Dental Anatomy, Morphology and Occlusion
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
Front Plane divides body into
Anterior and Posterior portions
Sagittal Plane divides body into
Left and right portions
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane divides body into
Superior and inferior portions
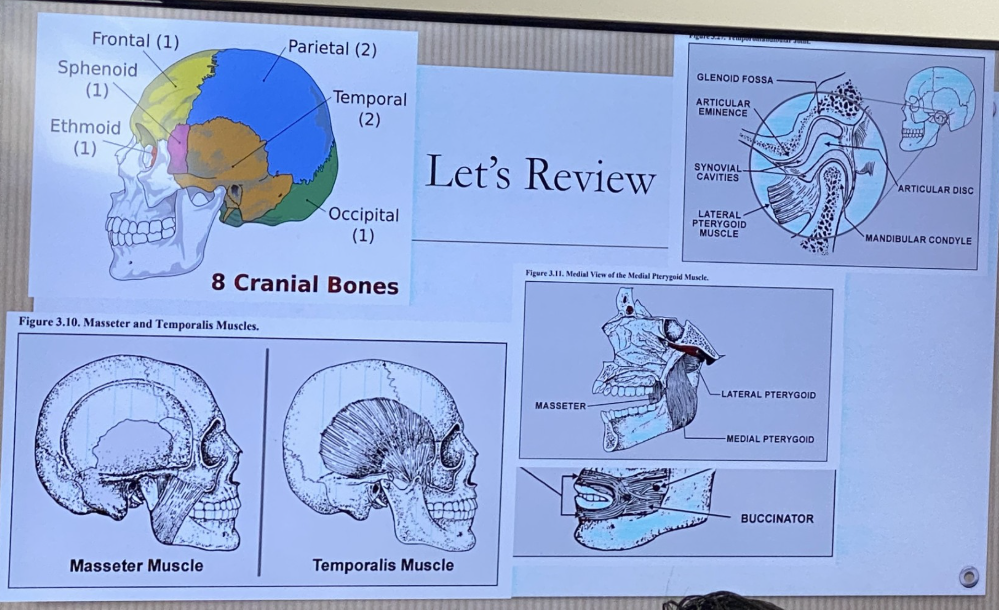
Name 2 out of 8 cranial bones
Left and Right Temporal
Where is the Left and Right Temporal located and shape?
Fan shape
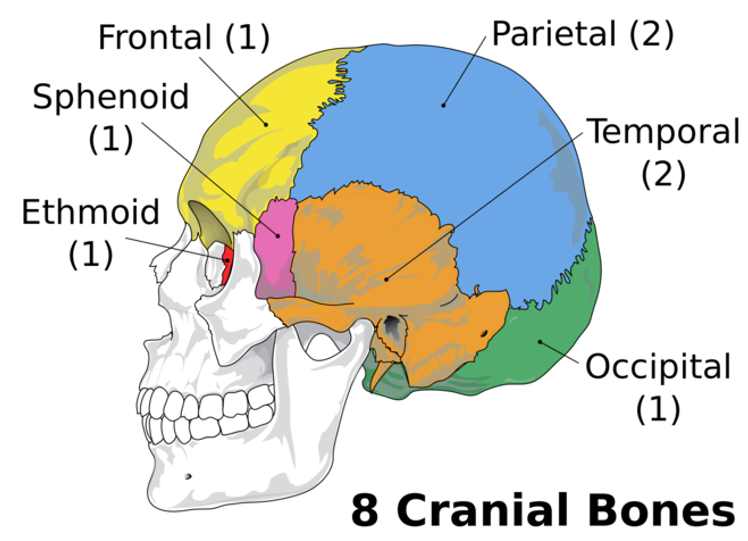
Name 2 important Temporal Bones
Glenoid Fossa
Articular Eminence
How many bones are in the facial portion of the human skull?
