BSCI170: Active Transport
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
notes from 10/17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
what does active transport do?
pumps charged, polar molecules AGAINST concentration AND electrochemical gradient using energy
Electrochemical gradient: Where is Na+ and K+, in or out of the cell?
Na+ is out of the cell
K+ is in the cell
so, K+ needs to get out of the cell and Na+ needs to go in the cell
Electrochemical Gradient: + or - charges in and out of the cell
+ charge out of the cell
- charge in the cell (even though K+ is +, it’s attached to - charged things)
Primary active transport…
moves ions from low concentration to high concentration using ATP hydrolysis (breaking ATP to release energy)
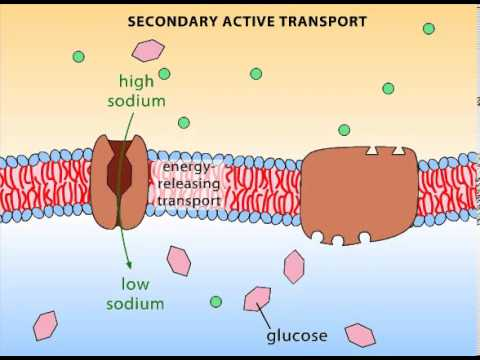
Secondary active transport…
moves ions from low concentration to high concentration using the energy of 1 ion moving to move another ion
relies on primary transport
