Gene Linkage and Gene Mapping
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is chiasma?
Site of crossover
What is crossing over?
Reciprocal exchange of homologous chromatid segments
What does crossing over result into?
Recombinant chromosomes
How could a cross over not alter chromosome arrangement?
Crossover which occur outside the region between 2 genes will not alter their arrangement
What are homologous chromosomes?
Paired chromosomes that carry the same genes but different alleles of those genes
1 member of each homologous pair comes from mom and the other from dad
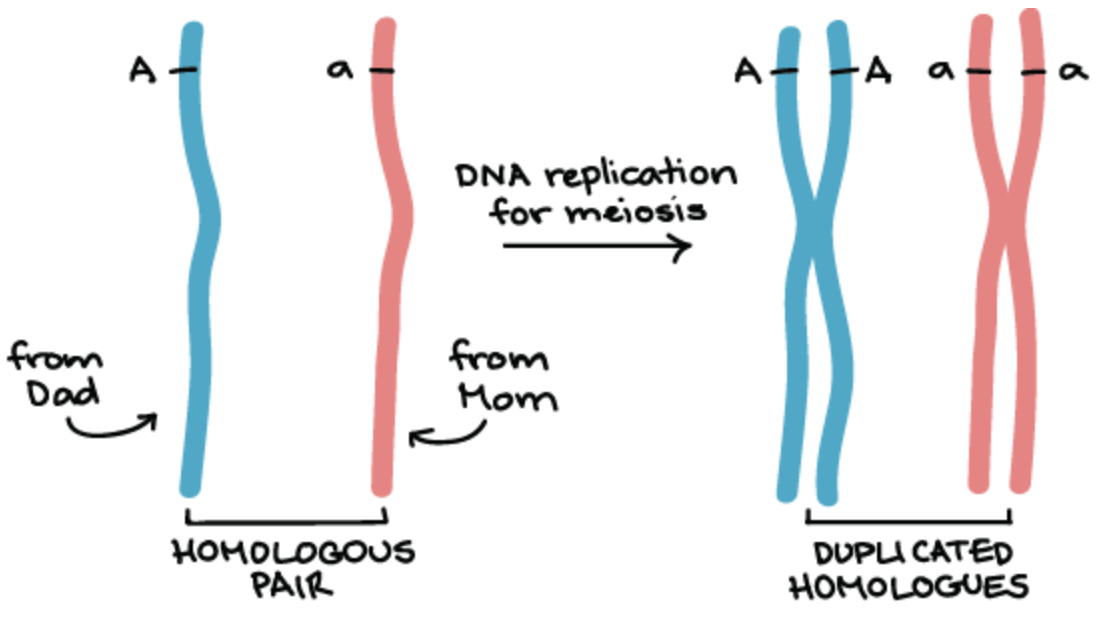
What are linked genes?
Genes that are close together on the same chromosome
How are linked genes inherited?
Inherited as a unit together
Therefore, what is genetic linkage?
Refers to the tendency of genes that are located close together on the same chromosome to be inherited together more often than would be expected
So how can we see if 2 genes are linked and how tightly?
By using data from genetic crosses to calculate recombination frequency
What are unlinked genes?
Genes that are on different chromosomes (non-homologous chromosomes) OR far apart on the same chromosome
Therefore how are unlinked genes organized?
They are assorted independently
What does independent assortment mean?
When genes go into gametes, the allele received for one gene doesn’t affect the allele received for the other
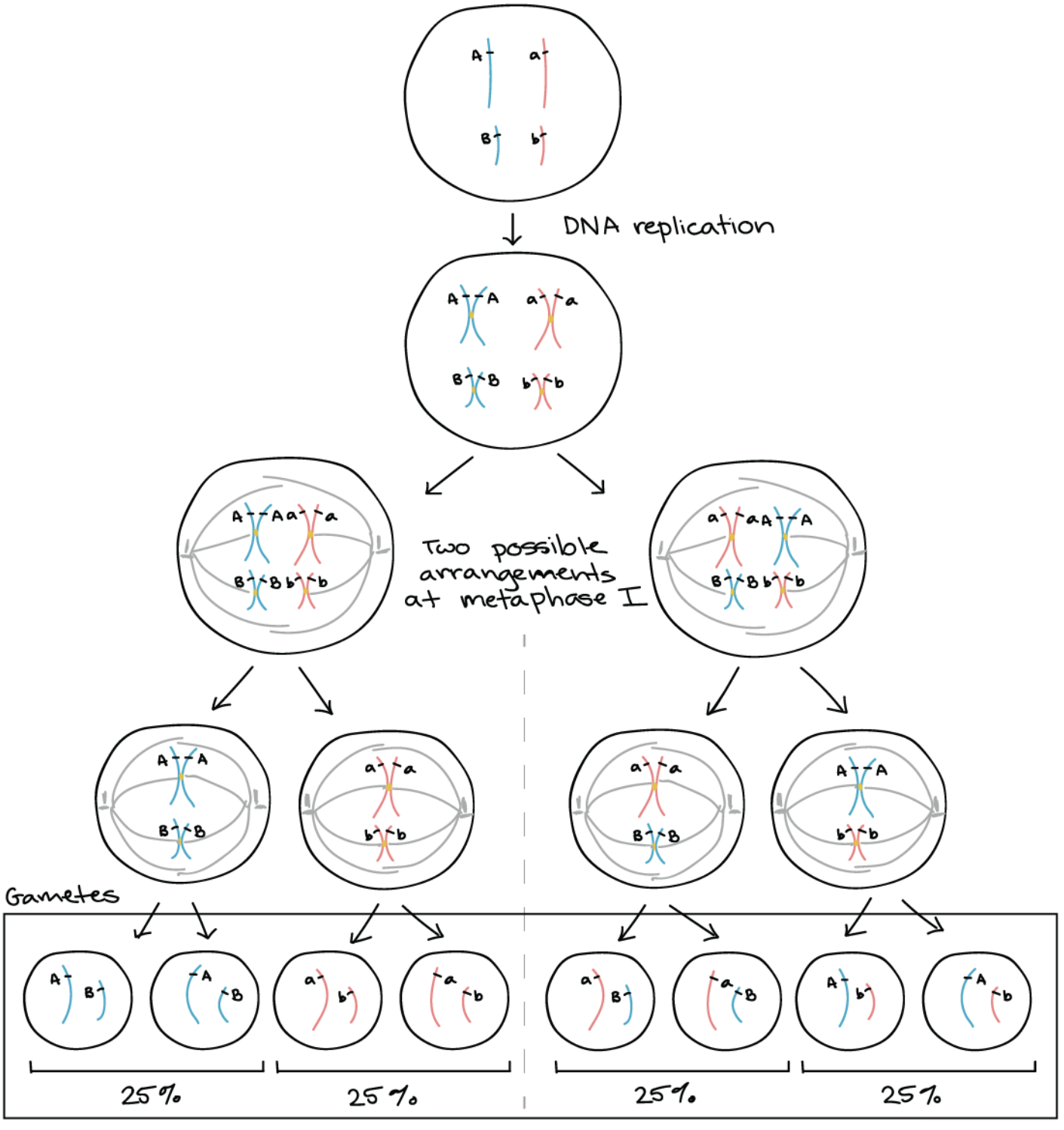
Therefore for double heterozygous (AaBb) regardless on different chromosome or far apart on same chromosome, what is the result of gamete formation? And what is the ratio?
