Chemistry: Matter, Properties, and Separation Techniques
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is chemistry?
The study of the composition of matter and the changes it undergoes.
Define matter.
Anything that has mass and volume.
What is volume?
The amount of three-dimensional space an object occupies.
What is mass?
A measure of the amount of matter.
What is an atom?
The smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical identity of that element.
Define an element.
A pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances and is made of one type of atom.
What is a compound?
A substance made of two or more different kinds of elements combined through a chemical reaction.
What are the three phases of matter?
Solid, liquid, and gas.
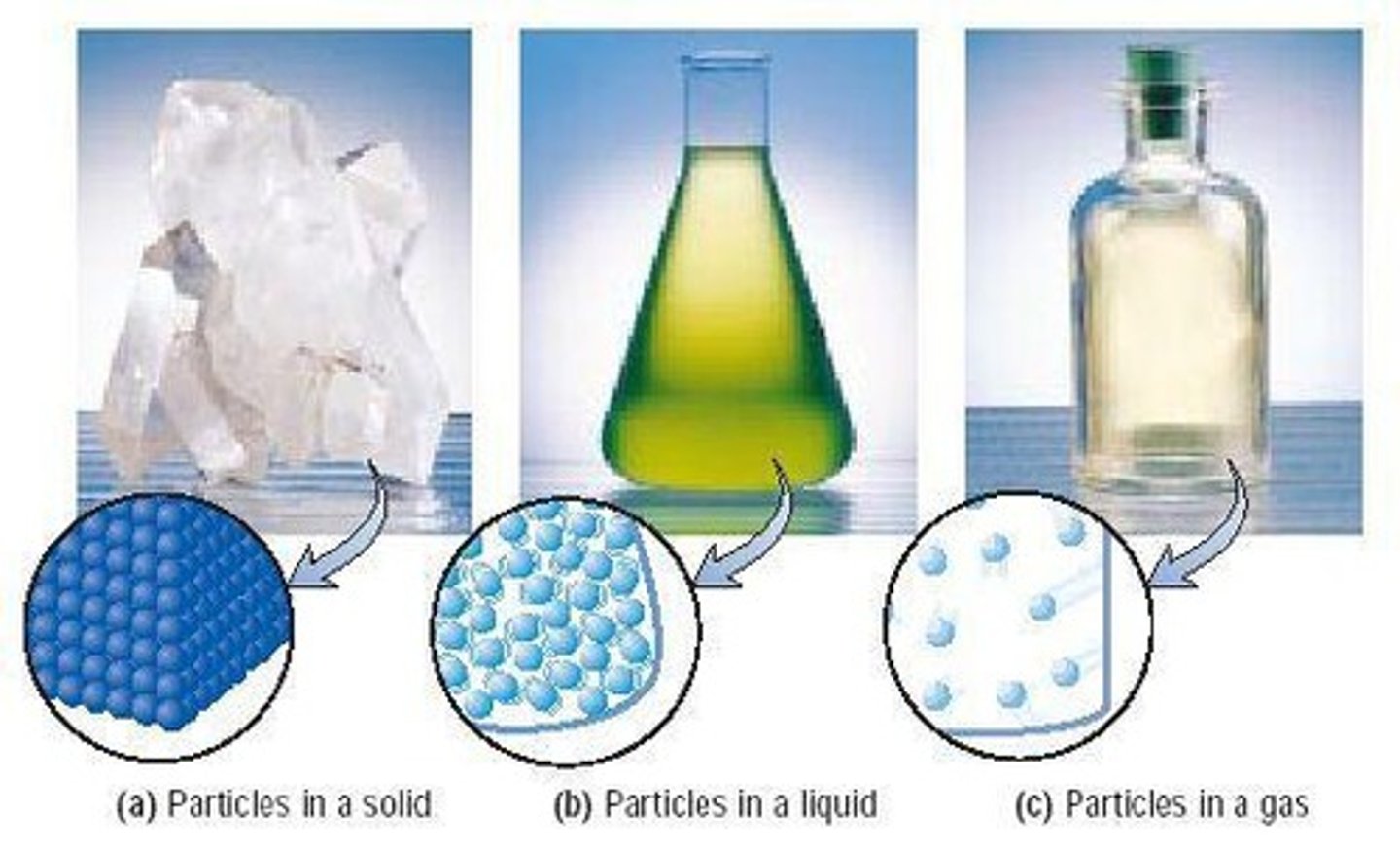
Describe the properties of a solid.
