Hearing science
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Mass (kg)
Amount of matter that is present
Propagation
the process by which a sound wave, carrying energy, travels through a material medium like a gas, liquid, or solid
Sound Generation
applying energy to cause rapid back-and-forth motion in an object, such as plucking a guitar string or striking a drum
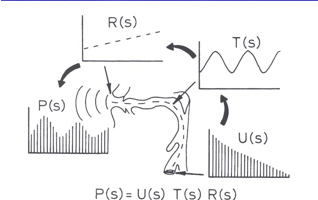
Source Filter Theory for vowel prod
peaks are formants
Source and filtering
–P(f) = U(f) T(f) R(f)
–U(f) and R(f) is considered to be constant
fundamental physical quantities of a wave
mass, time, length
Derived (secondary) physical quantities
Displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, pressure
Vowel sound source
vocal folds and glottis
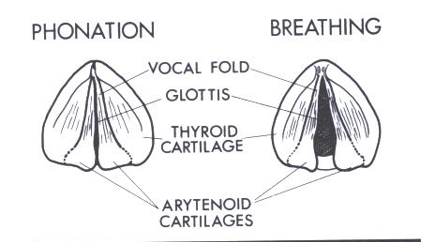
Phonation
Rapid variation of the narrow glottis aperture to produce a pulsing sound source
Phonation mechanism
A series of high-speed
cinematography for one cycle
of glottal action on phonation
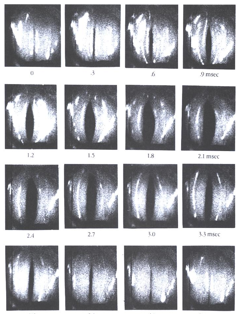
Glottal area/airflow
The waveform of the glottal sound source

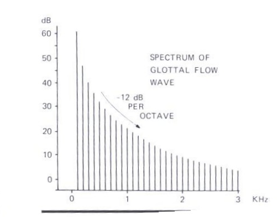
Spectrum
Two characteristics of the glottal ____
–F0 and the harmonics
–The amplitude pattern of the components over frequency: -12 dB/octave
Length (meter)
Distance between two points
Time (t)
Standard unit: second
Displacement (meter)
Change in spatial position
Vector
Direction sensitive (how much + which way) (ex: Force 50N downward)
Scalar
Direction independent (size, amount, value) (ex:temp and speed)
Velocity (v)
The displacement in a unit of time (m/s)
Acceleration (a)
Change in velocity in time (a= v2 - v1/ t)
Force (N)
Push or pull that generates acceleration (F=m x a)
Pressure (p)
The force applied on an area (p= F/Area(m2))
Amplitude/ Magnitude (dB
Maximum displacement (bigger means louder)
Frequency (Hz)
How fast? (Cycles per second) (pitch
To find Frequency
1/T
Pitch
Highness or lowness of sound
Elasticity
Ability for object to return to its original state after being deformed
Angular velocity
object's angular position changes over time (how fast it rotates or revolves
Inertia
Resistance to changes in motion
Sine wave
simplest sound in nature
- d = Amp sin(2 pi f t)
Acoustic parameters of sine wave
amplitude, frequency, phase
Ratio
Ix/Ir (Ix= the target sound intensity, Ir= 10-12 w/m2 reference sound intensity
logarithm
math tool that helps to compress giants numbers to smaller (finding the exponent) 2?=8 = log2 (8)
dB IL
10 Bel = 10 log10 (Ix/Ir)
Bel: to compress a big number into a much smaller number
log10 (Ix/Ir)
millisecond and second
1 sec = 0.001 ms
Sound acoustic energy
1 second/ meter2
Sound Intensity (w/m2 )
amount of sound energy transmitted in one second over and area of m2
Intensity range of Sound
10-12 w/m2 ~ 1 w/m2
dB SPL
deciBel Sound Pressure Level
dB IL
deciBel Intesity Level
I(intensity sound level), p(sound pressure), Z(acoustic impedance)
I=p(2nd power)/Z
Sound Power (watt)
The amount of sound energy that is transmitted in one second
Phase = 0
Starts at 0 moves +
Phase = pie/2
Starts at max displacement on the + side
Phase = 3pie/2
Starts on the max displacement on - side
Phase = pie
Starts at 0 moving -
Scientific motion
change in an object's position over time relative to a frame of reference.
Simple harmonic motion
repetitive, back-and-forth movement where the restoring force (the force that pulls the object back to its center) is always directly proportional to the object's displacement from its equilibrium (or middle) position and always acts in the opposite direction of the
Uniform circular motion
object moving along a circular path at a constant speed
Complex sound
the sound that is composed of two or more than two sine waves
any sound that is not sinusoidal
Source-filter theory of
speech production
Glottal sound source
Filter by the vocal tract
Radiation characteristics of the mouth-opening
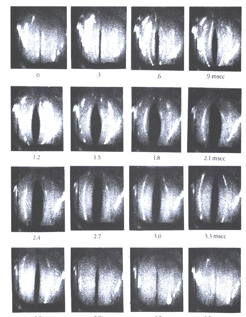
Phonation Mechanism
A series of high-speed
cinematography for one cycle
of glottal action on phonation
The waveform of the glottal sound source
contains:
area
airflow

