GI system
1/261
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
262 Terms
4 layers of the oesophagus (GI tract) + histological features
Mucosa: non-keratinised stratified squamous
Submucosa: loose connective tissue
Muscularis propria: smooth + skeletal m. → inner circular, outer longitudinal
Adventitia/serosa
How do adventitia and serosa differ
Adventitia → secures organ to surrounding tissue (more fibrous)
Serosa → covers external surface of organ
What are the layers of oesophagus mucosa
Non-keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
Lamina propria (loose connective tissue)
Muscularis mucosa (smooth muscle)
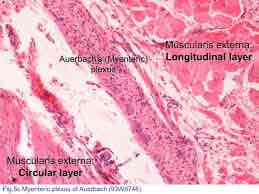
Auerbach’s plexus function + location
Allows for peristalsis
Found between circular + longitudinal muscle layers
Oesophagus, stomach + small/large intestine
What is Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GORD) + complication?
Acid reflux caused by weakened oesophageal sphincter
Can lead to barret’s oesophagus
Signs + symptoms of GORD
heartburn
Acid regurgitation
Dysphagia
GORD/ Barret’s oesophagus risk factors
smoking
Alcohol
Obesity
Caffeine
Bulimia
What is Barrett’s oesophagus+ complication
Metaplasia of squamous epithelium to columnar (premalignant lesion) due to chronic acid exposure (lower 1/3) + goblet cells
Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma
GORD treatment/management
weight loss
Avoiding large meals + trigger foods
Lying flat after eating
Antacids
Proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole)
Barrett’s oesophagus investigations
Endoscopy w/ biopsy in all 4 quadrants
Three anatomical regions of stomach (top to bottom)
Cardia → contains mucous secreting glands
Fundus → body containing gastric glands
Pylorus → secretes mucus + gastrin
Gastric/fundic gland cells + secretions
Surface mucous: alkaline fluid
Mucous neck: acidic fluid
Parietal: intrinsic factor + HCL
Chief: pepsinogen + gastric lipase
G: gastrin
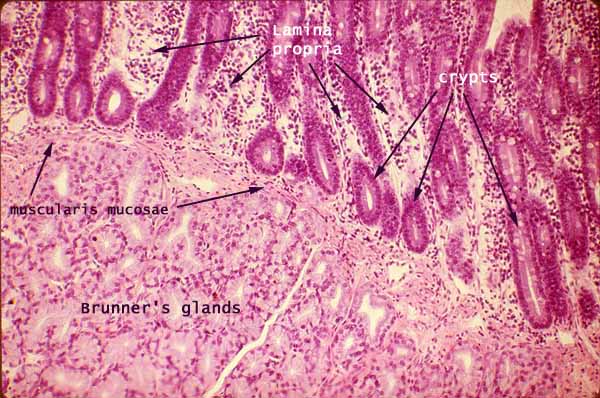
Brunner’s Glands
found in duodenum submucosa → secrete alkaline mucus to neutralise acidic chyme
Protects membrane + optimal pH for digestion
Plicae circulares
Villi covered folds in mucosa/submucosa →slow passage + increased absorption SA
Primarily found in jejunum
