Flipped Lesson 5: Haplotypes & Consanguinity
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a gene in the context of gene mapping
A gene is a biological determinant of a Mendelian character (trait).
Considered a functional unit of DNA that contributes to a specific phenotype.
Define haplotype (haploid genotype).
A haplotype is a set of polymorphisms (alleles or genetic markers/SNPs) that are grouped tightly together on a single chromosome and tend to be inherited together through many generations because they are not separated by crossing over.
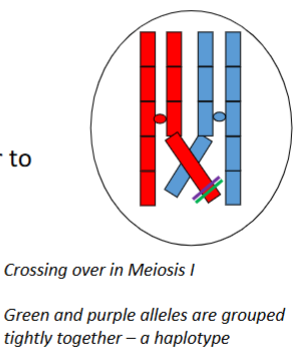
Haplotypes are aka
DNA/genetic signature — essentially a "chunk" of a chromosome.
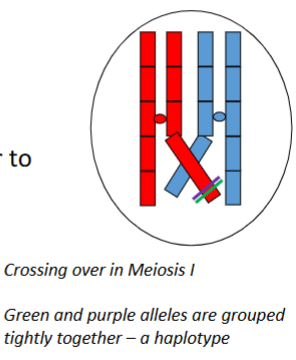
Why do haplotypes tend to be inherited together through generations
Because the polymorphisms are physically close on the same chromosome and crossing over between them is rare, so recombination does not separate them frequently.
What is the difference between a haplotype and a haplogroup
A haplotype is one specific combination of polymorphisms on a chromosome, while a haplogroup is a group of similar haplotypes sharing a common ancestor defined by a particular SNP mutation; haplogroups often describe deep lineage (e.g., mtDNA haplogroups).
Who provided early evidence for chromosome theory, linkage, and mapping via genetic recombination & with what
Thomas Hunt Morgan with experiments on Drosophila (fruit fly), demonstrating sex-linked inheritance and genetic recombination.
How did Morgan’s student Sturtevant contribute to Thomas Hunt Morgan’s research
Morgan’s student Sturtevant predicted that genes more closely grouped on chromosomes were separated less frequently by crossing over
Proposed first chromosomal linkage map
Closely linked genes e.g. vermillion eyes and miniature wings were more likely to belong to the same haplotype (chunk)
What is the strategy for mapping human genes using haplotypes
Examine haplotypes of related individuals who share the same trait
Find a haplotype common to affected individuals using polymorphic markers (microsatellites or SNPs)
Infer that the causal gene lies within that chromosomal region.
What percentage of the human genome is noncoding, and what is the use of that part of the genome in gene mapping
About 98% of the human genome is noncoding; it contains many repeat sequences (tandem repeats and interspersed repeats) that can be used as polymorphic markers for mapping.
What is a tandem repeat
A sequence where a unit of nucleotides is directly repeated head-to-tail several time
e.g. (ATGCCG)(ATGCCG)(ATGCCG)n
The length and number of repeats vary between individuals. (n)
Name three classes of tandem repeats and their general properties. (array length, repeat length, use)
Satellite DNA:
very large arrays (100kb & several Mb)
repeat length >100 bp
e.g. α (alphoid) DNA found in centromeric heterochromatin
Minisatellite DNA:
arrays 100 bp–20 kb
repeat unit length: 10–100 bp
high mutation rate → high diversity in population (VNTRs).
Microsatellite DNA:
arrays usually <100 bp total
repeat units typically 2–4 bp
used as markers for a trait/disease in linkage analysis.
aka Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) / Short Tandem Repeats (STR)
Where in the genome are microsatellites usually located
Dispersed throughout chromosome
Often in intergenic regions or introns, sometimes in exons (coding sequences).
What type of microsatellites are mutation hot spots & why?
Microsatellites in exons are mutation hot spots
Error prone: During replication DNA polymerase tends to make errors in copying repeated units, e.g. may skip over a repeat unit or copy it twice
Makes microsatellite mutations unstable & highly polymorphic (many different forms)
What fraction of the human genome is composed of microsatellites
Approximately 2% of the genome (~60 Mb) is composed of microsatellite sequences.
