic - Diastolic)/3)+Diastolic
20
New cards
Cunningham Equation
RMR = 500+22(LBM in kg)
21
New cards
1 kg =
2\.205 lbs
22
New cards
1 Met =
3\.5ml O2/ kg
23
New cards
Walking METS
3\.3 METS
24
New cards
Physiological Efficiency
Employing only the amount of mental and physical energy required to perform the Task
25
New cards
Ideal Performance State Characteristics
Absence of fear - No fear of failure
No thinking about performance
Narrow Focus of Attention on Task
Sense of effortlessness
Sense of personal Control
Distortion of Time/Space - Time seems Slow
No thinking about performance
Narrow Focus of Attention on Task
Sense of effortlessness
Sense of personal Control
Distortion of Time/Space - Time seems Slow
26
New cards
Emotions
A Temporary Feeling states that occur in response to events and have physiological and psychological components.
27
New cards
Arousal
A Blend of physiological and psychological activation in an individual and refers to the intensity of motivation at any given movement.
28
New cards
Anxiety
A Sub category of arousal and is a negatively perceived emotional state characterized by nervousness, worry, apprehension or fear.
29
New cards
Cognitive Anxiety
Mental Part of anxiety, Thinking Fast
30
New cards
Somatic Anxiety
Evidence through physical symptoms such as tense muscles, tachycardia, upset stomach
31
New cards
State Anxiety
Subjunctive experience of apprehension and uncertainty
32
New cards
Trait Anxiety
Everyday Anxiety
33
New cards
Stress
Imbalance between demand and response capability; Failure has consequences
34
New cards
Stressor
Event that causes stress
35
New cards
Distress
Negative Stress
36
New cards
Eustress
Positive Stress
37
New cards
Drive Theory
As arousal or state anxiety increases, so does performance
38
New cards
Inverted U theory
Arousal increases performance to an optimal state, then it decreases performance
39
New cards
Individual Zones of optimal functioning
Different people in different environments responds at different levels of arousal
40
New cards
Catastrophic theory
Arousal can cause a sharp decline in performance
41
New cards
Reversal theory
Athletes have the power to change how they Interpret arousal
42
New cards
Motivation
Intensity and direction of effort
43
New cards
Intrinsic Motivation
Driven form the athlete by the love of the game or how they feel from it
44
New cards
Extrinsic motivation
Comes from external source, Ex: Trophy, Praise
45
New cards
Achievement Motivation
Persons effort to master a task
46
New cards
Motivation to achieve success (MAS)
Pride in ones success, challenges one ability
47
New cards
Motivation to avoid failure (MAF)
Protecting ones self esteem, avoiding shame
48
New cards
Positive Reinforcement
Act of increasing probability of occurrence of a behavior by positive action
49
New cards
Negative reinforcement
Increases probability by removal of an act
50
New cards
Positive punishment
Decreases a behavior by a presentation of something (adding pushups)
51
New cards
Negative punishment
Decreases a behavior by removing something (Removing freetime)
52
New cards
Attention
Defined as the processing of both environment and internal cues that comes to awareness
53
New cards
Selective Attention
Being able to suppress irrelevant cues
54
New cards
Self efficacy
Perception of ones ability to perform a given task
55
New cards
Process Goals
Athlete has control, focus on actions to perform task
56
New cards
Outcome goals
athletes have little control over (ex: focused on winning)
57
New cards
Short term goals
Related to current training
58
New cards
Long term goals
Big goals that short term goals add up to
59
New cards