AaBb gamete results in 4 possible types of gametes with equal 25% frequency
Ratio: 1:1:1:1
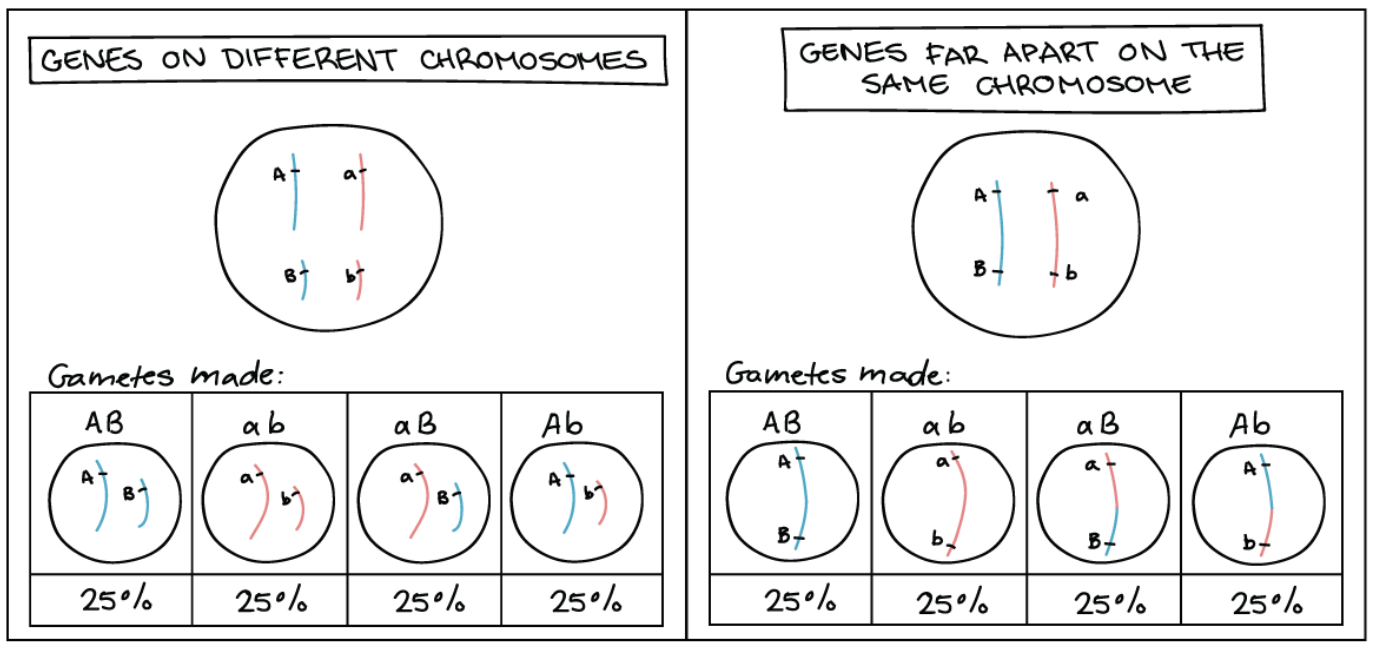
Why do AaBb on SEPARATE CHROMOSOMES results in 4 gametes with equal 25% frequency?
Assort independently
Due to the random orientation of homologous chromosomes pairs during meiosis
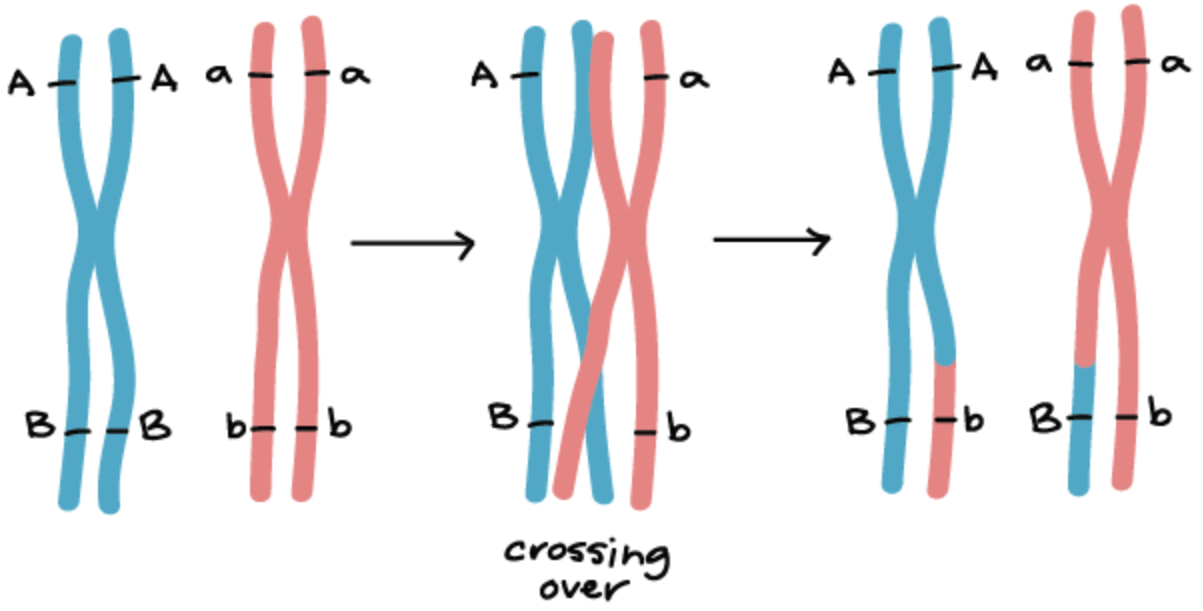
Why do AaBb on SAME CHROMOSOME BUT VERY FAR APART result in 4 gametes with equal 25% frequency
Assort independently
Due to crossing over (homologous recombination)
Resulting in new alleles to be put together in combination on same chromosome
Causing them to go into same gamete
What is another way to represent the gamete percentage in unlinked genes?
50% show similar phenotype of parent
50% show recombinant phenotype
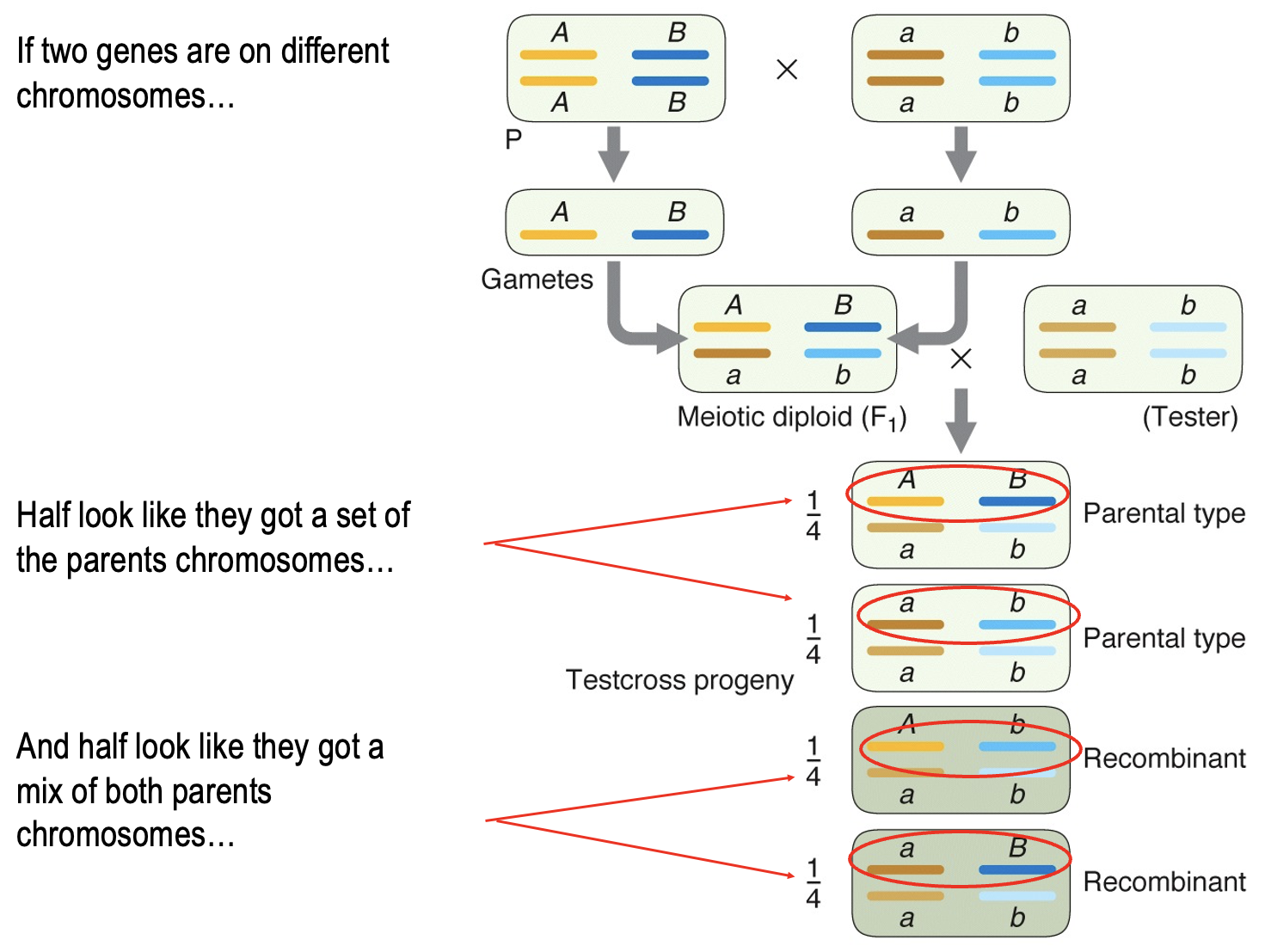
What does recombinant mena?