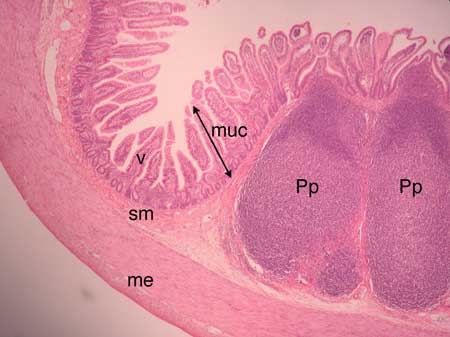
Peyer’s patches
Organised lymphoid follicles found in lamina propria/submucosa of ileum
Involved in immune defence against microbial + dietary antigens (M cells)
Serosa
Visceral peritoneum → connective tissue+ mesothelium
Mesothelium lubricates peritoneal cavity
Ulcerative colitis
Autoimmune→ affects colon + rectum
Superficial ulcers
Clinical features of ulcerative colitis (5 Ps)
pseudopolyps
Poo → diarrhea, tenesmus, blood
Pyrexia
Proctitis
Lead Pipe appearance (xray)
Anaemia
Weight loss
IBD investigations
bloods → FBC, ESR/CRP, LFT, U&Es, B12, iron
Colonoscopy w/ biopsy (diagnostic)
Faecal calprotein
Complications of ulcerative colitis
toxic megacolon (bowel dilates risk of perforation)
Colorectal cancer
Treatment/management of Ulcerative Colitis
corticosteroids
Biologics
Aminosalicylates
Colectomy (curative)
Smoking (protective)
Crohn’s Disease
autoimmune → can affect anywhere in GI (ileum most common) transmural
Associated with non-caseating granulomas
Clinical features of Crohn’s
Cobblestone mucosa
pyrexia
Skip lesions
Abdominal pain
Malabsorption + weight loss
Fistula formation
Crohn’s management
Antibiotics
Corticosteroids
immunosuppressants
Biologics
Aminosalicylates
Smoking cessation
What type of epithelium is found at recto-anal junction
Simple columnar → stratified squamous non-keratinised
What cells are found in hepatic sinusoid + functions
endothelial:
Kupffer: macrophages
Pit:
Fat-storing:
Functions of the liver
Bile production
Detoxification
Glycogen storage
Clotting factors, CRP, etc synthesis
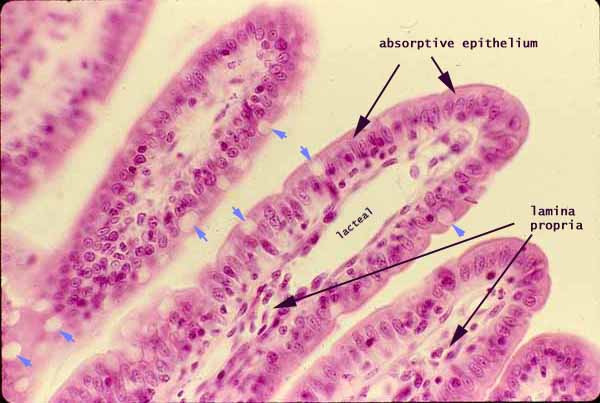
Lacteals
dilated lymph vessels involved in fat absorption in duodenum/jejunum
Paneth cells
located in crypts
Contain red cytoplasmic granules → produce defensin + lysosymes
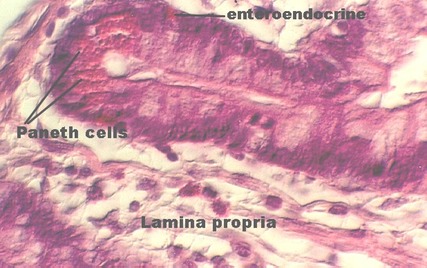
Enteroendocrine cells
found in duodenum + jejunum
Produce gastric inhibitory peptide → suppresses acid secretion
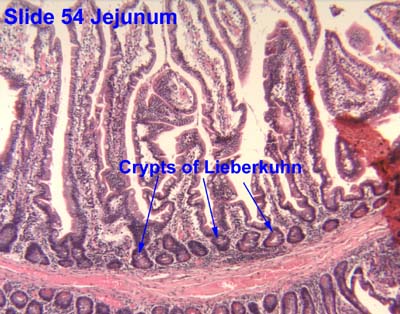
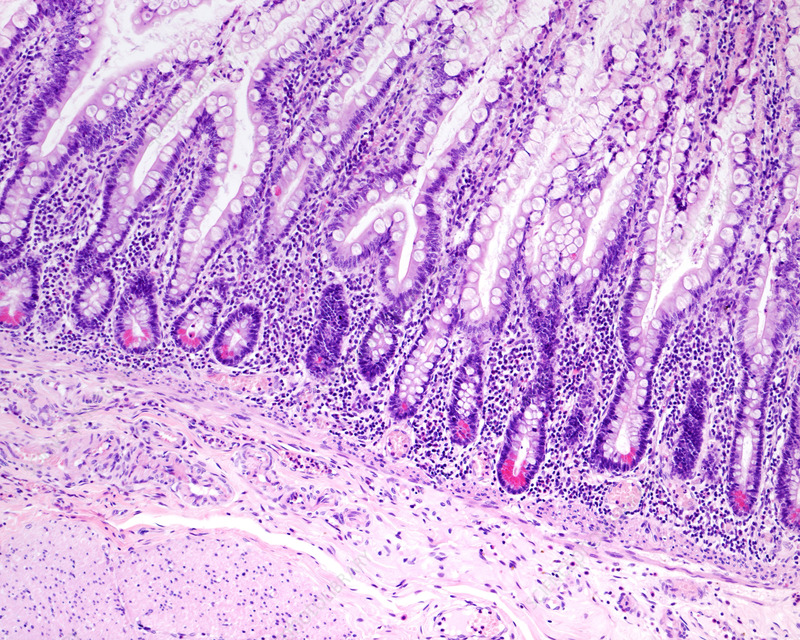
Crypts of lieberkuhn
Pits between villi (extend down to muscularis mucosa) → contain stem cells
How does small intestine structure help to aid in digestion/absorption
1) secretes enzymes + mucous producing glands
