Protein Synthesis Test Review
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
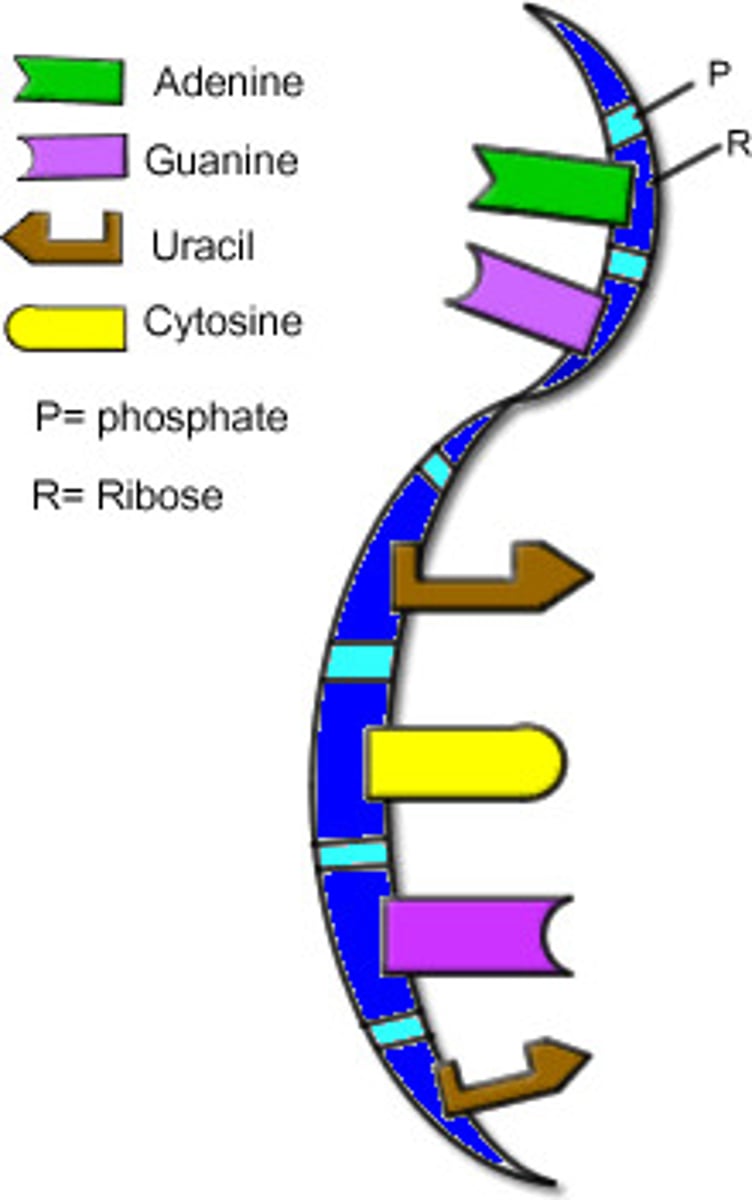
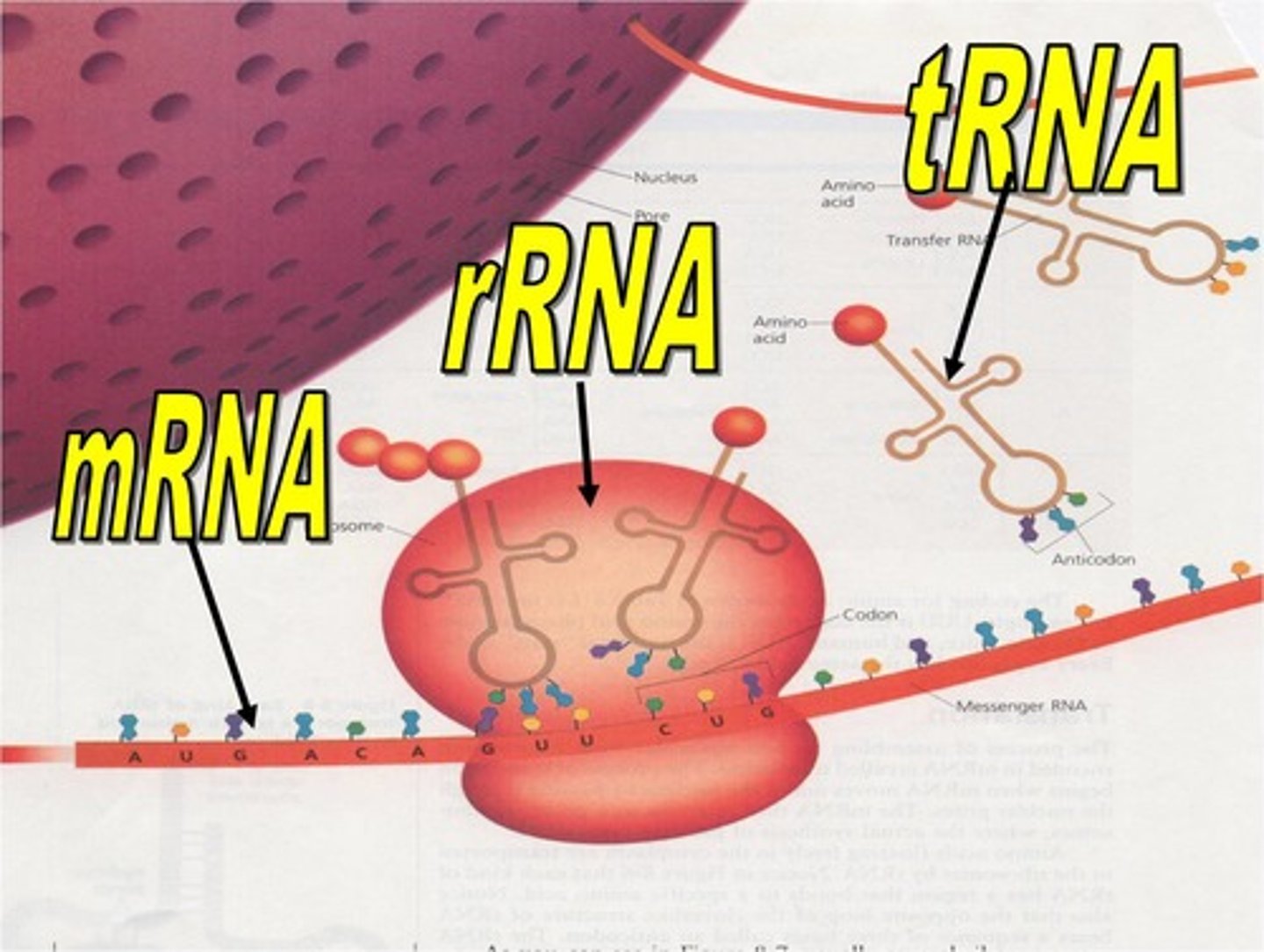
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
ANALOGY: Xerox copy of 1 chapter of the reference book
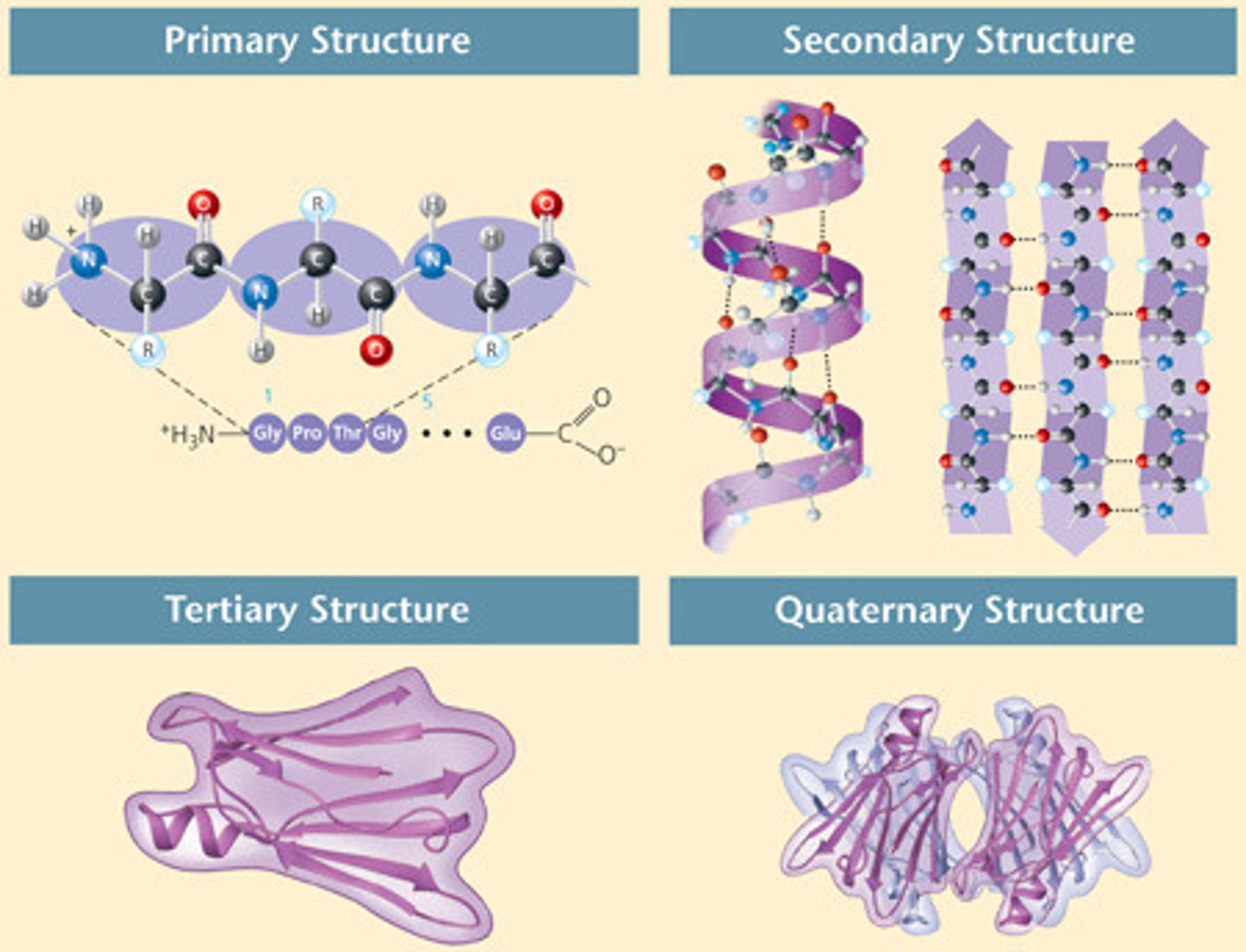
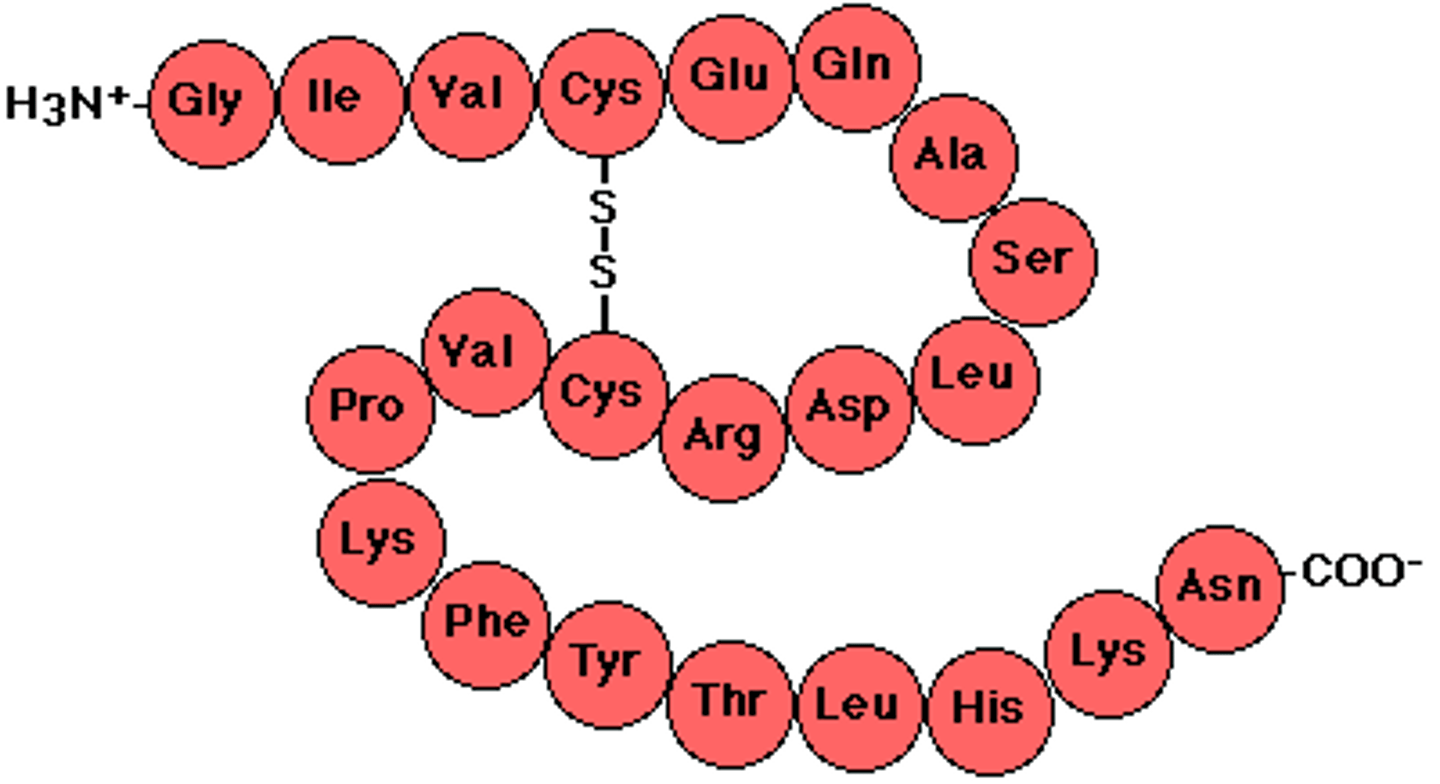
protein (polypeptide)
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
ANALOGY: Your final paper you write
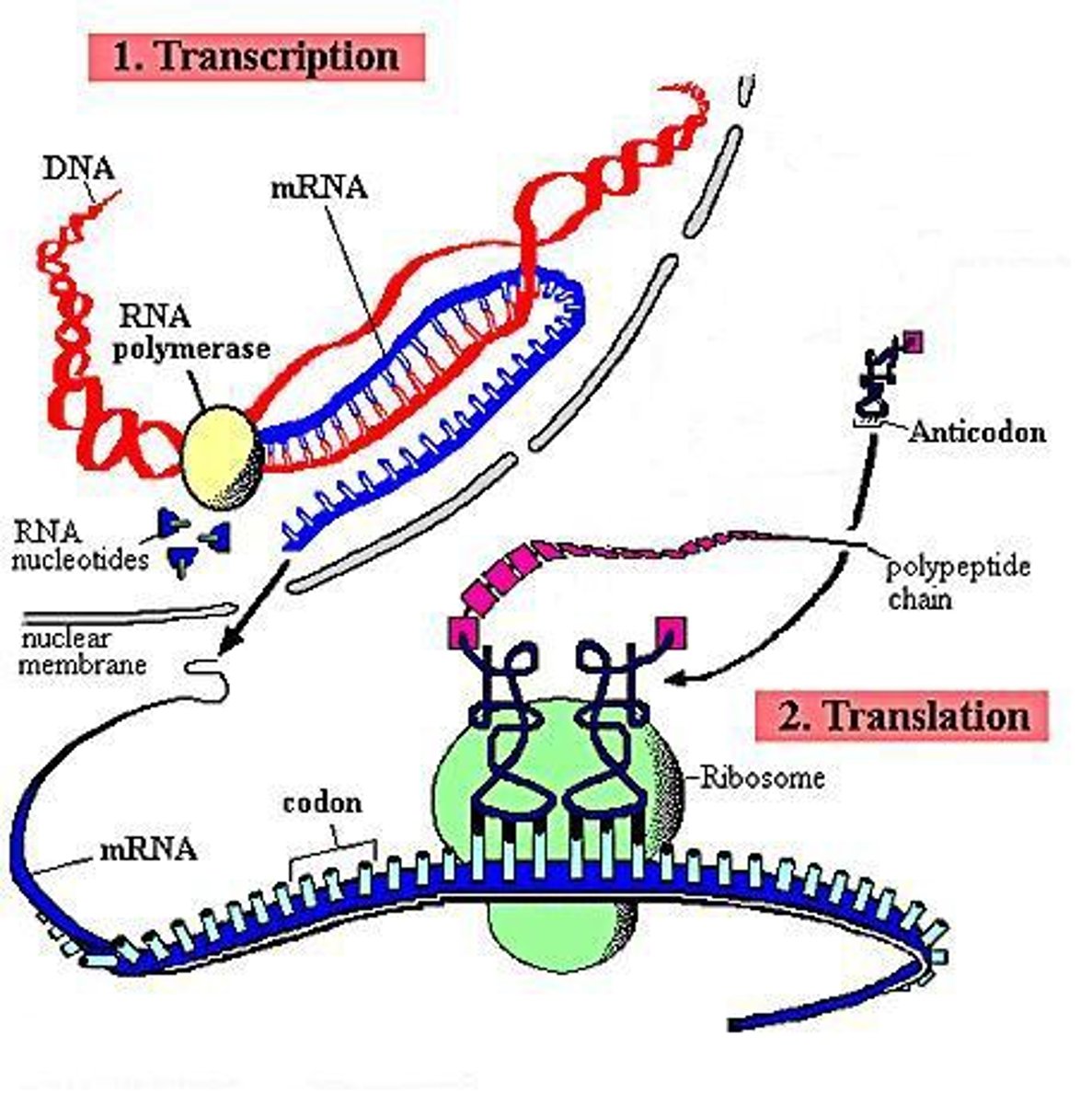