14
Name 5 important facial skeletal bones
Left and Right Maxilla
Left and Right Palatine
Mandible
Locate the Maxilla
Form the anterior 2/3 of the hard palate
Nasal cavity
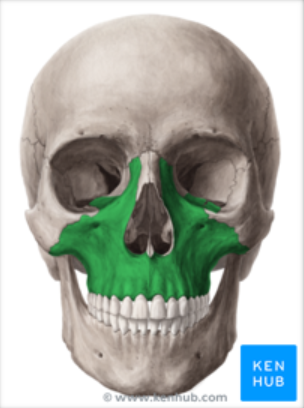
Maxilla supports what
Supports natural teeth in bony sockets by the alveolar process
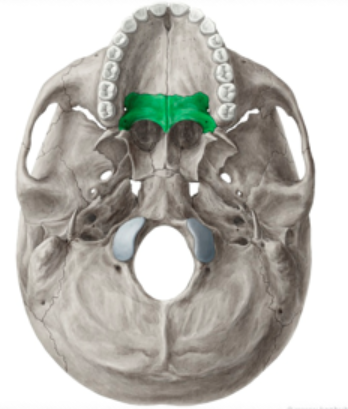
Locate the Palatine Bone
Parts of the floor and outer wall of the nasal cavity
Hard palate
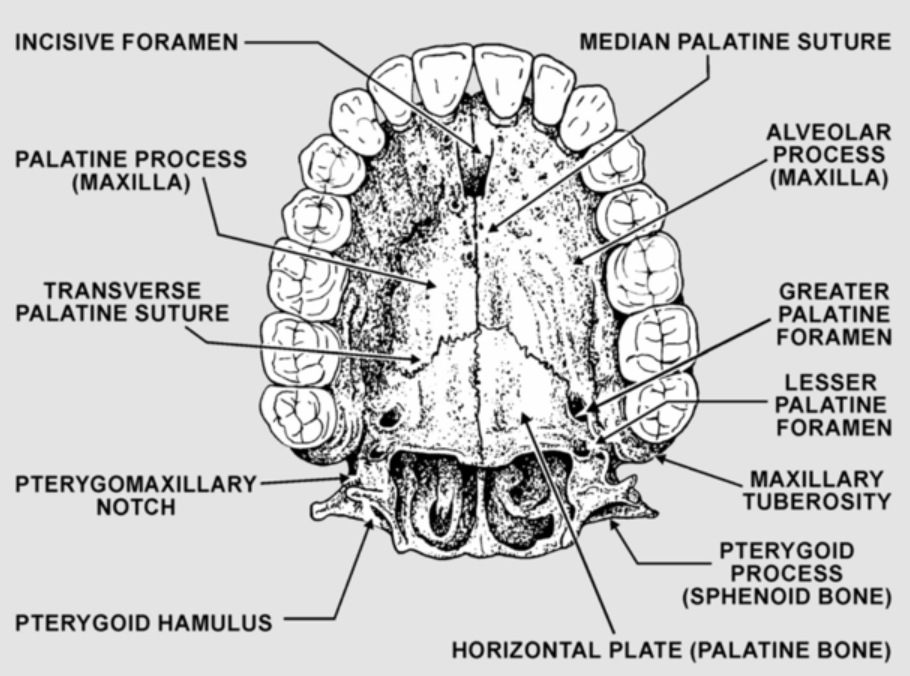
What does the occlusal view of the Maxilla look like
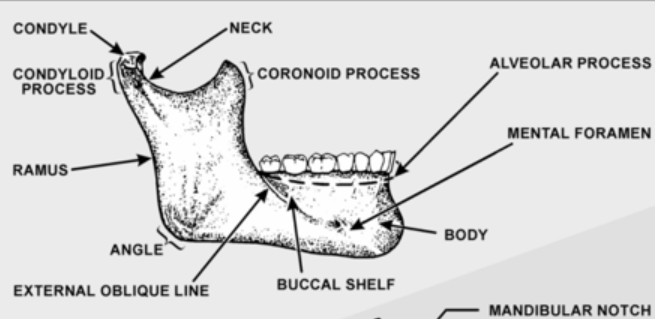
Locate the Mandible
Few movable bones of the skull
Lower Jawbone
Ramus
Vertical projections of the mandible. Connects masseter muscle for movement of mandible
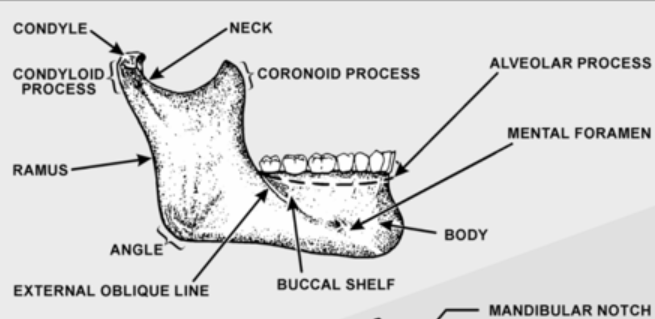
Alveolar process
Bone that supports natural dentition of the teeth
Supports the teeth and ginival
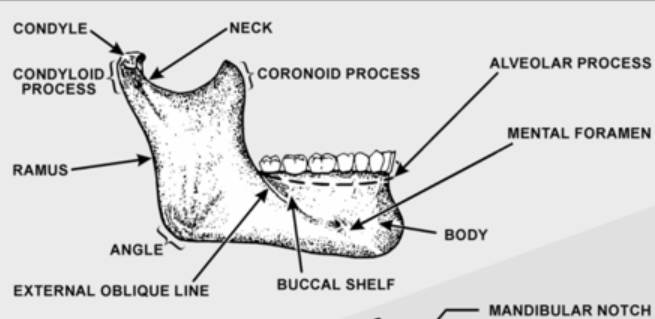
Mental Foramen
Anterior opening of the mandibular canal. Found between the 1st and 2nd premolar root tips. Mental nerve is passed through this opening
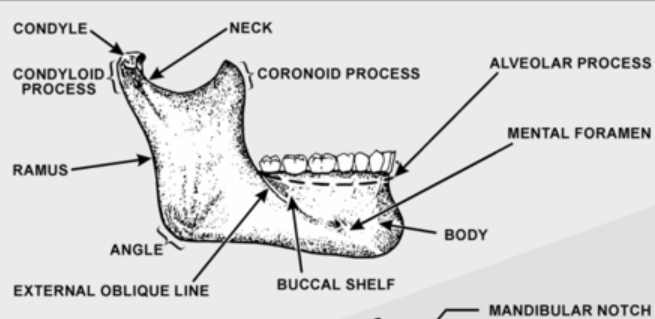
Condyl
-Fits into the glenoid fossa of the temporal bone that makes up the Temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
