Reliability
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What does “reliability” mean outside of psychometrics?
Consistent, dependable, repeatable
How are reliability and repeatable related?
They are independent concepts; just because something is reliable does not ensure it is valid
What is the key question of reliability?
To what extent can we expect an individual to obtain the same score if we repeat the same measurement process?
How do we get the “true” measurement from multiple measurements on a scale?
Assuming that measurement errors are random, they will cancel each other out. Averaging the repeated measurements = estimate of true score
What are the two things you want when calculating reliability?
Some estimate of the true score and some estimate of the variability of observed scores around the true score (estimate of precision—typically a standard deviation)
How can physical measurements be repeated?
Numerous times, with numerous measuring instruments, without changing either the object being measured or the properties of the object
How does psychological measurement differ from physical measurement?
Psychological measurements cannot be easily repeated numerous times or with numerous measuring instruments without changing the object being measured
What are some sources of error in psychological measurement?
Individual sources (fatigue, illness, motivation, fluctuation over time in trait being measured)
External sources (testing situation, administration errors, scoring errors, content of test items)
What is test-retest reliability?
Administer the same test at two different time points to determine reliability; correlation between two sets of scores estimates reliability of that scores
What are some problems with test-retest reliability?
Motivation (might not want to retake; lowers reliability), memory (might recall how answered before; increases), learning (increase or decrease), people might change as result of measuring process, and trait might be changing over time and incorrectly viewed as a measurement error
Why do we need reliability theory?
Cannot measure people a number of times and take an average of their scores (test-retest problematic would be even worse with multiple replications), and cannot measure people with a number of instruments measuring the same construct (might not be a sufficient number for a trait)
What is the revolution of reliability theory?
Classical True-and-Error Score Theory
Infinite Parallel Tests Theory
Domain Sampling Theory
Generalizability Theory
What are the assumptions of classical true-and-error score reliability theory?
Observed score = True score + Error (X = T + E)
True score is an “expected” score/mean of observed scores
Errors are not correlated with true score (i.e. random) (rho of TE = 0)
Errors on two parallel tests are uncorrelated (rho of E1E2 = 0)
What are some additional conclusions we can make from true-and-error score theory?
Mean (expectation) of error scores for any examinee is 0
Observed score variance can be partitioned into true score and error score variance (sigma2 of X = sigma2 of T + sigma2 of E)
Reliability coefficient is the squared correlation between observed score and true score (rho2 of XT), and can be estimated by correlation between scores on two parallel tests
Reliability is ratio of true score variance to observed score variance (rho2 of XT = sigma2 of T/sigma2 of X)
Reliability is one minus proportion of observed score variance due to error (rho2 of XT = 1 - sigma2 of E/sigma2 of X)
Unsquared correlation between observed and true scores can be obtained by taking square root of reliability coefficient (rho of XT = square root of rho of X1X2); index of reliability (IR), can be used to obtain estimate of a person’s true score from their observed score
sigma2 of E = sigma2 of X(1-rho of X1X2)
sigma of E = sigma of X(square root of 1 - rho of X1X2); standard standard deviation of errors of measurement
What is the standard deviation of the errors of measurement?
Aka standard error of measurement (SEM); amount of observed score standard deviation that is due to unreliability, defines a confidence in which the “real” true score lies at a prespecified level of confidence
What are some problems with true-and-error score theory?
Reliability coefficients are sample-dependent (and subject to all problems of any correlation), SEM is sample-dependent, SEM is constant for all score levels (only one SEM for each reliability coefficient
What are parallel tests in true-and-error score theory?
Measure the same construct, their scores are highly correlated, have the same number of test items, have the same mean, have the same standard deviation
Very difficult to create
What is a shortcut to creating two parallel tests?
Split a test into two parts and get two scores
What is infinite parallel tests theory?
Relaxes restrictive assumptions of true-and-error score theory by assuming an infinite number of items for any construct, so any two tests of items from this infinite set will be randomly parallel
Psychometric quantities are the same as in true-and-error score theory: correlate scores on two tests for reliability coefficient, true score estimated from index of reliability, and SEM is the same
What is domain sampling theory?
Basic idea: any measuring instrument is composed of a random sample of items from a specified domain of items—items can be thought of mini-tests with length 1
Reliability is repeatability across random samples from the domain (correlation between scores on any two random samples)
What are the assumptions of domain sampling theory?
With repeated random samples from domain, the averages of the mean, standard deviation, and the correlation of items in the samples are the same as mean/sd/correlation of all items in domain
How is reliability conceptualized in domain sampling theory?