The production of new combinations of alleles at 2 or more loci
Mix of both parents chromosome
What would the result be for crossing over that occurs in genes that are very close together on same chromosome?
Gamete types produced is different compared to unlinked chromosomes
DO NOT assort independently
Instead genes tend to stick together during meiosis
Causing it to be passed as a unit to gametes
Ratio of gametes are in unequal proportions
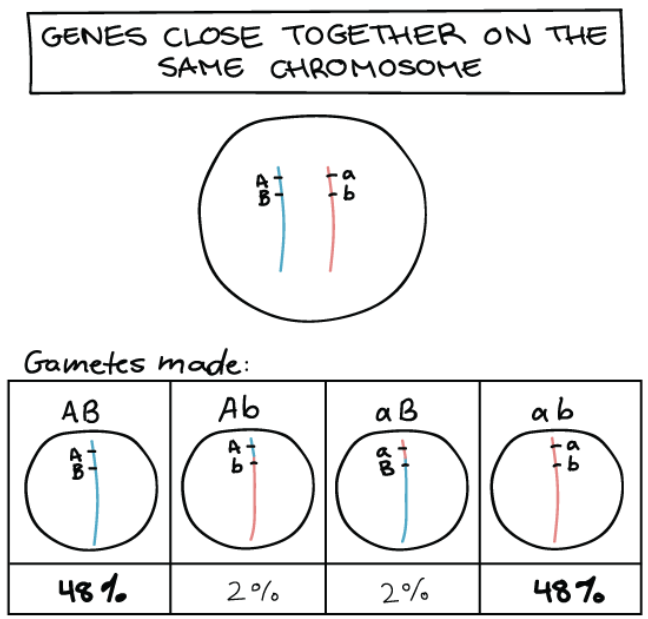
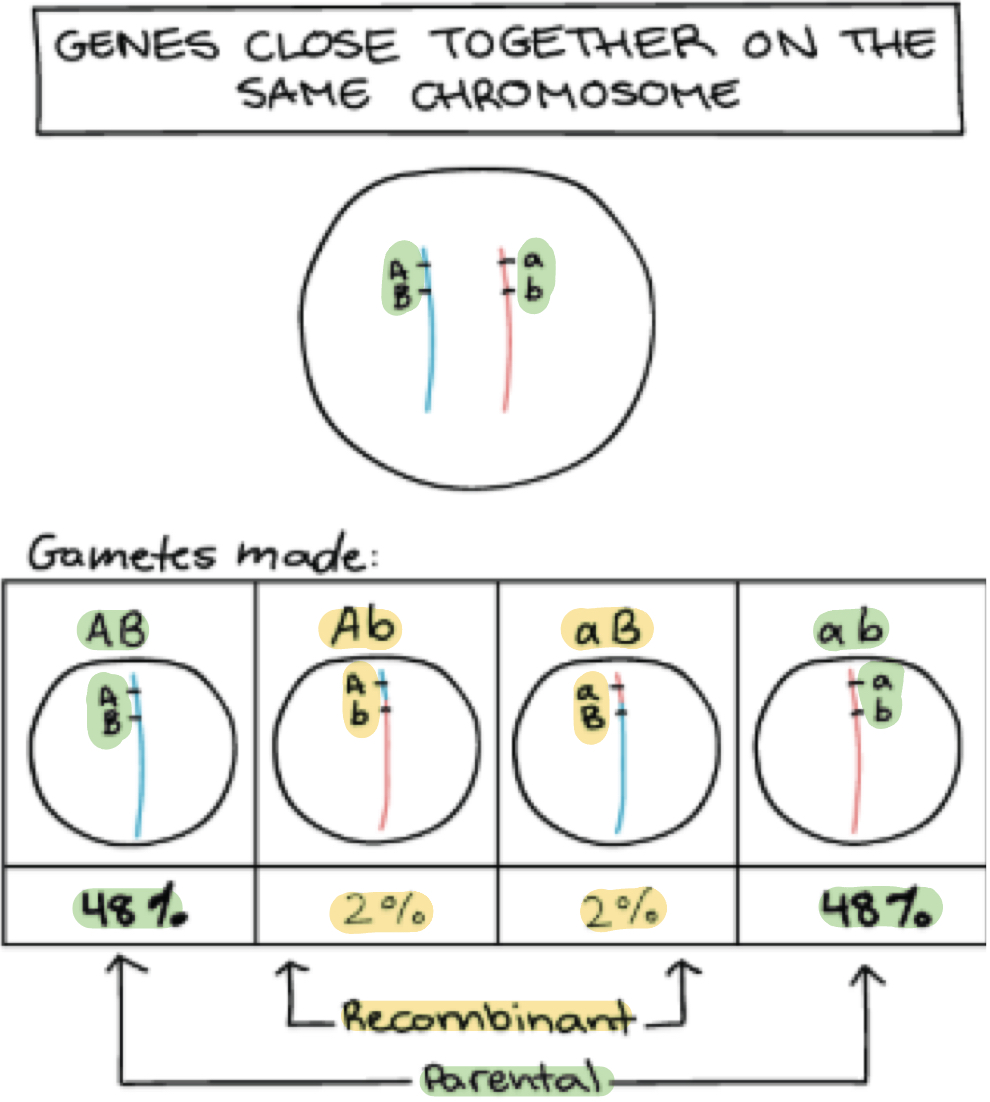
What are the 2 types of configuration does crossing over in linked chromosomes cause?
Parental configuration of alleles
Recombinant configuration of alleles
Therefore not what Mendel’s law predicted
Why did Mendel not discover linked and unlinked genes?
Because he only studied R (round vs wrinkled) and Gp (green vs yellow) genes which are both on chromosome V BUT are so far apart from each other
Thus, they segregate independently and there’s 1 cross over that occurs
Give an example of pea genes that are linked (Mendel didn’t cross this)
Le (long vs short internode) and V (inflated vs constricted pod) are linked because =
Both are on chromosome III
They are close together
Very few crossover occurs
Thus, they do not segregate independently
Which type of configuration is rare and when does it form?
Rare: Recombinant configuration of alleles
When: Only form if crossover (recombination event) occurs between genes which rarely happens
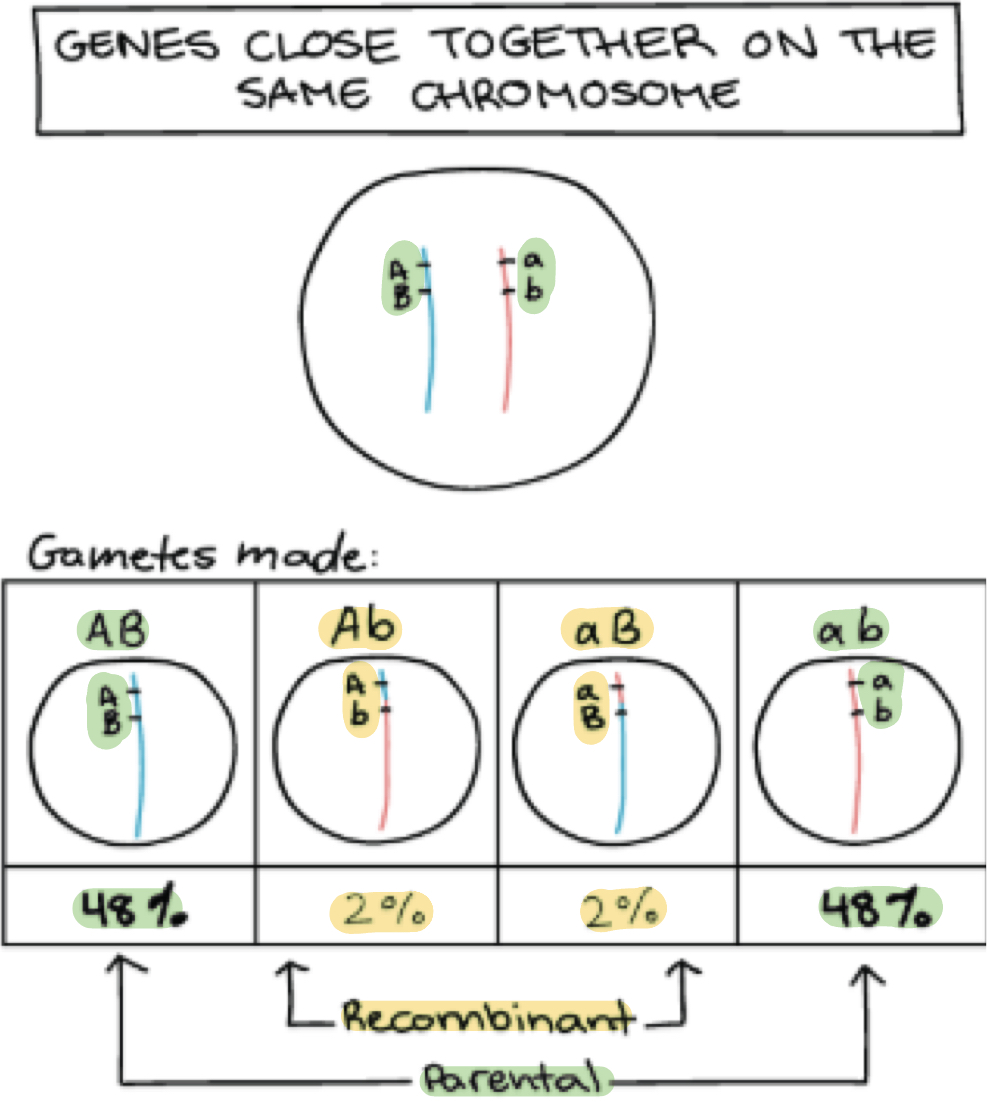
What is parental configuration of alleles?