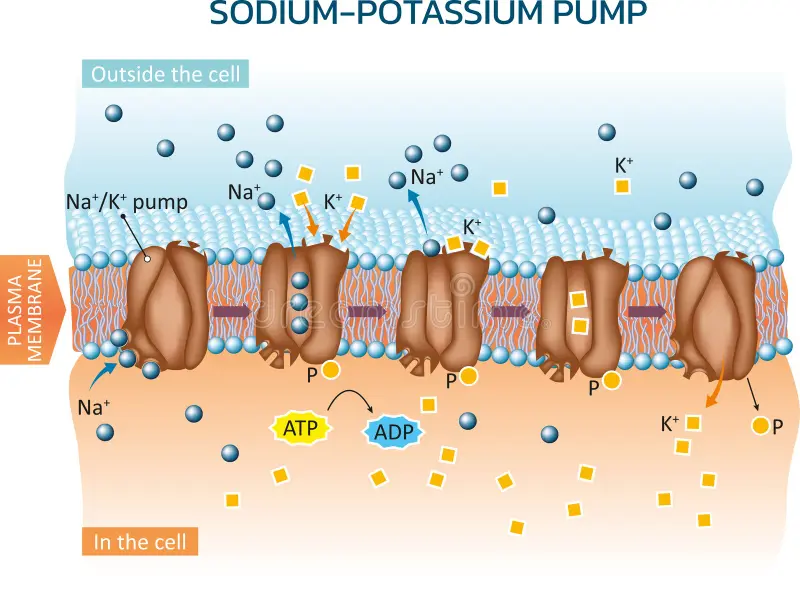
Steps of the Sodium-Potassium Pump
3 Na+ and 1 ATP bind to protein pump
ATP hydrolysis releases ADP and an amino acid goes into the pump
Shape changes causes Na+ to go OUT the cell and 2 K+ ions to go IN the cell
2 K+ ions bind to the pump
Pi is dephosphorylated, releasing 2 K+ ions into the cell
its going AGAINST the concentration gradient which is why Na+ is going out and K+ is going in
Example of secondary active transport
Na+ moves DOWN concentration gradient while glucose moves UP
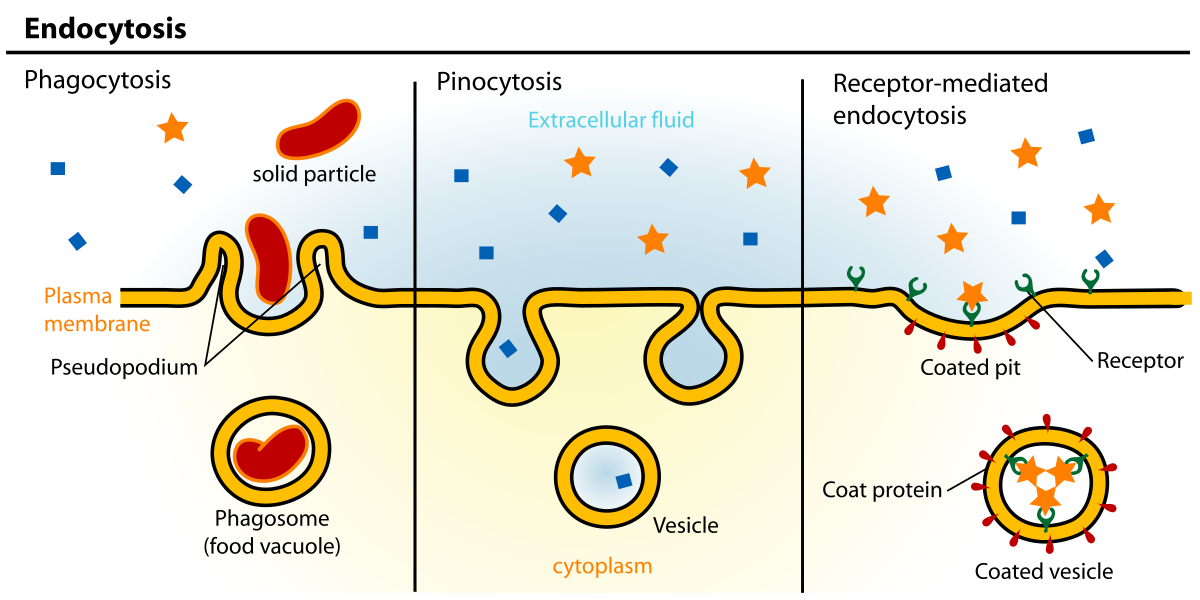
What is bulk transport?
the movement of large molecules through the membrane. Types are:
endocytosis
exocytosis
What is endocytosis?
the active process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane, and bringing it into the cell. Types are…:
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated endocytosis
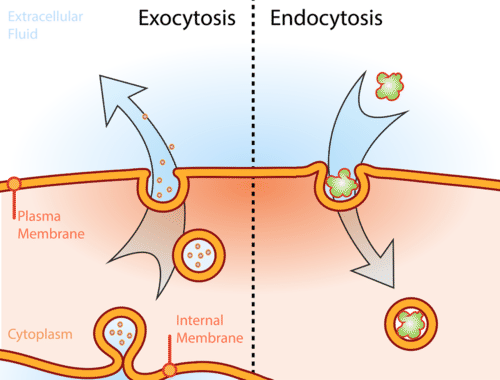
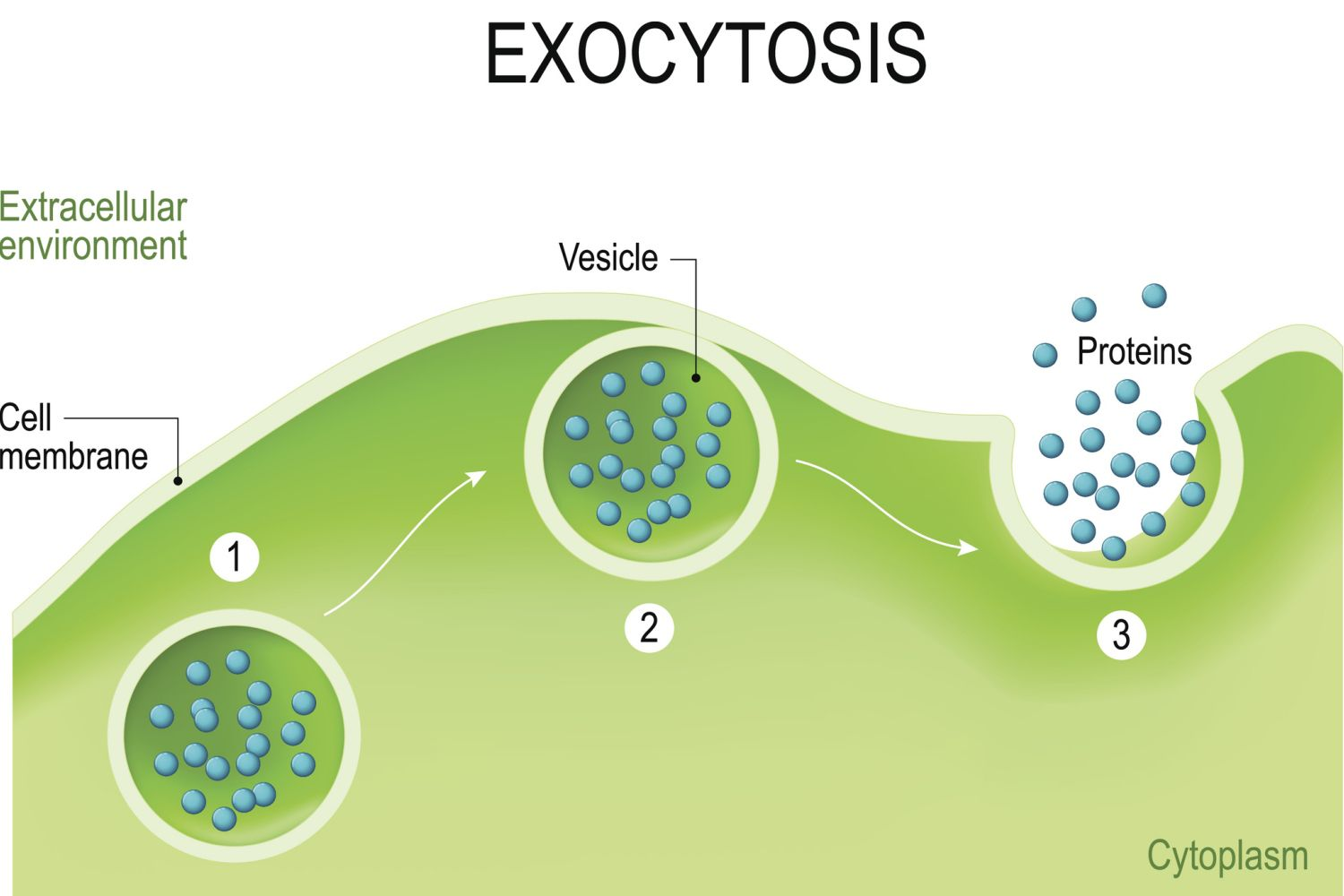
What is exocytosis?
the active process where a cell packages materials inside a vesicle, which then moves to and fuses with the cell membrane to release its contents outside the cell
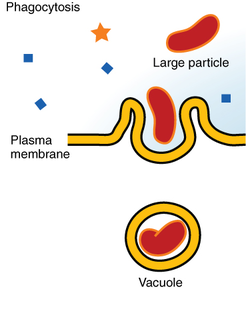
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis: membrane’s inner facing surface is coated with clathrin, extending and enclosing the particle. A vesicle merges with a lysosome to create an endosome, where it will merge with the plasma membrane and release the particle into the extracellular fluid
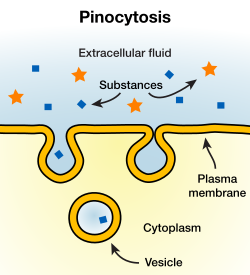
What is pinocytosis
takes in molecules and water from extracellular fluid. Smaller vesicle than phagocytosis, and vesicle doesn’t need to merge with a lysosome
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
clathrin attaches to receptor proteins in the plasma membrane, surrounding a particle and enclosing it. Brings specific substances that are normally in the extracellular fluid into the cell