Average correlation between scores on one “test” (item) with all other “tests” (items) in domain
Can be interpreted as proportion of observed score variance not attributable to error variance
What is the index of reliability (IR) in domain sampling theory? The SEM?
Correlation between observed scores on random samples of items that constitute a test and scores on the whole domain of items (i.e. true scores); SEM is standard deviation of individual scores over sets of items (varies from person to person in theory but is computationally the same for all examinees)
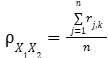
What is this?
Reliability coefficient in domain sampling theory, proportional to average item intercorrelation
What are some problems with parallel forms reliability?
Difficult to get explicitly parallel forms as required by true-and-error score theory
Scores on one form may affect scores on another due to memory/motivation
Time interval between administration of forms can have effect on correlation between parallel forms
Reliability coefficient depends on heterogeneity of group to which two forms are administered and other factors that affect correlations
Reliability correlation will reflect how reliable scores are as well as how parallel the tests are
Describe the split-test method for approximately parallel forms.
Operationalized as Pearson product-moment correlation between scores on split tests; Spearman-Brown formula used to inflate the split-test correlation to what it would be for number of items in complete test
What is the Spearman-Brown prophecy formula?
Predicts reliability that would result from adding a certain number of items to a test; doesn’t always estimate that well
Assumes new and original items have same standard deviation, difficulty, item intercorrelations, and measure the same trait
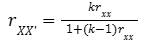
What is this?
The Spearman-Brown prophecy formula, used for predicting reliability that would result from changing length of the test
What is Rulon’s formula?
An alternate method to calculate split-test reliability
Compute total score for all items for each examinee; compute total score for each half for each examinee; compute difference score between two parts for each examinee; compute variance of all the difference scores; compute variance of all-items total scores; correlation = 1 minues variance of part score differences divided by variance of observed scores
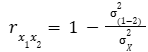
What is this?
Rulon’s formula for split-test reliability
Describe some characteristics of Rulon’s formula for split-test reliability.
Error variance is directly defines as variance of difference scores
Does not require Spearman-Brown correction; is not a correlation and doesn’t have problems inherent in correlations
What are some limitations of split-test estimates of reliability?
Not applicable to speeded tests; inflate reliability by including momentary fluctuations in performance with systematic variance; splits are frequently not equivalent (reduces reliability)
What is internal consistency reliability?
Logical extreme of split-test methods—consider each item as mini-test of 1, intercorrelate all items into a matrix, take average of those correlations to estimate reliability
Need to use Spearman-Brown formula to get reliability of 100-item test from average reliability of 1-item tests because item responses have low correlations with each other
What is Cronbach’s alpha coefficient?
Whole-test methods of internal consistency reliability
Error variance is summed variance of test items, implies reliability of a test is function of positive inter-item correlations, can apply to dichotomous or non-dichotomous, item intercorrelations assumed equal, not usable for speeded tests, varies from -infinity to 1.0
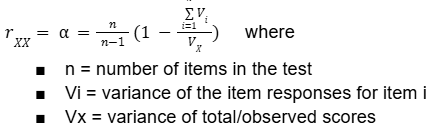
What is this?
Calculation for Cronbach’s alpha, a whole-test method of internal consistency reliability

What is this?
Kuder-Richardson formula 20 reliability coefficient for dichotomously scored test data; same as Cronbach’s alpha but only for dichotomous

What is this?
Hoyt’s internal consistency reliability coefficient; divides total variance in a persons by items matrix into components (variance between persons, between items, and interaction variance between items and persons), gives equivalent results to KR-20 and Cronbach’s alpha
How can internal consistency reliability be increased?
By deleting items that are different from other items/adding items that are similar to other items
What is interrater agreement?
Extent to which different judges tend to make exactly the same judgement about rated subject
What is interrater reliability?
Degree to which the ratings of different judges are rank-ordered in a similar fashion (i.e. are proportional)
How should interrater agreement and reliability be used?
Require evidence of both before ratings can be accepted
Describe reliability for criterion-referenced tests
Purpose of criterion-referenced test is to compare each individual to some specified standard—student variability is not essential
Type of precision needed reflected in purpose of the test (if intended for reference to a domain, focus is on precision of score itself; if purpose is to make classification, then focus on precision of decision consistency)
What is the purpose of test-retest reliability?
Evaluate stability of scores over time
What is the purpose of parallel forms reliability?
As an approximation to internal consistency reliability
What is the purpose of internal consistency reliability?
To evaluate repeatability within one measurement occasion