Lesson #2 - The Chromosomal Basis of Heredity
1/192
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
193 Terms
Genes
Are defined as a sequence of DNA
Chromosome
Are structures within the cell that contains genes
23 pairs and 46 in total
How many pairs of chromosomes do we have? How many in total?
Linear DNA, Circular DNA
What kind of DNA do eukaryotes have? How about Prokaryotes
1
How many chromosomes do prokaryotes have?
Chromatid
Refers to one of two identical halves of a replicated chromosome, present before the chromatids are separated during cell division.
Chromosome
Refers to the entire structure, which can be a single chromatid (before replication) or two sister chromatids (after replication) joined by a centromere.
Metaphase chromosome
Structure of a chromosome during the metaphase stage of cell division, either in mitosis or meiosis.
X-shaped apperance
What kind of appearance do metaphase chromosomes have?
Metaphase Chromosome
This is one of the most iconic and studied stages because the chromosomes are highly condensed, organized, and aligned, making them easier to observe under a microscope.
Chromatin, Centromere, Chromosome arms, Secondary constriction, satellite, and Telomere
What are the 6 parts of a metaphase chromosome?
Heterochromatin and Euchromatin
What are the two kinds of chromatin under metaphase chromosome?
Heterochromatin
Where the DNA is more condensed, and usually there is not much transcriptional activity. Some will remain condensed throughout the cell cycle.
Euchromatin
This is where the “active” genes are– usually this region is much less condensed.
Centromere
During mitosis, spindle fibers attached to this part of the metaphase chromosome via the kinetochore– a highly complex multiprotein structure that is responsible for the actual events of chromosome segregation (Anaphase)
Kinetochore
This is the site located in the centromere where spindle fibers attach
P arm and Q arm
What are the two kinds of chromosome arms?
Secondary Constriction
Site of nucleolus formation and are called “Nucleolar Organizing Region”
Satellite
This is the blob-like terminal part pf a chromosome extending beyond the secondary constrictions. It is rounded or elongated. It is also called Trabant.
Telomere
Represents the tip of a linear chromosome, one at each end and each has many repeats of DNA sequences.
Telomere
It prevents the adhesion of one chromosome to another at the ends.
Telomere
Is necessary for the attachement of chromosomes to the inner side of the nuclear envelope.
AGGGTT
What is the Telomere repeat sequence in Humans
As cells divide overtime, telomeres shorten, and eventually cell division stops
How are telomeres related to aging?
Lamp Brush Chromosome
Found in the growing oocytes (immature eggs) of most animals, except mammals. Organized into a series of chromomeres with large chromatin loops extended laterally giving a hairy appearance. What is this kind of chromosome structure?
Prophase I
Lampbrush chromosomes are present during what stage of meiosis?
Polytene Chromosome
Giant chromosome formed when multiple rounds of DNA replication produce many sister chromatids that remain synapsed together. Found in salivary gland cells in the larval stages of Drosophila.
Metacentric
What is the designation for a chromosome with the centromere in the middle?
X-shaped with equal arms
What is the metaphase shape of a metacentric chromosome?
Equal
What is the overall length of chromosome arms in metacentric chromosomes?
Between middle and end
Where is the centromere located in a submetacentric chromosome?
Submetacentric
What is the designation for a chromosome with the centromere between the middle and the end?
V
What is the anaphase shape of a metacentric chromosome?
P arm shorter than q arm
What is the metaphase shape of chromosome that is not classified as metacentric?
L or J
What is the anaphase shape of a submetacentic chromosome?
Close to end
Where is the centromere located in an acrocentric chromosome?
Acrocentric
What is the designation for a chromosome with the centromere close to the end?
i
What is the anaphase shape of an acrocentric chromosome?
At end
Where is the centromere located in a telocentric chromosome?
Teloccentric
What is the designation for a chromosome with the centromere at the end?
Single vertical line with no p arm
What is the metaphase shape of a telocentric chromosome?
I
What is the anaphase shape of a telocentric chromosome?