Alleles that are already together on the chromosome before meiosis
On chromosome it got from parents
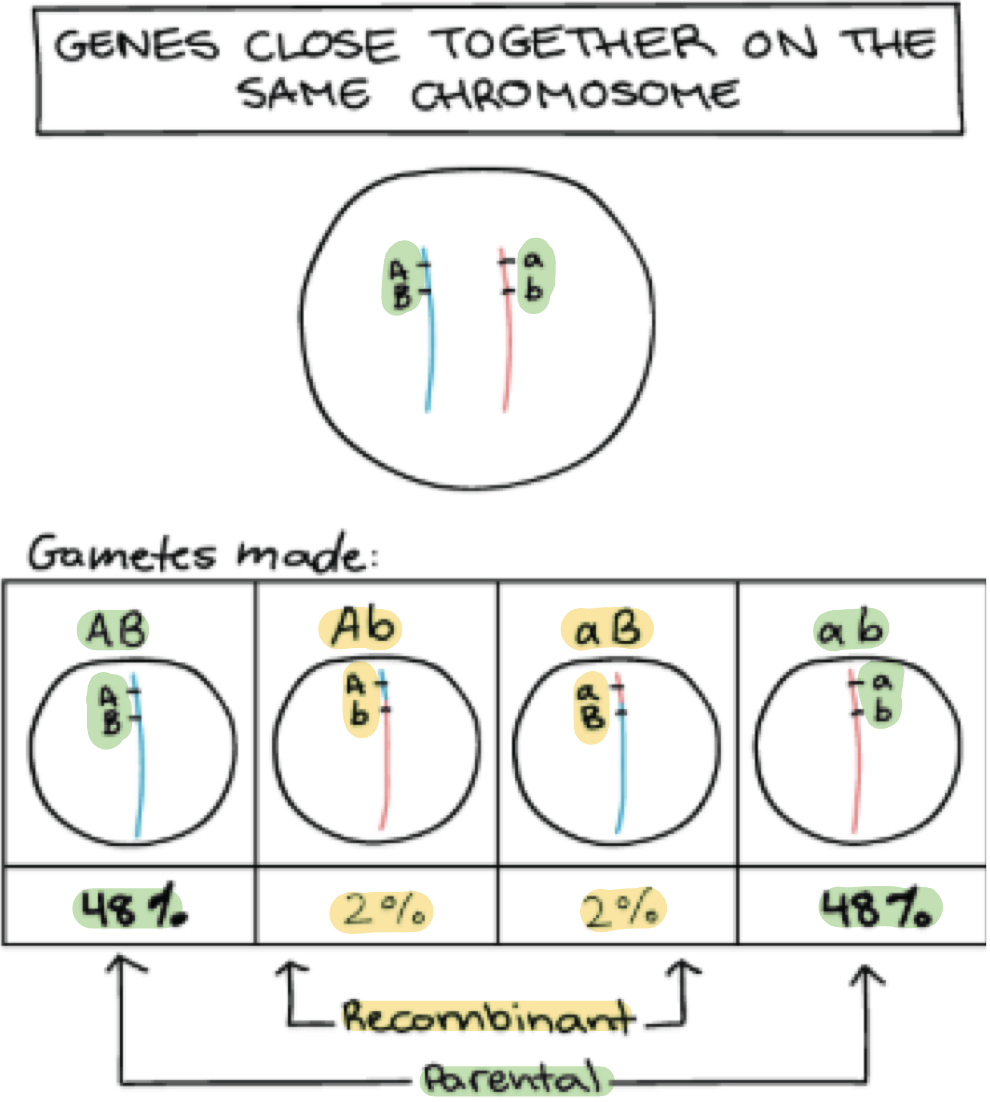
Therefore how does this relate to recombination frequency?
What is it?
The frequency of recombination events between 2 genes is used to estimate their relative distance apart on chromosome
Close-together genes = few recombination events
Slightly further apart genes = more recombination events (less tightly linked)
Example of how to find recombination frequency
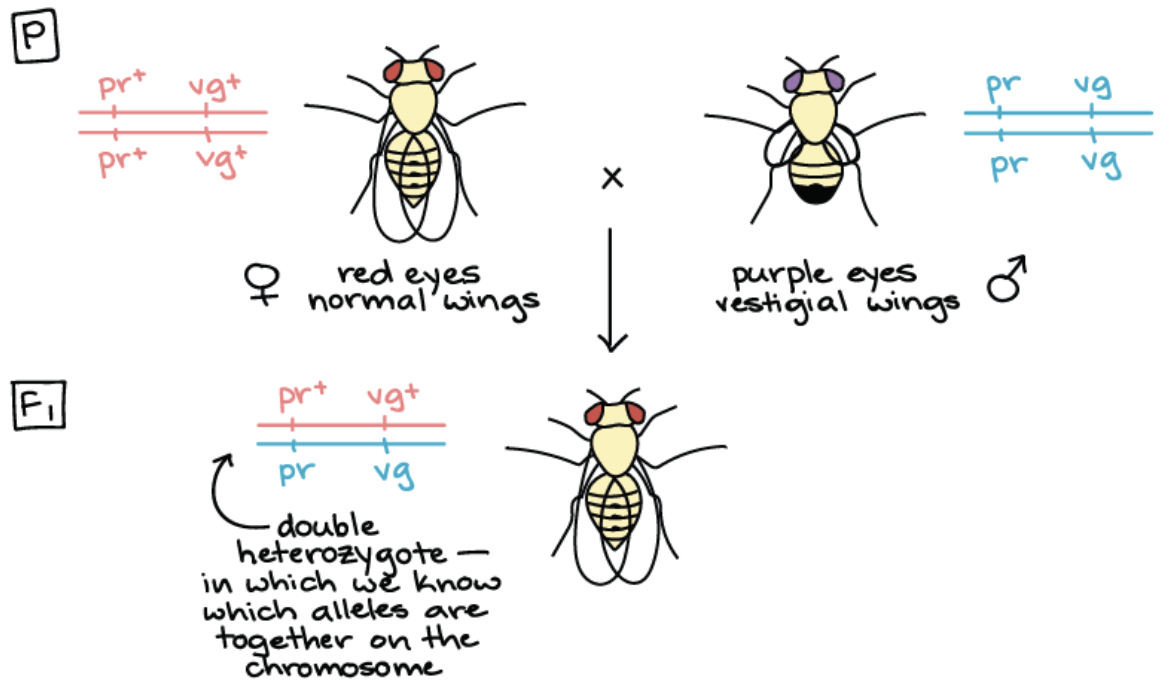
We want to see if 2 genes in fruit flies are linked and if so, how tightly linked =
Purple gene =
Dominant pr+ allele = Normal red eyes
Recessive pr allele = Purple eyes
Vestigial gene =
Dominant vg+ allele = Normal, long wings
Recessive vg allele = Short “vestigial” wings
Q: What is step 1 and why do we need to do it?