2) highly folded mucosa → villi/microvilli/plicae circulares
Meissner’s plexus location + function
secretion
Mucosal movement
Localised blood flow
Found in submucosa
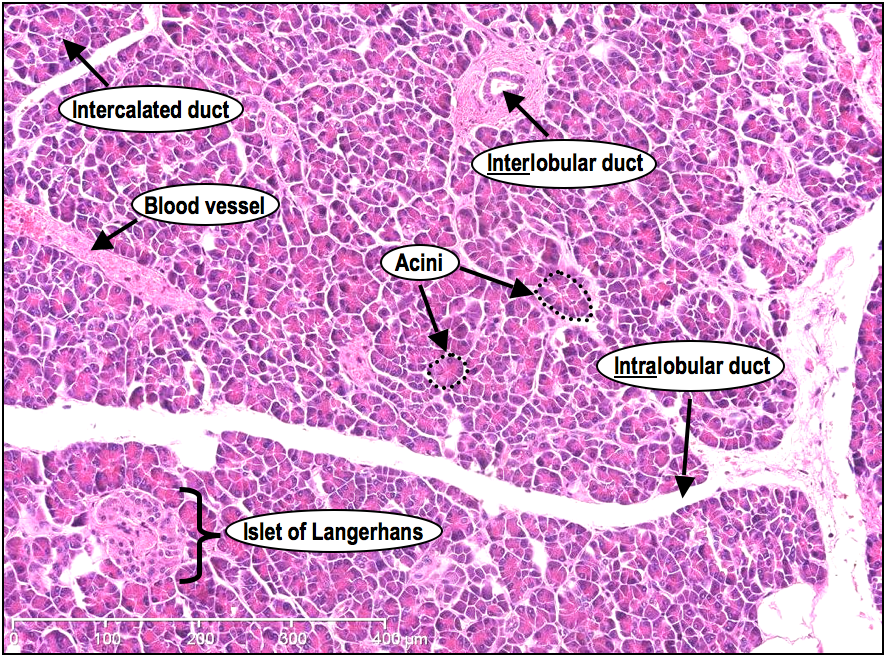
What cells are found in the pancreatic islets of Langerhans + what do they produce
a → glucagon
b → insulin
Gamma → Pancreatic polypeptide
Delta → somatostatin
How does somatostatin affect pancreas + GI tract
pancreas → inhibits release of insulin, glucagon, gastrin + digestive enzymes
GIT → reduces gastric secretion + GI hormones
Gall bladder function
stores bile
Contracts + expels bile into duodenum via CCK (Sphincter of oddi relaxes)
Gall bladder → common bile duct → duodenum
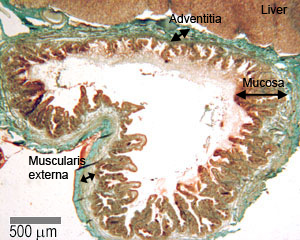
Gall bladder histology (+ what is NOT present)
mucosa → simple columnar epithelium + microvilli
NO muscularis mucosa + submucosa
Muscularis externa
Adventitia where it connects with liver
Serosa elsewhere (mesothelium + loose CT)
What type of cell is found in gall bladder ducts
cuboidal cholangiocytes
Small intestine divisions
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
large intestine divisions
Cecum
Colon → ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid
Rectum
Anal canal
3 main functions of gastrointestinal system
Digestion
Absorption
Excretion
Receptive relaxation of stomach
Fundus relaxes as food moves down oesophagus so no significant pressure difference
How is the stomach involved in digestion
secretes acid + proteolytic enzymes → forms chyme
Muscle contractions mix together
Large intestine functions
Where final water + electrolyte absorption occur
Microbial flora synthesise vitamin K + B12
Mix + propel luminal contents
Haustrations ensure faecal material is exposed to absorptive surface
Where does faeces accumulate
Descending + sigmoid colon → rectum
Parenteral nutrition
Intravenous feeding via peripheral or central vein (bypasses GI)
Used in: short bowel syndrome, IBD, obstruction
Enteral nutrition
Liquid supplemental nutrition orally or via tube
Used when GI system is still functional
Mouth + oral cavity functions
mastication
Salivation
Bolus formation
Swallowing
Mastication muscles
masseter
Temporalis
Medial + lateral pterygoid
Innervated by trigeminal + facial n.
