Chapter 1: Key Concepts and Body Systems
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another.
Physiology
The study of the function of the body's structural machinery.
Levels of Organization
The hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems that define life, from atoms to organisms.
Atom
Matter is composed of atoms, which are composed of subatomic particles.
Molecule
Atoms join to form molecules.
Macromolecule
Small molecules may combine to form larger macromolecules.
Organelle
Organelles consist of aggregates of interacting macromolecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Cell
Cells are composed of organelles; the basic unit of structure and function of the body.
Tissue
Tissues are specialized cells that assemble into layers or masses that have special functions.
Organ
Organs are complex structures with specialized functions formed by groups of different tissues.
Organ system
Organ systems are groups of organs that function closely together.
Organism
Organisms are interacting organ systems.
Movement
Changes in position of the body or of a body part; motion of an internal organ.
Responsiveness
Reaction to a change inside or outside the body.
Growth
Increase in body size without change in shape.
Reproduction
Production of new organisms and new cells.
Respiration
Obtaining oxygen, removing carbon dioxide, and releasing energy from foods.
Digestion
Breakdown of food substances into simpler forms that can be absorbed and used.
Absorption
Passage of substances through membranes and into body fluids.
Circulation
Movement of substances in body fluids.
Assimilation
Changing of absorbed substances into different chemical forms.
Excretion
Removal of wastes produced by metabolic reactions.
Metabolism
The collection of chemical reactions in cells that support life.
Major Requirements of Organisms
Water, Food, Oxygen, Heat, Pressure.
Homeostasis
The body's ability to keep its internal conditions stable so that cells can survive, despite changes in outside environment.