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
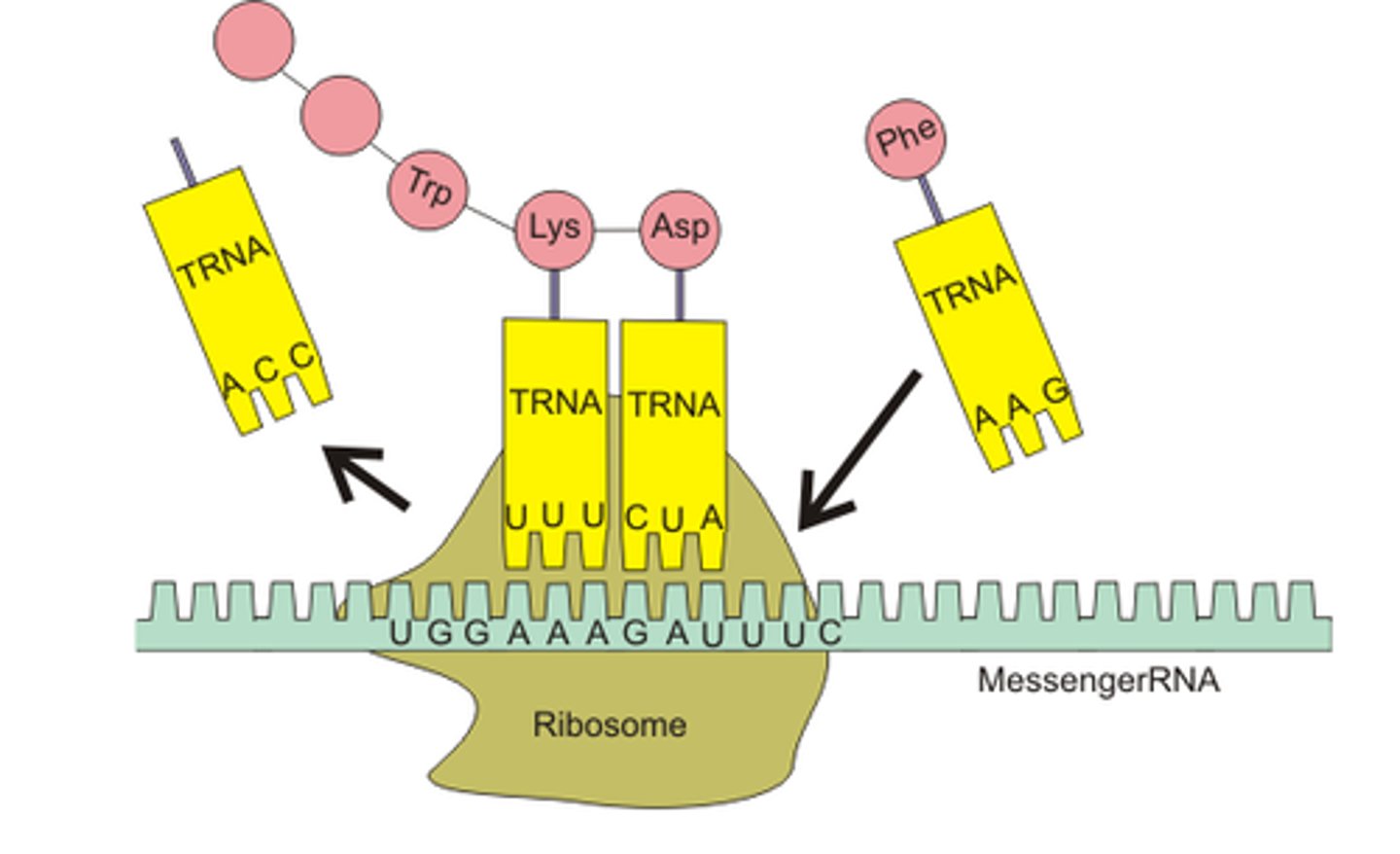
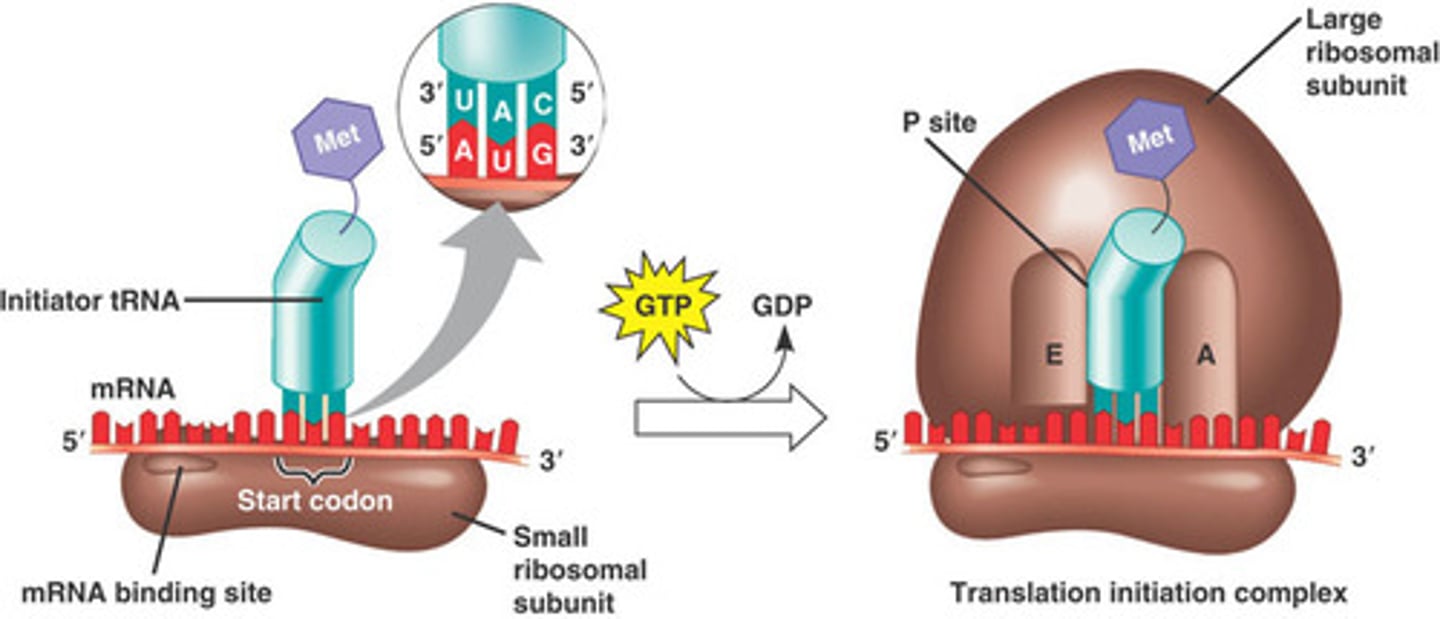
initiation of translation
mRNA is attached to a subunit of the ribosome, the first codon is always AUG
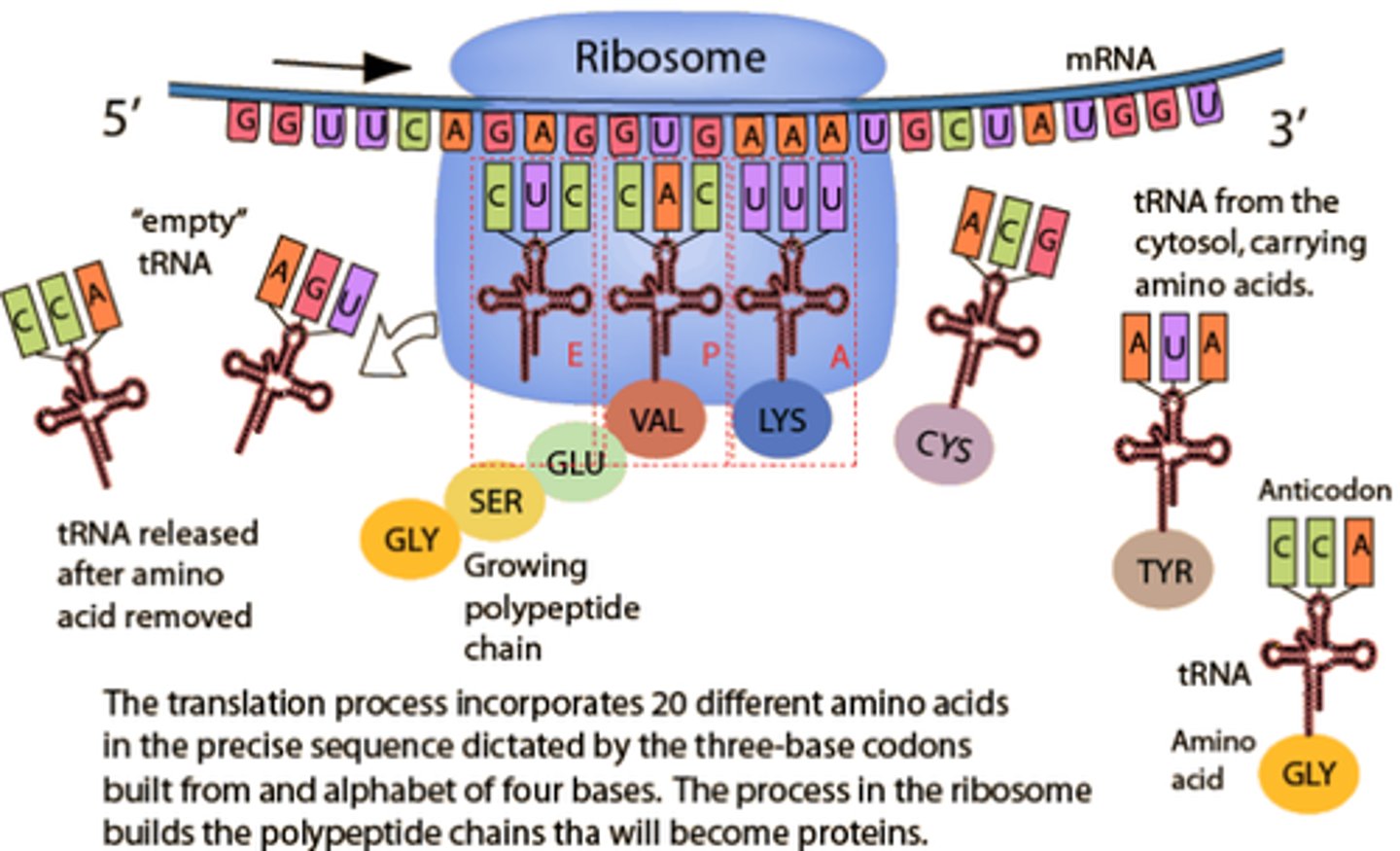
elongation (translation)
synthesis of an amino acid strand from start codon to stop codon
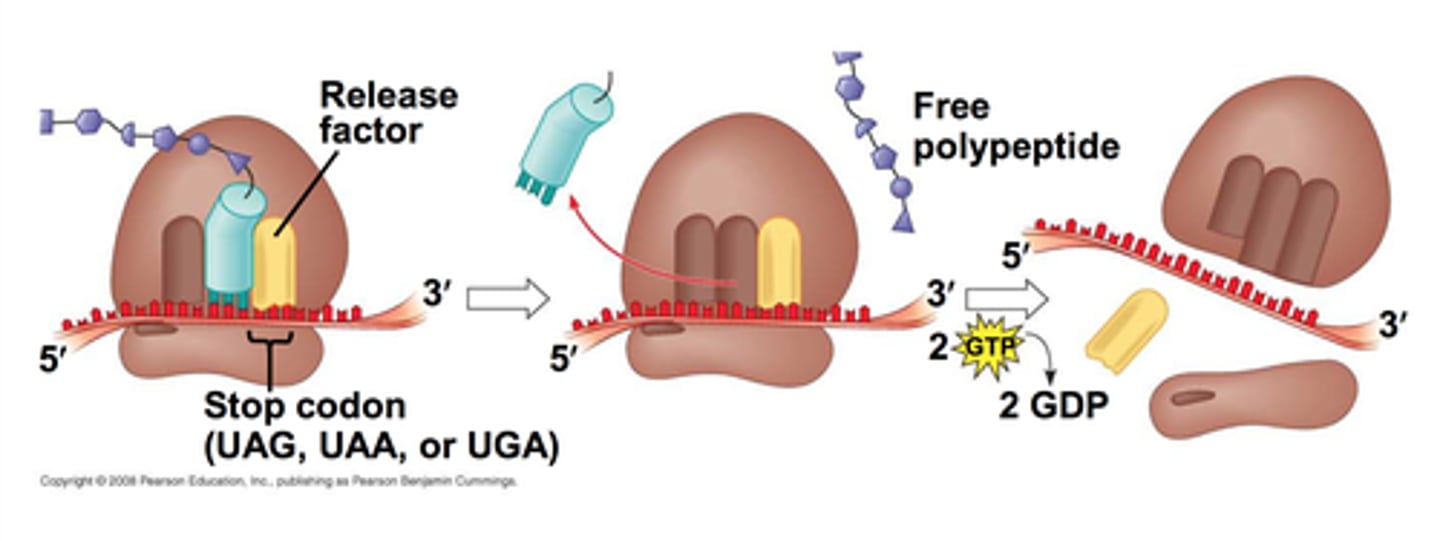
termination of translation
complex disassembles at stop codon releasing completed polypeptide
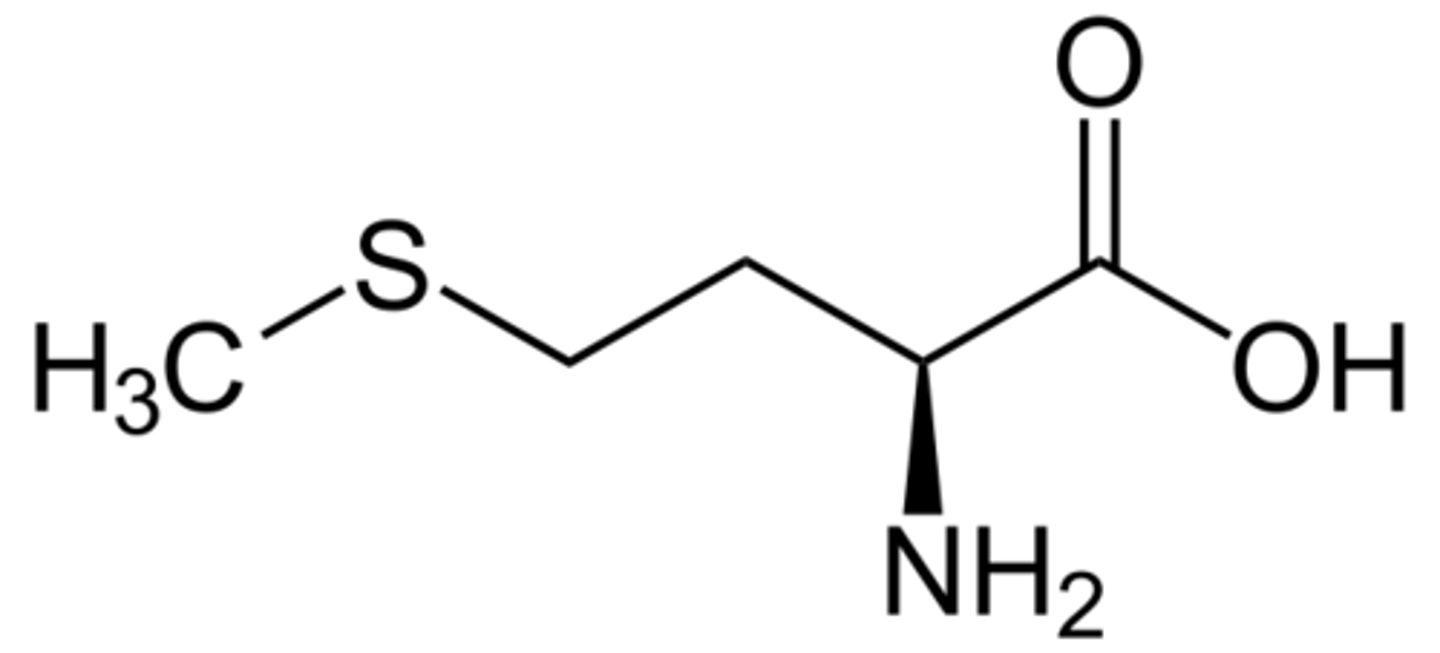