-Oval shaped structure found on the end of the condyloid process of the mandible
-Located in the lower
TMJ acronym for
Temperomandibular Joint
The right and left TMJ are places where the
where the mandible connects with the rest of the skull at the temporal bone
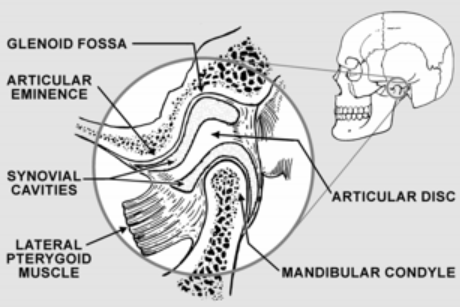
TMJ is formed by
Glenoid Fossa
Articular Eminence
Condyl
Glenoid fossa
Deep hollow on the undersurface of the zygomatic process of the temporal bone. Condyle stays in the fossa during opening and closing jaw movements
Located in the upper
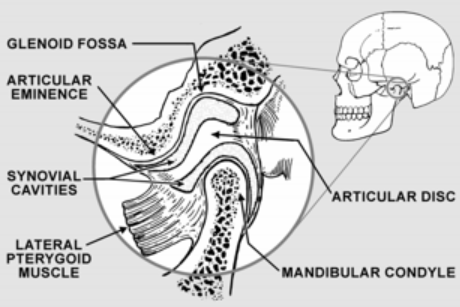
Articular Eminence
Ramp shaped prominence that extends the forward and downward from the anterior boundary of the glenoid fossa
Located in the upper
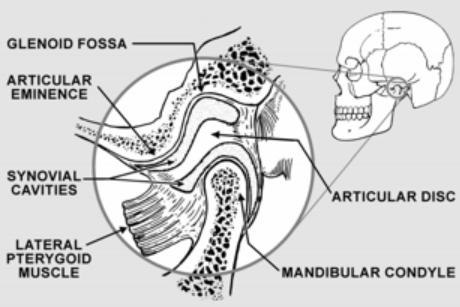
Articular disc
Pad of tough, flexible fibrocartilage situated between condyle and glenoid fossa. Shock absorbing mechanism
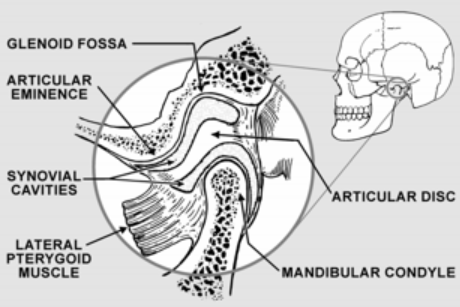
Synovial cavity
Upper and lower joint compartments. Upper disc found between the top of the disc and glenoid fossa. Lower synovial cavity is found between the bottom of the disc and the condyle of the mandible. Synovial membrane lines the cavity making a lubricating liquid called the synovial fluid
