psych
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
What is the cognitive dissonance theory?
Theory holding that inconsis-tent cognitions arouses psychological tension that people become motivated to reduce
2
New cards
Know strategies to reduce cognitive dissonance.
Change your attitude. “I don’t really need to be on a diet.”
Change your perception of the behavior.“I hardly ate any ice cream.”
Add consonant cognitions. “Chocolate ice cream is very nutritious.”
Minimize the importance of the conflict.“I don’t care if I’m overweight—life is short!”
Reduce perceived choice. “I had no choice; the ice cream was served for this special occasion.”
Change your perception of the behavior.“I hardly ate any ice cream.”
Add consonant cognitions. “Chocolate ice cream is very nutritious.”
Minimize the importance of the conflict.“I don’t care if I’m overweight—life is short!”
Reduce perceived choice. “I had no choice; the ice cream was served for this special occasion.”
3
New cards
Know the study on cognitive dissonance by Festinger & Carlsmith (1959).
Cognitive dissonance and attitude change are more likely to occur when there is insufficient justification or insufficient deterrence for an attitude-discrepant non-behavior.
4
New cards
How is arousal related to cognitive dissonance?
dissonance seems to create arousal, but *attitude change sustains rather than reduces the arousal*
5
New cards
Know the necessary conditions for arousal and reduction of cognitive dissonance.
for cognitive dissonance to work effectively there are three necessary conditions: aversive consequences, freedom of choice, and insufficient external justification
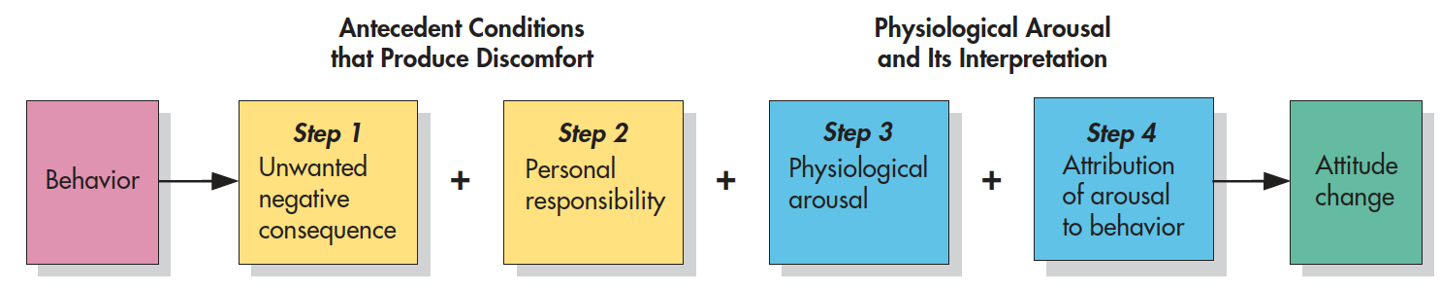
6
New cards
Know alternative routes of self-persuasion: self-perception theory, impression-management theory, self-esteem theory. Understand the differences.
•Self-perception theory
•We infer how we feel by observing ourselves and the circumstances of our own behavior
•Impression-management theory
•What matters is not a motive to be consistent but rather a motive to *appear* consistent
•Self-esteem theories
•Acts that arouse dissonance do so because they threaten the self-concept
•We infer how we feel by observing ourselves and the circumstances of our own behavior
•Impression-management theory
•What matters is not a motive to be consistent but rather a motive to *appear* consistent
•Self-esteem theories
•Acts that arouse dissonance do so because they threaten the self-concept
7
New cards
What is social facilitation? How is this related to task difficulty?
being in the presence of others improves individual task performance. That is, people do better on tasks when they are with other people rather than when they are doing the task alone
8
New cards
What is social loafing?
a person exerting less effort to achieve a goal when they work in a group than when working alone.
9
New cards
How can social loafing be reduced?
limit team size
encourage open communication
encourage open communication
10
New cards
What is deindividuation?
generally thought of as the loss of self-awareness in groups, although this is a matter of contention.
11
New cards
What is brainstorming? What is the criticism of brain storming?
a problem-solving strategy in which ideas are generated spontaneously and uninhibitedly, usually in a group setting, without any immediate critical judgment about their potential value
If the brainstorming environment is cooperative—meaning that group members' goals are aligned—criticism is likely to stimulate creativity
If the brainstorming environment is cooperative—meaning that group members' goals are aligned—criticism is likely to stimulate creativity
12
New cards
What is groupthink? How can it be prevented?
occurs within a group of people in which the desire for harmony or conformity in the group results in an irrational or dysfunctional decision-making outcome.
increase diversity
increase diversity
13
New cards
Understand the prisoner’s dilemma.
a paradox in decision analysis in which two individuals acting in their own self-interests do not produce the optimal outcome
14
New cards
What causes people to become friends? Know the proximity effect and the mere exposure effect.
reasons that motivate friendship may be divided into those for true friendship and those for opportunistic friendship.
related to the time that people spend together
people tend to develop a preference for things or people that are more familiar to them than others.
related to the time that people spend together
people tend to develop a preference for things or people that are more familiar to them than others.