Step 1: Cross 2 homozygous flies together
Why: Produces a double heterozygous
In which we know which alleles are together on the chromosome
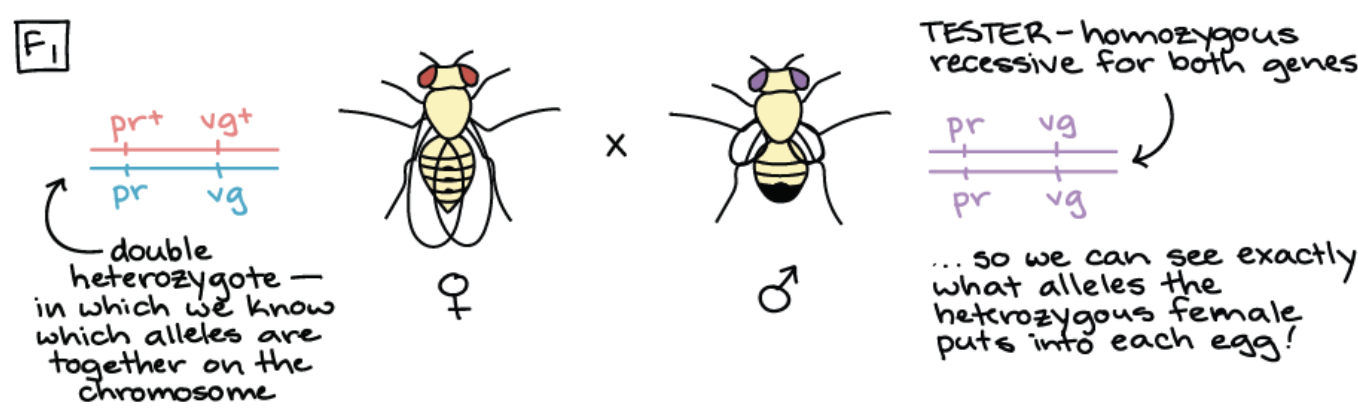
Cont. example of how to find recombination frequency
Step 2: Cross double heterozygous with a tester
Q: Why does this need to occur and what is the tester?
Tester: A fly that is homozygous recessive for all genes
Why this occurs: Tester ensures that alleles from non-tester parent fully determines the phenotype
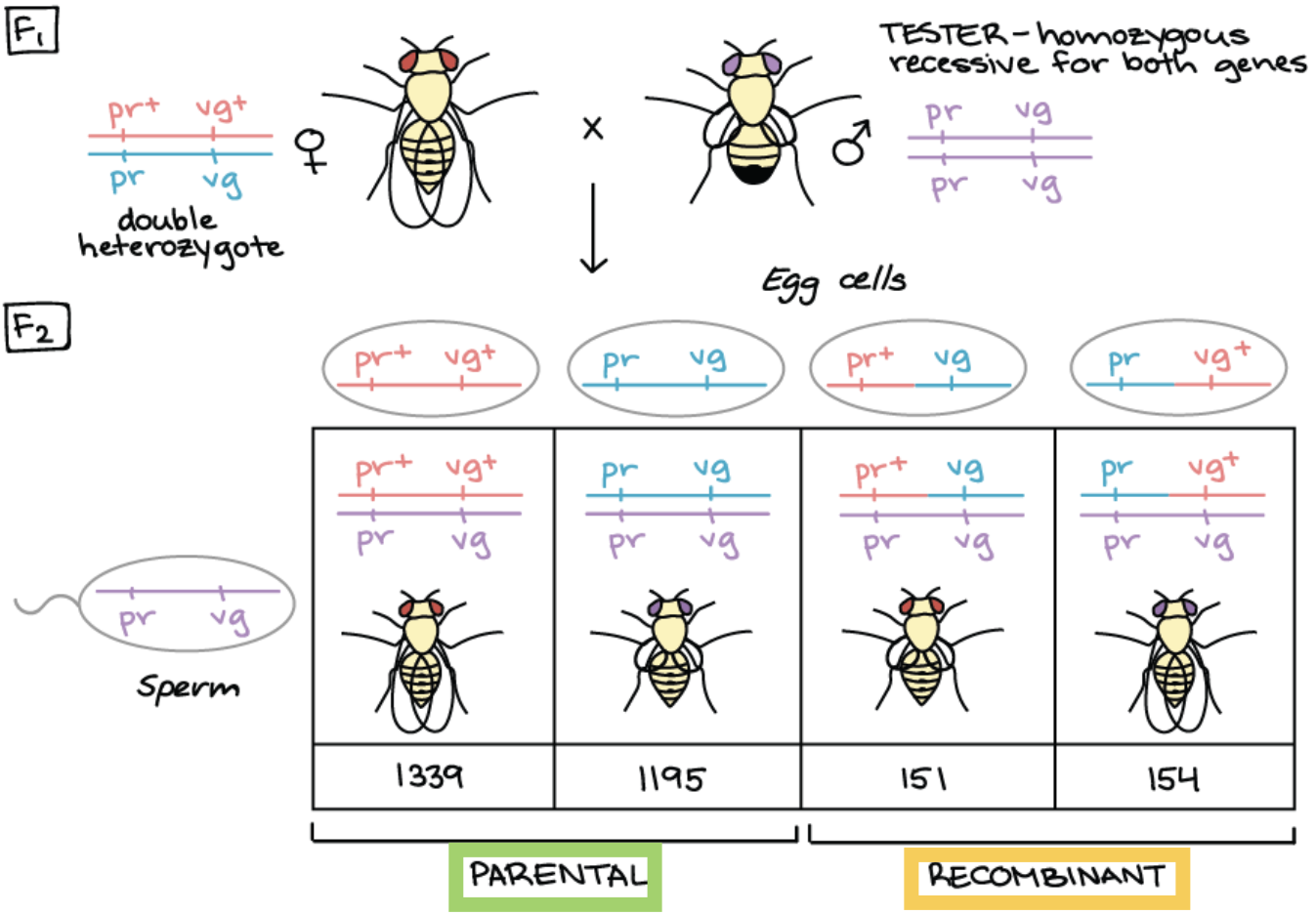
Cont. example of how to find recombination frequency
What is produced when double heterozygous is crossed with tester AND how can we tell that the purple and vestigial genes are linked?
Produced 4 different gametes each with different phenotypes
Genes are linked because: The 4 classes of offspring is not produced in equal numbers
Parental chromosome configurations (pr+ vg+/pr vg AND pr vg/ pr vg) = over-represented
Recombinant chromosome configurations (pr+ vg/pr vg AND pr vg+/pr vg) = under-represented
Why is red-eyed, vestigial-wing files (pr+ vg/pr vg) AND purple-eyed, long winged files (pr vg+/pr vg are recombinant?
2 reasons why:
They inherited a chromosome from their mother that has undergone a recombination event
They are the underrepresented classes
Cont. example of how to find recombination frequency
As a result =
Parental chromosome configuration:
pr+ vg+/pr vg = 1339
pr vg/ pr vg = 1195
Recombinant chromosome configuration:
pr+ vg/pr vg = 151
Red eyed, vestigial winged flies
pr vg+/pr vg = 154
Purple eyed, long winged flies
Q: What is the equation for recombination frequency (RF) and use it to calculate the RF for this case
Equations: Recombinant frequency = Recombinants/Total Offspring x 100%
Calculate: (151 + 154)/(1339 + 1195 + 151 + 154) x 100% = 10.7%
ANOTHER EXAMPLE OF GENETIC LINKAGE: MORGAN’S EXPERIMENT
There is a mutation that makes fly’s eyes white and their wings miniature (recessive) and is found only on X chromosome
Dominant:
(w+) red eye gene
(m+) normal wings gene
Recessive:
(w) white eye gene
(m) miniature wings gene
P generation =
w m/w m
Recessive female with white eyes and miniature wings
w+ m+/Y
Dominant male with red eyes and normal wings
Wild type
Q: What is the F1 generation as a result of the crossing of P generation?