Hinge
Opening or closing motions on the horizontal axis common to both condyles
Protrusion and Retrusion Translatory aka
Sliding movements - translatory
Protrusion
Forward movement of mandible
Retrusion
Backwards movement of mandible
Left and Right lateral movements of the mandible
Working side is the area you chew on one side
Non working side is the opposite end of the chewing
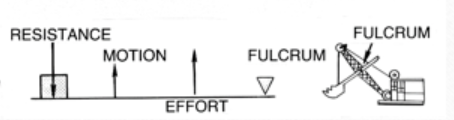
How many classifications of levers are there
3
What Class Lever is the normal mandibular jaw
Class 3 - like a fishing pole
Fulcrum is the TMK and the load is where the food goes
How many muscles of Mastication are there? Name them
4
Masseter Muscle
Temporalis Muscle
Medial Pterygoid
Lateral Pterygoid
Masseter action
Elevates the mandible, aid in the protruding of the mandible
Temporalis action and shape
Fan shape
Closes the jaws / can dislodge without it
Retrude or pull back the mandible
Medial Pterygoid action
Closes the lower jaw
Move the mandible sides or lateral excursion
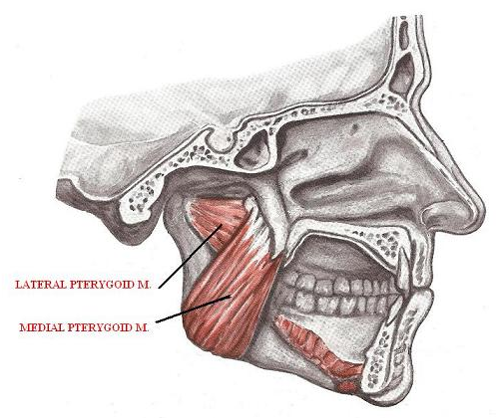
Lateral Pterygoid action
Both lateral pterygoid muscles contract together. Mandible is pulled forward into protrusion.