3 phases of swallowing
oral: voluntary: bolus formed
Pharyngeal: involuntary (PANS): swallow reflex
Oesophageal: involuntary (Cranial n. X): bolus moves down to stomach
Peristalsis
Wave of muscular contractions that push food down
Neurological causes of dysphagia
stroke
Motor neurone disease
Parkinson’s
Myasthenia Gravis
Achalasia
Intramural causes of dysphagia (obstructive)
stricture caused by GORD,radiotherapy
Oesophageal cancer
Oesophagitis
Achalasia pathophysiology
progressive degeneration of myenteric neurones
aperistalsis + impaired relaxation of lower oesophageal sphincter
Clinical features of achalasia
intermittent dysphagia (solid+liquid)
regurgitation
Heart burn
achalasia investigations
CXR - dilated oesophagus
barium swallow - Bird’s beak
Endoscopy
achalasia management
botulinum toxin injection
endoscopic dilation (pneumatic balloon)
Causes of upper GI bleeds
gastritis
Peptic ulcer disease
Malignancy
Mallory-weiss tear
Oesophageal varices (enlarged veins)
Causes of lower GI bleeds
IBD
Diverticulitis
Haemmaroids
Polyps
Malignancy
gastritis
inflammation of stomach mucosa - acute or chronic
causes of acute gastritis
NSAIDs
stress
alcohol
burns (Curling’s ulcer)
Head trauma (cushing’s ulcer)
Causes of chronic gastritis
H. pylori
Autoimmune - type IV hypersensitivity occurs in fundus + body of stomach
autoimmune gastritis pathophysiology
autoantibodies against intrinsic factor/parietal cells → loss of parital cells
presents with pernicious anaemia
less gastric acid + intrinsic factor secretion = B12 malabsorption
Gastritis/H.pylori investigations
bloods → anaemia, H.pylori IgG
carbon-isotope urea breath test
stool antigen test
endoscopy w/ biopsy
gastritis treatment
proton pump inhibitor
antacids/H2 receptor antagonists
H. pylori treatment (Triple therapy regime)
PPI + amoxicillin + clarithromycin (TD) for 7 days
Amoxicillin allergy = clarithromycin + metronidazole
H. pylori pathogenesis
Gram -ve bacteria colonises gastric antrum
uses urease: urea → co2 + ammonia (neutralises acid)
H. pylori complications
gastric/duodenal ulcers
strictures
MALT lymphoma
gastric adenocarcinoma
How do NSAIDs lead to mucosal damage
inhibit COX1 pathway = less prostaglandin production (E2 + I2)
decreased gastric defence mechanisms
Symptoms of upper GI bleed
haematemesis
Melaena
Haematochezia
Epigastric pain
Haemodynamic instability
Gastric outlet obstruction
blockage that impairs normal stomach emptying
Causes: benign, malignant, functional
Gastric outlet obstruction management
acid suppression therapy
Avoid NSAIDs
Test/treat H. Pylori
Endoscopic balloon dilation
Surgical intervention
Clinical presentations of ulcers/PUD
epigastric pain
Bloating
Vomiting
Belching
Melaena
Haematemesis
Peptic ulcer disease
gastric ulcers → lesser curvature of stomach, increased pain while eating due to HCL production, weight loss
Duodenal ulcers → duodenal bulb, decreased pain while eating, weight gain
Main causes: NSAIDs, H.Pylori
Complications of PUD
malignancy
Perforation
Bleeding
Clinical presentation of ulcer perforation
severe epigastric pain
Tachycardia
Hypotension
Guarding
Abdominal distension
Perforation diagnosis
bloods
Imaging → xray or CT (gold standard)
Perforation management
Resuscitation
IV PPI
NG tube for gastric decompression
Surgical intervention
Broad spectrum antibiotics
What is the most common congenital GI defect
Meckel’s diverticulum → pouch on distal ileum (true)