Metacentric, Submetacentric, Acrocentric, and Telocentric
Types of Chromosome based on Centromere Position
Karyotype
Complete set of chromosomes in a cell of an organism
Karyotyping
Laboratory process of preparing and analyzing the karyotype of an organism's cells.
Trisomy, 21
Down syndrome is an a condition caused by? In what chromosome?
Trisomy 18
Edwards Syndrome is a genetic birth defect that causes the baby to ahveve an elongated skull, short neck, short breastbone, malformed ears and mentally deficient. What causes this genetic defect?
Trisomy 13
Patau Syndrome is cause by what genetic defect?
Metafemale(47-XXX)
Is a genetic disorder that affects 1 in 1000 females that is caused by a Trisomy in the X chromosome
Klinefelter Syndrome (47-XXY)
A chromosome anomaly in which a male has an extra X chromosome is characterized by conditions such as infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles.
Jacob Syndrome (44-XYY)
An aneuploid genetic condition in which a male has an extra Y chromosome typically presents with few symptoms. Possible signs may include above-average height and an increased risk of learning disabilities.
Richard Speck
A wrong case of Jacob’s Syndrome where this man raped and killed 8 women.
Cri-du-chat or Cat’s Cry Syndrome
A rare genetic disorder due to a partial chromosome deletion on chromosome 5
Turner Syndrome
A condition that affects only females, results when one of the X chromosomes (sex chromosomes) is missing or partially missing.
Cell cycle
Is an ordered sequence of events for cell division
Interphase and Mitosis(PMAT)
What are the two stages of cell division?
G1, S, G2
What are the three phases of Interphase?
G1
Is known as the 1st intermediate gap phase of interphase, where growth occurs and also an increase in cytoplasm
S or synthesis
This stage of interphase is when the duplication of chromosomes occur
G2
Is known as the 2nd intermediate Gap Phase where additional growth occur and the cell prepares for division
Mitosis
Is known as the division of Somatic cells, and also the division of the nucleus
Cytokinesis
Is the division of the cytoplasm that slightly overlaps with the telophase
Mitosis cell cycle, Binary Fission
Eukaryotic cells undergo/follow the? While Prokaryotic cell cycle differs in name/process as they undergo?
Meiosis
division of germ/sex cells (animals), spores (plants, fungi, algae), zygotes (common in fungi and protist but also found in other eukaryotes)
5
The G1 phase takes how many hours to complete?
7
The S phase takes how many hours to complete?
3
The G2 phase takes how many hours to complete?
1
The M phase takes how many hours to complete?
G1 Phase
Cell grows in size; synthesizes various proteins/enzymes needed for the S phase (e.g enzymes involved in DNA replication).
G1 phase
Some organelles replicate (e.g mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum): to ensure that the daughter cells will have the necessary cellular machinery.
G1 checkpoint (G0 or apoptosis)
Cell passes through a checkpoint at the end of G1 and check if it can undergo DNA replication.
G0
Is a state where cells exit the active cell cycle and stop dividing.
DNA Replication and Centrosome Duplication
What are the two main things that occur dung the S phase or Interphase?
S Phase
Cell replicates its entire genome (DNA Replication) : synthesis of a new complementary strand; formation of two identical sister chromatids for each chromosome.
S Phase
Centrosome Duplication: spindle apparatus during mitosis, is also duplicated
Chromatin
During the S Phase of Interphase, histone proteins are also synthesized to package the newly formed DNA into?
Chromatin
Eukaryotic chromosomes are composed of?
DNA + histone proteins
Chromatins are mainly made up of what two materials?
Highly Compact
To prepare for division, the chromatin becomes ______ ______, which make chromosomes visible with a microscope.
G2 phase
Cell continues to grow and produce proteins/enzymes necessary for mitosis, such as those involved in spindle formation and chromosome segregation.
G2 checkpoint (DNA repair or Apoptosis)
This checkpoint ensures that DNA replication is complete, that the DNA is undamaged, and that the cell is ready to enter mitosis.