Simplification
Adjust tasks by changing task characteristics to make it easier
60
New cards
Pure Part Training
Practicing all subcomponents independently then adding it all together
61
New cards
Progressive part training
First two parts isolated then added together then practice 3rd component then add all together
62
New cards
Amount of rest time in between 1RM Attempts
3 Minutes
63
New cards
Amount of attempts for vertical/long jump attempts
3
64
New cards
Validity
The degree a test measures what it is suppose to measure
65
New cards
Face Validity
The appearance to the athlete that the test measures what it is suppose to measure
66
New cards
Criterion-Referenced Validity
The test scores are associated with some other measure of the same ability
67
New cards
Concurrent validity
Test scores are associated with measuring same ability
68
New cards
Convergent Validity
high positive correlation between results of tests
69
New cards
Predictive Validity
Test score corresponds with future behavior or performance
70
New cards
Intrasubject Variability
Lack of consistent performance by the person being tested
71
New cards
Interrater Reliability
The degree which different raters agree in their test results
72
New cards
Intrararater Variability
The lack of consistent scores by a given tester
73
New cards
Order of battery of tests
1. Non Fatiguing tests
2. Agility tests
3. maximum power/strength tests
4. sprint tests
5. local muscular tests
6. fatiguing anaerobic capacity
7. aerobic tests
74
New cards
Sarcomere
Basic contractile unit of muscle fiber
75
New cards
Calcium binds to “x” when a muscle contracts
Troponin
76
New cards
What happens when calcium binds to troponin
tropomyosin moves, unblocking myosin binding sites
77
New cards
Z Disk
On each end of a sarcomere, where actin are attached
78
New cards
A Band
Dark colored bands containing myosin
79
New cards
I bands
Lighter bands only containing actin
80
New cards
M line
Line in middle where Myosin are attached
81
New cards
H zone
Space between Actin filaments
82
New cards
First Class Lever
A lever which the muscle force and resistive force act on opposite sides of the fulcrum
83
New cards
Second Class Lever
A lever which the muscle force and resistive force act on the same side of the fulcrum, with the force acting through the moment arm longer which the resistive force acts. Less muscle force required.
84
New cards
Third Class Lever
A lever which the muscle force and resistive force act on the same side of the fulcrum, with the the muscle force acting through a moment arm shorter which the resistive force acts. More muscle force required.
85
New cards
Example of a First Class Lever
Elbow extension (Tricep Extension)
86
New cards
Example of a Second Class Lever
Plantar Flexion (Calf Raise)
87
New cards
Example of a Third Class Lever
Elbow Flexion (Bicep Curl)
88
New cards
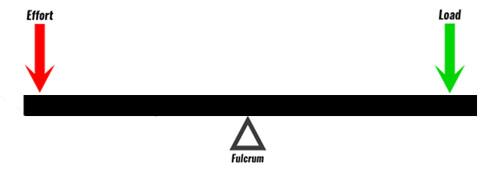
1st Class Lever
89
New cards
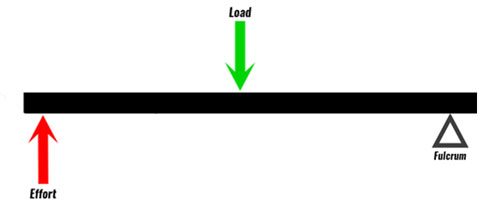
2nd Class Lever
90
New cards
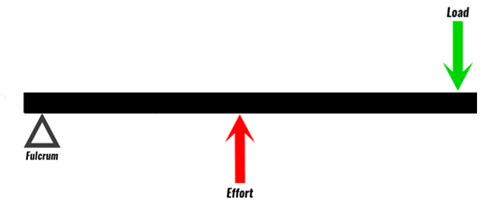
3rd Class Lever
91
New cards
P-Wave
Depolarization of Atria
92
New cards
QRS Complex
Depolarization of Ventricles
93
New cards
T-Wave
Ventricle repolarization
94
New cards
SA Node
Pacemaker
95
New cards
AV Node
Impulse is delayed before going to ventricles
96
New cards
AV Bundle
Conducts impulse to ventricles
97
New cards
Connective Tissue Order (Outside to Inner)
1. epimysium
2. perimysium
3. endomysium
98
New cards
Glycemic Load =
GI of food \* grams of carbs per serving / 100
99
New cards
Correct Stance for medball throws
Shoulder width
100
New cards
How many steps to stop from a full speed accel drill
6 steps