Dual blood supply + venous drainage of liver
hepatic artery proper (25%) + hepatic portal vein (75%)
Hepatic veins → IVC
LFTs: blood markers + significance
bilirubin: quantifies jaundice
Albumin: liver synthesis function
AST+ALT: hepatocellular injury
Alkaline phosphate: raised in biliary obstruction
Gamma-GT: chronic hepatocellular injury
Bilirubin + its metabolism
Haemolysis: haem from RBCs broken down into uncojugated bilirubin
albumin binds + moves to hepatocytes
conjugated with glucuronic acid → bilirubin (water sol)
Bilirubin → urobilinogen → sterobilin (faeces colour)
Urobilinogen recycling
reabsorbed into blood + oxidised → Urobilin
Sent to liver - recycled into bile
kidneys - excreted giving urine yellow colour
Jaundice
yellowing of skin + sclera due to accumulation of bilirubin
Clinically detectable >34 µmol/L
Divided into: prehepatic, hepatic + post hepatic
Why does sclera show earliest sign of jaundice
tissue is high in elastin → bilirubin binds with high affinity
Pre-hepatic jaundice causes (excessive haemolysis)
G6PD deficiency
Sickle cell anaemia, Thalassaemia
Hereditary spherocytosis
Malaria
Rifampicin
Unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia
Intrahepatic causes of jaundice
hepatitis
Alcoholic liver disease
cirrhosis
Haemochromatosis
Crigler Najjar syndrome
Gilbert’s syndrome
Crigler Najjar syndrome
rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder
Bilirubin conjugating enzyme (UGT1A1) decreases/absent
Unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia
Can cause neurological impairment
Gilbert’s syndrome
autosomal recessive
Decreased activity of UGT enzyme → less conjugation
Bilirubin increases during physiological stress (episodic)
Causes of hepatitis
viral → A-E
Alcohol
Drug induced
Autoimmune
Clinical features of liver cirrhosis
anaemia
Jaundice
Bruising
Palmar erythema
Dupuytren’s contracture
Post-hepatic causes of jaundice
head of pancreas carcinoma
Pancreatitis
Gall stones
Cholangiocarcinoma
Bile function + components
Concentrated detergent that aids in lipid absorption + digestion. Composed of:
Bile acids + salts
Cholesterol + lecithin
Pigments
Bicarbonate
Bile acids
primary: Synthesised from cholesterol in liver (cholic + chenodeoxycholic acid)
Secondary: synthesised by intestinal bacteria (deoxycholic + lithocholic acid)
95% recycled
Bile salt synthesis
Formed when primary acids are conjugated w/ glycine or taurine
Regulates rate of bile production + can be recycled up to 20 time
What structural feature of bile salts enables emulsification
Amphipathic → hydrophilic + hydrophobic regions
Allows emulsification (smaller particles = larger SA) + transport of lipids → micelles
Consequence of inadequate bile/pancreatic lipase secretion
Poor fat digestion = steatorrhea
Fat soluble vitamins A,D,E +K not absorbed
Exocrine pancreas function
Produces + secretes pancreatic juice → enzymes (produced from acinar cells) + alkaline fluid (ductal epithelial)
Juice flows through pancreatic duct to duodenum
Constitutes for 98% of pancreatic tissue
Functional anatomy of exocrine pancreas
Serous acinus: secrete enzymes into intercalated ducts
Intercalated ducts: lined w/ cuboidal epithelium that secrete HCO3-
(Dark pink= exocrine pancreas, light pink= endocrine)
Examples pancreatic digestive enzymes + location of synthesis
trypsin
Amylase
Lipase
Elastase
Carboxypeptidase
Chymotrypsin
Synthesised on RER + transported via Golgi