Effector
An organ or cell that acts in response to a stimulus to restore balance.
Body cavities
Spaces within the body that separate compartments, allowing for communication and containment of infection.
Cranial cavity
The space within the skull that houses the brain.
Vertebral canal
The canal formed by the vertebrae that contains the spinal cord.
Thoracic cavity
The chamber of the body that is protected by the rib cage and contains the lungs and heart.
Abdominopelvic cavity
The cavity that encompasses both the abdominal and pelvic regions.
Serous membranes
Double-layered structures that line organs and secrete serous fluid to reduce friction.
Integumentary system
Protects tissues, regulates body temperature, and supports sensory receptors.
Skeletal system
Provides framework, protects soft tissues, provides attachment for muscles, produces blood cells, and stores inorganic salts.
Muscular system
Causes movements, maintains posture, and produces body heat.
Nervous system
Detects changes, receives and interprets sensory information, and stimulates muscles and glands.
Endocrine system
Controls metabolic activities of body structures.
Cardiovascular system
Moves blood through blood vessels and transports substances throughout the body.
Lymphatic system
Returns tissue fluid to the blood, carries certain absorbed food molecules, and defends the body against infection.
Digestive system
Receives, breaks down, and absorbs food while eliminating unabsorbed material.
Respiratory system
Responsible for the intake and output of air and the exchange of gases between air and blood.
Urinary system
Removes wastes from blood, maintains water and electrolyte balance, and stores and eliminates urine.
Male reproductive system
Produces and maintains sperm cells and transfers sperm cells into the female reproductive tract.
Female reproductive system