One muscle contracts independently from one another, the mandible shifts into lateral excursion
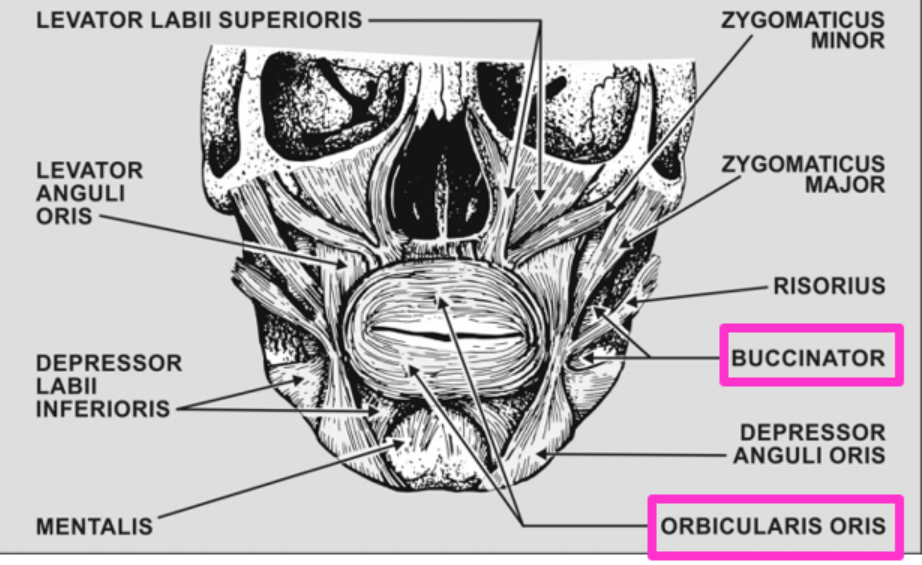
Buccinator location and action
Pulls corners of the mouth laterally and hold food between teeth while chewing
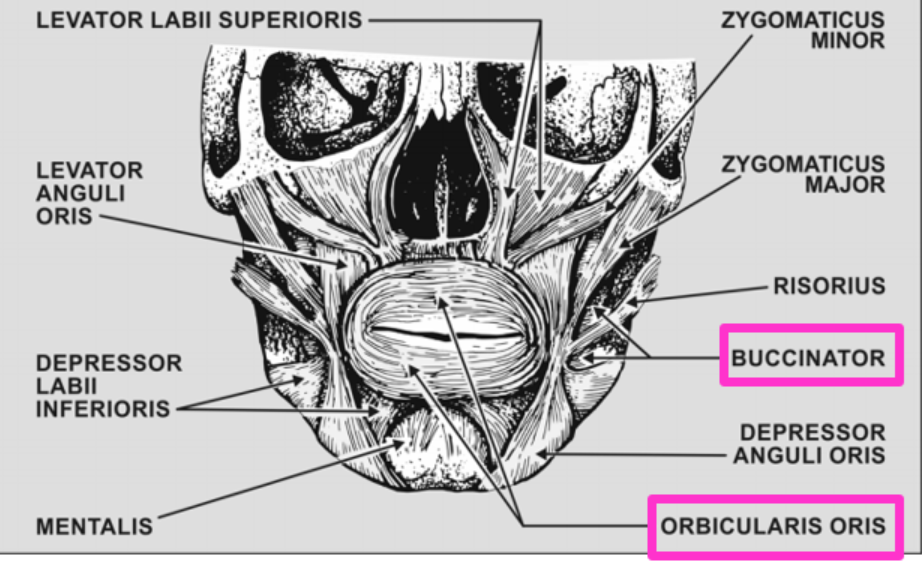
Orbicular Oris location and action
Closes the lips
Mylohyoid muscle
Forms the floor of the mouth (lower)
Can dislodge a mandibular denture
Geniohyoid Muscle
Sits directly on top of the mylohyoid muscle
How many systems to identify teeth? Names?
3
Universal
FDI
Palmer
What is the Universal Tooth Numbering System?