15
New cards
What is the need to belong?
a human emotional need to affiliate with and be accepted by members of a group
16
New cards
What is beauty? Which characteristics of faces are perceived as attractive?
symmetry
17
New cards
What is altruism?
the belief in or practice of disinterested and selfless concern for the well-being of others.
18
New cards
What is reciprocal altruism?
behaviour whereby an organism acts in a manner that temporarily reduces its fitness while increasing another organism's fitness, with the expectation that the other organism will act in a similar manner at a later time
19
New cards
Why do we help? Empathy, joy of giving, reward, reciprocity, egoism, etc.
one of the ways that people create, maintain, and strengthen their social connections.
20
New cards
What is the empathy-altruism hypothesis?
feelings of empathy for another person produce an altruistic motivation to increase that person's welfare.
21
New cards
Why do we volunteer?
Volunteering increases self-confidence.
22
New cards
What is the bystander effect? What may cause it? (Lack of noticing or interpreting the event as an emergency, diffusion of responsibility, embarrassment (audience inhibition), time pressure)
states that individuals are less likely to offer help to a victim when there are other people present.
23
New cards
What facilitates people to intervene? What reduces the bystander effect?
the presence of individuals who have skills relevant to the situation
24
New cards
How does mood affect the bystander effect?
diffusion of responsibility and social influence
25
New cards
Know aggression, proactive, reactive, instrumental, predatory, intermale, fear-induced, irritable, territorial, and maternal aggression.
* hostile or violent behavior or attitudes toward another; readiness to attack or confront.
* goal-directed behavior designed to achieve an objective beyond physical violence
* aggressive behavior in response to perceived threat or provocation
* when an individual intentionally acts aggressively to achieve a particular purpose
* involves such activities as stalking other animals for a kill, the violence that ensues when one animal infringes upon the marked territory of another, or the posturing and attacks exhibited by nursing mothers when any animal, even the mate, approaches the nest.
* used to establish social rank
* a form of aggression in which an animal attacks after it has been severely threatened or cornered.
* in response to pain or deprivation of an item required for survival
* the act of defending a defined space (a territory) by fighting or threatening intruders of the same species.
* form of aggression in nonhuman animals in which females defend their offspring against potential threats from intruders by means of threat displays or attack behavior.
* goal-directed behavior designed to achieve an objective beyond physical violence
* aggressive behavior in response to perceived threat or provocation
* when an individual intentionally acts aggressively to achieve a particular purpose
* involves such activities as stalking other animals for a kill, the violence that ensues when one animal infringes upon the marked territory of another, or the posturing and attacks exhibited by nursing mothers when any animal, even the mate, approaches the nest.
* used to establish social rank
* a form of aggression in which an animal attacks after it has been severely threatened or cornered.
* in response to pain or deprivation of an item required for survival
* the act of defending a defined space (a territory) by fighting or threatening intruders of the same species.
* form of aggression in nonhuman animals in which females defend their offspring against potential threats from intruders by means of threat displays or attack behavior.
26
New cards
What is the difference between aggression and anger?
While anger is a feeling/emotion, aggression is the behaviour or action taken that is hostile, destructive and/or violent
27
New cards
What are gender differences of aggression?
males are more likely to commit a physical or armed assault against another person, especially other males
28
New cards
What is the biological basis of aggression?
genetics, medical and psychiatric diseases, neurotransmitters, hormones, substances of abuse, and medications.
29
New cards
Is aggression learned. Understand the Bobo Doll experiment. Know social learning theory.
Aggression can be learned in the home, in the school, and from television programs.
he studied children's behavior after watching an adult model act aggressively towards a Bobo doll
suggests that social behavior is learned by observing and imitating the behavior of others
he studied children's behavior after watching an adult model act aggressively towards a Bobo doll
suggests that social behavior is learned by observing and imitating the behavior of others
30
New cards
What are the challenges of corporal punishment?
physical and mental ill-health, impaired cognitive and socio-emotional development, poor educational outcomes, increased aggression and perpetration of violence.
31
New cards
Know the frustration-aggression hypothesis.
aggression is a result of frustration
32
New cards
What is displacement and catharsis?
It uses the concepts of catharsis (relieving emotional tension) and displacement (unconscious defense mechanism whereby the mind diverts emotions from their original source to a less threatening, dangerous or unacceptable one to avoid experiencing anxiety
33
New cards
How do negative affect and heat relate to aggression?
excessive heat increases aggression when the total amount of negative affect a person experi- ences is in the low to moderate range
34
New cards
Know aggressive cues.
in the angered person's thoughts or in the external situation "activate" an aggressive response sequence which does not attain completion until the anger instigator is injured.
35
New cards
What is the I cubed theory?
metatheoretical framework for understanding an individual's behavior regarding a given target object in a particular context, such as Koestler's aggression toward Sartre following the latter's seduction efforts.
36
New cards
Know the general aggression model.
