query, join relates, spatial selection
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
queries
tools used to search for and select a subset of features and table record
questions posed to a database
three basic methods - selection, by attribute, by geography
selection query
attribute or spatial
can still see other records which don’t meet our criteria
what gets selected
definition query
filter subsets
can isolate info to what we want to see, what we see
select by location
highlight particular features by examining their position relative to other features
vector features can be selected to occur in relation with an area of another layer
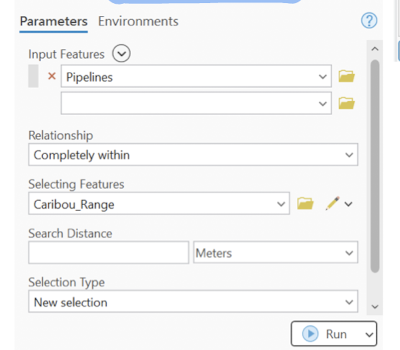
select layer by location - spatial relation
completely within, are identical to, boundary touches, share a line segment with, etc, etc,
within select by location
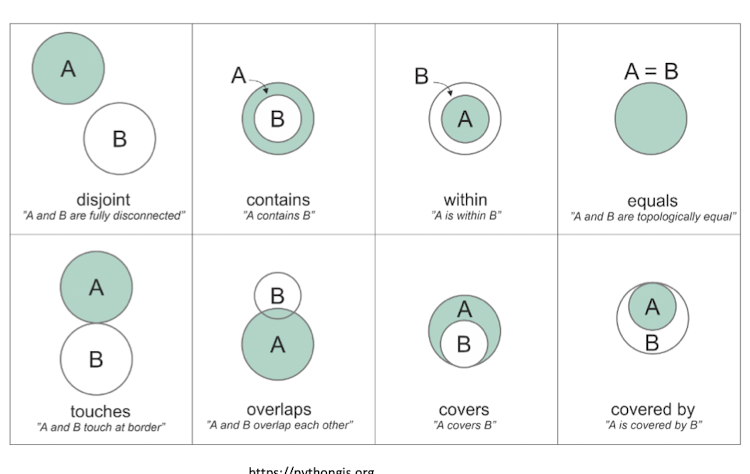
structured query language (SQL)
computer language developed to query attribute data within a relational database management system
allows retrieving a subset of attribute information based on specific criteria, user defined
implements clauses to structure database queries
includes “select, from, where, order by, and having” statements/clauses
other operators include relational, arthimetic, and boolean
select - query clause
denotes what attribute table fields you wish to view
mandatory statement
from - query clause
denotes the attribute table in which information resides
mandatory statement
where - query clause
denotes the user defined criteria for the attribute information that must be met in order for it to be included in the output set
optional used to limit output set
order by - query clause
denotes the sequence in which the output set will be displayed
optional
having - query clause
denotes the predicate used to filter output from the order by clause
optional
Relational SQL operator
employs the statements equal to, less than, less than or equal to, greater than, greater than or equal to
arithmetic SQL operator
mathematical functions including addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
different methods of extracting information
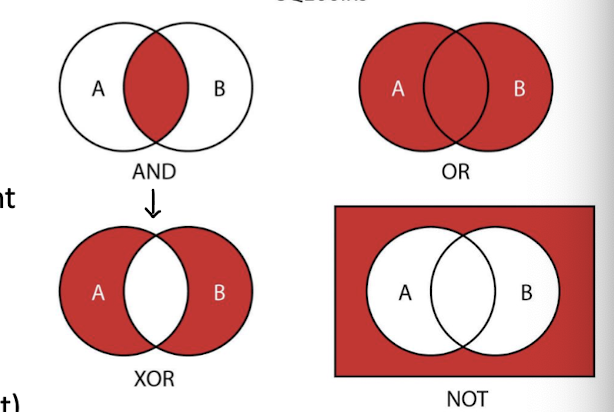
Boolean SQL operator
includes and - satisfies both expressions, intersections
or - either one or both, represents union
XOR - satisfies one and only one, opposite of and
not - negate expression that otherwise would be true
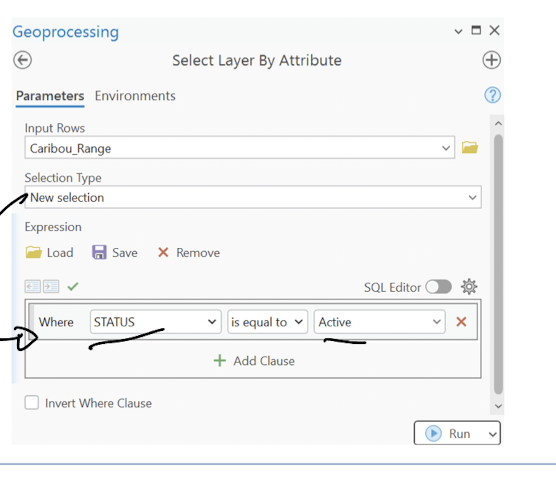
select by attribute
select based on active status, or area size, etc
can have compound expressions, or group selections
includes new selection, add to current, remove from current, select subset from current, switch the current, clear the current
SQL Null values
values that haven’t been specified or entered, always IS or IS NOT
**
associating tables
data obtained from multiple tables
can be joined to a layer is values are found in both → link the non-spatial and geographic features (join/relate)
join
append columns of records
stored in map document
requires common field, only 1:1 or 1:n cardinality supported
used for label, symbol and query
cardinality
the nature of the relationship between records in one table and records in another, facilitated by a common field - numerical association
destination and origin
four types
1:1 cardinality
a single record in one table relates to a single record in another
for ex each province has a capital city
1:many cardinality
where on record in the first table can relate to multiple records in the second
for ex. a bird may visit many forest polygons
many:1 cardinality
where many records in the first table can relate to one record in the second
for ex. cities related to stanley cups, edmonton won 5 stanley cups while calgary has won 1
many:many cardinality
multiple records in one table can relate to multiple records in another
for ex students may be related to classes
table join
combines two tables based on the value of a field that can be found in both tables
aka a common field