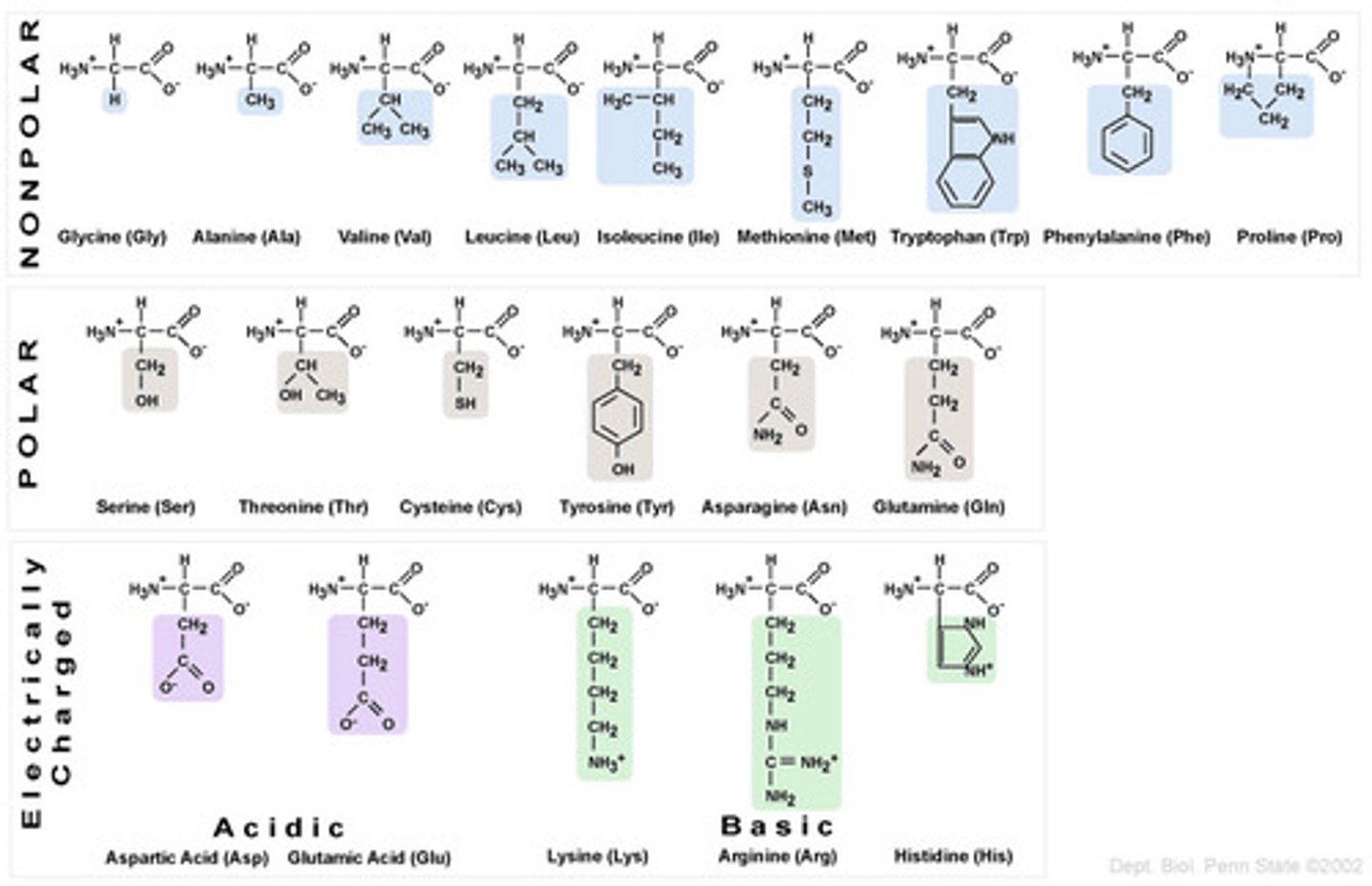
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
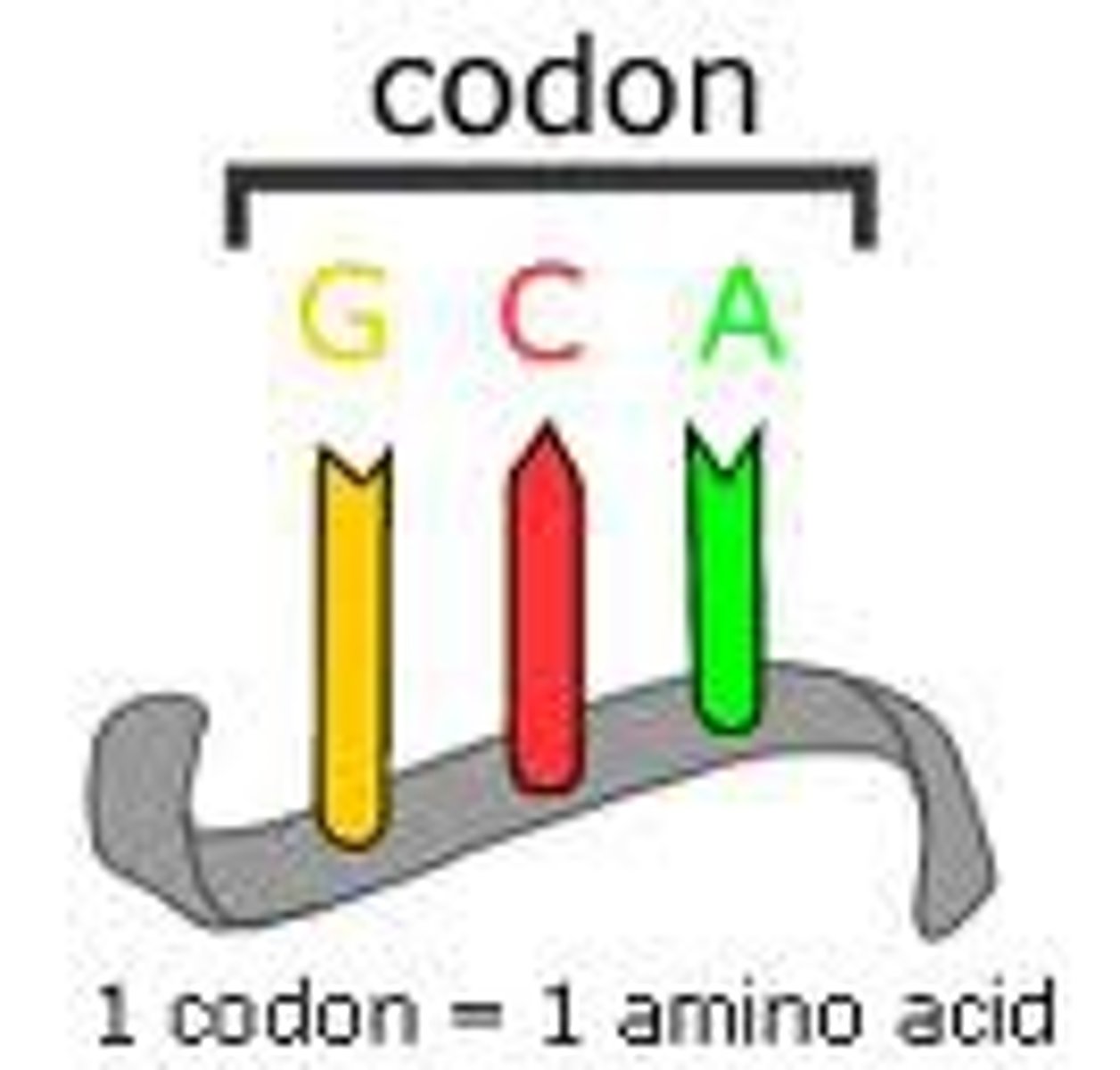
Codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
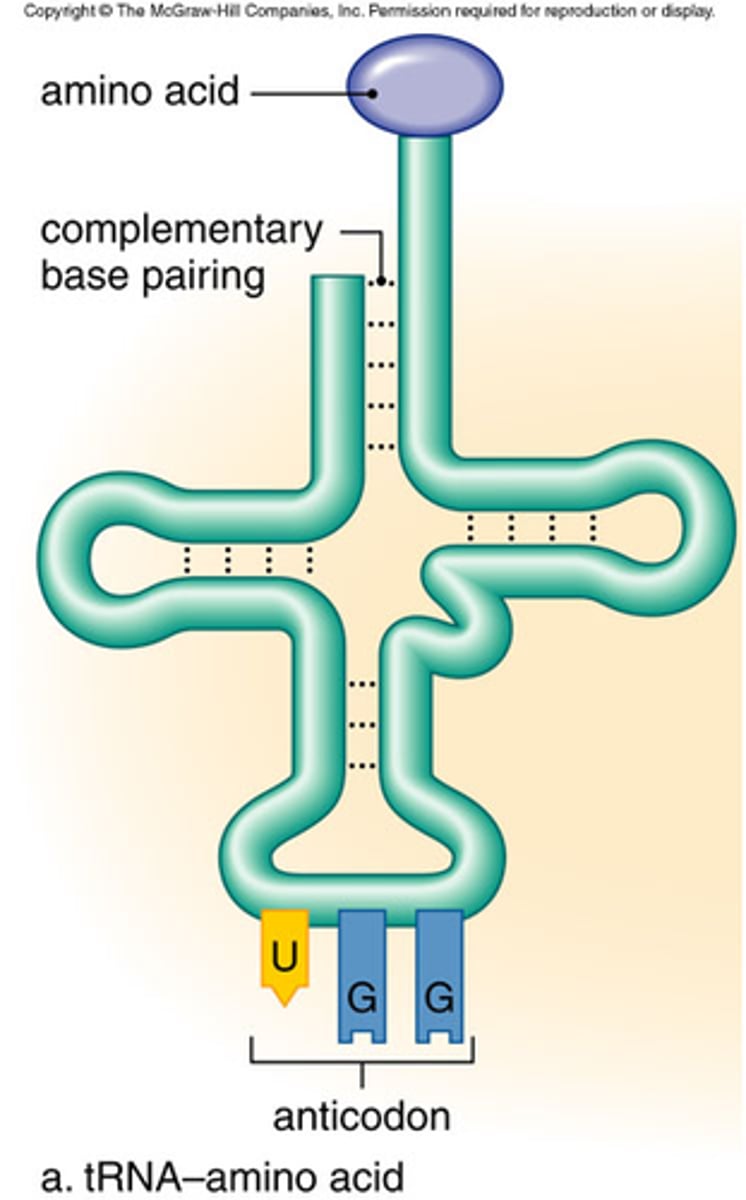
Anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
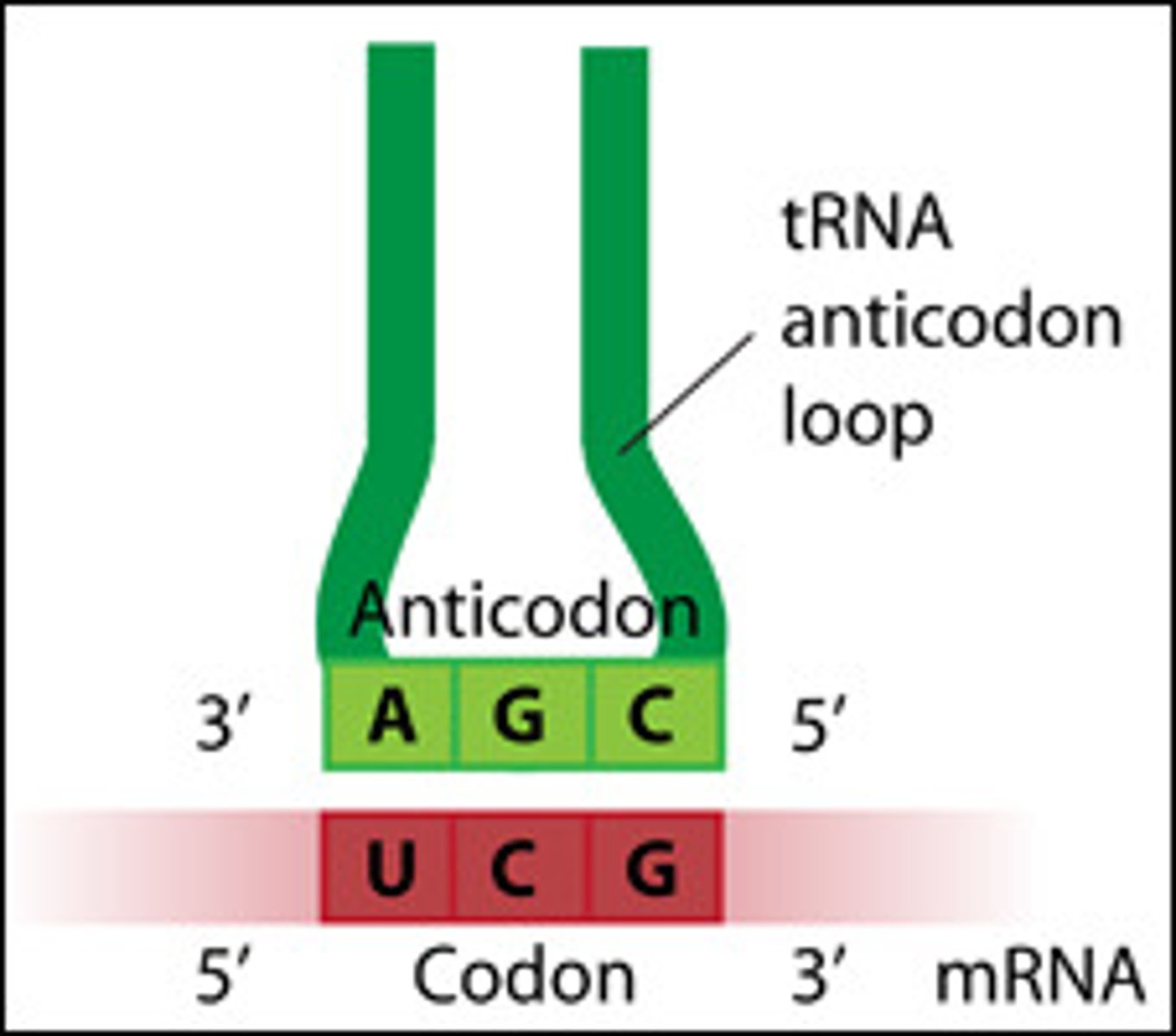
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
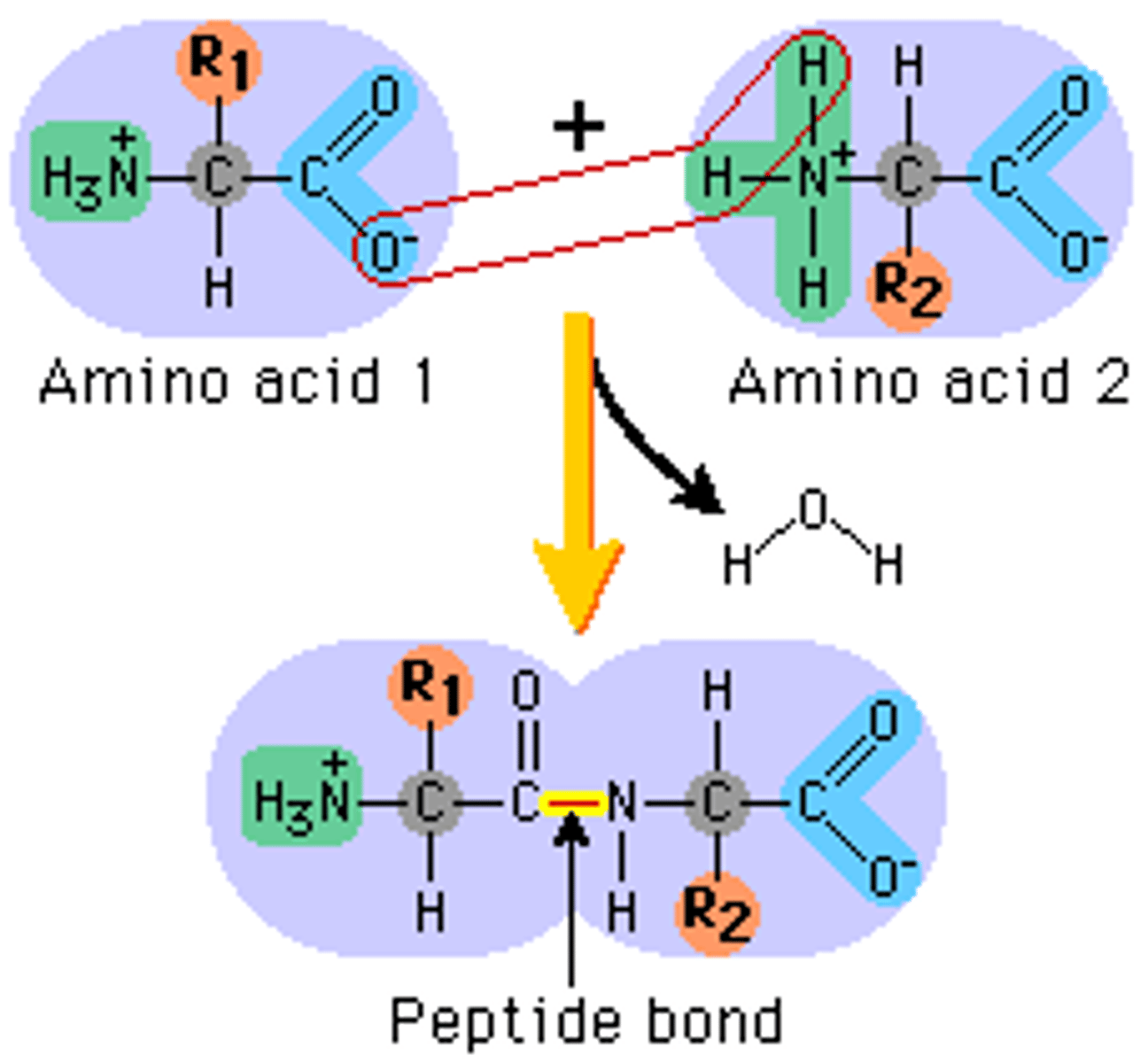
peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
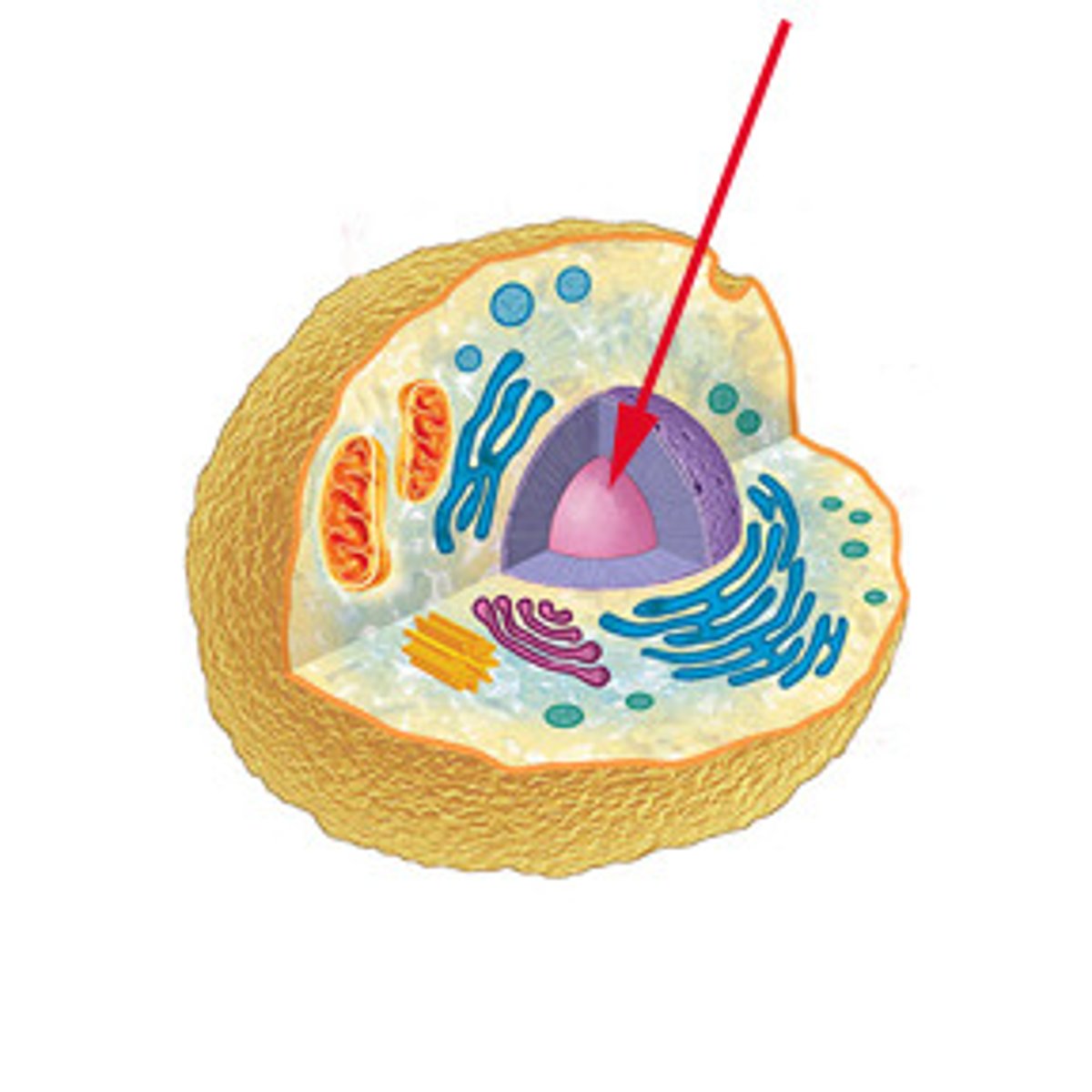
Nucleus
Site of transcription