w+ m+/w m
Dominant female with red and normal wings
w m/ Y
Recessive male with white and miniature wings
Hemizygous recessive (only has one member of chromosome pair)
CONT. MORGAN’S EXPERIMENT
F2 generation
What are the genotypes
Which are parental and recombinant
So are genes linked or unlinked
Genotype:
w m/w m
w+ m+/Y
w m+/w m+
w+ m/Y
Parental:
w m/w m
w+ m+
Recombinant: Occurred about only 37% (below 50%)
w m+/w m+
w+ m
Genes are: Linked
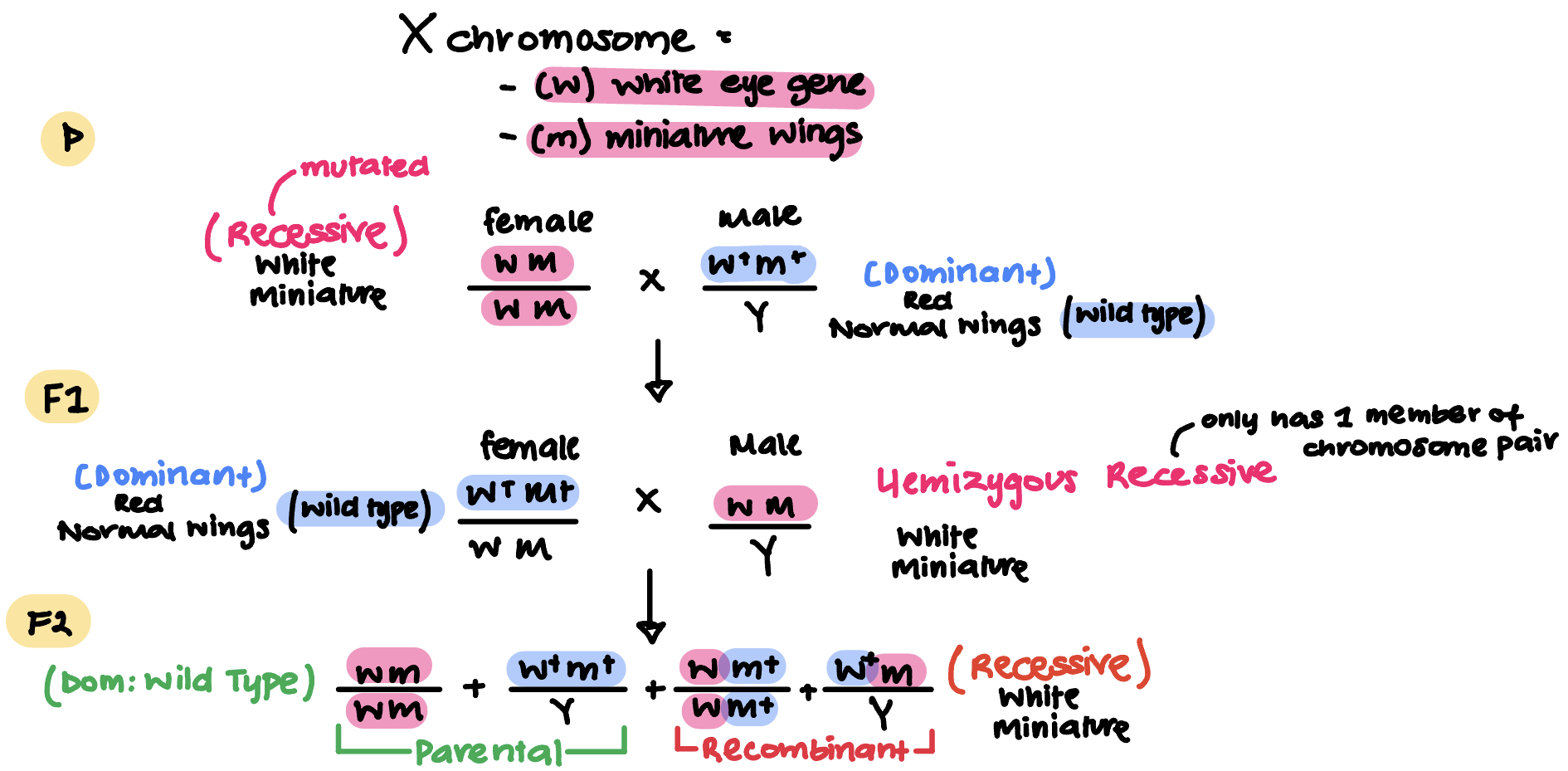
Therefore what acts like a test cross to discover whether genes are linked or not?
F1 interbreeding
What type of chromosome configuration would meiosis with NO crossover result to?
All parental chromosome configuration
What type of chromosome configuration would meiosis WITH crossover result to?
Parental and recombinant chromosome configuration
What is the relationship between recombination frequency and distance between genes?
Increasing distances between genes = RF increases
What do linkage (gene) maps determine?
Determines =
Order of genes
Relative distance between genes in map units
What is the mapping function?
Shows the relation between genetic map distance and the frequency of recombination
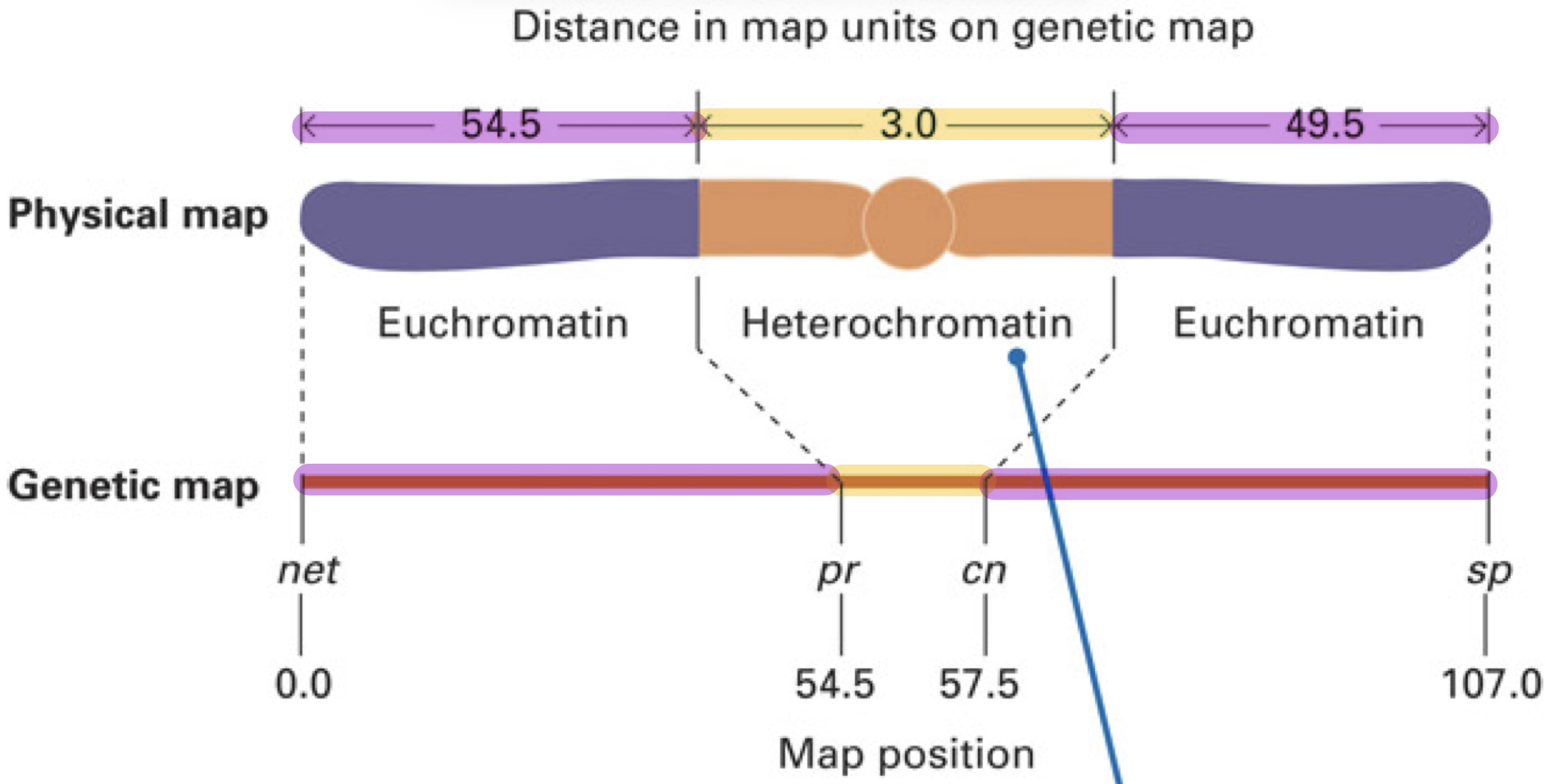
Why is the distances in the physical map and the genetic map different?