Has a fixed volume, rigid shape, and molecules that do not move.
Describe the properties of a liquid.
Has a fixed volume, assumes the shape of its container, and molecules can slide past one another.
Describe the properties of a gas.
Compressible, assumes the shape and volume of its container, and molecules are separated by large distances.
What is a pure substance?
A substance with a fixed composition composed of just one type of particle (atom or molecule).
What distinguishes a compound from an element?
A compound has properties that differ from the elements that make it up, while an element cannot be broken down further.
What is a mixture?
A physical combination of two or more substances that retain their individual properties.
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
A mixture that does not appear the same throughout and has particles large enough to be seen and separated.
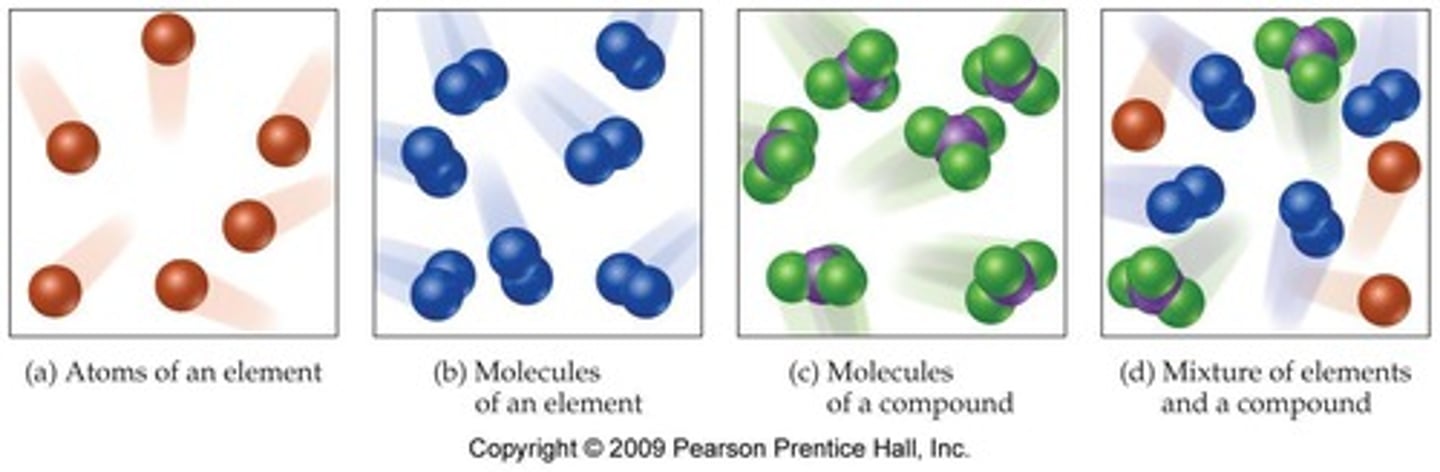
What is a homogeneous mixture?
A mixture that appears the same throughout and does not settle out when left standing; also called a solution.
What is a solution?
A homogeneous mixture made up of a solute (what is dissolved) and a solvent (what does the dissolving).
How can mixtures be separated?
By physical means, as the identities and properties of the individual substances are retained.
What is the difference between a compound and a mixture?
A compound has a definite composition and properties different from its elements, while a mixture does not have a definite composition and retains the properties of its components.
Give an example of a heterogeneous mixture.
Oil and water.

Give an example of a homogeneous mixture.
Saltwater.

What is the significance of the properties of water compared to its elements?
The properties of water are different from those of oxygen and hydrogen, illustrating how compounds can have unique characteristics.
What is the chemical formula for table salt?
NaCl
Is Neon gas an element, compound, or mixture?
Element
What is the chemical symbol for Neon?
Ne
Is salad an element, compound, or mixture?
Mixture
What is the chemical formula for pure water?
H2O
Is Aluminum an element, compound, or mixture?
Element
What is the chemical symbol for Aluminum?
Al
Is lemonade an element, compound, or mixture?
Mixture
What is the chemical symbol for Silver?
Ag
Is sand an element, compound, or mixture?
Mixture
What are diatomic elements?
Elements that are only found in pairs in their pure state, such as H2, N2, O2, etc.