ANALOGY: The Library
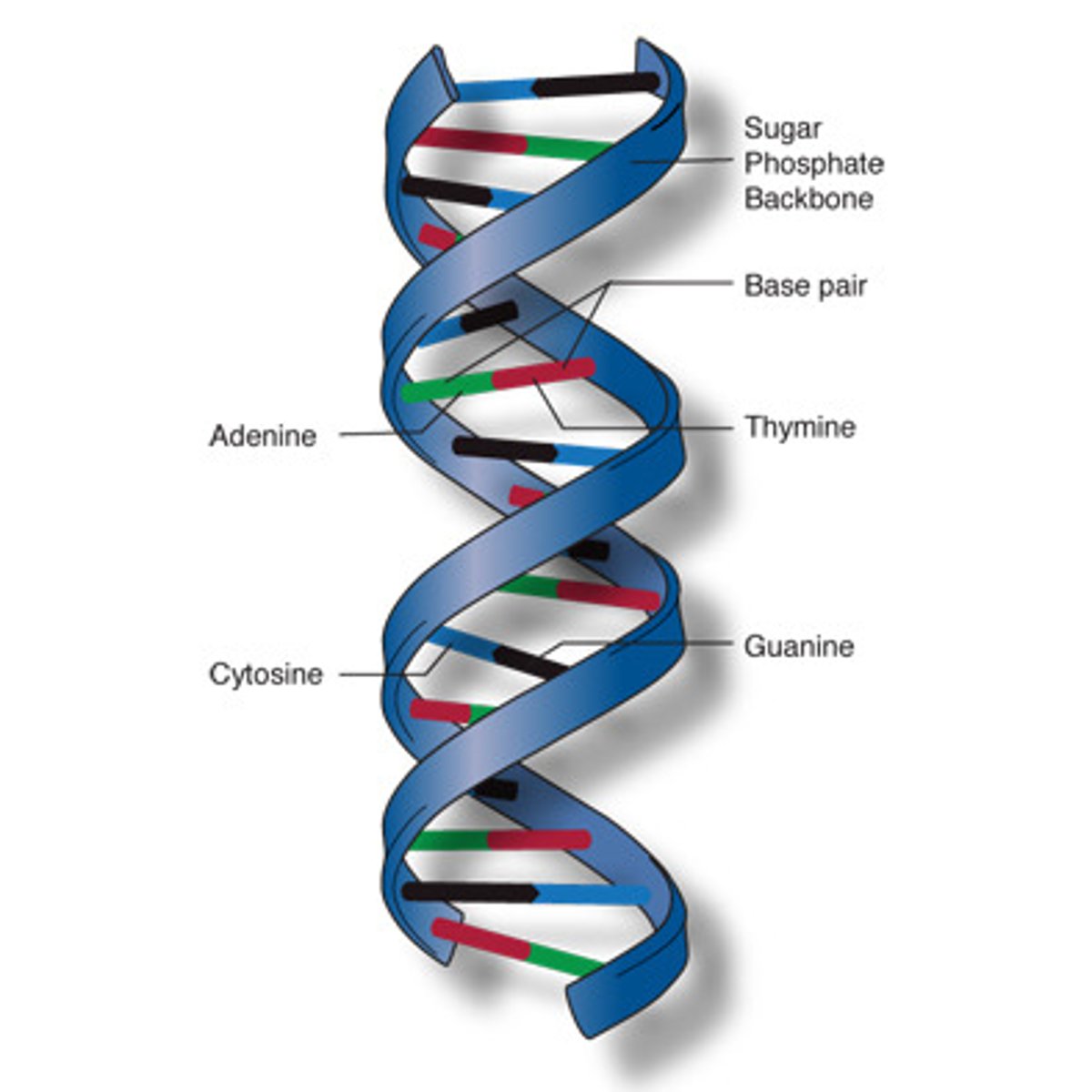
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that contains genes and makes up the chromosomes.
ANALOGY: Reference book
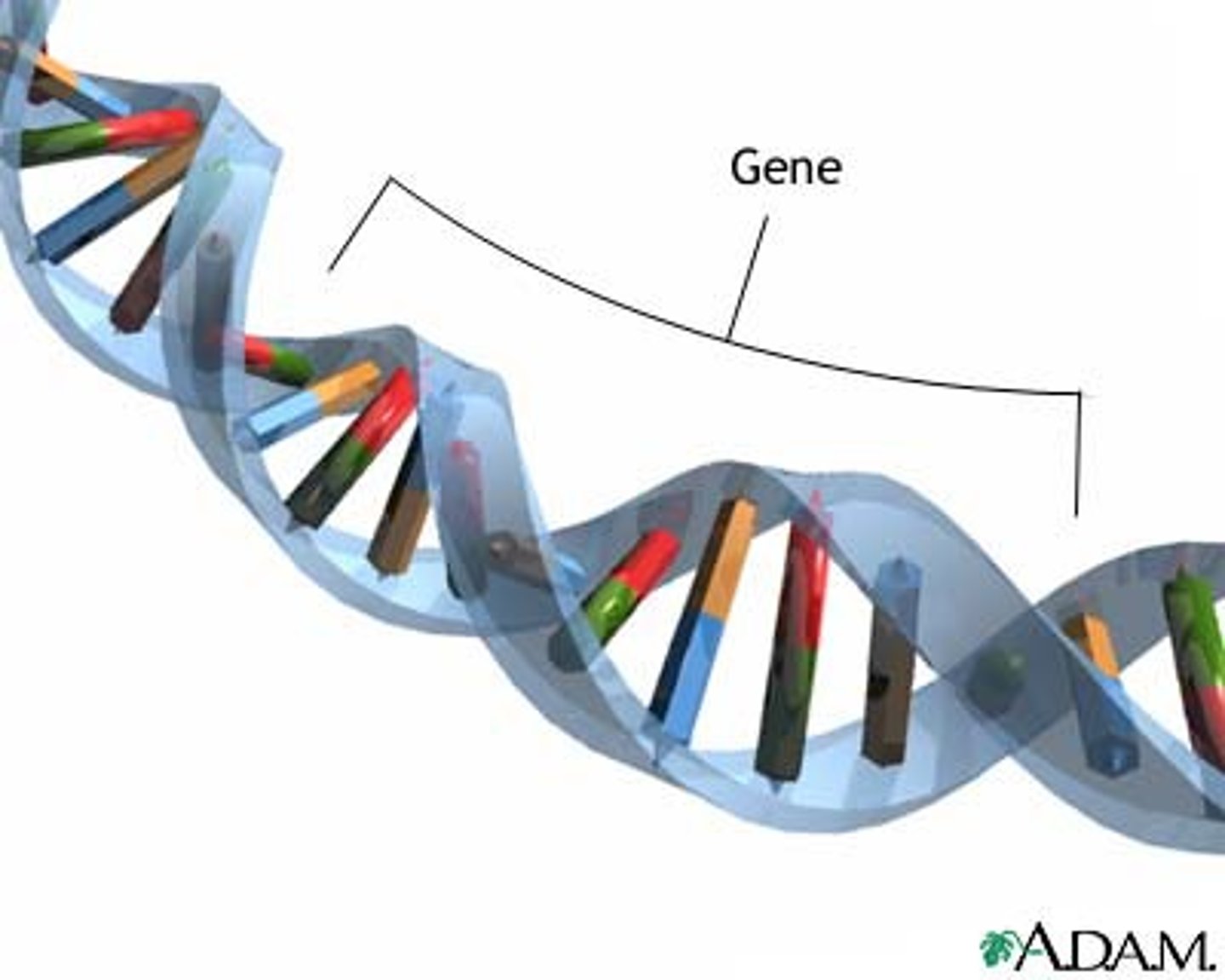
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait/protein
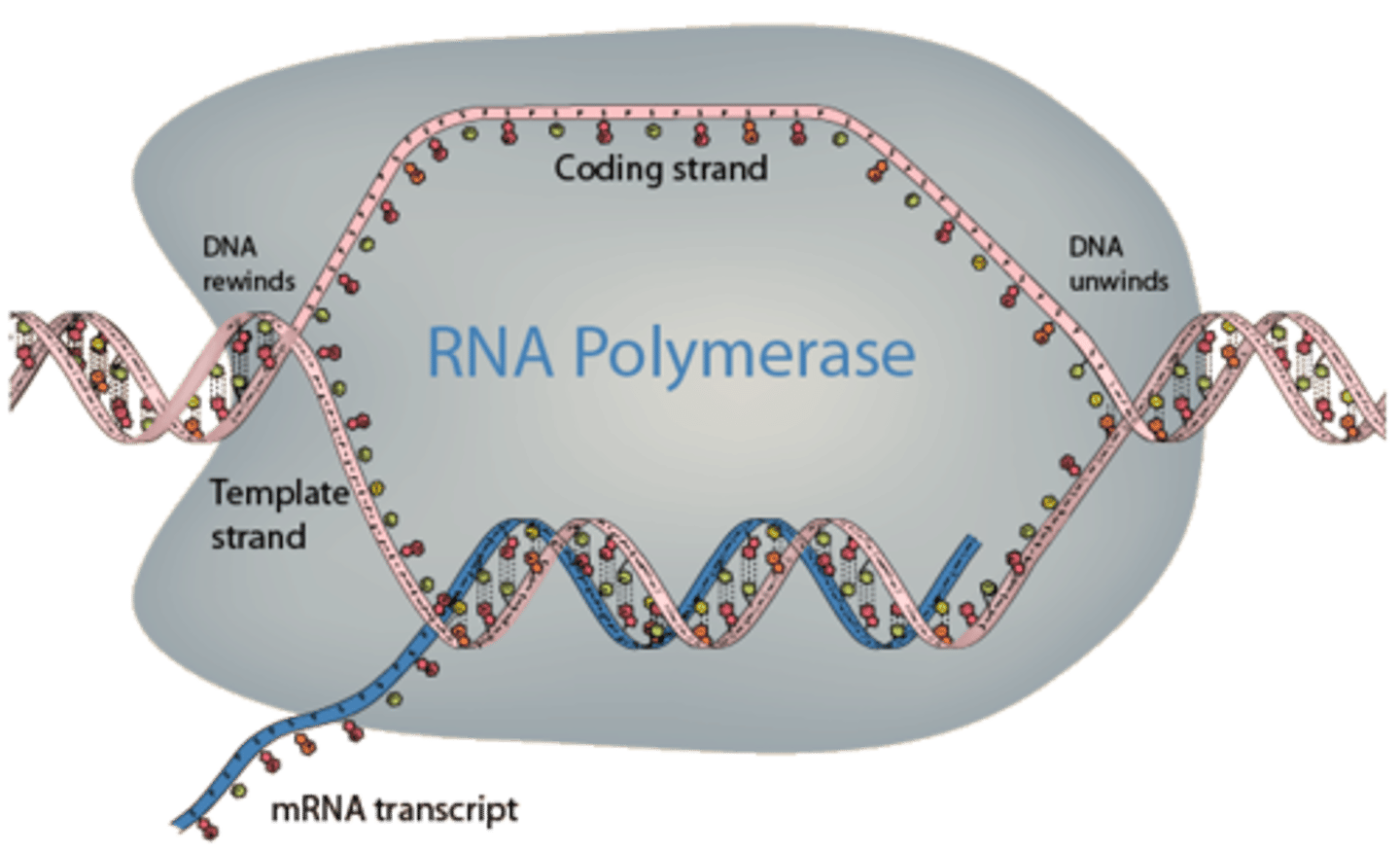
RNA polymerase
enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using a DNA strand as a template
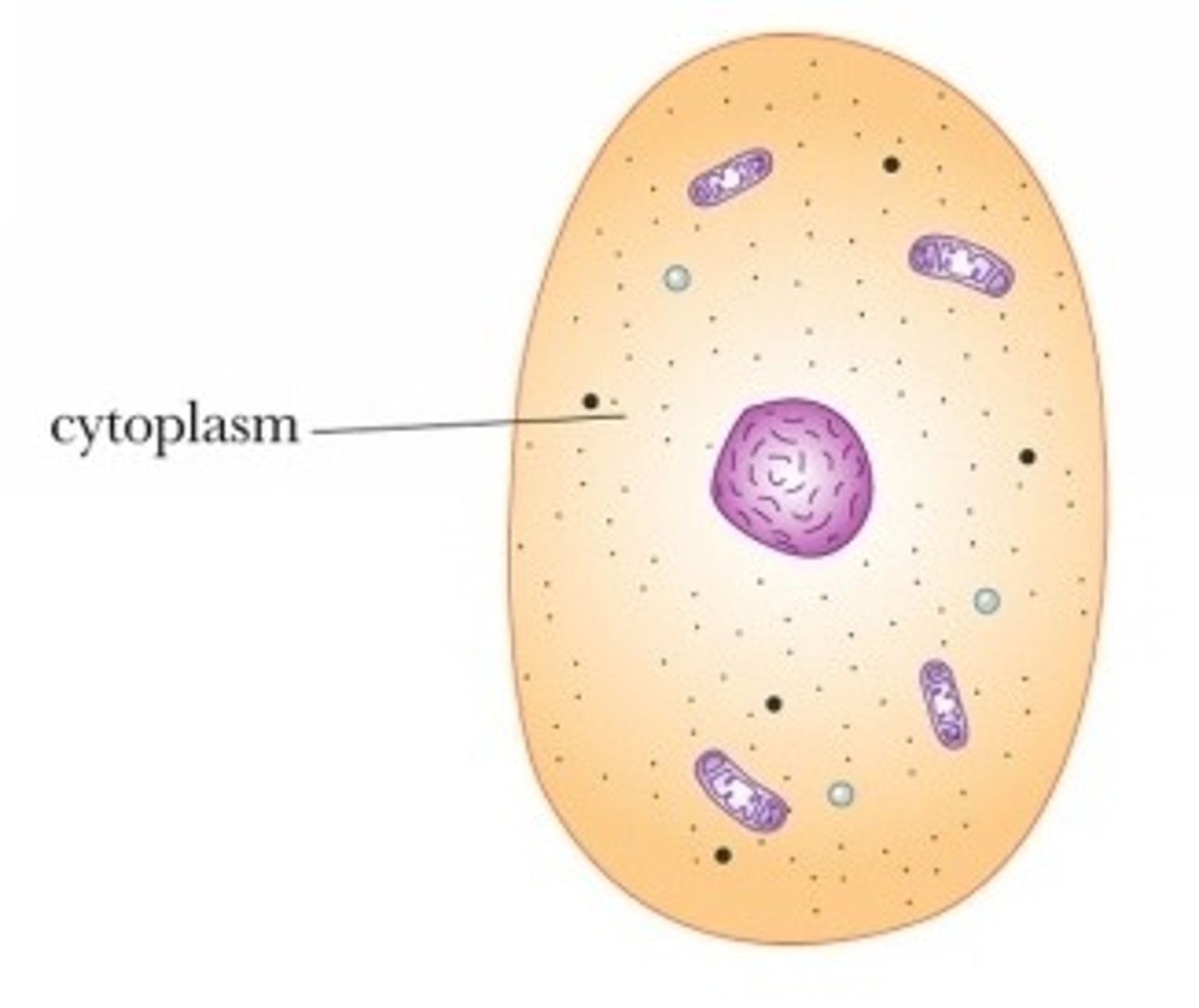
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended. Location of translation.
