AALDEHYDES AND KETONES
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Aldehydes and ketones are both carbonyl compounds
both contain the C=O carbonyl functional group
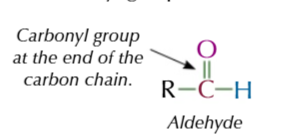
aldehyde carbonyl group
ON THE ENDDDD
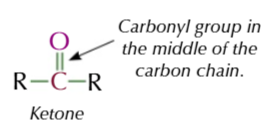
Ketone carbonyl group
IN THE MIDDLE
NaBH4 is a reducing agent
which can convert aldehydes and ketones back into primary and secondary alcohols
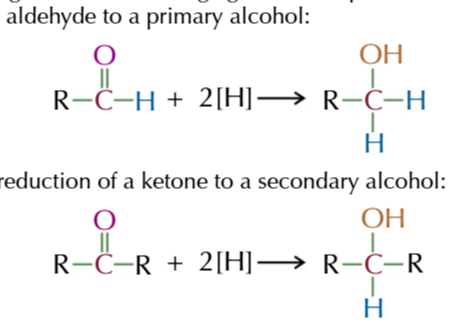
LiAlH4 (still strong but abit weaker)
also reduces aldehydes and ketones to their respective alcohols
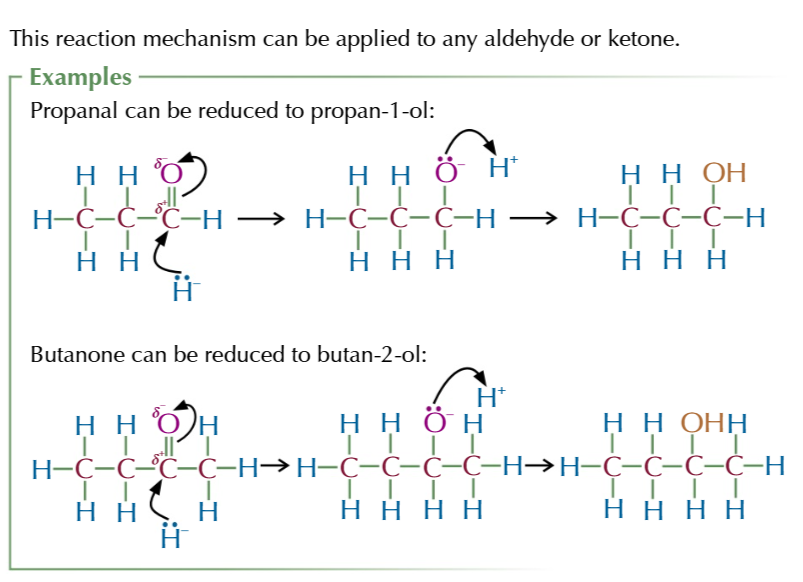
the mechanism of aldehydes/ketones into alcohols is
NUCEOPHILIC ADDITION
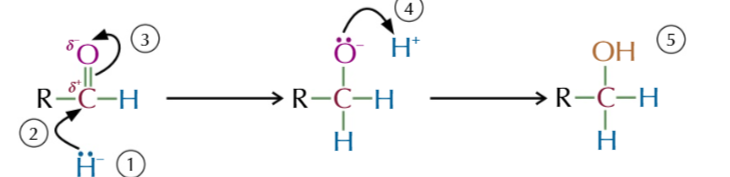
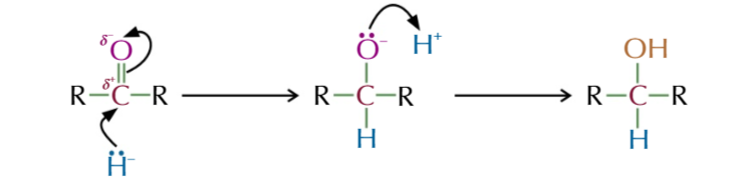
nucleophilic addition of aldehydes/ketones to make alcohols
C=O bond is polar
Cð+ and attracts the negative lone pair of electrons on H-
H- attacks positive C and donates it alone pair electrons forming a bond with C
this causes 1 bond between carbon and oxygen to break giving oxygen a lone pair of electrons
oxygen donates its lone pair of electrons to a H+ ion (from water)
forming an alcohol
hydroxynitriles are:
molecuels containing a hydroxyl group OH