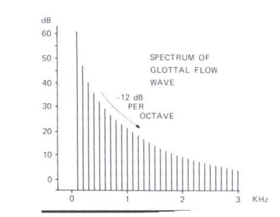
Spectrum
Two characteristics of the glottal ___
F0 and the harmonics
The amplitude pattern of the components over frequency: -12 dB/octave
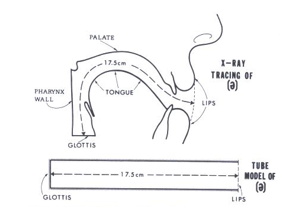
Shaping of the Vocal Tract
Model of the pharyngeal-oral tract
Vowel shaping by the configuration of the pharyngeal-oral tract.
Tube model: resonate the vocal sound
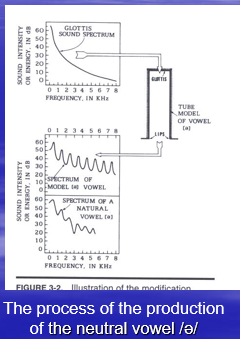
Spectrum of the neutral vowel /ə/
Resonant frequencies
500, 1500, 2500 Hz …
Spectrum Format
Resonance of the vocal tract
- Formant: F1, F2, F3, and F4 …
Location of formant frequency
Length of the vocal tract
Location of the constriction
Degree of the narrowness of the constriction
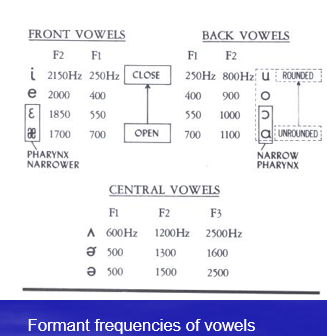
F1 Rule
Pharyngeal Constriction = Longer = lower __
(vertical)
ex: females have higher __ cause their pharyngeal constriction is shorter
F2 Rule
Oral Cavity smaller = Higher ___ freq
(horizontal)
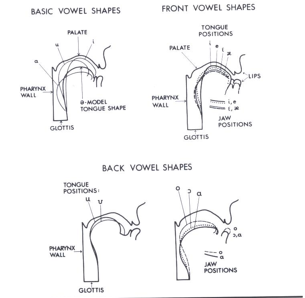
Lip Rounding rule
Used for back vowel
Radiation Characteristic
The additional filtering effect when the speech sound is radiated beyond the month into the atmosphere.
High-pass filter: +6 dB/Oct
(U)s
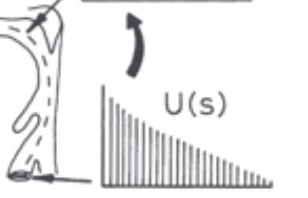
glottal sound
(T)s
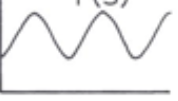
(P)s
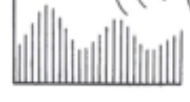
Vertical lines: harmonics
has 3 Resonant peaks
(R)s

Vowel Formants
Includes: (constrictions) Front, Back, and Central Vowels: shorter = higher F2, longer pharyngeal = lower F2
Talker difference
Adults – children, male – female
Phonetic context difference
different adjacent consonants or vowels
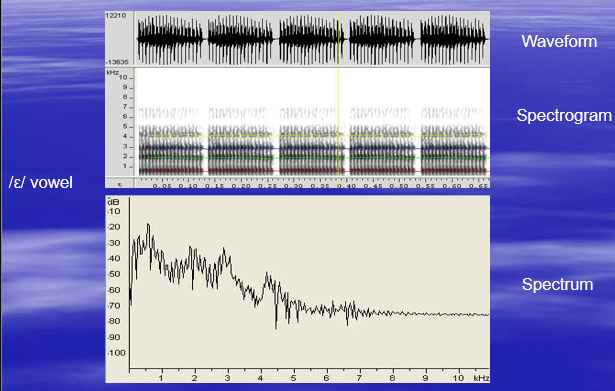
Acoustic Analysis of Speech
Spectral information
Spectrum
Spectrogram
F0
F0 and f0 contour
Amplitude
Speech intensity and intensity contour
Duration
Misperception
taking past information of formants to fill in blanks of sound they think/ or didnt hear
ex: hearing loss, foreign language