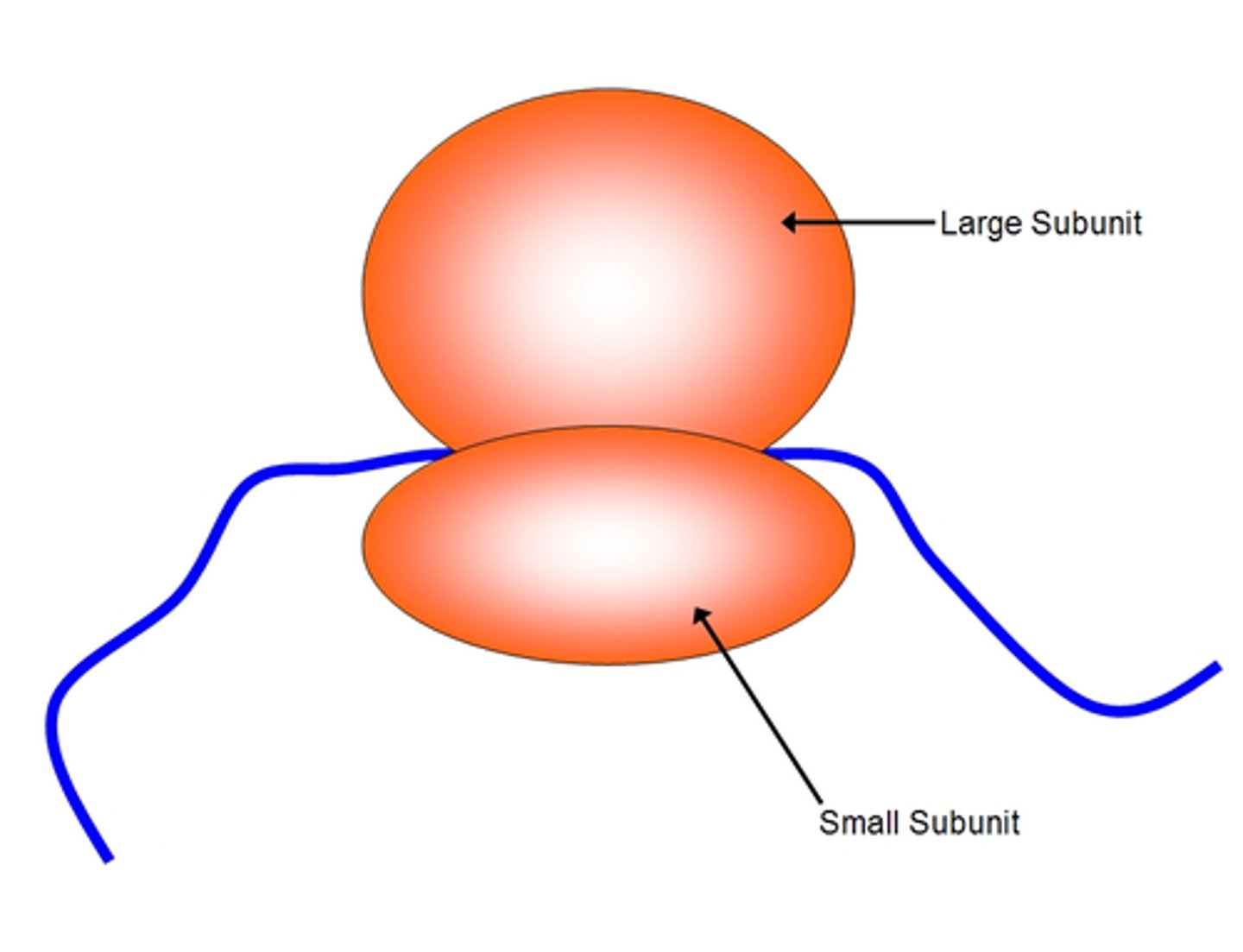
Ribosome
organelle: site of translation
ANALOGY: Room
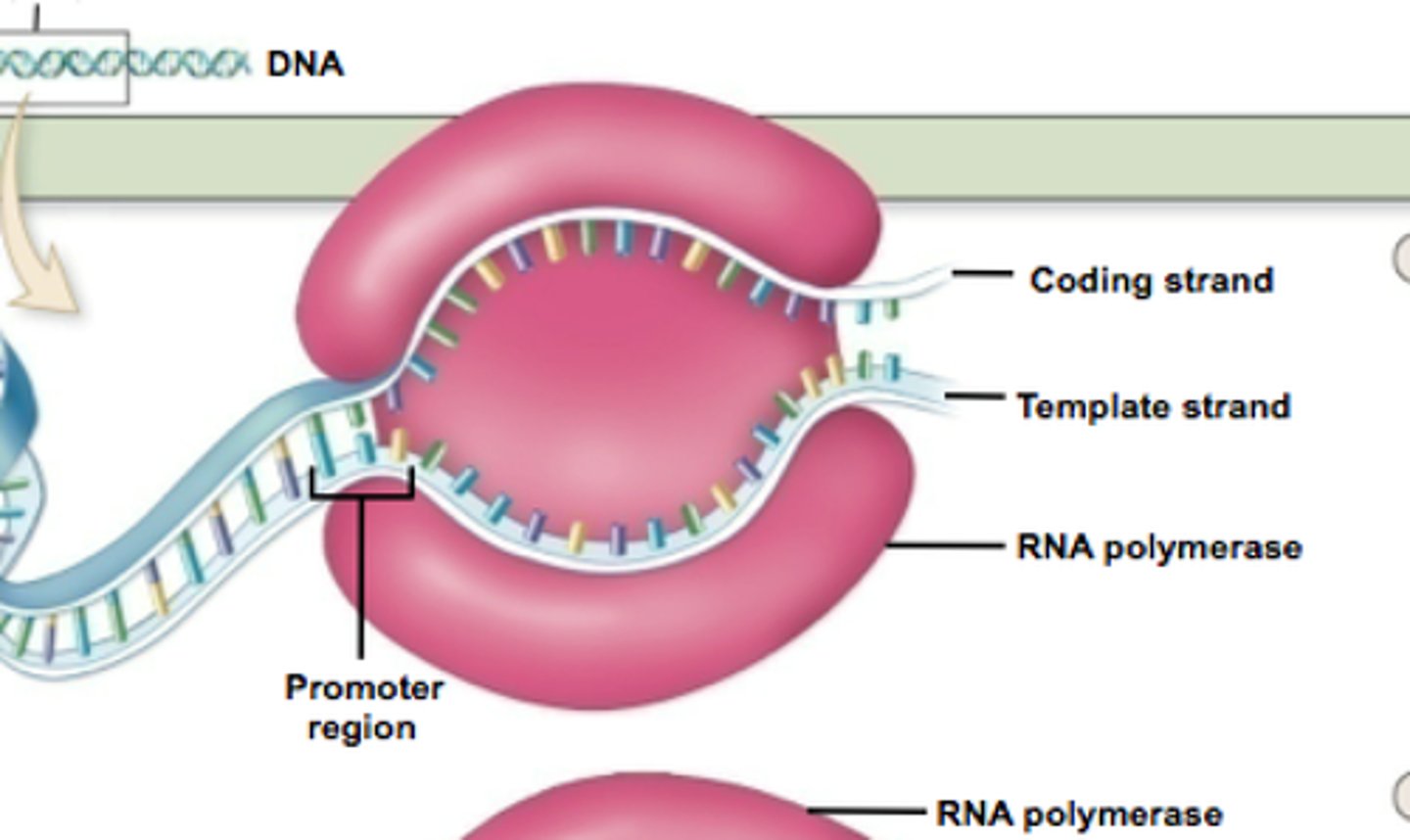
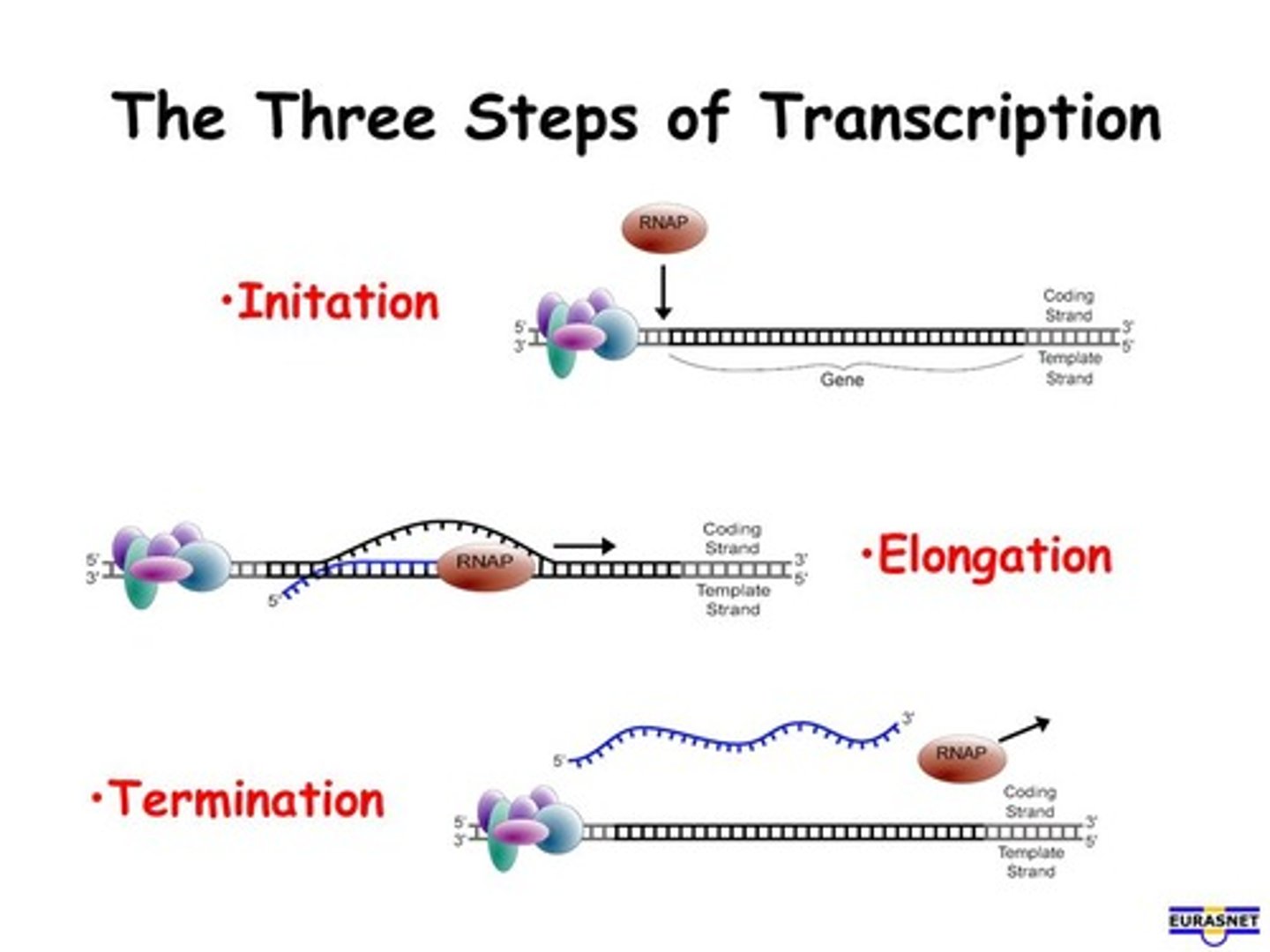
initiation of transcription
RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter region on the DNA and begins to unzip the DNA into two strands.
elongation (transcription)
RNA polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the DNA template to create a mRNA copy
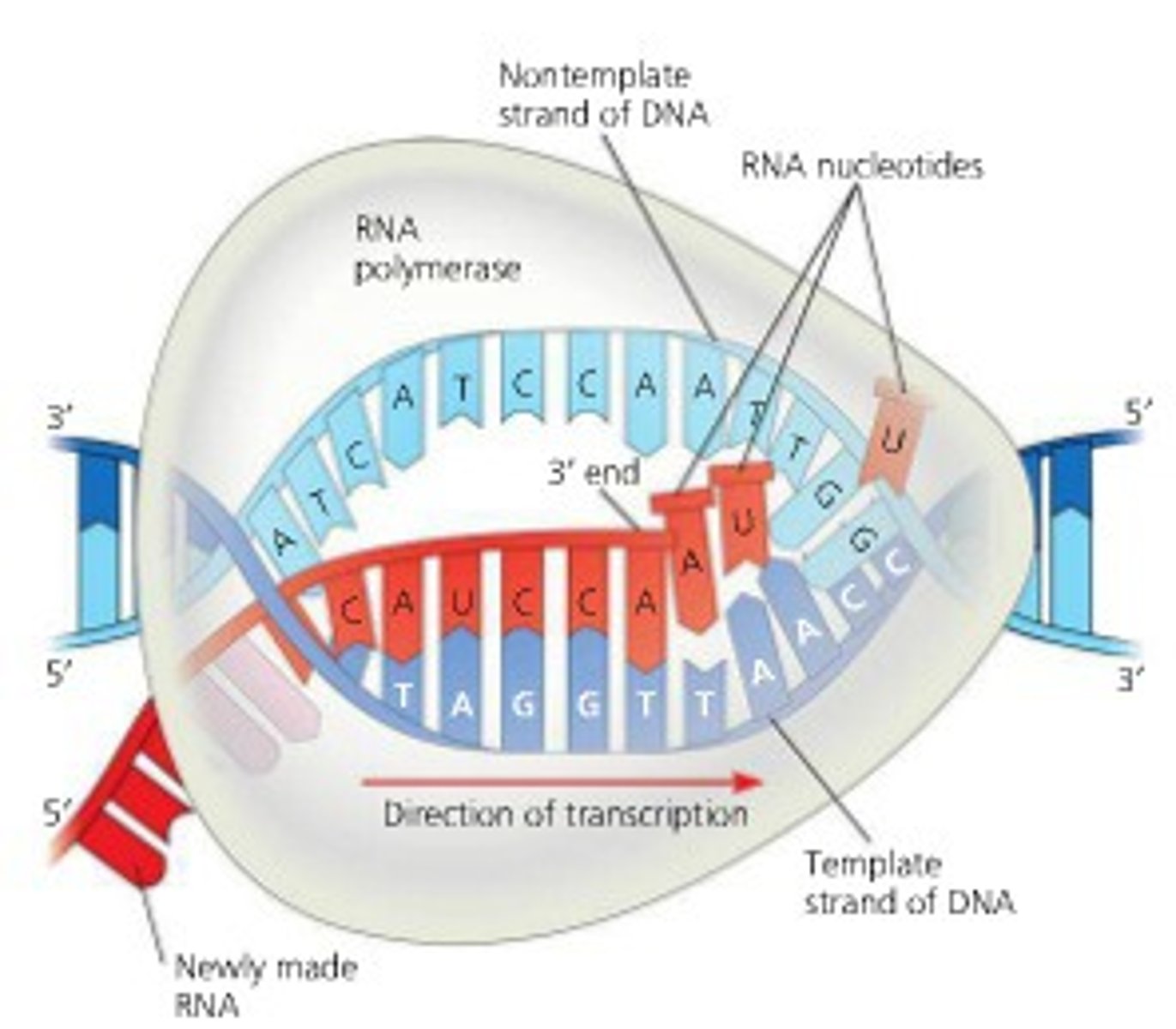