\
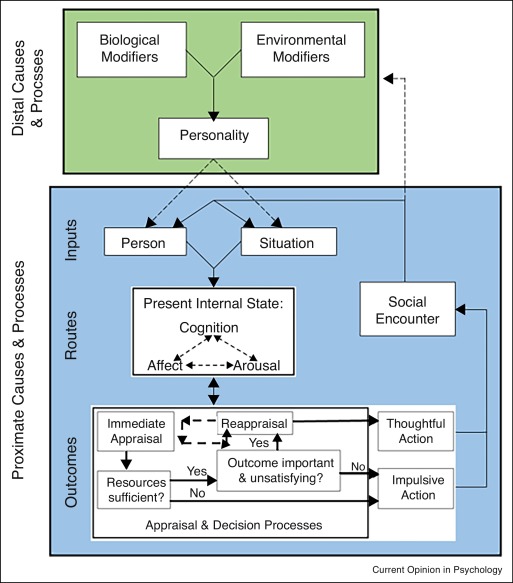
37
New cards
What is multisystemic therapy?
an intense, family-focused and community-based treatment program for juveniles with serious criminal offenses who are possibly abusing substances
38
New cards
What are the psychological challenges of eyewitness testimonies? (cross-race identification bias, weapon focus effect, misinformation effect)
They (like the rest of us) can make errors in remembering specific details and can even remember whole events that did not actually happen.
39
New cards
How do questions affect eyewitness reports?
leading questions can impact on the testimonies provided by eyewitnesses in trials, influence referendum outcomes and affect the accuracy of survey results
40
New cards
What are the challenges of line-ups?
law enforcement officers intentionally or inadvertently may give the eyewitness signals to identify the suspect. I
41
New cards
What is health psychology?
study of psychological and behavioral processes in health, illness, and healthcare.
42
New cards
Understand stress and the challenges associated with the definition of stress.
Permanent distress leads to burnout and exhaustion, as well as increased vulnerability to physical and emotional issues such as anxiety, heart attacks and ulcers.
43
New cards
Know the transactional stress model.
a person's capacity to cope and adjust to challenges and problems is a consequence of transactions (or interactions) that occur between a person and their environment.
44
New cards
Understand the general adaptation syndrome.
describes the process your body goes through when you are exposed to any kind of stress, positive or negative
45
New cards
How is the immune system affected by stress?
the immune system's ability to fight off antigens is reduced.
46
New cards
What is learned helplessness?
a state that occurs after a person has experienced a stressful situation repeatedly
47
New cards
Know the depressive explanatory style.
often attribute unwanted or adverse events to their life as internal, global, and stable
48
New cards
Understand resilience. What are resilience factors? (self-efficacy, dispositional optimism, etc.)
competence, confidence, connection, character, contribution, coping and control
49
New cards
What is proactive coping?
a method of assessing future goals and setting the stage to achieve them successfully
50
New cards
Know negotiation and conflict-resolution strategies.
avoid being provoked into an emotional response. · 2. Don't abandon value-creating *strategies*. · 3. Use time to your advantage.
51
New cards
Relationship between rumination, higher order cognition, and aggression
angry rumination temporarily reduces self-control, which can increase aggression.
52
New cards
How can aggression be reduced through cognitive reappraisal, self-control training, cognitive control training, mindfulness? What are these?
* Cognitive reappraisal is an antecedent-focused emotion regulation strategy, occurring in the early stages of the experience of the emotion.
* self-control therapy
a form of behavior therapy that involves self-monitoring (e.g., diaries of behavior), self-evaluation, goal setting, behavior contracts, self-reinforcement, and relapse prevention. Also called **self-management therapy**. \[developed by Austrian-born U.S. clinical psychologist Frederick H. Kanfer (1925–2002)\]
* cognitive control
the set of processes that organize, plan, and schedule mental operations
* mindfulness
*n.* awareness of one’s internal states and surroundings. The concept has been applied to various therapeutic interventions—for example, mindfulness-based cognitive behavior therapy, mindfulness-based stress reduction, and mindfulness meditation—to help people avoid destructive or automatic habits and responses by learning to observe their thoughts, emotions, and other present-moment experiences without judging or reacting to them
* self-control therapy
a form of behavior therapy that involves self-monitoring (e.g., diaries of behavior), self-evaluation, goal setting, behavior contracts, self-reinforcement, and relapse prevention. Also called **self-management therapy**. \[developed by Austrian-born U.S. clinical psychologist Frederick H. Kanfer (1925–2002)\]
* cognitive control
the set of processes that organize, plan, and schedule mental operations
* mindfulness
*n.* awareness of one’s internal states and surroundings. The concept has been applied to various therapeutic interventions—for example, mindfulness-based cognitive behavior therapy, mindfulness-based stress reduction, and mindfulness meditation—to help people avoid destructive or automatic habits and responses by learning to observe their thoughts, emotions, and other present-moment experiences without judging or reacting to them
53
New cards
What are problem and emotion-focused coping strategies? Know coping strategies.
Problem-focused coping involves handling stress by facing it head-on and taking action to resolve the underlying cause. Emotion-focused coping involves regulating your feelings and emotional response to the problem instead of addressing the problem.
54
New cards
External resources
anything outside of one's self that provides a sense of calm, support, strength, and capability
55
New cards
Internal resources
anything internal that provides relaxation, pleasure, support, strength, and safety