and nitrile group CN
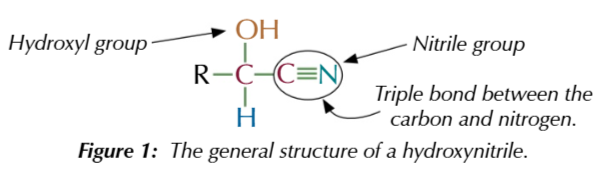
hydroxynitrile suffix
-NITRILE

aldehyde/ketone + potassium cyanide, dilute acid→ hydroxynitrile
ANOTHER NUCEOPHILIC ADDITION
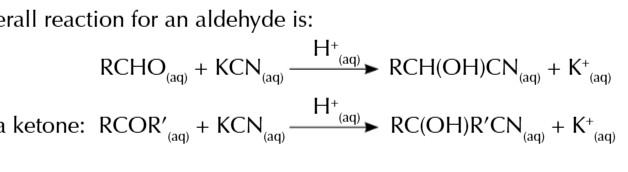
nuceophilic addition of aldehydes/ketones to make hydroxynitriles
potassium cynide is an ionic compound
potassium cyanide dissociates in water to form K+ Ions and CN- ions
KCN⇄K+ + CN-
CN- attacks partially positive carbon and donate a pair of electrons forming a bond with the carbon
a pair of electrons from C=O is pushed onto O
oxygen bonds with H+ (from dilute acid) to form OH hydroxyl group
and hydroxynitrile is produce
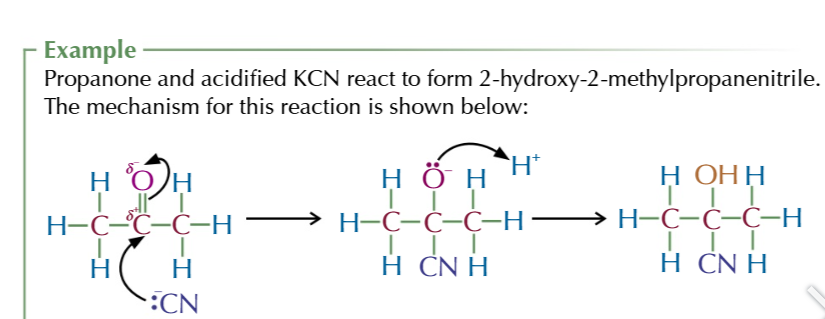
aldehydes/ketones + hydrogen cyanide → hydroxynitrile
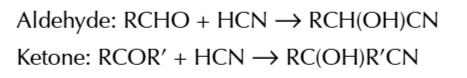
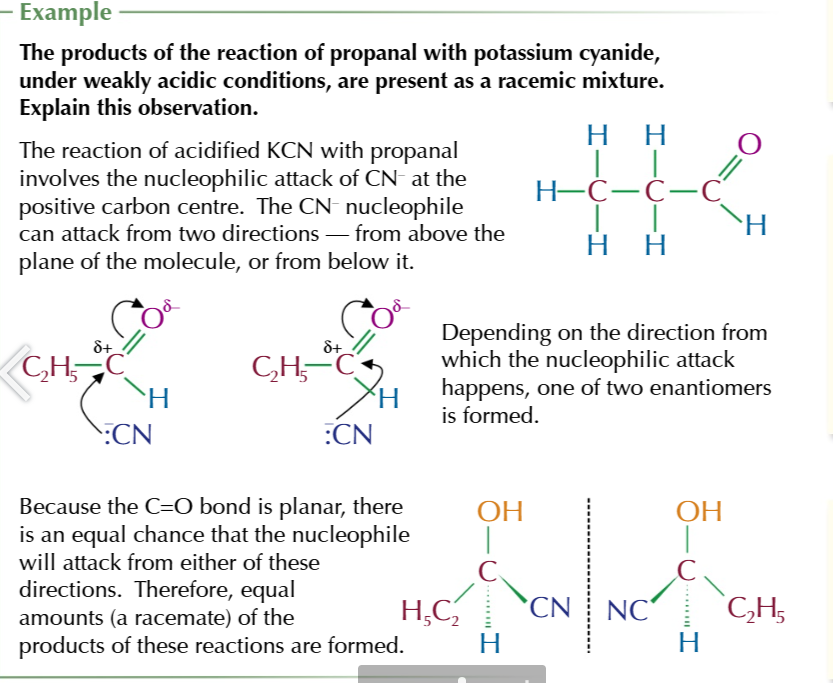
double bonds are planar
so when nuceophiles attack they can attack from either above or below the plane of the bond
nucleophiles attacking from each side of the bond will produce
a different enantiomer
nucleophile+ aldehyde/ UNSYMMETRIC ketone →
racemic mixture of hydroxynitriles
risk assesment
KCN is toxic- done in fume cupboard as there is a risk of HCN gas being released from the solution
