Manufacturing Management
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
232 Terms
Description of Capital vs return on investment
Assessment of length of time an investment takes to pay back
Trade-off for Capital vs return on investment
Cost vs time and quality
Cycle time
the length of time a part spends at each workstation
Utilisation of a plant
Measurement of proportion of available plant time that is spent generating value - linked to capacity
Trade-off of Utilisation of plant
Time vs cost and quality
Description of Capacity versus responsiveness to demand
Capacity is the theoretical maximum volume of production - spare capacity allows faster response to orders
Trade-off for Capacity versus responsiveness to demand
Time vs Cost
Description of Inventory vs responsiveness to demand
Inventory is the amount of manufacturing material kept on site - more inventory allows faster response to orders
Trade-off of Inventory vs responsiveness to demand
Time vs Cost
Efficient use of resources allows
Simultaneous improvement of cost, time and quality
Effective use of resources allows
Survival and growth of the business
What are the transforming resources in a manufacturing business?
a) Components and raw materials
b) Plant and raw materials
c) Plant and staff
d) Staff and raw materials
c) Plant and staff
low volume processes produce a ______ variety of product
high
High volume processes produce a _____ variety of products
low
The approach to managing an individual process depends where it falls on the _______________ spectrum
Volume-variety
Production process groups examples
Mass production
Batch production
Job production e.g. consultancy companies
Project e.g. buildings, bridges
Project processes
Discrete, highly customised products
Dedicated resources
Long production timescale
e.g. buildings, bridges, large infrastructure
Job shops
Generally similar but may be one-offs
Shared resources
High skill level
e.g. tooling, patterns
Batch production
1+ item at a time produced
Processes repeated
Processes similar to job shop but management is different
Wide range of volumes
e.g. machine tools, automotive components, customised electronics
Mass production
High volume, relatively low variety
Variants possible if do not affect basic process flow
Highly repetitive and predictable
e.g. car factories, consumer electronics
Set up time
time it take to set-up machine so as to switch production from one product to another
e.g. through changing of tooling
Work in Progress (WIP) Inventory
The amount of unfinished product on the shop floor
Control
The ability of management to know and control the state of production at any given moment
Throughput time
The length of time it takes a single product to undergo all stages of production
Utilisation
The proportion of available plant time that is spent generating value
Advantages of Batch manufacturing
Set up time - only needs to be set up once
Flexibility - Wide variety of products and volumes can be handles without changes to the process layout
Disadvantages of Batch manufacturing
High throughput time whole batch processed at each step
High WIP Inventory
Process layouts
Different layouts of machines and staff for the most efficient processing of product depending on the production
3 main types of process layouts
Product Layout
Process Layout
Hybrid Layout
Process layout
Low volume and job shop manufacturing
High flexibility but complex product flow paths
Load distance calcs used to find optimum layout
Advantages of product layout
Smooth product flow
Short throughput
Low WIP inventories
Product layout
Generally used for high volume manufacturing. Has the advantage of simple product flow but is inflexible. Precedence diagrams and line balancing can be used to find the optimum layout.
Disadvantages of product layout
Low flexibility for intro of new product design
Any work interruption stops wholes process
Advantages of Hybrid Layout (Group Technology)
High Utilisation
Short throughput time
Reduced machine set-up time
Low WIP inventories
More flexible than product layout
Hybrid layout
generally used for medium to high volume batch manufacturing
Disadvantages of Hybrid Layout (Group Technology)
Less flexible than process layout
More complex to control than product layout
Group Technology
Grouping together or parts or products into families by processing operations
Influence of group technology on manufacturing industry
Simplifying parts
Standardisation of processes