Why might an SNP not be detected when analysing PCR products only by size?
How would SNPs be detected?
Because the SNP does not change the fragment length; size-based analysis detects length differences only, so sequencing is required to reveal SNPs.
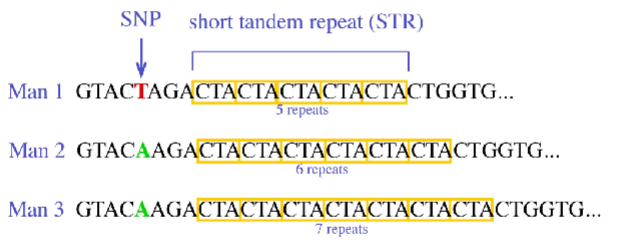
What are flanking sequences in PCR for microsatellites
The unique sequences upstream (5’) and downstream (3’) of a microsatellite where primers are designed to bind for amplification.
List the steps on how to use a microsatellite as a marker.
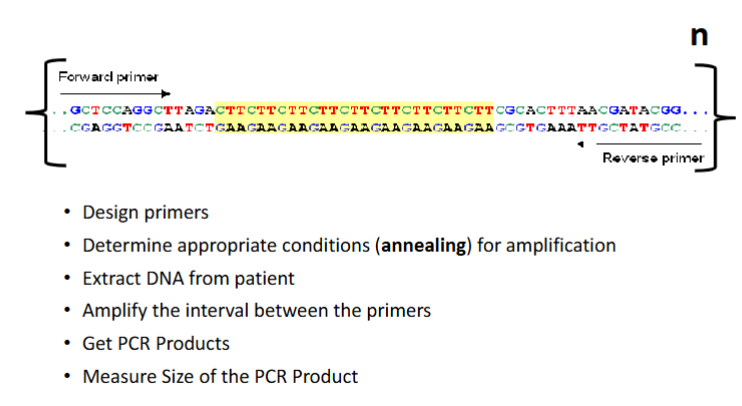
If primers are 20 bp each and the repeat unit is 8 bp repeated 3 times, what is the PCR product size
PCR product = 20 + 20 (primers) + (3 × 8) = 20 + 20 + 24 = 64 bp.
What is linkage
Linkage is a relationship between loci.
Explain the principle behind linkage analysis.
If a mutation causing a trait is physically near a genetic marker (microsatellites / SNPs), they will be inherited together more often than by chance. Identifying markers shared only by affected family members suggests the causal gene is in that region.
How to identify trait-related haplotype (chunk)
Perform genomic analysis of polymorphic DNA markers associated with the trait for all family members
Can use the dbSNP database to find appropriate markers
See which markers are carried only by members with the trait
High probability (odds) that trait causing gene is linked to this marker (same location on chromosome)
If Dad is Bb = Brown hair & Mum is bb = red hair, how many PCR products would their son (brown hair) & daughter (red hair) have
Son = Bb = 2 PCR products
Daughter = bb = 1 PCR product
(Meaning? Homozygous individuals have two identical alleles. Both alleles produce the same PCR product (same size and sequence) - on a gel, you’ll see one band (one PCR product).
Are haplotypes ever on different chromosomes
No! A haplotype (haploid genotype) is a set of polymorphisms (alleles or genomic markers) that are grouped tightly together on a single chromosome and tend to be inherited together through many generations (not separated by crossing over)
Microsatellites (a.k.a. Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) or Short Tandem Repeats (STR)) are ________ genetic markers
Microsatellites (a.k.a. Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) or Short Tandem Repeats (STR)) are polymorphic genetic markers
Microsatellites (a.k.a. Simple Sequence Repeats (SSR) or Short Tandem Repeats (STR)) are composed of arrays with a variable number of tandem repeats of ______ bp.
2-6 bp
Why are Microsatellite DNA sequences highly polymorphic
Because replication of repeat units is very error prone → many different forms