Mitosis
Progresses to a series of stages known as PMAT.
Mitosis
A process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells from a single parent cell.
Mitosis
This process is crucial for growth, development, and repair in multicellular organisms.
Microtubules
What are mitotic spindles made of?
Mitotic Spindle
Is required to divide the chromosomes. They are produced by centrosomes.
Prophase
○Chromosome/chromatin condenses.
○ Mitotic spindle are formed.
○ Centrosome move towards opposite poles guided by growing spindle fibers.
○ Nuclear envelope start to break down (allows spindle fiber to access the genetic material)
THIS PAHSE OF MITOSISIS?
Prometaphase and Metaphase
What are the two types of Metaphase?
Prometaphase
This picture is a diagram of what phase in mitosis specifically?
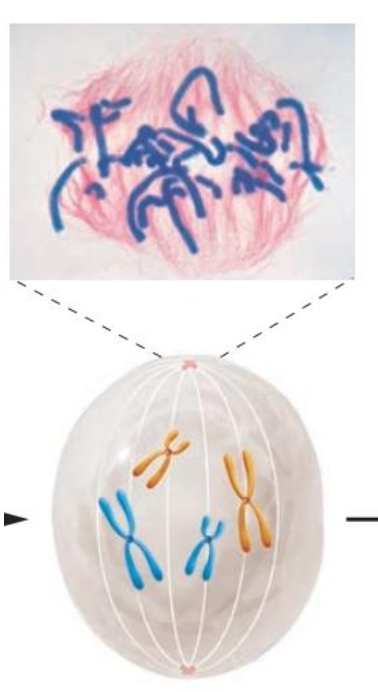
Metaphase
This picture is a diagram of what phase in mitosis specifically?
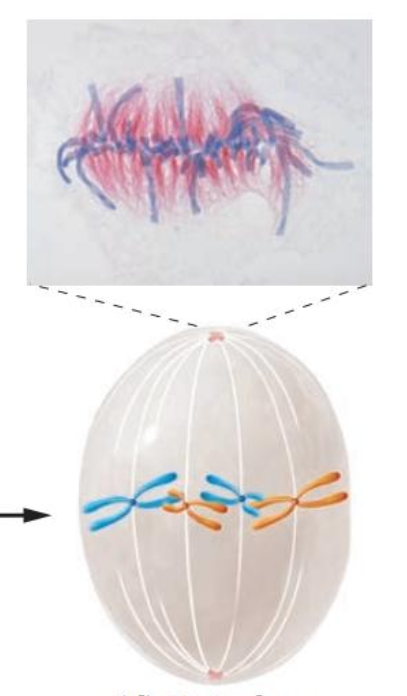
Prometaphase
○ Nuclear envelope completely disintegrates (breaked down)
○ Kinetochore forms at the centromere of each sister chromatid.
○ Spindle fibers attach to kinetochore of the chromosome.
WHAT STAGE OF MITOSIS IS THIS?
Metaphase
Chromosome aligns in the middle (metaphase plate), this occurs during what stage of mitosis?
Spindle Checkpoint
This check if all chromosomes are attached to spindle fibers
Anaphase
○ Centromeres split; sister chromatids are pulled apart trough shortening spindle fibers.
○ Sister chromatids move toward opposite poles (ensures that each pole or cell will have an identical set of chromosome).
○ The cell elongates.
WHAT STAGE OF MITOSIS IS THIS?
Telophase
Marks the end of mitosis
Telophase
○ Chromosome reach opposite poles. New nuclear envelope forms on each set of chromosome.
○ Chromosome begin to uncoil back into chromatin (interphase state: less condense form)
○ The nucleoli, which had disappeared during prophase, reappear within each new nucleus.
Prophase
Chromosome/chromatin condenses and mitotic spindles are formed
Prophase
Centrosomes move towards opposite poles guided by growing spindle fibers
Prophase
Nuclear envelope start to breakdown (allows spindle fibers to access the genetic material)
Prometaphase
Nuclear envelope completely disintegrates/broken down