Maxillary has 1-16
Mandibular has 17-32
FDI acronym for
Federation Dentaire Internationale
Whats the numbering system for FDI
Top Right from midline = 11-18
Top Left from midline = 21-28
Bottom Right from midline = 31-38
Bottom Left from midline = 41-48
Whats the numbering system for Palmer
4 quadrants, from midline 1-8
Child’s teeth term and how many
20 Deciduous Teeth
First deciduous teeth to erupt is
Mandibular cental incisor
First permanent dentition to erupt
First molars - 6 year molar
Exfoliation
Shedding of primary teeth to be replaced by permanent teeth
Purpose of incisors and canine
Incisor - cut food
Canine - tear food
Purpose of premolar / bicuspid / molars
Grind food
How many embrasures types are there
4
Facial
Lingual
Gingival / Cervical / Apical / Interproximal Space
Occlusal / Incisal
Emergence Profile
Contour of a tooth as it relates to the adjacent tissue
Overditching a die will
cause an unnatural emergence profile
How many contact surfaces are there? Name them
3
Mesial and Distal aka Proximal
Occlusal / Incisal
Maxillary 1st molar shape
Rhomboidal
Mandibular 1st molar shape
Trapezoidal
How many lobes do teeth have?
Lobes are developmental grooves = 4 to 5
Which tooth has the most lobes
Mandibular first molar with 5 lobes
How many surfaces does a line angle have
2
How many surfaces does a point angle have
3
Whats a long axis and which way does it lean
Imaginary line passing lengthwise through the center of a tooth - distal lean
Incisals are sharper on which end
Mesioincisal point
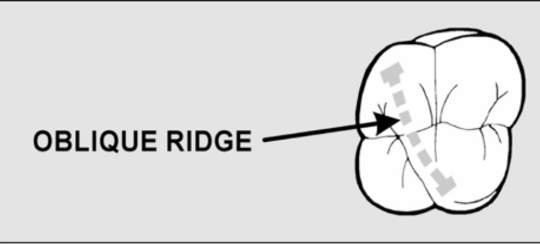
Only tooth with oblique ridge
Maxilary molars
Triangular ridge
Enamel from cusp to central sulcus
Transverse Ridge
Union of buccal and lingual triangular ridge
Lingual fossa is seen on
Anterior teeth
Triangular fossa is seen on
Posterior teeth
Centra fossa is seen on
Molars and mandibular second premolars
Mamelons
Small, rounded projections of enamel from the incisal edge of newly erupted anterior teeth
When do mamelons wear away
After age
Which tooth has the largest cingulum of all anterior teeth? And the longest tooth?
Maxillary Canine - Cuspid
Which way does the oblique ridge run on the maxillary first molar?
Mesiolingual cusp to distobuccal cusp
Cusp of Carabelli
Mesiolingual cusp of the 1st maxillary molar - nonfunctioning and secondary cusp
What teeth only occludes on 1 surface?