Visibility of part in flow production
Manufacturing Flexibility
The capability of producing different parts without major retooling
How fast a company can changes its processes from old product to new
Operational Flexibility
Efficiently produce highly customized and unique products
Customer Flexibility
Exploit various dimensions of speed of delivery
Strategic Flexibility
A company to offer a wide variety of products to its customers
Capacity Flexibility
Rapidly increase or decrease production levels or to shift capacity quickly from one product or service to another
Examples of automated operations tasks
Programmed control of manufacturing operations
Storage
Automated transfer of parts between storage and production machines
Identification of parts
Orientation of parts
Loading and unloading of parts
Automated operation cycle
Examples of Automated setup tasks
Changeover of programmes
Tool and fixture storage
Transfer of tools and fixtures between storage and production machines
Automated tool and fixture changeovers
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)
-two or more cells doing different tasks
Can be thought of as an automated cell
High level of system automation
Wide variety of parts
Simultaneous manufacture of different parts
Flexible
High capital investment
e.g. aerospace industry and machine tool builders
Flexible Manufacturing cells (FMC)
-Two or more CNC machines doing similar tasks
-Multiple machines with similar capability
-Wide variety of parts
-Machines can be reconfigured to manufacture different parts
-High level of automation
-High capital investment
-e.g. repetitive part manufacturing environments
Advantages of FMS
Faster, lower - cost changes,- improved capital utlisation
Lower direct labour cost (reduction in no. of workers)
Reduced inventory (planning and programming precision)
Consistent and better quality (automated control)
Lower cost/ unit of output
Savings from indirect labour (reduced errors)
Disadvantages of FMS
Limited ability to adapt to changes
Substantial pre-planning activity
Expensive, costing millions
Dedicated Transfer Lines (DTL)
e.g. conveyors, robots
High volume of manufacture of a limited range of parts
Low flexibility
High reliability required
Agile systems
High volume of a limited range of parts
Agility in response to part variety changes
Routing flexibility
Breakdowns have limited effect on production
Equation for desired cycle time
C = time period / planned output
Equation for theoretical minimum number of workstations
TM = time for all operations / c
Equation for Utilisation %
(total work content x 100) / (No workstations x cycle time)
Equation for balancing delay%
100 - utilisation
Steps for designing a hybrid layout
Group parts that share common processes
Groups of processes form manufacturing cells
Deal with remaining processes
i. Duplicate process
ii. Use process layout
iii. Allow part to visit more than one cell
What is production planning
Deciding
-What product, amount, when
Scheduling
Planning
Why is a formal planning process needed
Align production activities and business plans
Ensure business plans are realistic
Handle complexities and large amounts of data
Use production resources efficiently while meeting constraints
Ensure resources are available when needed
Provide a plan against which progress can be measured
Aggregate planning is…
The task of identifying plans to produce products, expressed in specific quantities and dates, to fulfil a series of anticipated product demands and customers orders
MPS
Master Product Schedule
A Master Production Schedule is for
planning horizons which contains required production quantities for a specific product type together with the desired completion date
MPS must seek to reconcile the many requirements of the company functions such as
Sale requirements
Financial requirements
Production requirements
Resources and labour requirements
Patricks def of MPS is
Something which is related to time
Time is the key word
Date
Product
Quantity
We will make x many of y products for the zth of month
The production scheduling function is a combination of a number of tasks such as
-lot sizing
-process routing
-dispatch/loading
-sequencing
-works order generation
Common production scheduling constraints are to
Meet delivery dates
Minimise lead times
Reduce overall length of the required production period
Balance workload of resources
Ensure uniform rate of productivity
An MPS is usually in the form of
list of jobs with associated due dates