Because there are recombination hotspot regions and regions that underestimate the genetic length
BUT THIS DOESN”T MEAN THE PHYSICAL LENGTH OF THE REGION IS ALSO AS LARGE
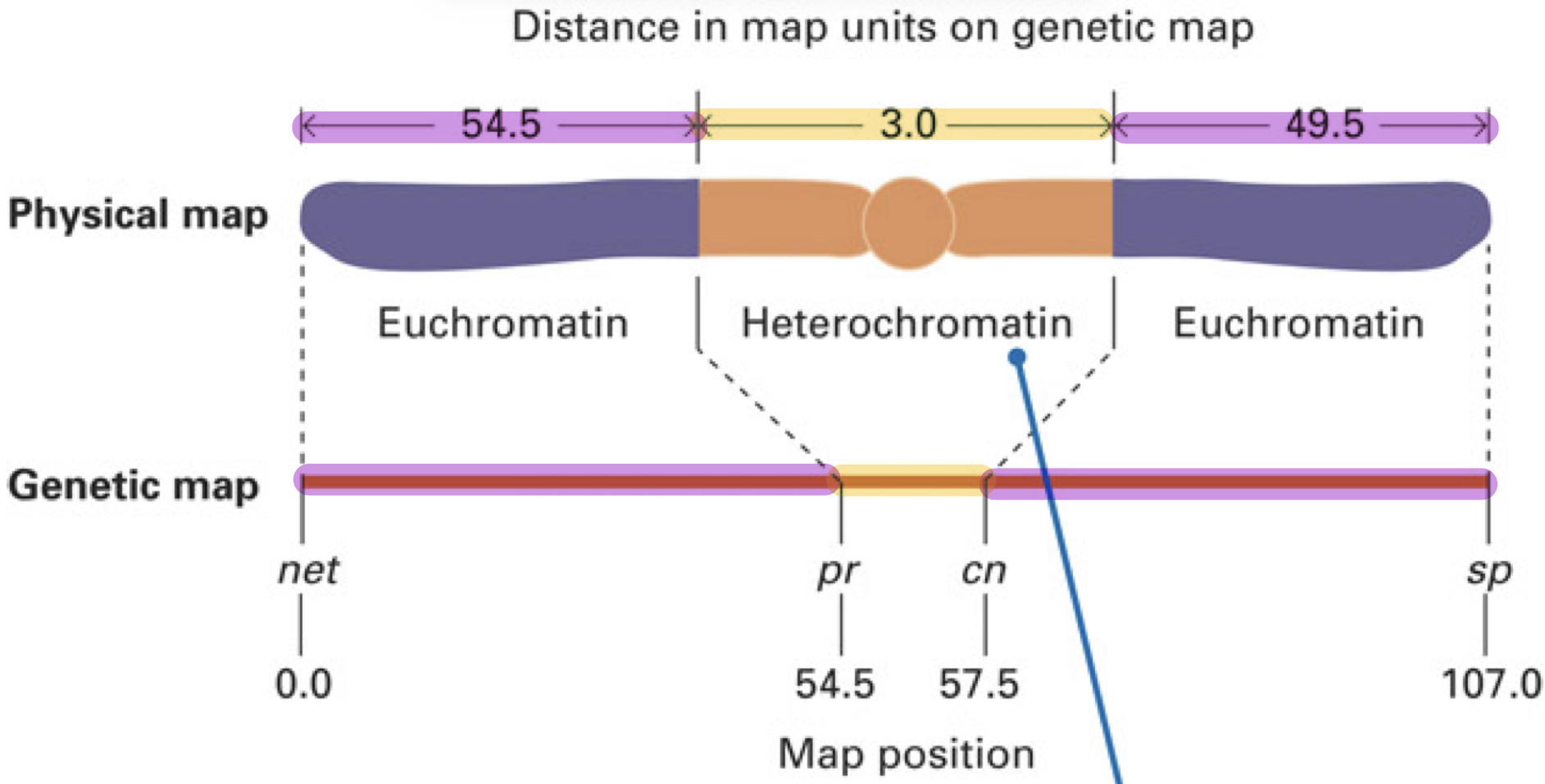
What are recombination hotspot and how does this affect the genetic length?
Because there are recombination hotspots which are regions on a chromosome where the frequency of recombination is higher
Therefore, this region will appear larger on a genetic map since there are more recombination events detected
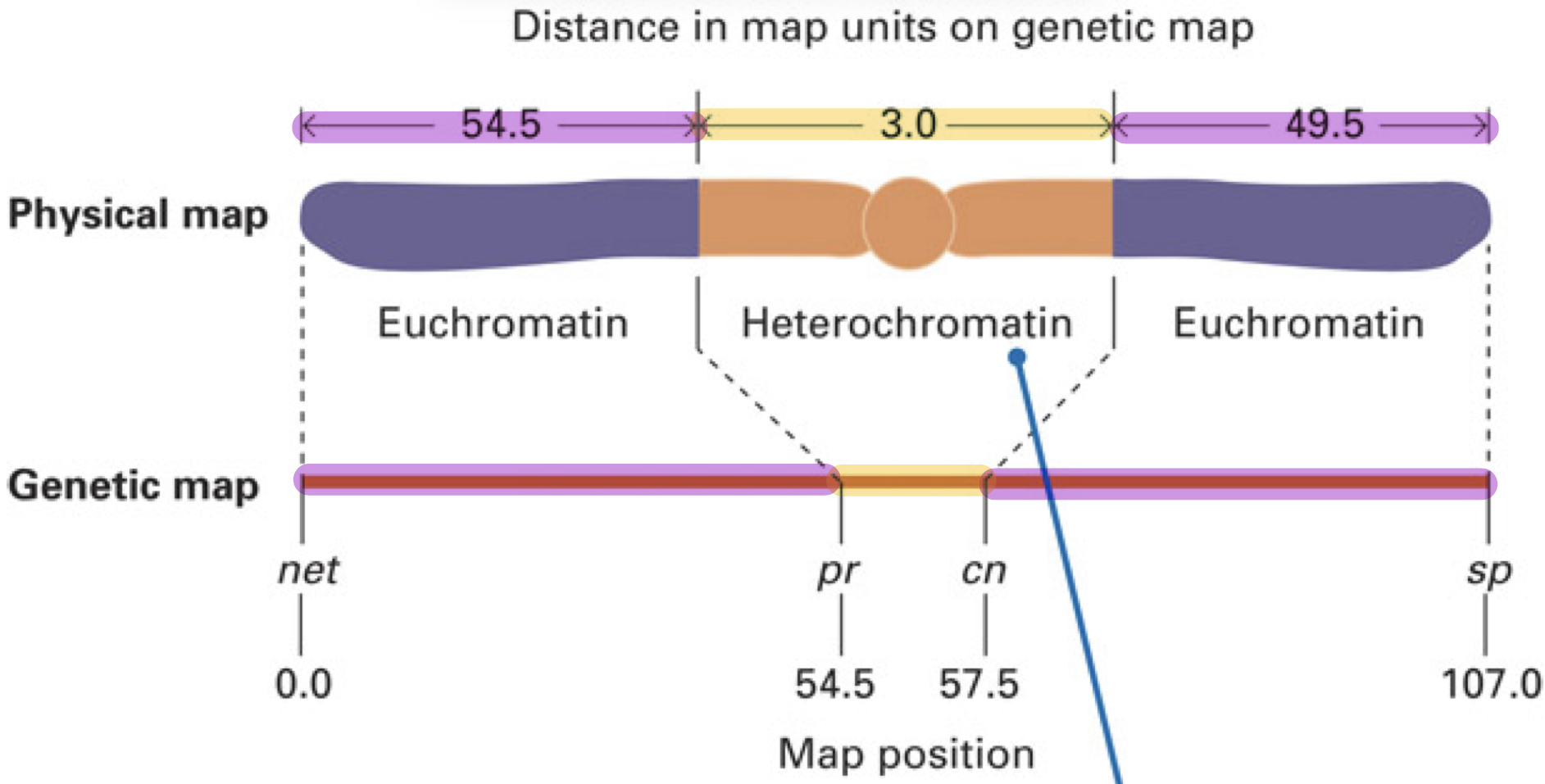
What are the regions that underestimate the actual physical length and how does this affect genetic map?
Regions: Heterochromatin (tightly packed DNA) and centromeres
Result: These regions appear shorter
Why is a linkage map is produced?
Because recombination frequency “maxes out” at 50%
So in order to figure out the map distance between genes further apart than 50%, we need to add up the RF of multiple pairs of genes
This builds a map
Why is the maximum recombination frequency 50%?
Because it corresponds to genes being unlinked or assorted independently
What is the importance of linkage maps?
Establish that chromosomes are linear
Established that each gene has its own specific place on chromosome
What 2 ways can recombination frequency be used to build linkage maps?