Mandibular central incisor and last Maxillary molar
How many variations of occlusal groove patterns? Name them
3: H, Y, and U pattern
Mandibular second premolar possesses 3 cusps, which is the largest
Mesiolingual cusp
Anatomic crown vs Clinical Crown
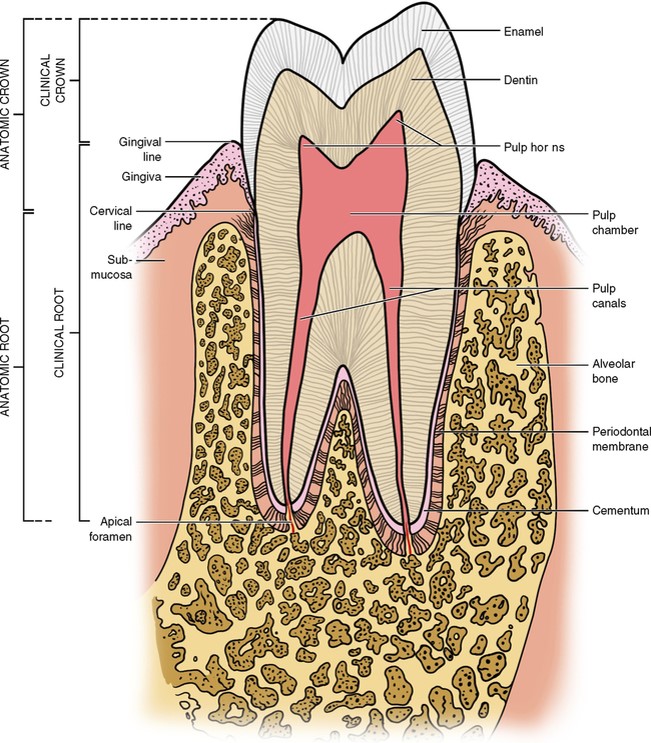
Enamel
White, compact, and very hard substance that covers and protects dentin of crown of teeth
What is enamel made up of and strength
96% inorganic materials and 384 MPA strength
Dentin
Tissue of the tooth under the enamel that makes up bulk of the tooth
Apex
Root tip
Apex Foramen
Opening of root tip that nerves and blood vessels enter and leave tooth
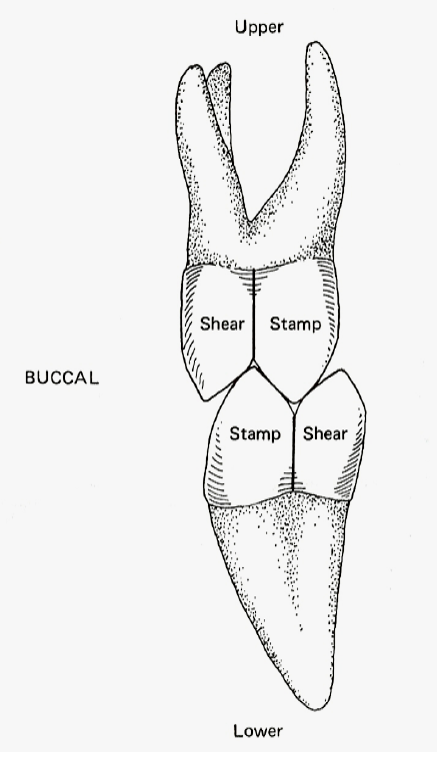
Shearing cusps
Guiding, Non loading baring cusps that do not normally occlude with opposing occlusal surface - BULL (Buccal Upper, Lingual Lower)
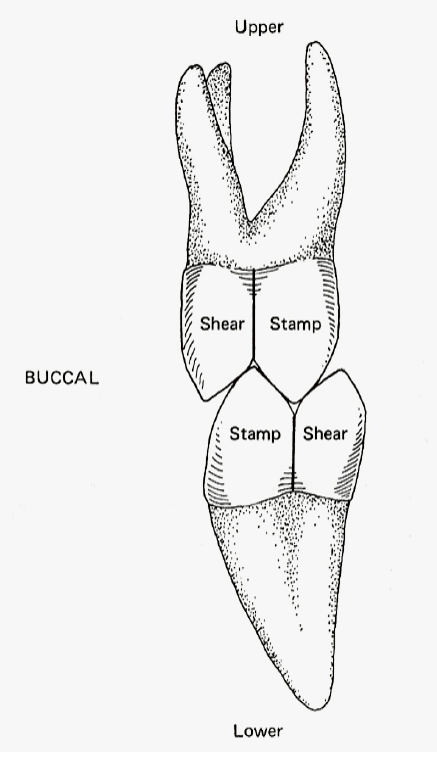
Stamping cusps
Supporting Cusp that occludes with the occlusal surface of the opposing teeth - LUBL (Lingual Upper, Buccal Lower)
Cusp to embrasure
Natural dentition
Cusp to fossa
