topic 6: the rate and extent of chemical change
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
two ways to measure rate
measure the rate at which a reactant is used up
measure the rate at which a product is formed
factors affecting rate
surface area
temperature
concentration
pressure
how can you calculate rate? give one of its units?
g/s OR cm³/s OR mol/s
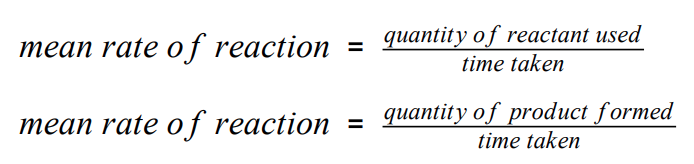
for any reaction to occur, particles must:
collide
collide w sufficient energy
(collide in the right way)
how does increasing the temperature affect rate?
particles move faster
more collisions
more collisions which occur w enough energy to react
more successful collisions
rate increases
what is concentration?
measure of the number of particles in a given volume
how does increasing concentration affect rate?
more reactant particles in the same volume
greater chance of particles colliding
more successful collisions
rate increases
how does increasing SA affect rate?
more particles exposed to other reactants
more successful collisions
rate of reaction increases
function of a catalyst
speed up chemical reactions but don’t get involved in them or get used up
provides an alternative pathway w/ a lower activation energy
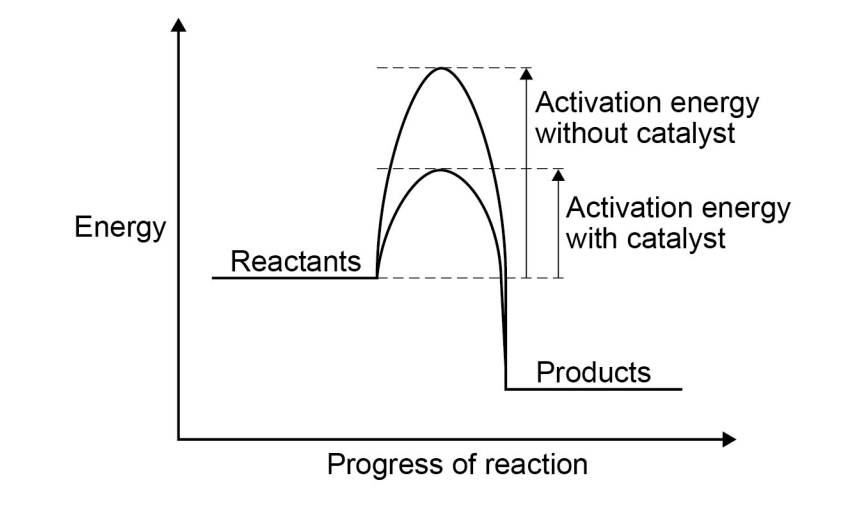
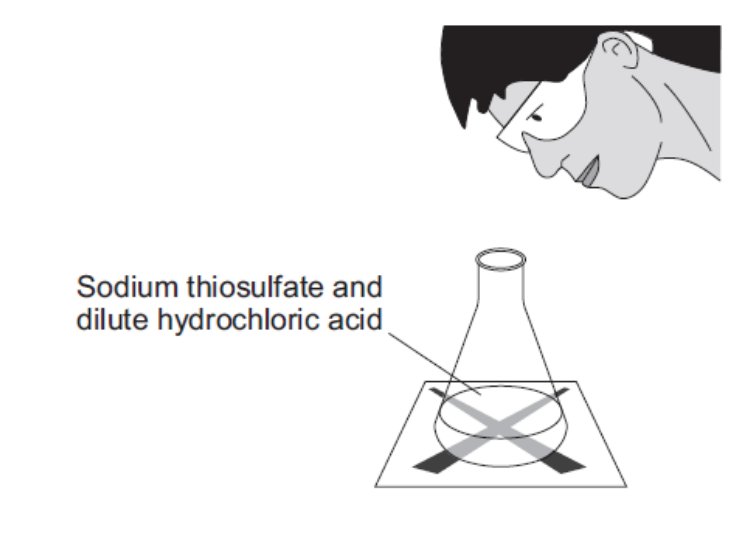
(required) describe an experiment to show the effect of increasing concentration on rate
measure a set volume of dilute sodium thiosulfate solution w/ a measuring cylinder and pour into the conical flask
put the conical flask on a piece of paper w/ a black cross drawn on it
measure a set volume of dilute HCl w/ measuring cylinder
pour this acid into the flask and at the same time swirl the flask gently and start the stopwatch
look down through the top of the flask and stop the stopwatch when the cross is no longer visible
record the time it takes for the cross to disappear in seconds in a table
repeat for different concentrations of sodium thiosulfate
what should be controlled in this experiment?
volume of dilute HCl
volume of sodium thiosulphate
what are the risks involved in this experiment? (i’m not sure if my answers are right it was just in the practical handbook)
breathing in sulfur dioxide fumes
breaking glassware and cutting yourself on it?
on a graph, how is the rate of reaction found? as this varies, what does it show?
gradient - the larger the gradient, the higher the rate
over time, the gradient will decrease as the reactants are used up
the fastest reactions will have the largest gradients and become flat in the least time

how does an increase in pressure affect the equilibrium?
position of equilibrium shifts to the side w/ the fewer number of particles
how does an increase in temperature affect the equilibrium of a reaction?
position of equilibria shifts in the direction of the endothermic reaction
how does an increase in concentration of the reactants affect the equilibrium?
position of equilibrium shifts towards the products
how does an increase in concentration of the products affect the equilibrium?
position of equilibrium shifts towards the reactants