Provides an estimate of physical distance of genes:
Larger RF = genes are farther apart
Smaller RF = genes are closer together
Used to figure out order of genes on chromosome
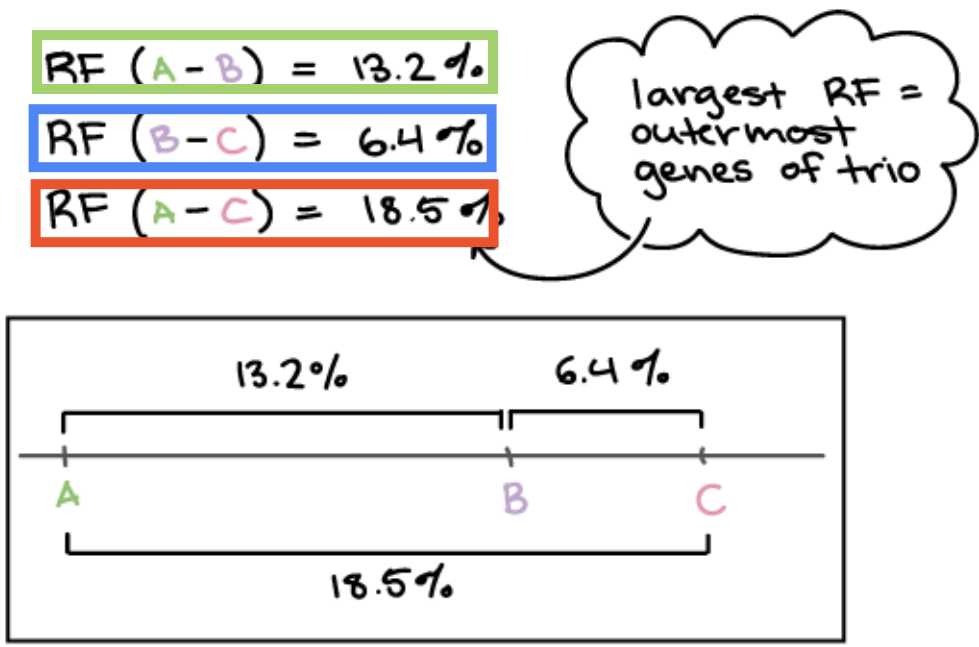
How can recombination frequency be used to figure out order of genes and produce linkage maps? Examples uses 3 genes (A,B,C)
Genes with largest RF = outermost genes
RF (A-C)
Genes with inbetween RF = middle genes
RF (A-B)
Genes with smallest RF = innermost genes
RF (B-C)
How do you get the recombinant frequency for only 2 genes if 3 is present? (used to find the order of genes)
Add the number of recombinants for those genes together then use the normal equation (RF = RECOM/TOTAL OFFSPRING x 100%)
EX: Find the RF for Ab + aB from
AbD = 45
Abd = 89
aBD = 94
aBd = 40
ANS:
(45 + 89) + (94+40) = 268
286/1448 (total) x 100% = 18.5mu
What are the units in linkage maps and how can we convert RF to it?
Units: Centimorgan or map unit
Convert: No need to convert because 1 RF = 1 centimorgan
Why is the direct RF is not the same as the map distance?
Because double crossovers can also occur
BUT they are invisible if only monitoring 2 genes because it would just put them back on original position
Therefore when there is more than 2 genes, double crossovers are detected making the direct RF measurement of 2 genes smaller than the map distance
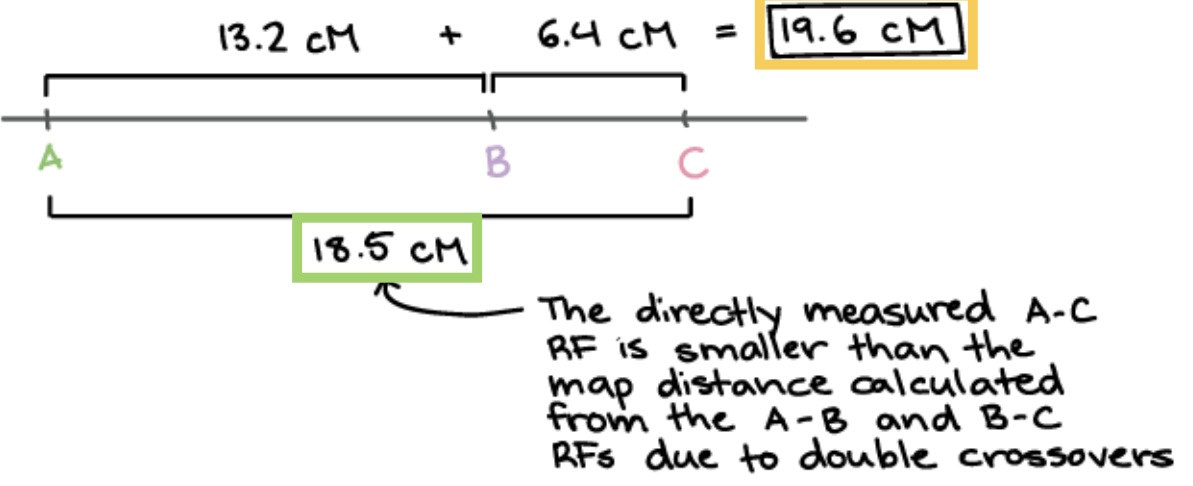
How can we minimize invisible double crossovers to occur?
When RF of closer-together genes pairs are added up because it is more rare
A-B = 18.5mu
B-D = 6.4mu
A-D = 13.2mu
Q: What is the order of genes an why doesn’t 13.2 + 6.4 NOT equal to 18.5
Order: A——D—B
13.2 + 6.4 not equal to 18.5: Because invisible double cross over occurs

What is chromosome interference?
Crossovers in one region decreases the probability of a second crossover close by
What is coefficient of coincidence?
Observed number of double recombinants divided by the expected number
Calculate the coefficient of confidence for the below when observed is only 8 double recombinants:
B-D = 0.064
A-D = 0.132
Expected:
0.132 × 0.064 = 0.008
For every 1448 (total) progeny: (1448 × 0.008) = 12.23 double recombinants
Coefficient of coincidence: Observed / Expected
8/12.23 = 0.65
How to calculate the interference with the coefficient of coincidence
Equation: Interference = 1 - Coefficient of coincidence
Example: 1 - 0.65 = 0.35
What 3 processes lead to the most genetic variation?
Independent assortment
Crossing over
Random fertilization
When does crossing over occurs?
Prophase 1 in meiosis
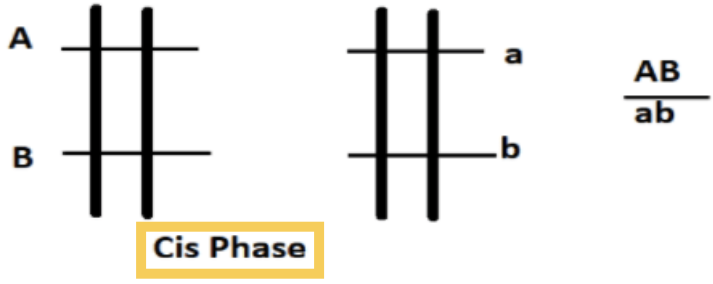
In a heterozygous with 2 loci, there are 2 arrangements of alleles. What are they?
Cis (coupling) arrangement
Trans (repulsion) arrangement
What is the cis arrangement (coupling) of alleles?
Has both wild type alleles on one homologous chromosome
And both mutants on the other
EX: AB and ab
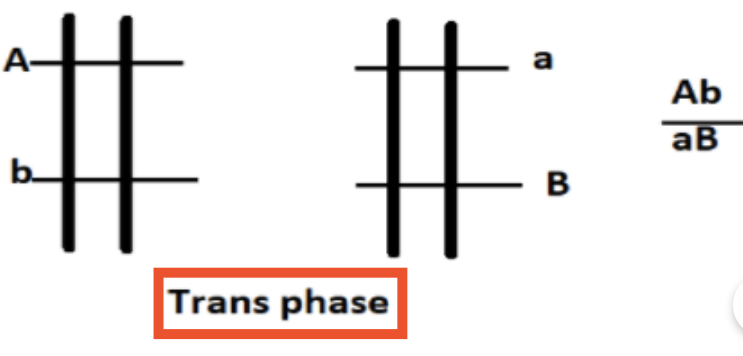
What is the trans arrangement (repulsion) of alleles?
Has one mutant and one wild-type on EACH chromosome
EX: Ab and Ba
What would each cross over result in?
Crossover between homologs in cis arrangement
Crossover between homologs in trans arrangement
Crossover cis arrangement: Results in homologous pair with trans arrangement
Crossover trans arrangement: Results in homologous pair with cis arrangement
What would be the recombination frequency for linked genes?
RF that is less than 50%
So if the recombination frequency is more than 50%?
Then the genes are unlinked
When does recombination (crossing over) take place?
Prophase of meiosis 1 = high frequency
Interphase of mitosis = low frequency