organic compounds are flammable so warm them in a water bath NOT bunsen
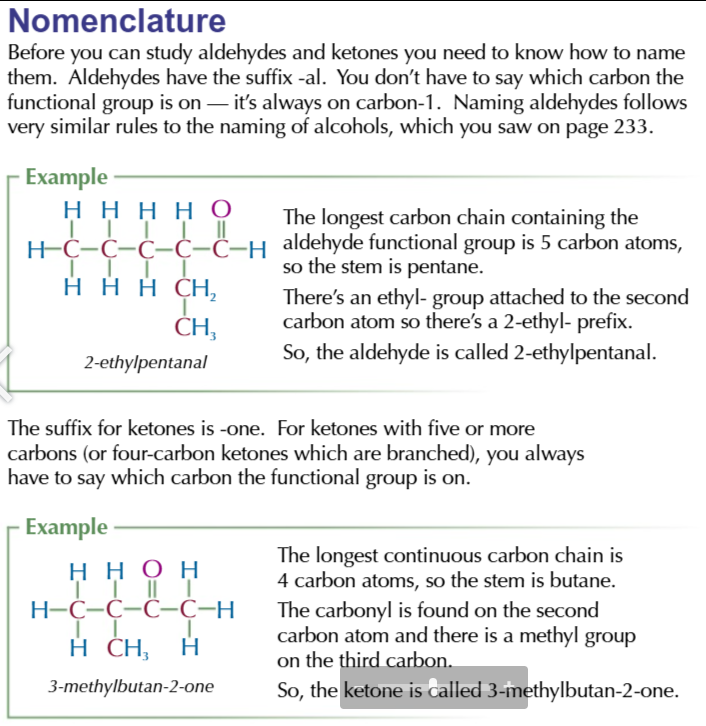
iUPAC Vs Common
meth vs form
eth vs acet
prop vs propion
physical properties of aldehydes n ketones
both colourless
both soluble in water because of hydrogen bonding
as the akyl chain increasaes, solubility decreases because akyl chain is non polar and water is polar
like dissolve theory
polar dissolves polar
non polar dissolves non polar
aldehyde preparation reaction
primary alcohol controlled oxidisation and product quickly distilled or carboxylic acid forms
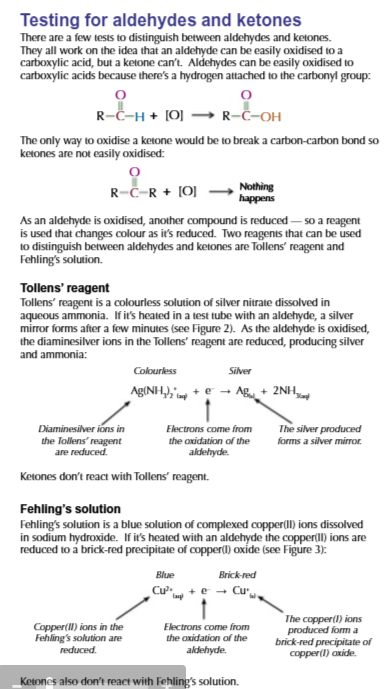
tollens reagent
AgI → [Ag(NH3)2]+
C=O can be reduces
C=C cannot be reduced
aldehydes MORE reactive than ketones
because there are less akyl groups attached to the functional carbon
C=O is a polar bond
the more δ+ the carbon the more reactive it is
akyl groups have a positive inductive effect
push electrons in bond towards attached carbon
decreasing the δ+ charge
makes the compound less reactive
C=O on the end of aldehydes
so only has 1 akyl group attached to functional carbon
C=O in the middle of ketones
so has 2 akyl groups attached to functional carbon