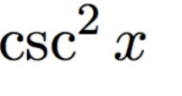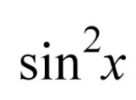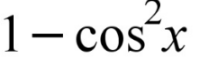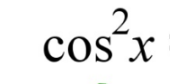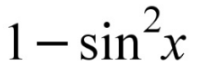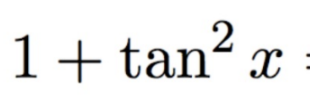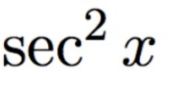Techniques of Integration
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
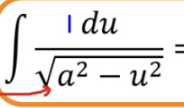
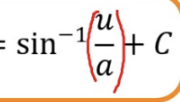
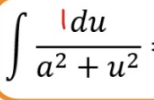
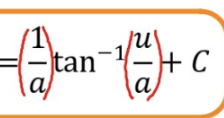
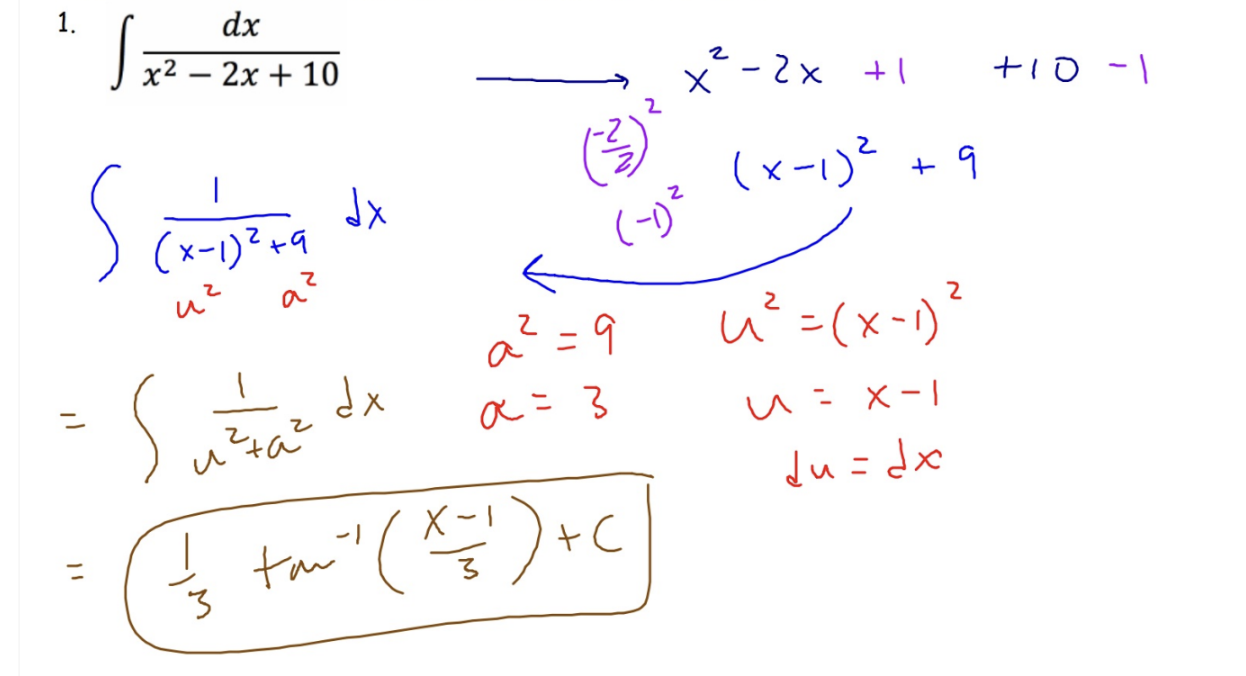
Completing the Square
Use this method when there’s a constant in the numerator & a quadratic in the denominator
Most common forms leads us to the inverse trig integrals of sin and tan but not always
Separation
Sometimes we need to split the integral into 2 separate integrals to find the antiderivative (one term in the denominator and 2 or more terms in numerator)
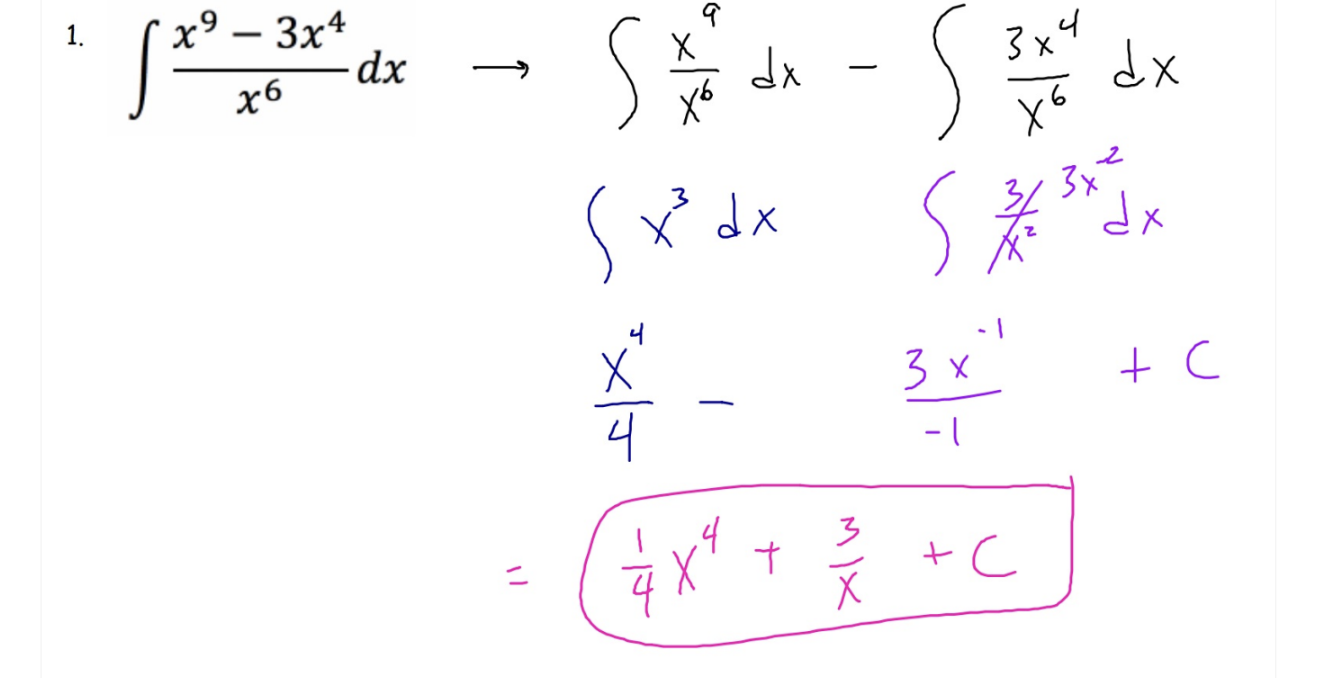
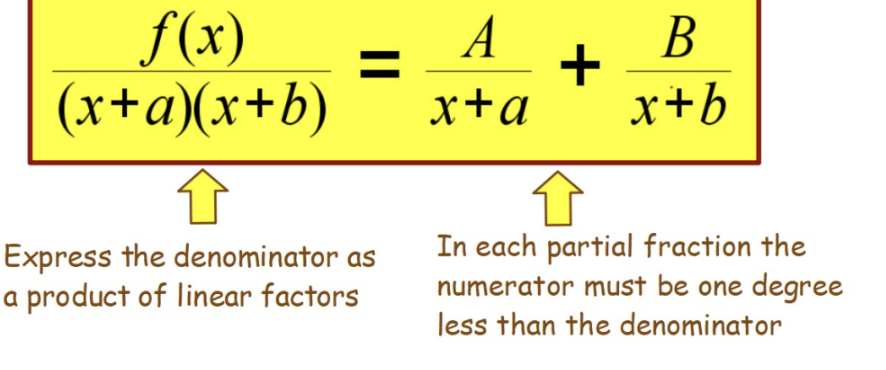