termination of transcription
The third, and last, phase of transcription in which the mRNA transcript is released when RNA polymerase reaches the terminator sequence
protein synthesis
The creation of a protein from a DNA template. Consists of 2 main steps: Transcription & Translation
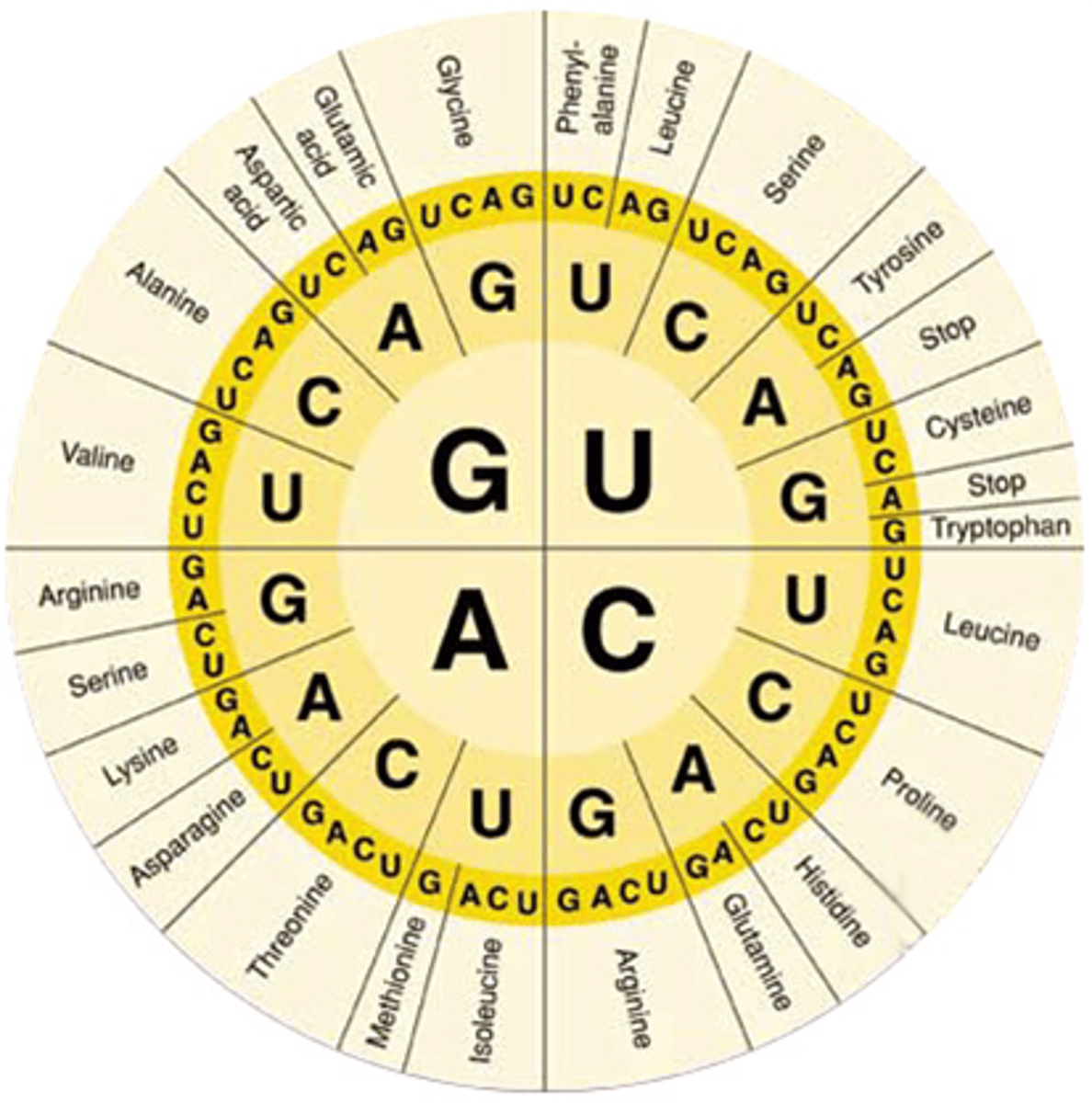
codon wheel
shows which codons correspond with each amino acid
start codon
codon that signals to ribosomes to begin translation; codes for the first amino acid (met) in a protein

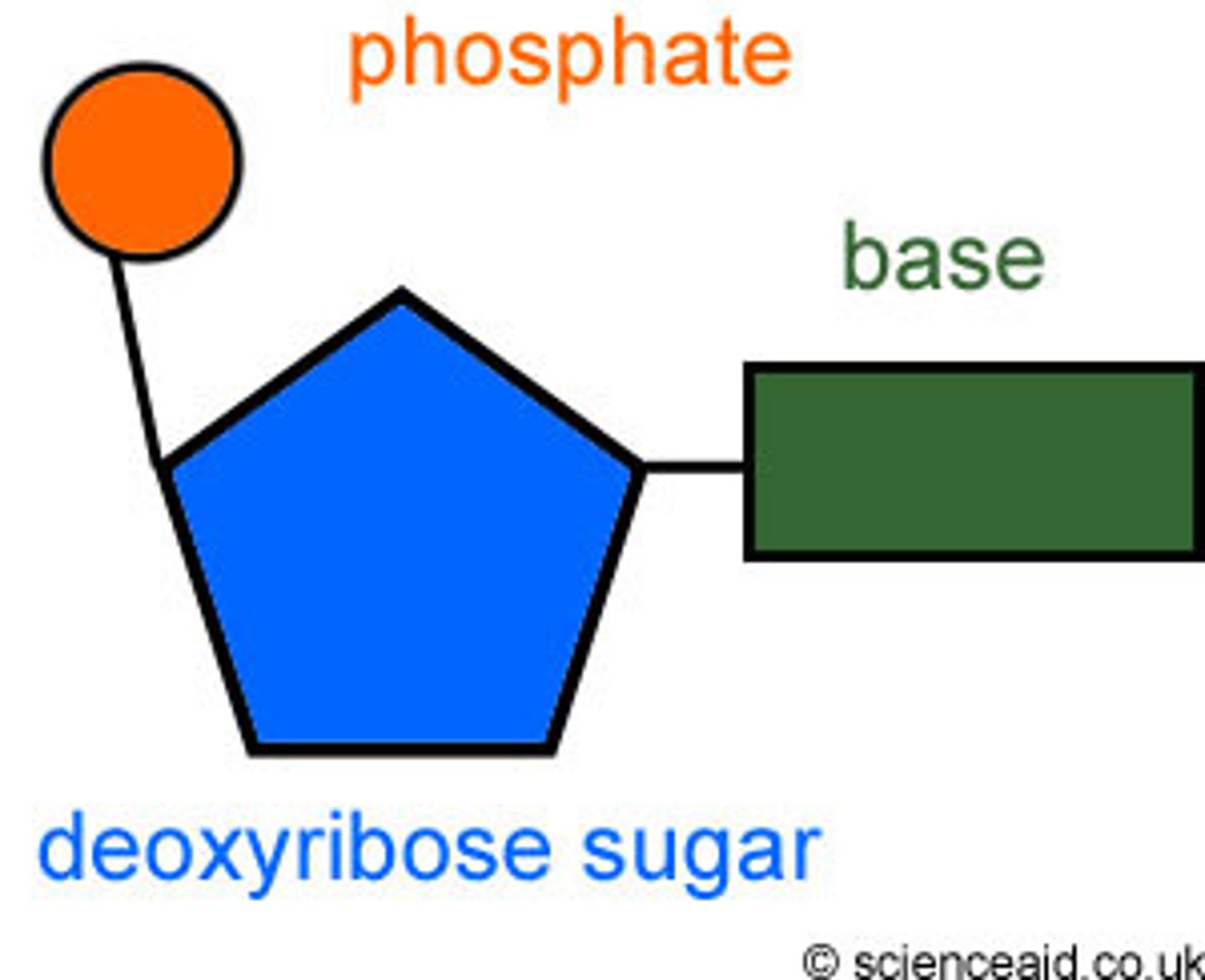