Lead time is the
time between customer order and order delivery
Production period is the
time between starting work on an order and completion
The major production activity control functions are
Policies for inspection
Support services
Policies for handling the breakdowns
Schedules for maintenance
Procedures for process monitoring
Data collection on production progress
Benefits of a smooth production profile?
Reduces the amount of unused production capacity
Why is inventory planning needed
A buffer between supply and demand
Decouples processes allowing work to continue if there is a problem upstream
Total Carrying cost =
H(Q/2) where,
H = Holding cost
Q = Quantity
Q/2 = Average inventory
Total ordering cost =
S(D/Q) where,
S = Order cost
D = Average annual demand
D/Q = Number of orders
EOQ =
D = average annual demand
S = order cost
H = holding cost
Weeks of supply =
Average inventory value / weekly sales
Inventory Turnover =
Annual sales / average inventory value
Fixed - Order Quantity System is
ordered whenever inventory drops to reorder level (ROL), so reorder date varies
Replenishments System is when
Reorder date is fixed and order quantity (Q) varies according to inventory level to fulfil the replenishment level
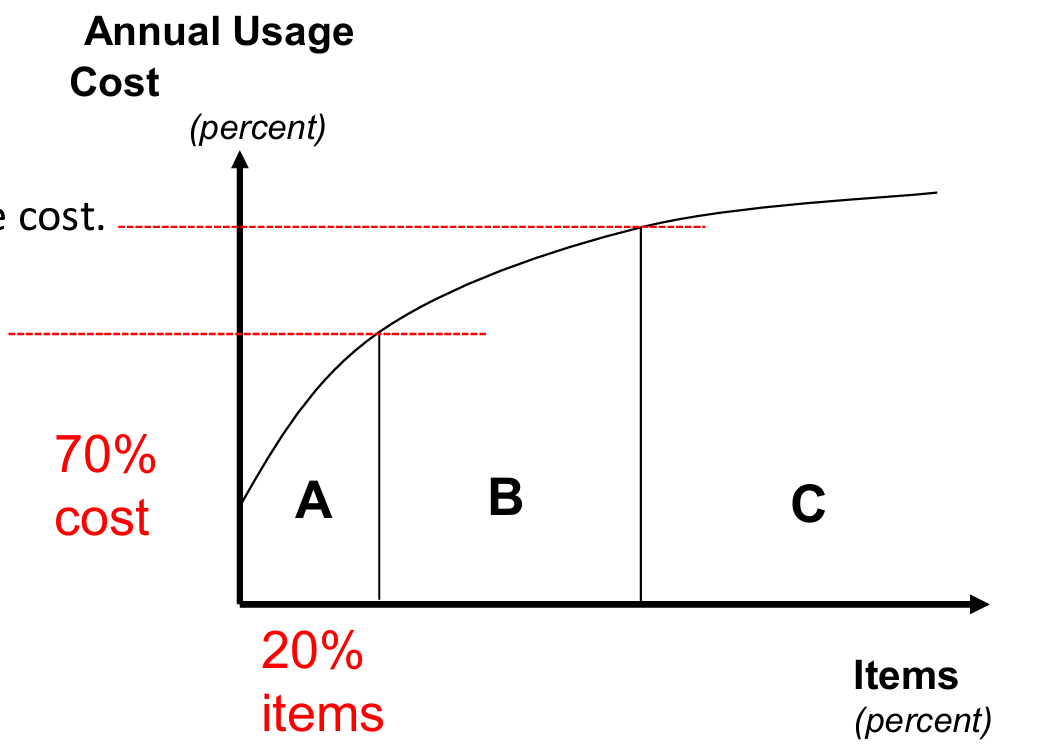
A-items
5-20% of inventory items incurring 50-70% of expenses.
High cost items that are vigorously controlled
B-items
30-50% of inventory items incurring 20-30% of expenses
Moderate costs items that are accurately controlled
C-items
40-70% of inventory items incurring less than 10-20% of expenses
Low cost items that their control are more relaxed
Pareto Analysis is used to
Separate the vital few from the trivial many, and often utilises a Pareto chart as a visual tool to identify the few problems that causes the greatest lost
Pareto chart used to generate ABC inventory classification by
Calculate annual usage cost
(unit cost x annual usage)
Rank items in descending order based usage cost
Find cumulative percentage of usage cost
Find cumulative percentages of total items
Plot results
Divide into ABC categories
What is the main reasons a company would try to identify an economic order quantity for a stock item
In order to reduce the costs of holding stock
What does MRP stand for
Materials Requirements planning
MRP is
planning to have the correct quantities of components and materials available at the correct time in order to fulfil the Master Production Schedule
Some MRP characteristics are…
Product Oriented using a BOM
Future Oriented uses info from the master production schedule to calculate future component requirements
Priority Planning determines the production requirements to meet the master schedule
LT stands for
Lead Time (days)
TYP - M vs TYP-B
M is manufacture
B is bought
What is a Business Plan?
sets out the long term future of a company as series of financial statements and targets
What is a Marketing Plan?
gives in general terms what is to be sold and what income will be derived to meet the figures in the business plan
What is a Production Plan?
sets out what is to be produced, what resources will be needed and what this will cost
Resources Requirements Plan
Identifies the loads on the resources imposed by production plan and to compare this with theoretical capacity
In a JIT approach it is wasteful to
Store large amounts of anything
Produce more goods than immediately required
Move in-process materials and goods around
Product scrap
Carry out unnecessary work
JIT aims to…
Reduce waste in all forms, where waste is defined as everything that adds to the cost but not to the value
A Kanban system is designed to…
Minimise WIP quantities
It is a pull system
OPT stands for
Optimised production technology
OPT defined ten rules for planning and controlling production…
-Utilisation of a non-bottleneck resource system not determined by its own capacity
-Activation of a resource not the same as utilisation
-Time lost at a bottleneck operation is time lost for the total production system
-Time saved at non-bottleneck operation is an illusion
-Transfer between operations may not and often should not equal process batches
-Process batch sizes should be variable
-Capacity and priority should be considered simultaneously, not sequentially
-The unexpected is not unknown, it can be isolated and minimised
-Plant capacity should not be balanced, flow should be
-Sum of local optimisation factors is not equal to the optimisation of the whole system