Used for fixed prosthetic dentistry to avoid fracture and food traps
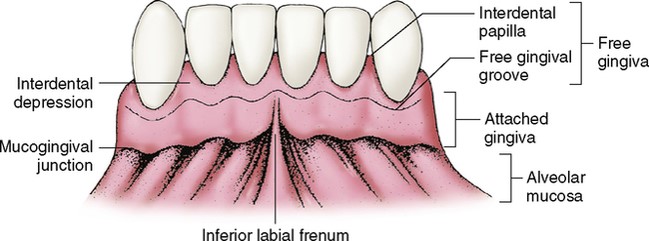
Attached gingiva
Gingiva that is tightly bound to bone
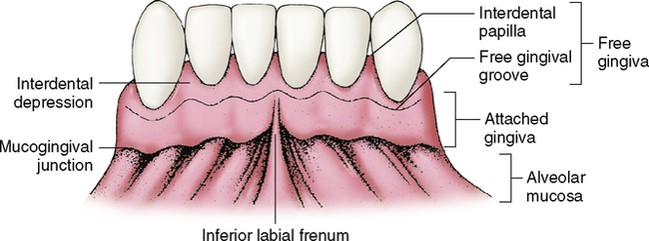
Free gingiva
About 0.5mm wide and is found at the neck of the tooth
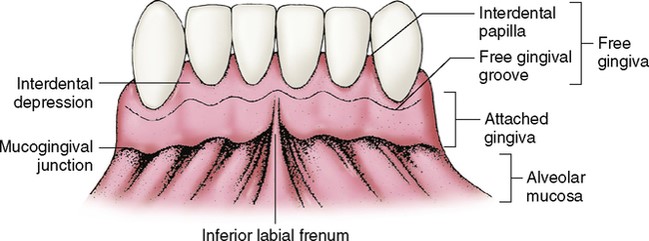
Interdental Papilla
Potion of the free gingiva that fills the proximal space between contact areas of adjacent teeth. Prevents food traps
Curves of Occlusion
Curve of Spee
Curve of Wilson
Monson’s Sphere
Curve of Spee
Anterior posterior seen from the side
Curve of Wilson
Lateral curve seen from the anterior
Monson’s Sphere
Ideal occlusion touches an imaginary sphere - 8 inches in diameter
Compensating Curve
Combination of Curve of Spee and Wilson
Centric Relation
RUM - Rearmost, Uppermost, Midmost Condyler position
No contact between teeth
Space is known as Freeway Space
Centric Occlusion
MIP - Maximum Intercuspation
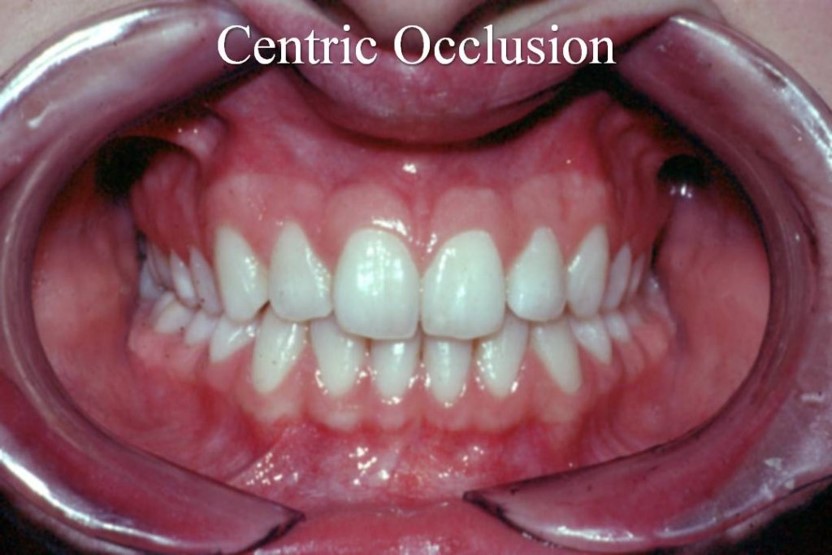
Maximum Intercuspation
Complete intercuspation of the opposing teeth independent of the condyler position