humanities revision (WW1)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
whos was in the triple alliance?
Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy
who was in the triple entente?
France, Russia and Britain
An Australian vote on a single political question for a direct decision.
defintion of trench warfare
A type of combat in which opposing troops fight from trenches facing each other.
what occured after the assassination?
WW1 begins when Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia
what is a front?
A 'front’ in war refers to a contested zone where opposing military forces are in contact or where battles are fought.
what were the major fronts?
Western Front (France and Belgium) and Eastern Front (Eastern Europe, such as Russia agasint Austria-Hungary)
Gallipolli and Italy
what was the ottoman empire?
The ottoman empire is modern day Turkey
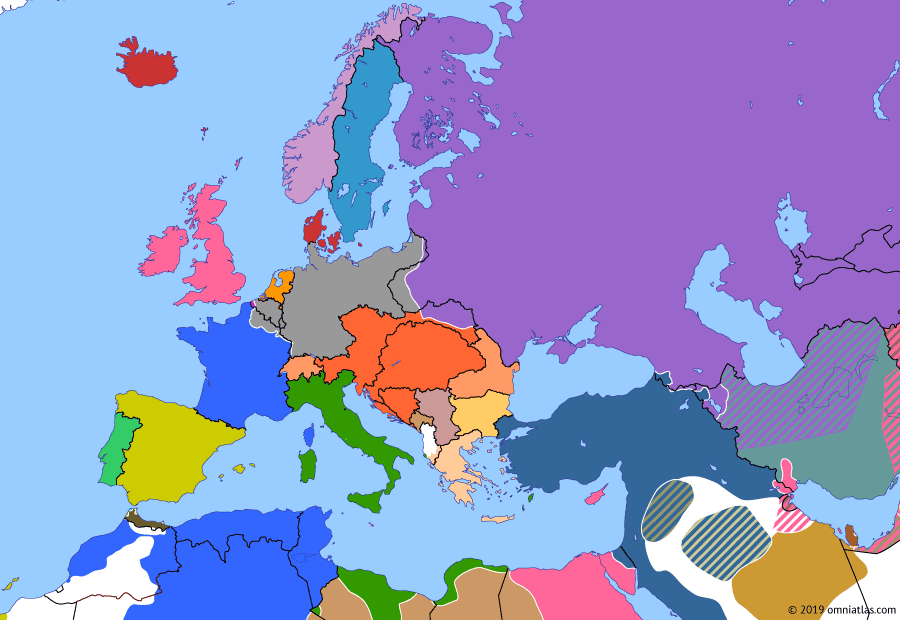
name all the european countries during ww1
purple: Russia, grey: Germany, light blue: France, orange: Austria-Hungary, dark blue: Turkey/Ottoman Empire, pink: Great Britain, green: Italy
who was the prime minister of australia for most of ww1?
Billy Hughes
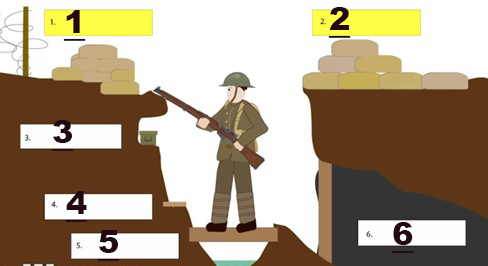
what part of the trench is shown at 1
Parapet
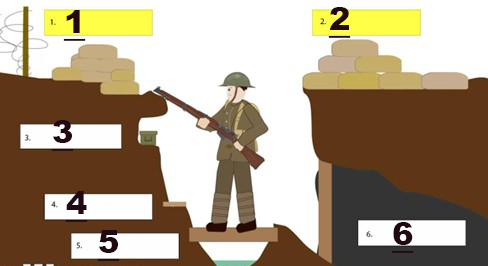
what part of the trenc is shown at 2
Parados
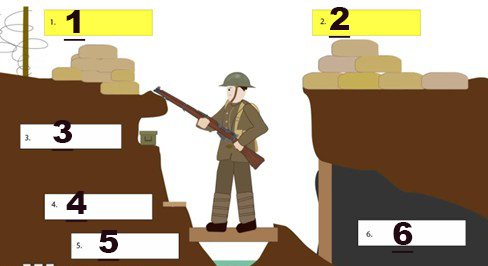
what part of the trench is shown at 3
Ammo shelf
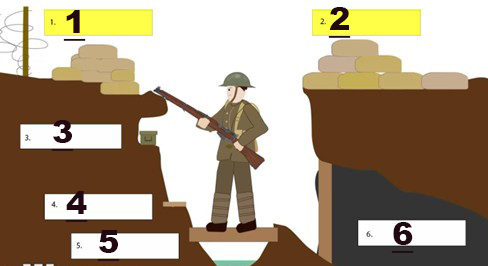
what part of the trench is shown at 4
Firestep
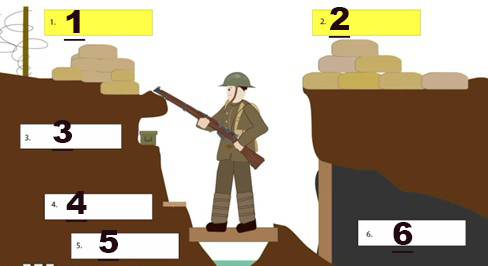
what part of the trench is shown at 5
Duckboard
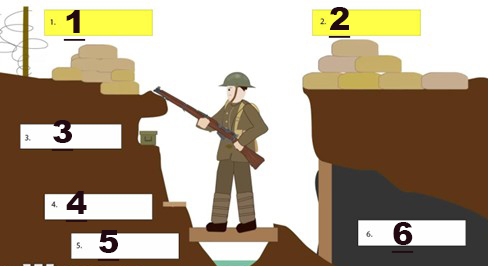
what part of the trench is shown at 6
Dugout
what is a stalemate?
A period within a war where neither side gains any advantage.
An attempt to gain access to Russia.
when did the anzacs first land on gallipoli?
25 April, 1915
whats the anzac legend?
The ANZAC legand is a concept representing the spirit of courage and endurance by Australian and New Zealand soldiers.
what does anzac stand for
Australian and New Zealand Army Corps
No, all soldiers volunteered.
what event led great britain to declare war on germany?
Germanys invaion of Belgium
WW1 ended with an armistice on November 11, 1918 when Germany surrended to allied forces, bringing the fighting on the western front to a halt. The war officially conluded a year later with the signing of the Treaty of Versailles on June 28, 1919, causing Germany having to pay reparations.
what did germany sign in 1919?
The war officially conluded a year later with the signing of the Treaty of Versailles on June 28, 1919, causing Germany having to pay reparations.