Produces and maintains egg cells, receives sperm cells, supports embryo development, and functions in the birth process.
Anatomical position
Standing upright with face and toes forward, arms at sides with palms facing forward, and feet parallel.
Body Planes
Imaginary lines that divide the body into sections, including sagittal, transverse, and frontal.
Axial skeleton
The part of the skeleton that includes the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage.
Appendicular skeleton
The part of the skeleton that includes the limbs and pelvic girdle.
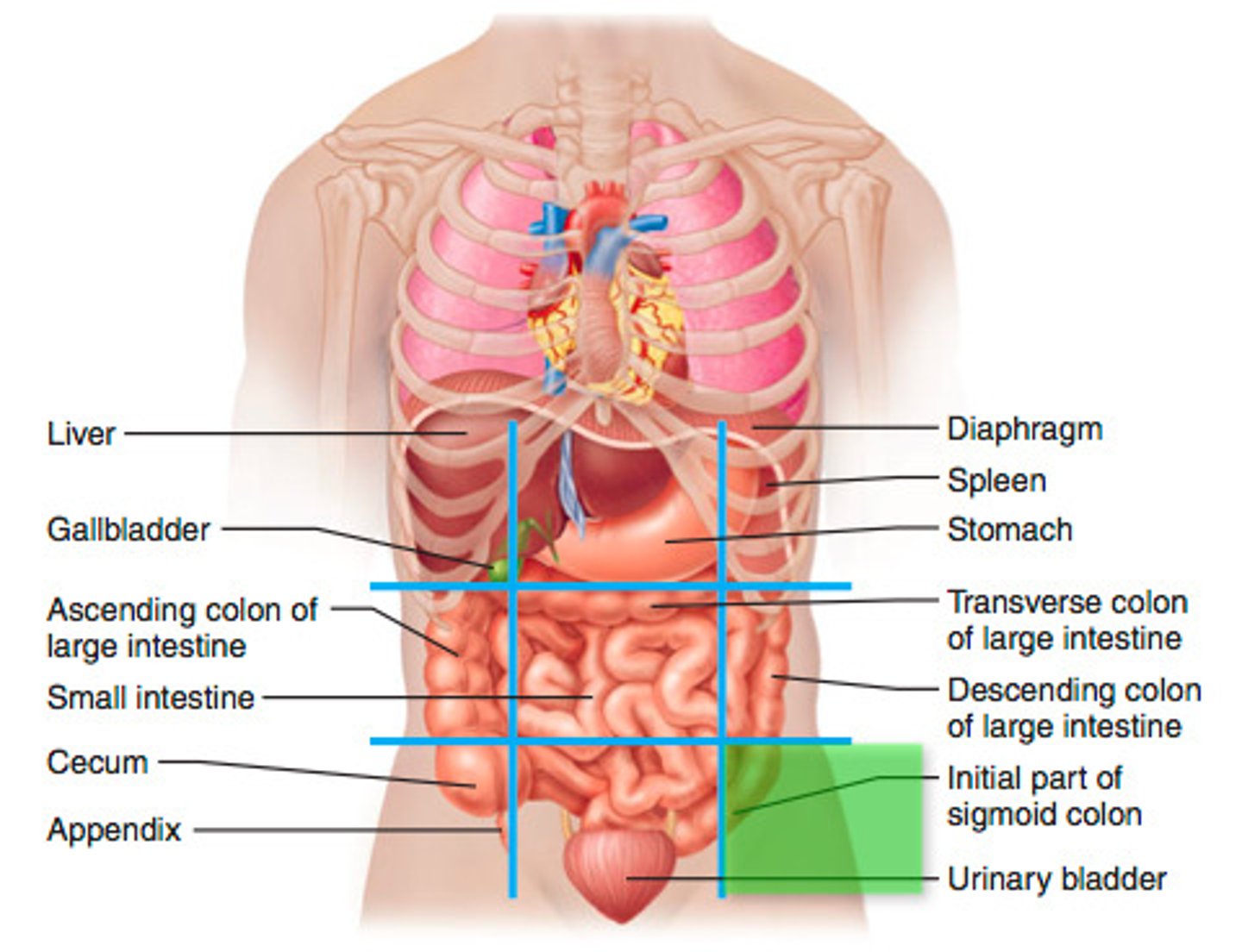
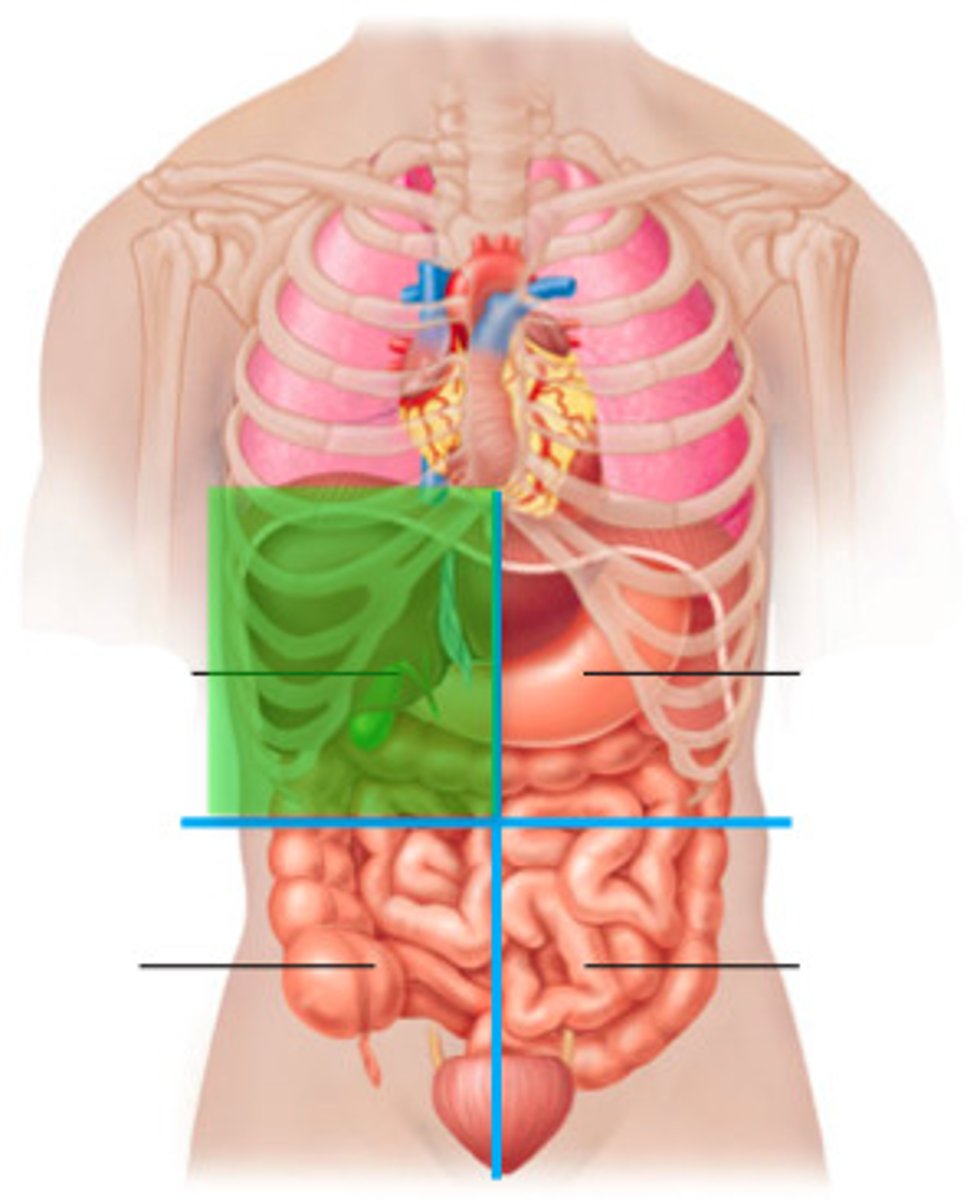
Right upper quadrant
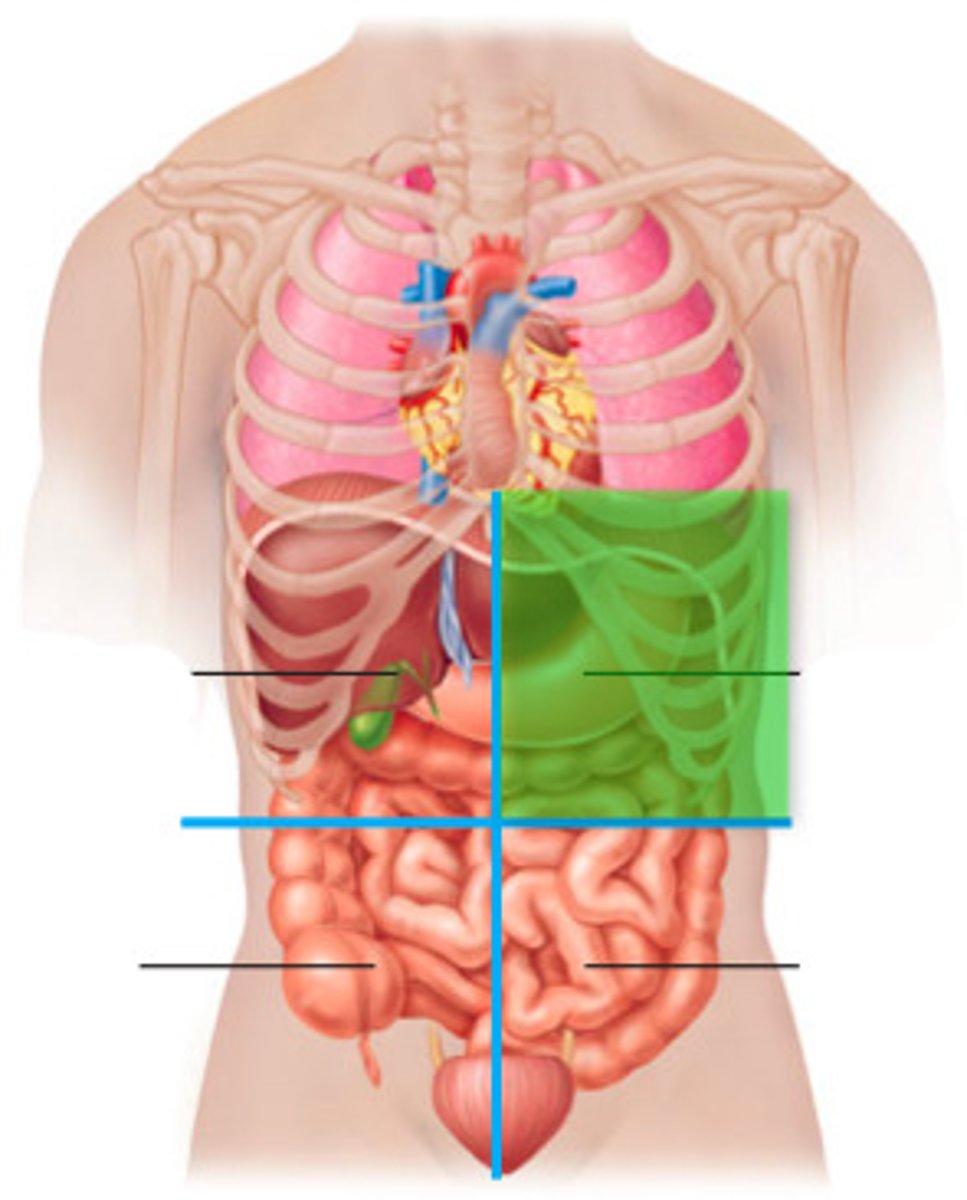