Partial Fractions: Decomposition (Case I: Linear Factors)
The following method only works for Proper Rational Expressions where the degree of the numerator is less than the denominator
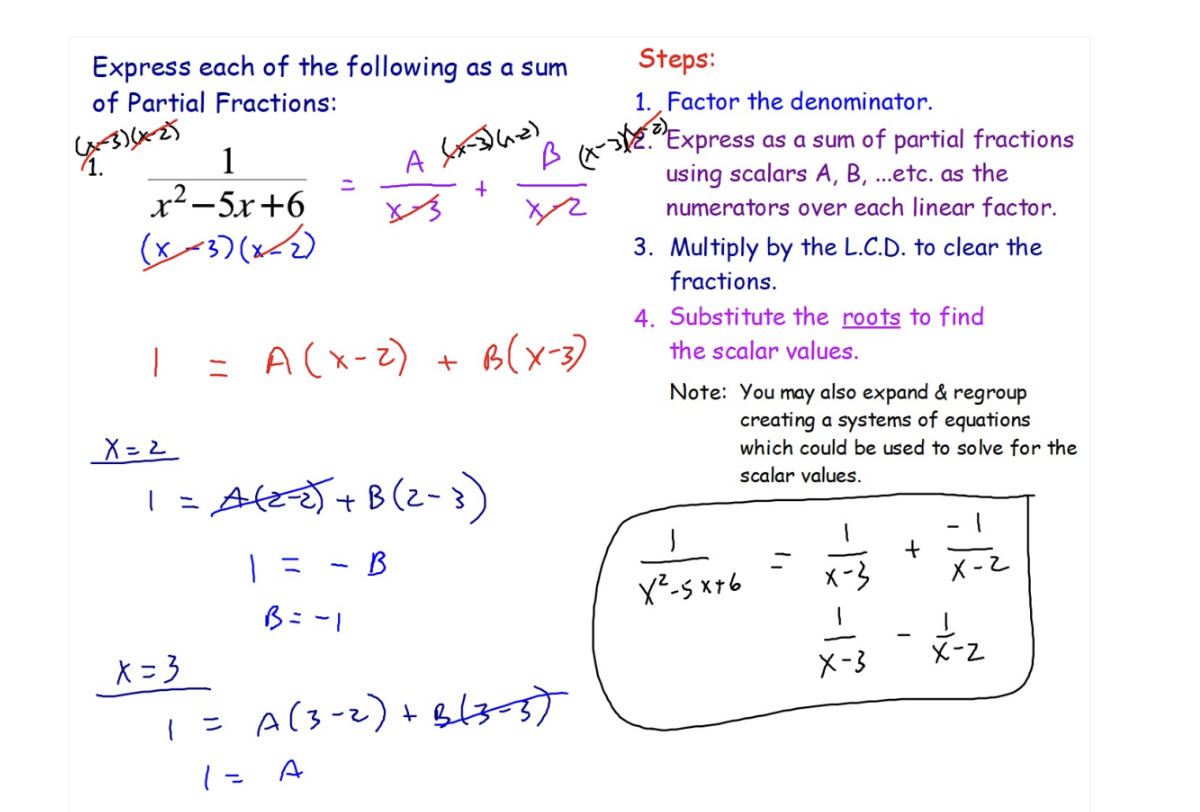
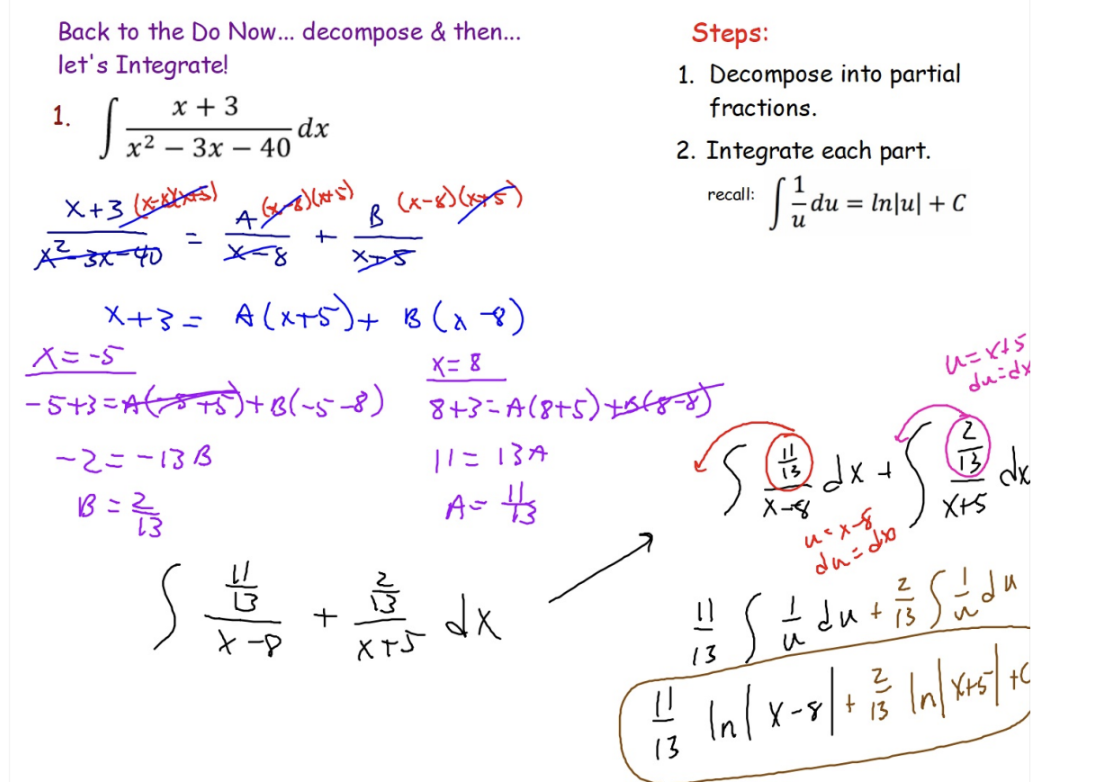
Steps/ Example of Partial Fractions: Decomposition (Case I: Linear Factors)
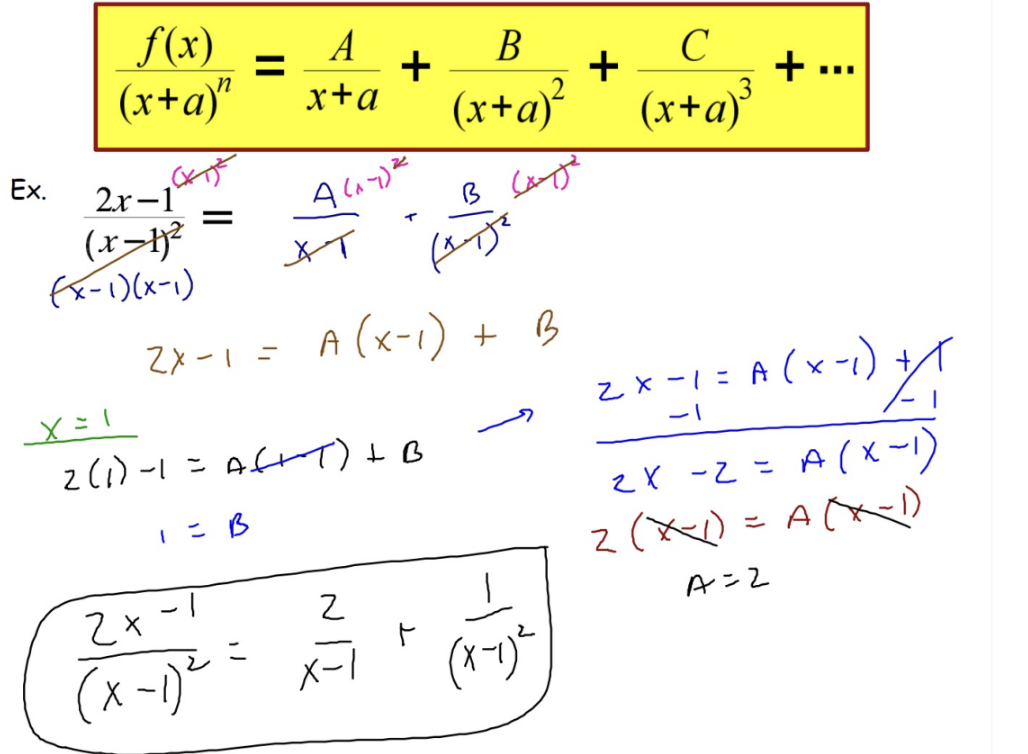
Partial Fractions: Decomposition (Case II: Repeated Linear Factors)
Partial Fractions: Integration