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA and RNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar bonded to a nitrogen base and a phosphate group.
Keratin
hard protein material found in the epidermis, hair, and nails
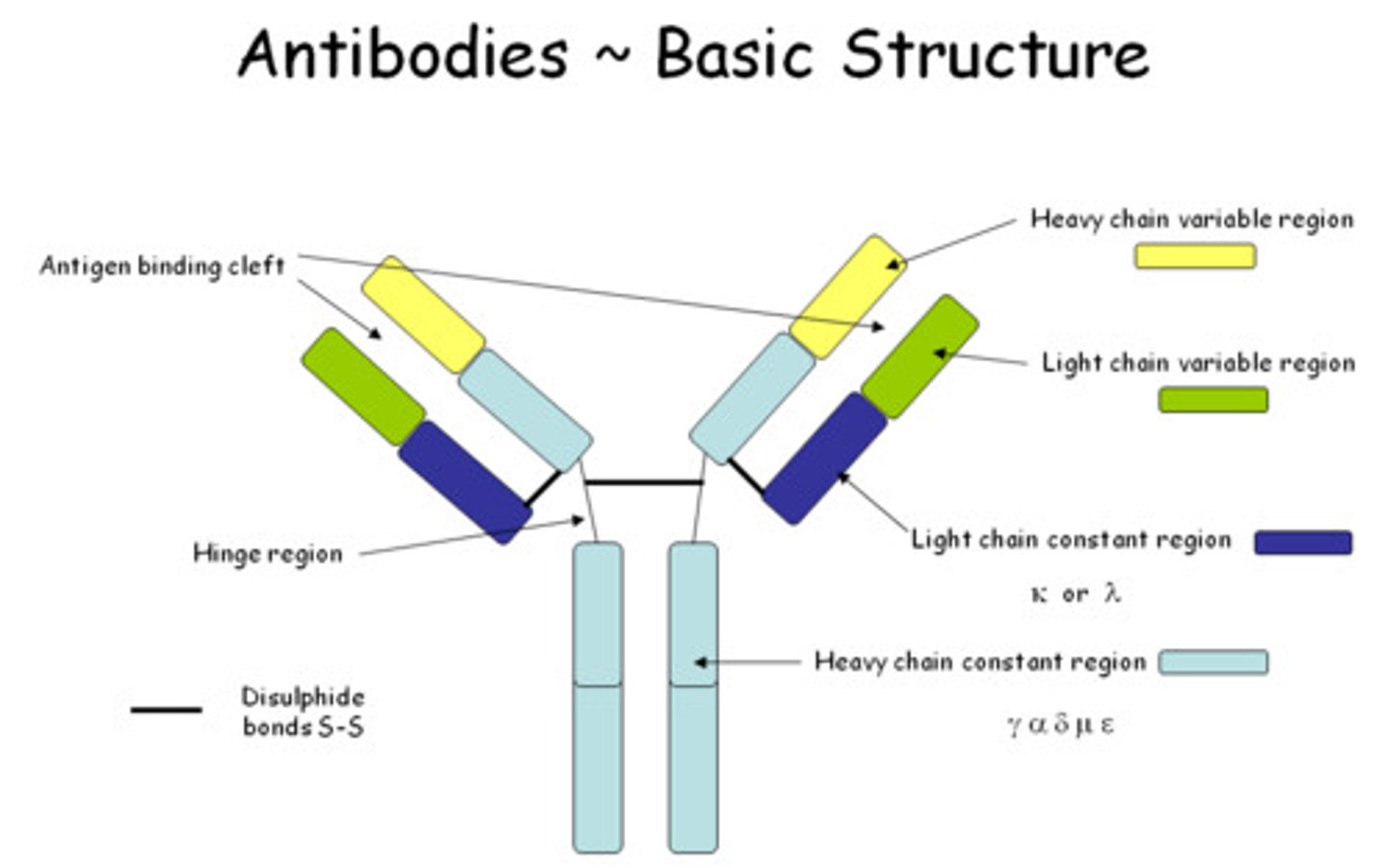
Antibodies
Specialized proteins that aid in destroying infectious agents/pathogens
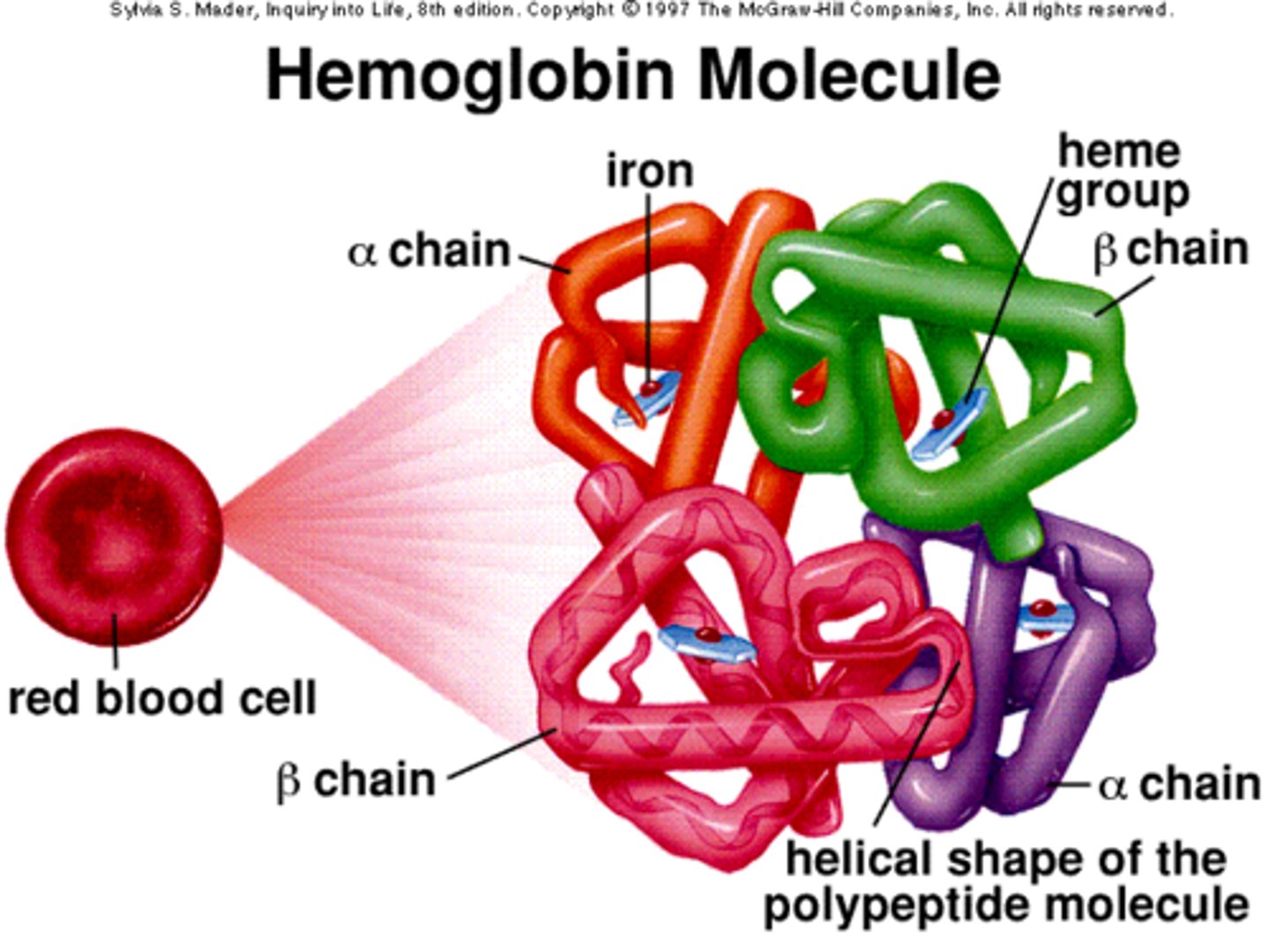
Hemoglobin
iron-containing protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen for delivery to cells
Insulin
A protein hormone synthesized in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues
Melanin
a dark brown to black pigment occurring in the hair, skin, and iris of the eye in people and animals. It is responsible for tanning of skin exposed to sunlight.

rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
Intron (honors only)
sequence of DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein
Exon (honors only)
expressed sequence of DNA; codes for a protein
Methionine
The 1st amino acid in proteins. Coded for by the mRNA sequence AUG