Left upper quadrant
Left lower quadrant
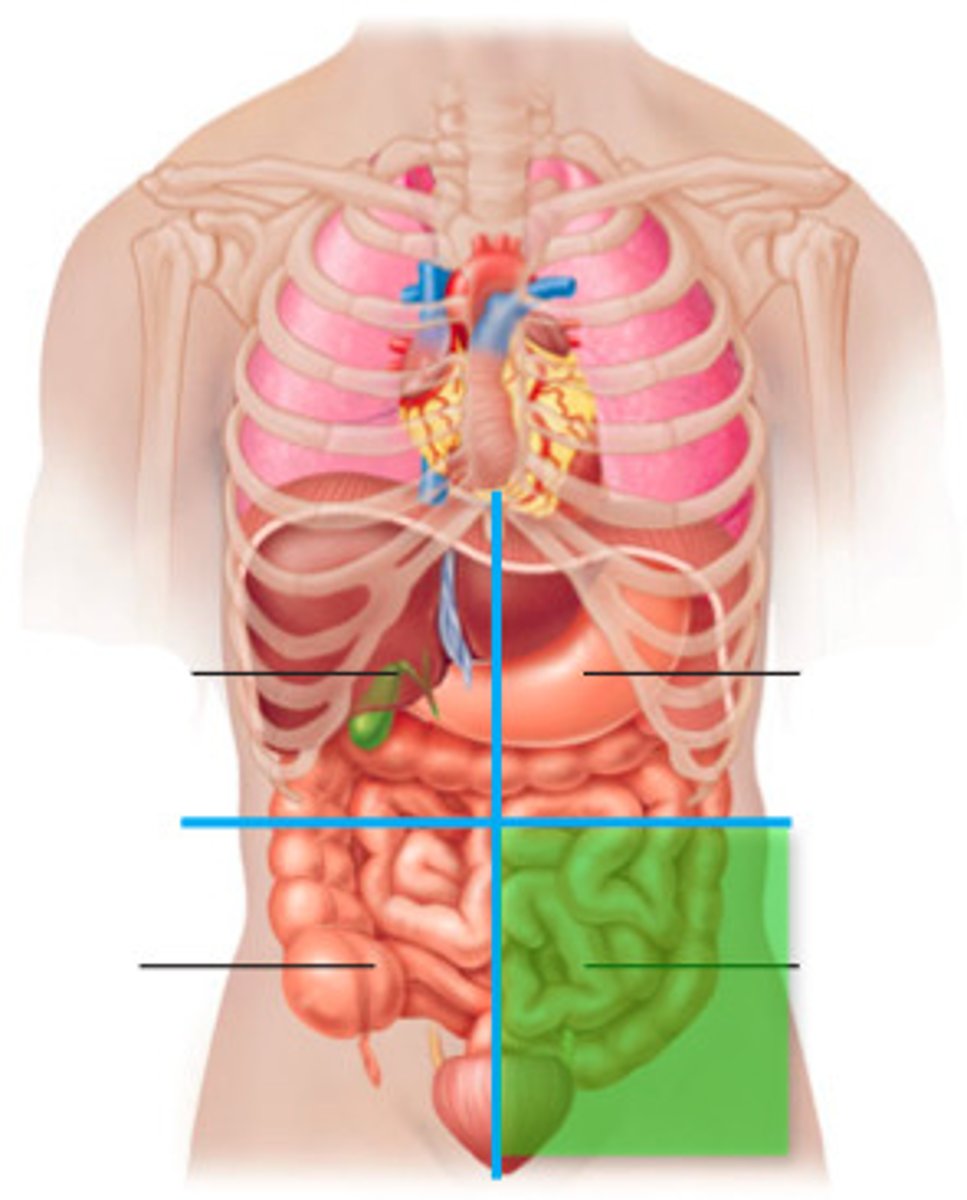
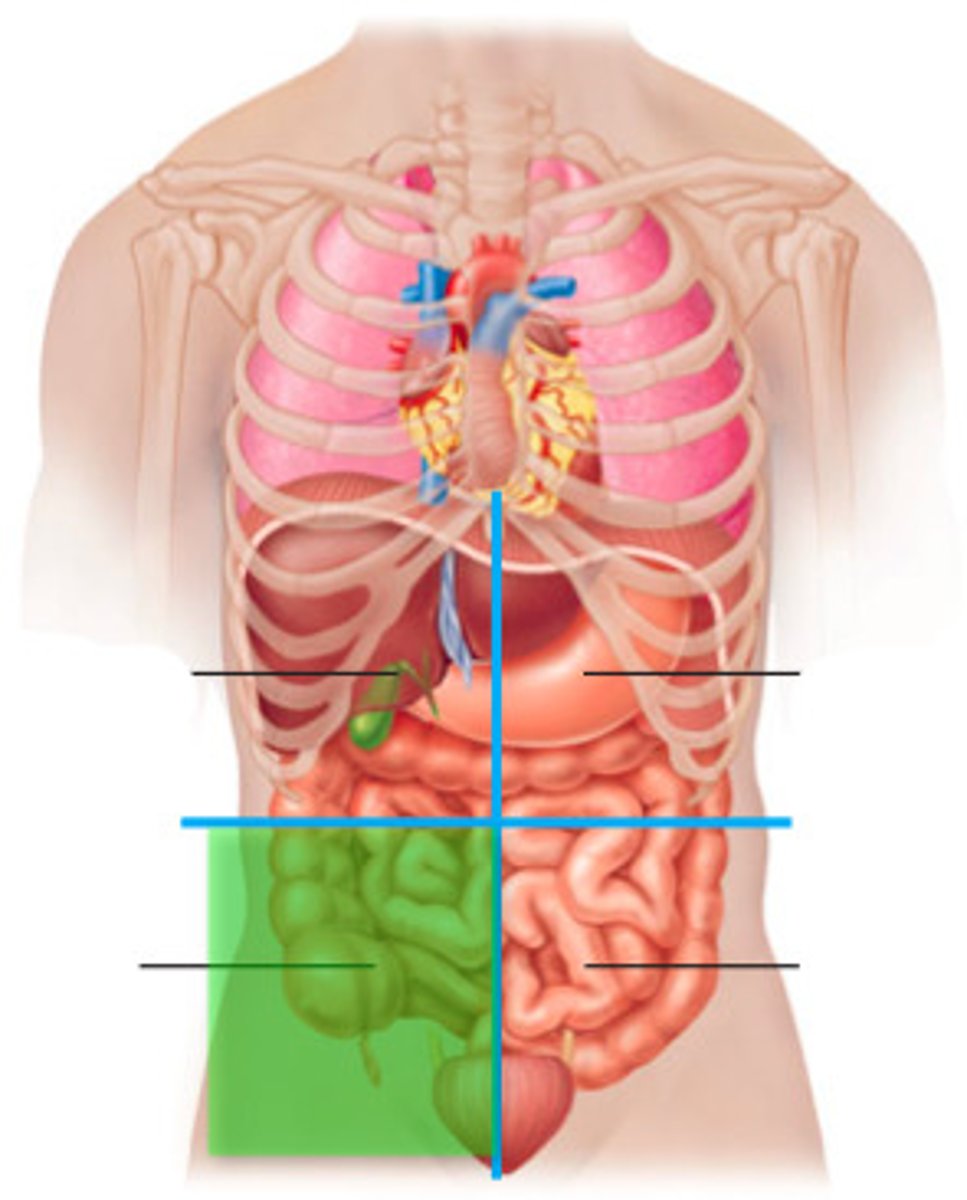
Right lower quadrant
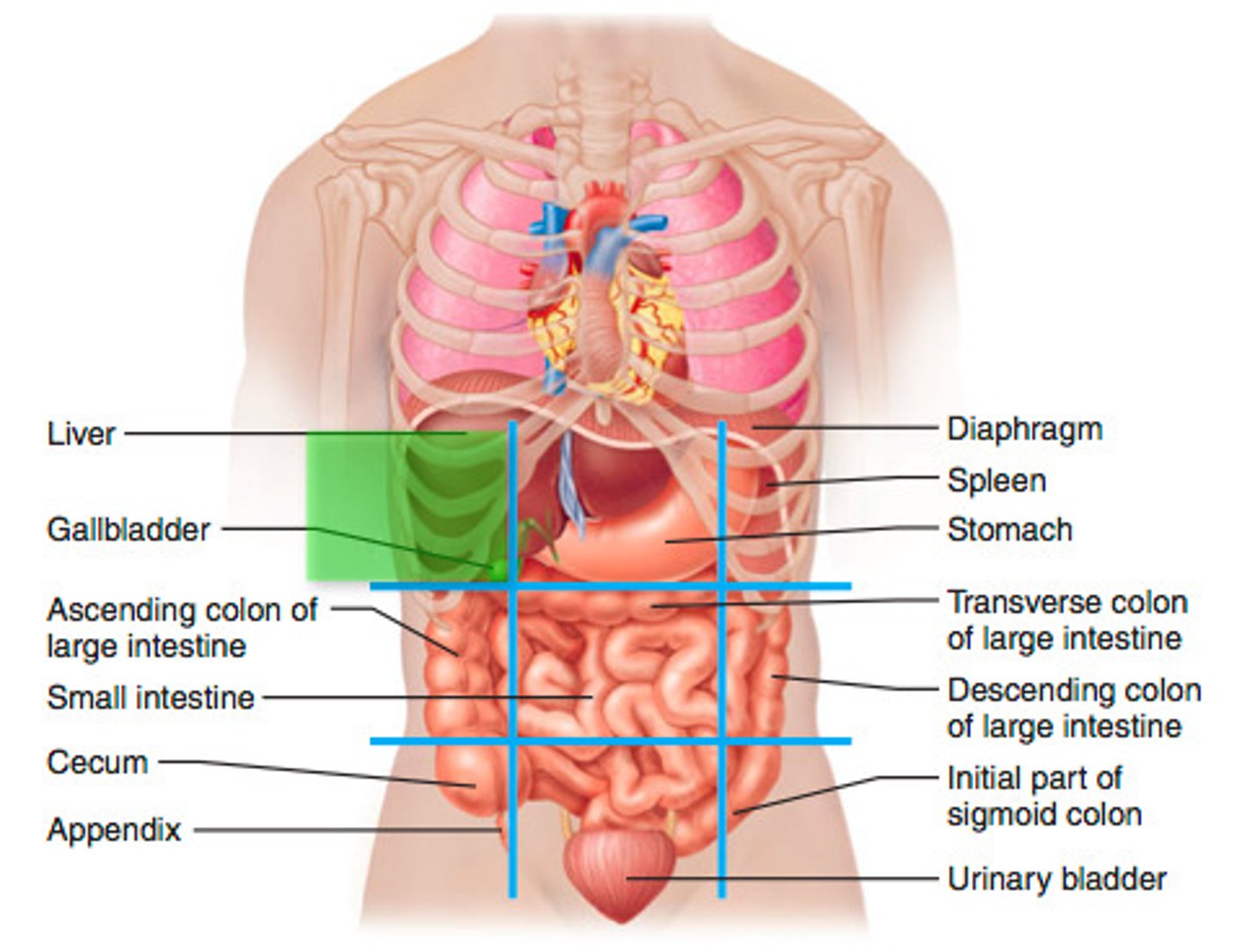
Right hypochondriac region
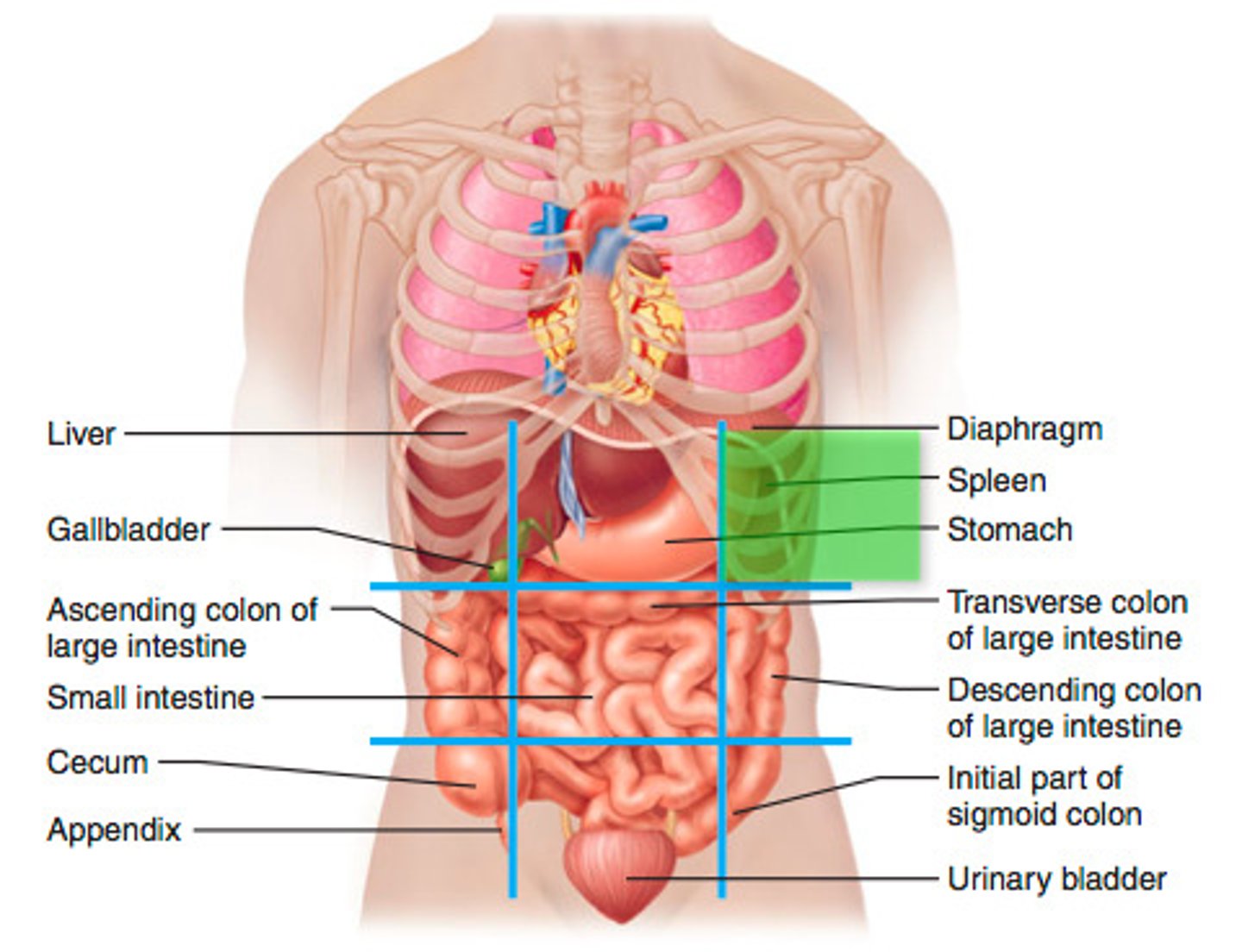
Left hypochondriac region
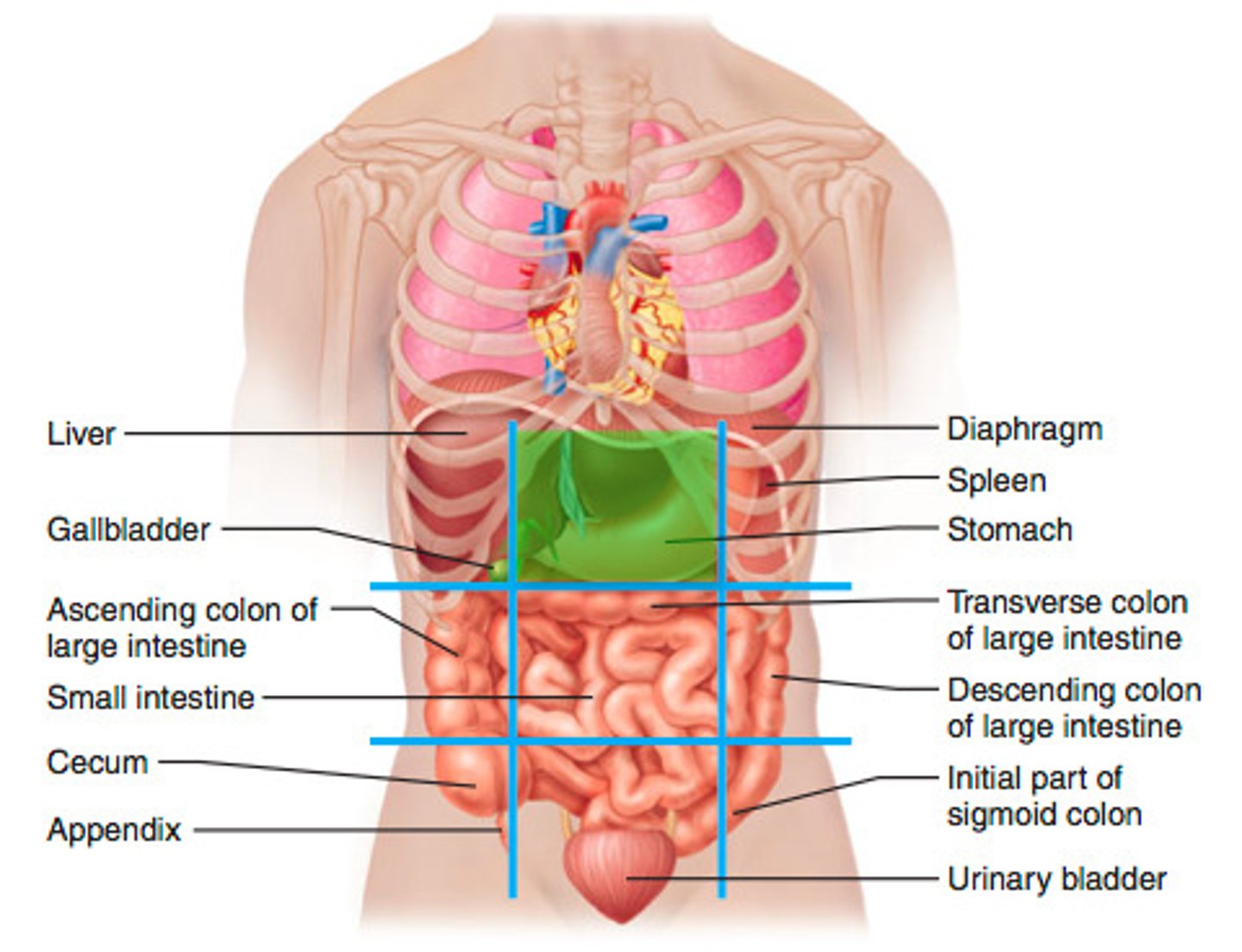
Epigastric region
Right lumbar region
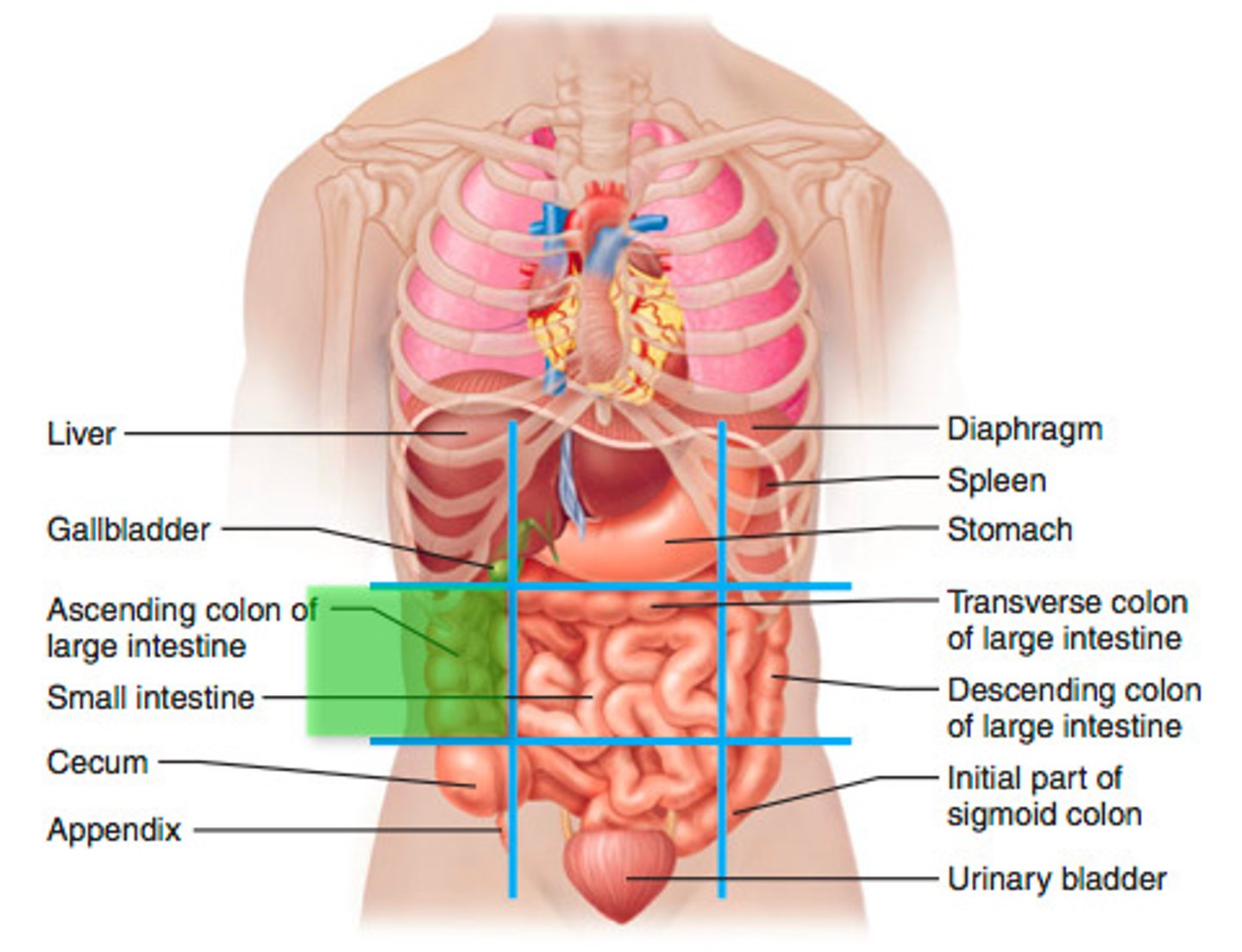
left lumbar region
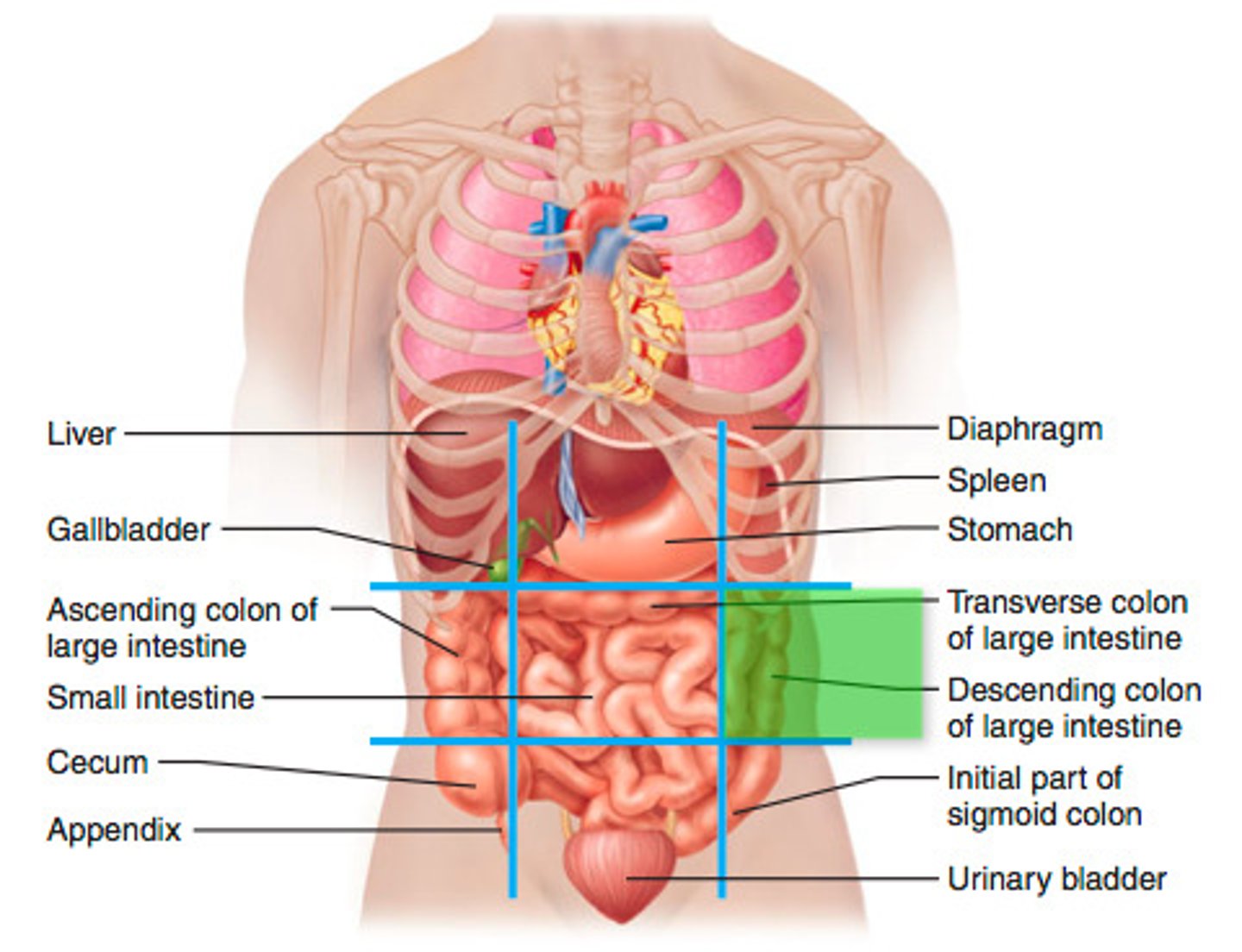
umbilical region
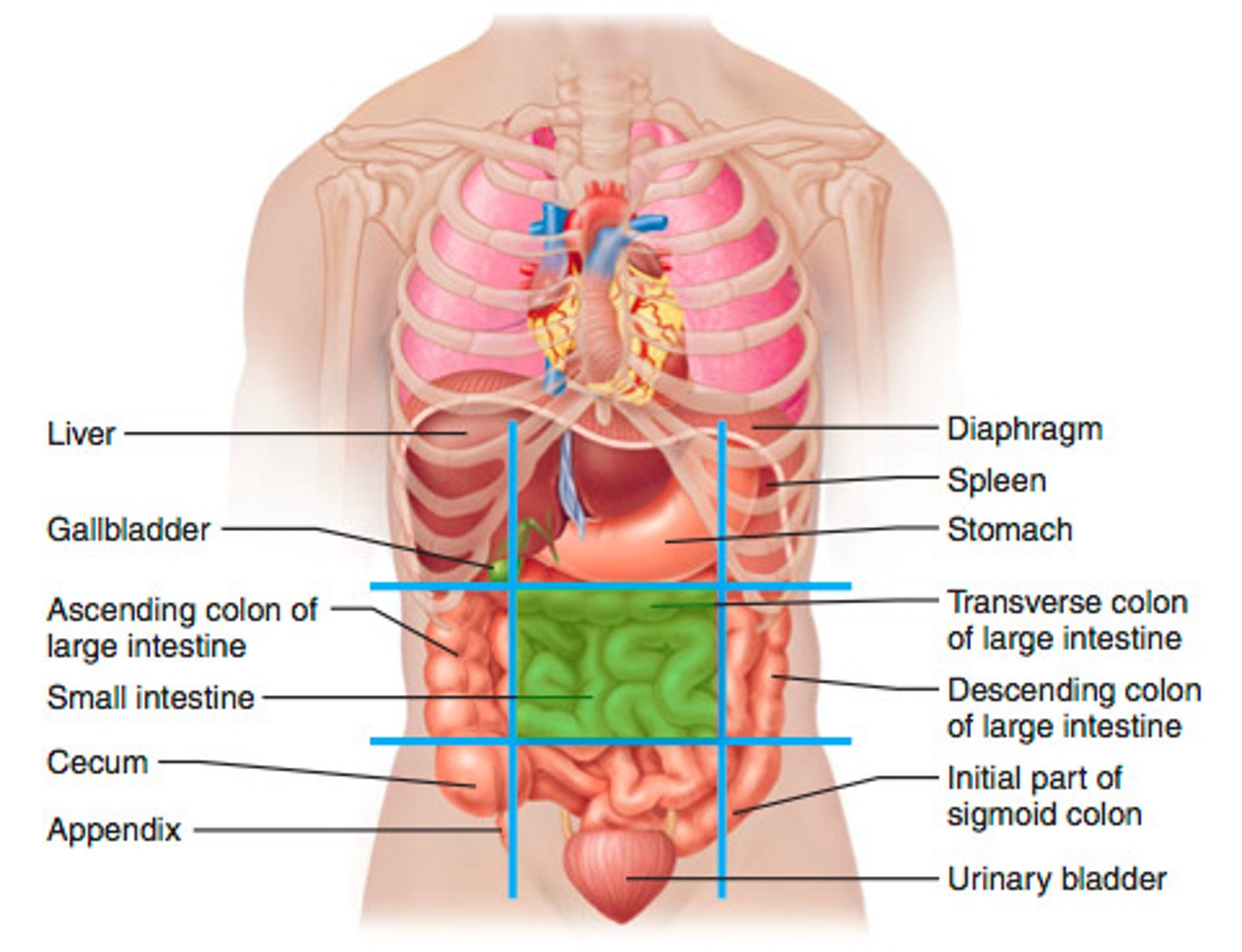
Right iliac region
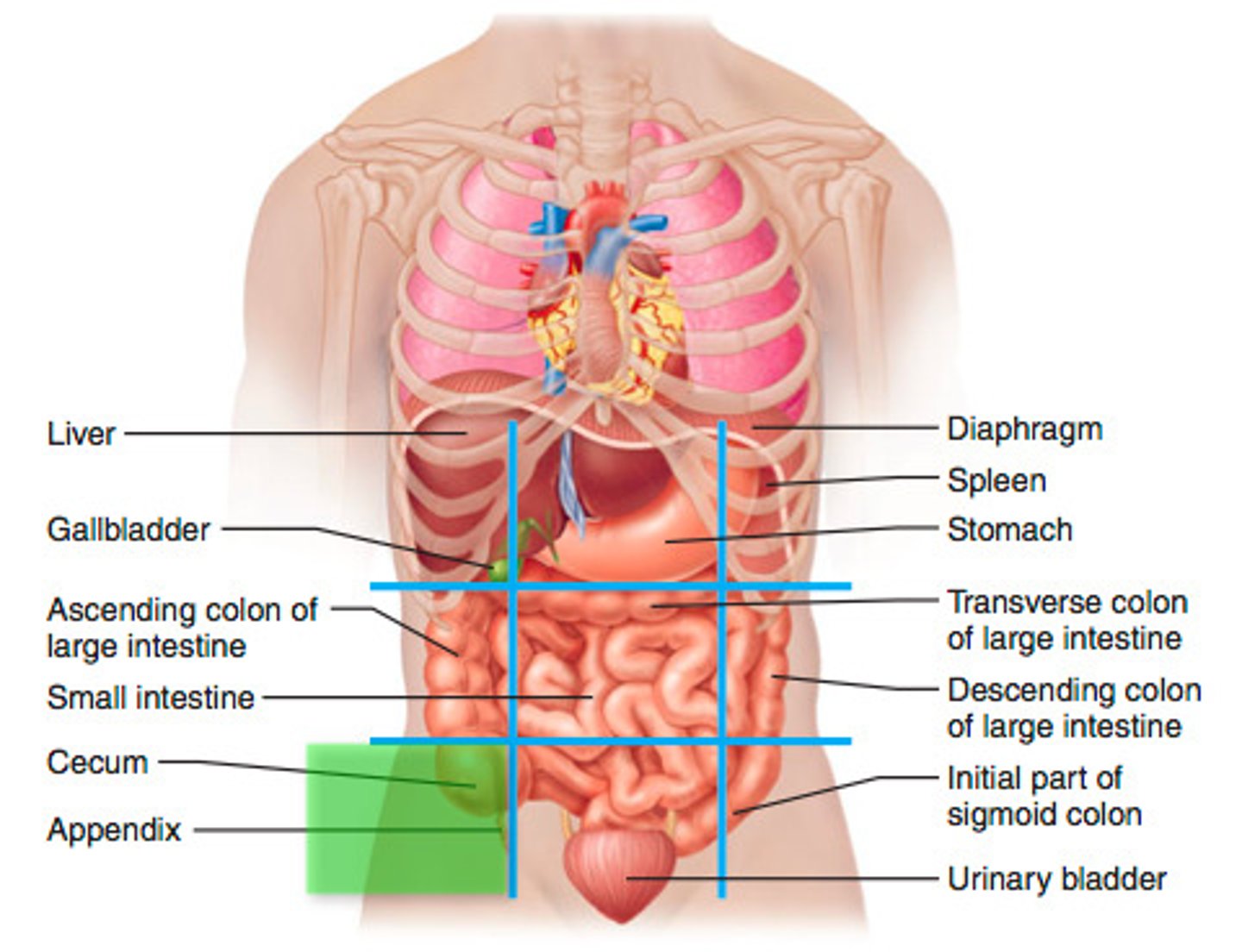
Hypogastric region
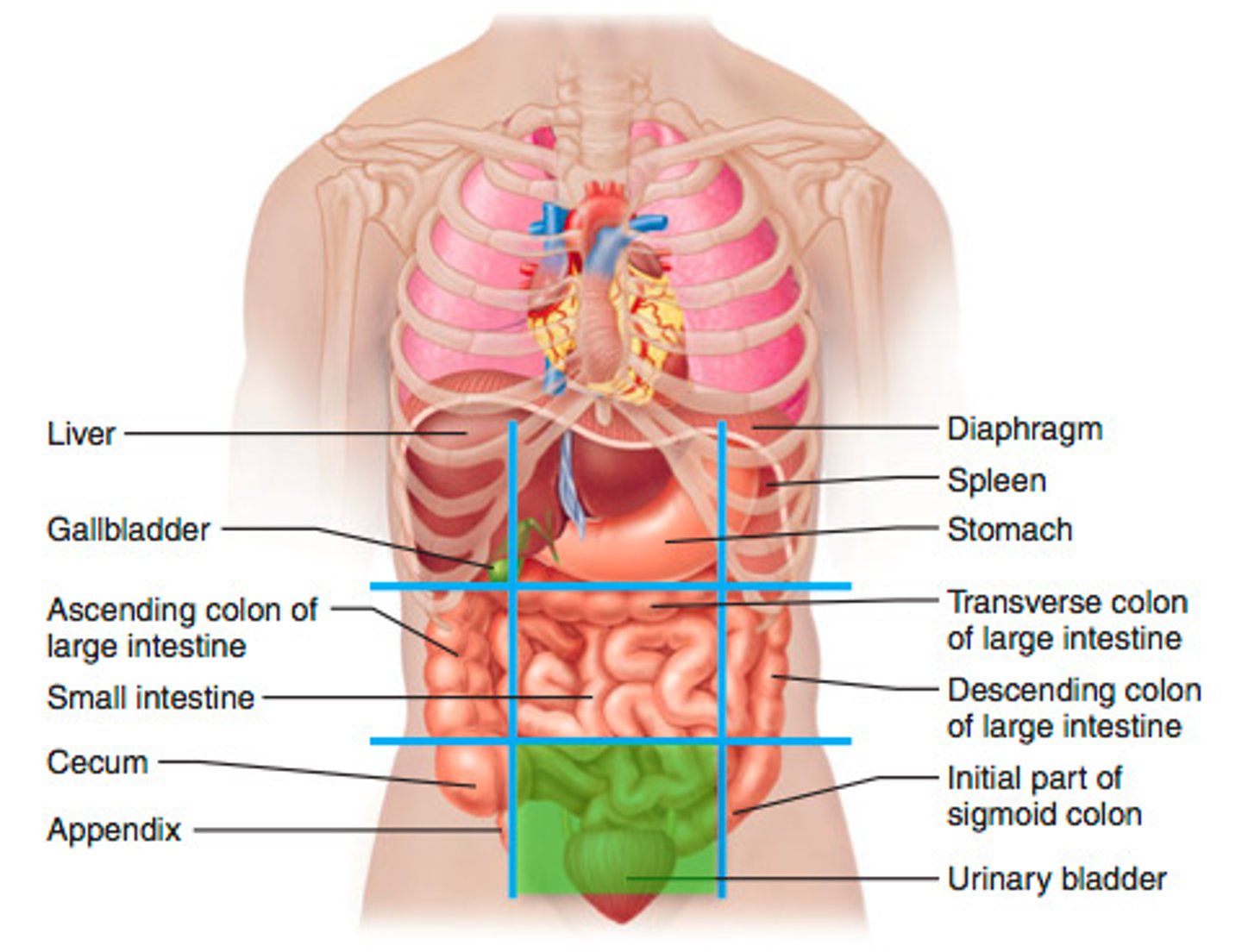
Left iliac region