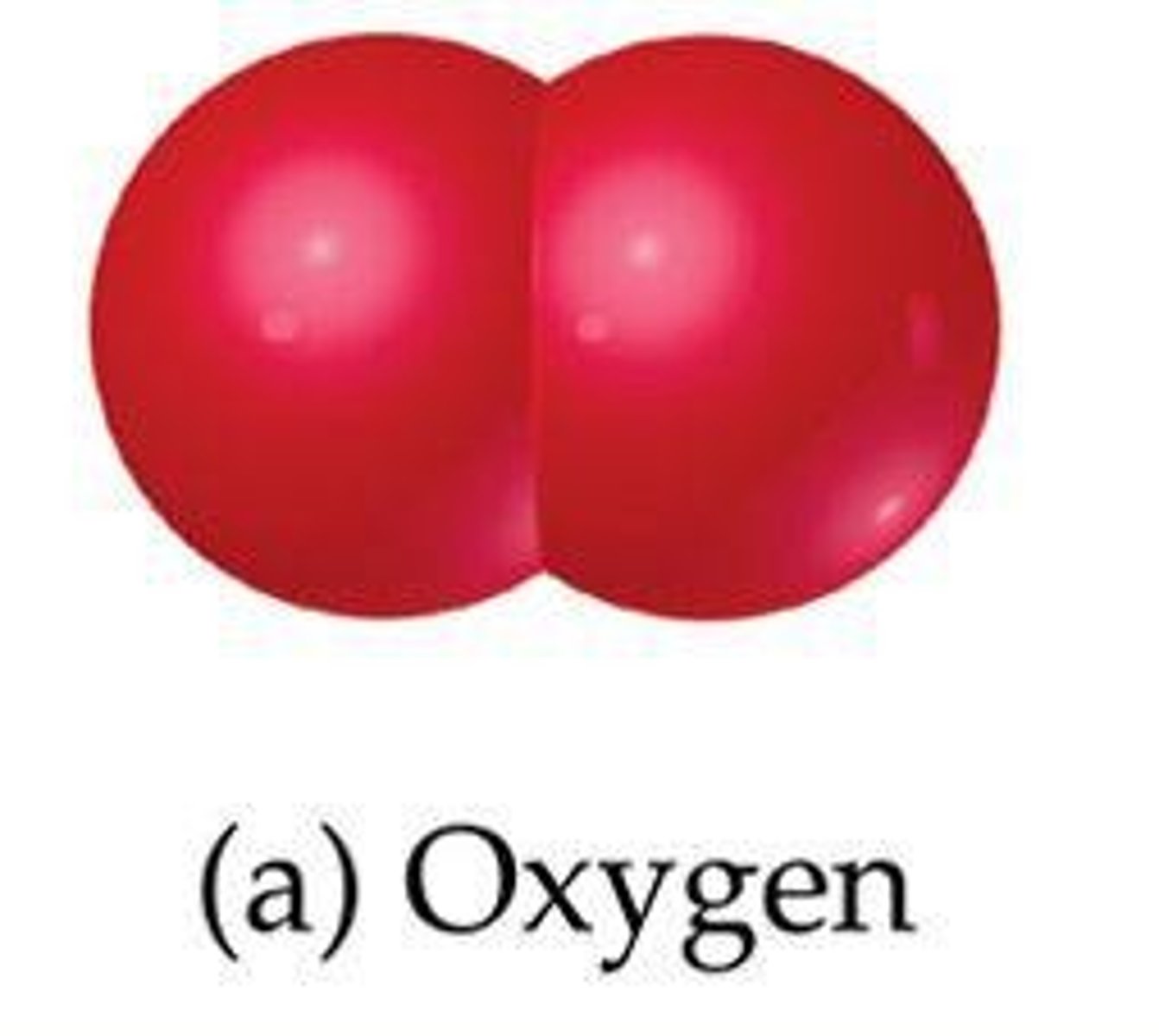
List the seven diatomic elements.
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
What distinguishes physical properties from chemical properties?
Physical properties can be observed without changing the substance's identity, while chemical properties can only be observed by altering chemical bonds.
Give an example of an extensive physical property.
Mass or volume
Give an example of an intensive physical property.
Density, boiling point, color, malleability, or ductility
What is a physical change?
A change that does not alter the chemical composition of a substance.
What is a chemical change?
A change that alters the chemical composition, resulting in new substances.
What is the process of filtration?
Passing a mixture through a porous material to separate substances based on size.
What is evaporation used for in separating mixtures?
To separate a solid from a liquid by vaporizing the liquid.
What is distillation?
A method of separating liquid mixtures based on differences in boiling points.
What is decanting?
Pouring off the liquid layer to separate it from solids.
What is chromatography?
A technique used to separate mixtures based on the movement of different components through a medium.