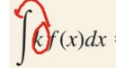

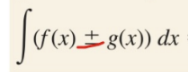
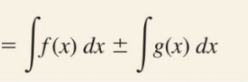
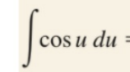
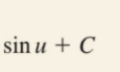
Power Formula
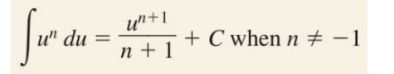
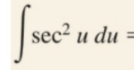
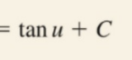

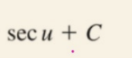
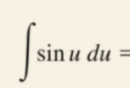
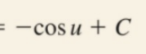
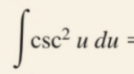
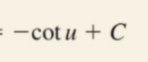
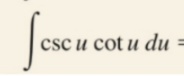
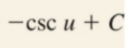
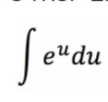
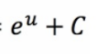
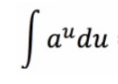
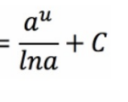
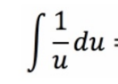
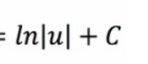
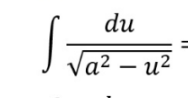
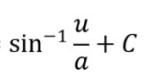
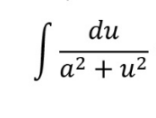
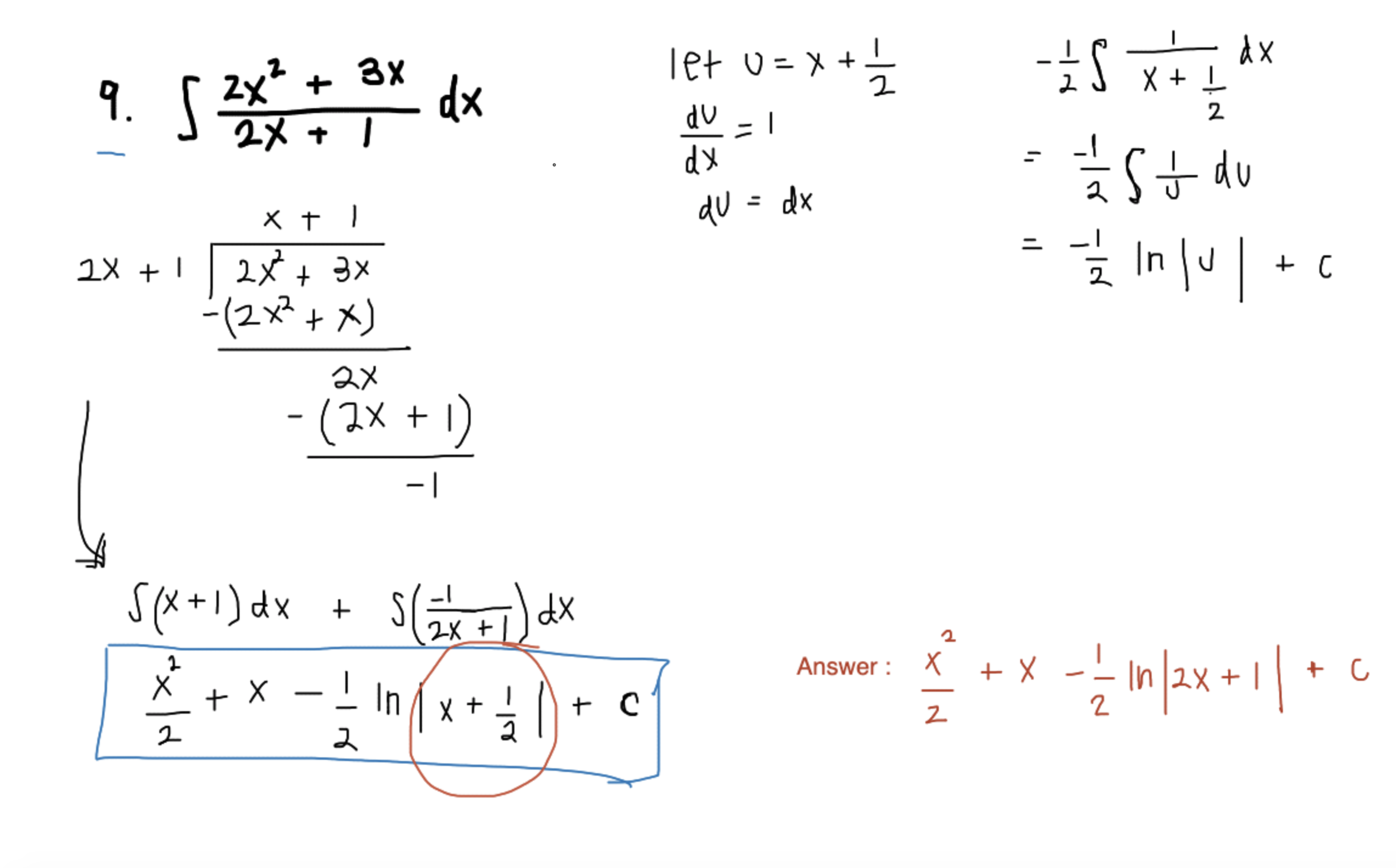
Partial Fractions: Integration (Long Division)
For improper rational expressions (degree of numerator is greater than or equal to degree of denominator) long division is 1st required before you integrate
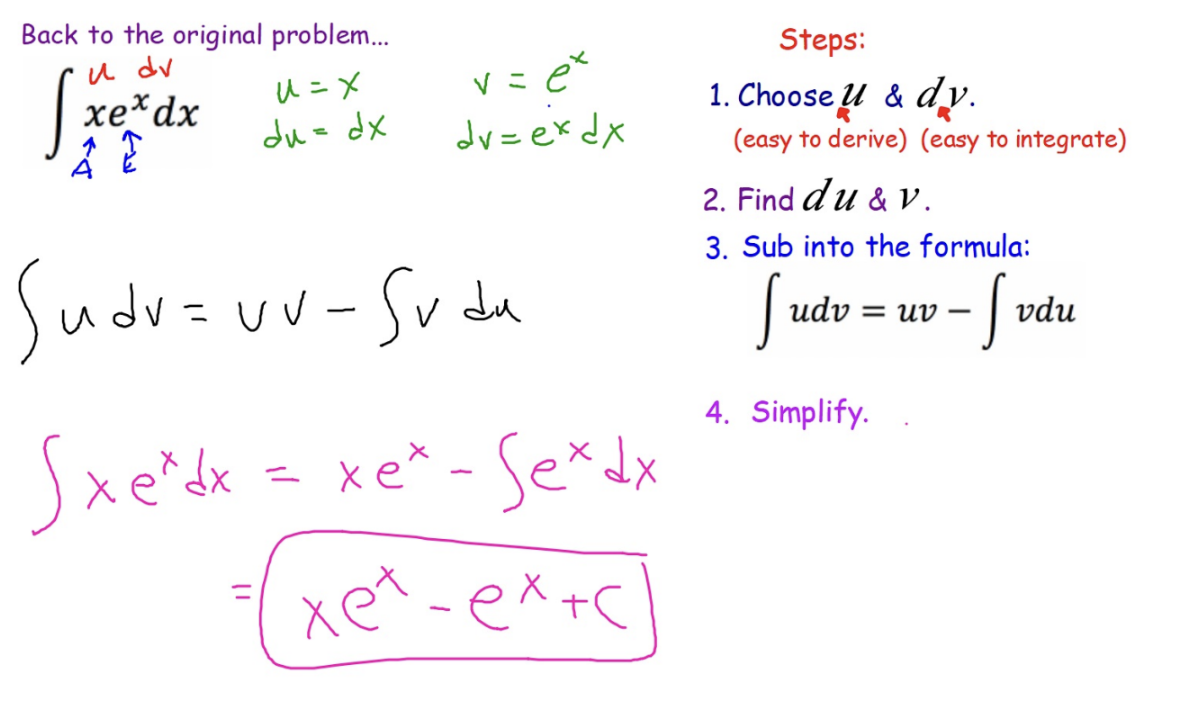
Integration by parts
formula: integral of udv= uv- integral of vdu
Tabular Method

Trig Identity Substitution (odd integers)
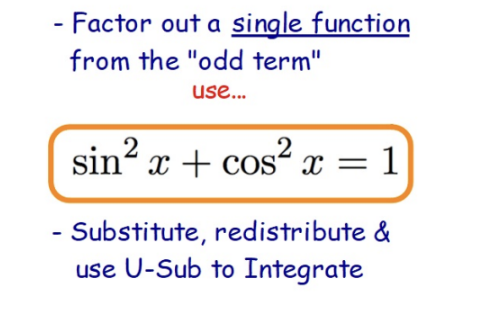
Trig Identity Substitution (even integers)