AP Chemistry Unit 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:17 PM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
intermolecular forces
forces of attraction between molecules (not chemical bonds)
2
New cards
van der Waals forces
intermolecular forces of attraction
3
New cards
dipole-dipole interactions
- molecules have permanent dipoles attracted to one another
- positive end of one attached to negative end of the other
- these forces matter when molecules are close to each other
- more polar -> higher boiling point
- positive end of one attached to negative end of the other
- these forces matter when molecules are close to each other
- more polar -> higher boiling point
4
New cards
permanent dipole
permanent separation of electrical charge in a molecule due to unequal distributions of bonding and/or lone pairs of electrons
5
New cards
hydrogen bonding
- H is bonded to N,O, or F
- bonding caused by high electronegativity and small size of N, O, and F
- bonding caused by high electronegativity and small size of N, O, and F
6
New cards
London dispersion forces
- attractions between an instantaneous dipole and an induced dipole
- present in all covalent molecules, weakest bond
- present in all covalent molecules, weakest bond
7
New cards
instantaneous dipole
temporary dipole that occurs for a brief moment in time when the electrons of an atom or molecule are distributed asymmetrically
8
New cards
induced dipole
a dipole temporarily created in an otherwise nonpolar molecule, induced by a neighboring charge
9
New cards
polarizability
the ease with which the electron distribution in the atom or molecule can be distorted
10
New cards
viscosity
a liquid's resistance to flow (related to ease with which molecules move pass each other)
11
New cards
surface tension
the force that acts on the surface of a liquid and that tends to minimize the area of the surface (caused by attraction between liquid molecules)
12
New cards
melting point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid
13
New cards
boiling point
the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas
14
New cards
cohesion
an attraction between molecules of the same substance
15
New cards
adhesion
an attraction between molecules of different substances
16
New cards
capillary action
- the spontaneous rising of a liquid in a tube
- happens when a liquid is strongly attracted to the tube
- ex: water climbs through plant's xylem
- happens when a liquid is strongly attracted to the tube
- ex: water climbs through plant's xylem
17
New cards
vapor pressure
the pressure caused by the collisions of particles in a vapor with the walls of a container
18
New cards
amorphous solids
the particles are not arranged in a regular pattern
19
New cards
crystalline solids
highly regular arrangement of their components (can be any repeating structure, not just cubic)
20
New cards
lattice
a three-dimensional system of points designating the positions of the centers of the components of a solid (atoms, ions, or molecules)
21
New cards
ionic solids
- ion-ion interactions are the strongest
- lattice points occupied by ions
- held together by electrostatic attraction
- hard, brittle, high melting point
- poor conductor of heat and electricity
- lattice points occupied by ions
- held together by electrostatic attraction
- hard, brittle, high melting point
- poor conductor of heat and electricity
22
New cards
network atomic solids
- stronger than IMFs but weaker than ion-ion
- lattice points occupied by atoms
- held together by covalent bonds
- hard, high melting point
- poor conductor of heat and electricity
- lattice points occupied by atoms
- held together by covalent bonds
- hard, high melting point
- poor conductor of heat and electricity
23
New cards
metallic atomic solids
- weaker than covalent bonds, but can be in the low end of covalent bonding
- lattice points occupied by metal atoms
- held together with metallic bonds
- soft to hard, low to high melting points
- good conductors of heat and electricity
- lattice points occupied by metal atoms
- held together with metallic bonds
- soft to hard, low to high melting points
- good conductors of heat and electricity
24
New cards
molecular crystals
- lattice points occupied by molecules
- held together by IMFs
- soft, low melting point (lowest)
- poor conductor of heat and electricity
- held together by IMFs
- soft, low melting point (lowest)
- poor conductor of heat and electricity
25
New cards
network solids
- diamond/graphite
- silicon dioxide/nitride
- boron nitride
- silicon dioxide/nitride
- boron nitride
26
New cards
pressure equation
P=force/area
27
New cards
barometer
measures air pressure
28
New cards
Boyle's Law
P1V1=P2V2
29
New cards
Charles' Law
V1/T1=V2/T2
30
New cards
Gay-Lussac's Law
P1/T1=P2/T2
31
New cards
Combined Gas Law
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2
32
New cards
Avogadro's Law
V1/n1=V2/n2
33
New cards
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
34
New cards
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures
the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the pressures of all the gases in the mixture
35
New cards
mole fraction
ratio of the number of moles of a given component in a mixture to the total number of moles in the mixture (does not change with temp)
36
New cards
kinetic molecular theory of gases
a model used to explain the behavior of (ideal) gases
- volume of individual particles is negligible because particles are so small
- particles are in constant motion (cause pressure)
- gas molecules do not exert attractive or repulsive forces on each other
- volume of individual particles is negligible because particles are so small
- particles are in constant motion (cause pressure)
- gas molecules do not exert attractive or repulsive forces on each other
37
New cards
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
shows the spread of energies that molecules of gas or liquid have at a particular temperature
38
New cards
diffusion
the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
39
New cards
effusion
a process by which gas particles pass through a tiny opening into a chamber
40
New cards
Graham's law of effusion
- states that the rate of effusion for a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass
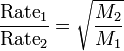
41
New cards
Henry's Law
the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas on the surface of the liquid
42
New cards
solution
a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
43
New cards
solute
the substance that is dissolved; present in smaller amounts
44
New cards
solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves; present in larger amounts
45
New cards
miscible
liquids that dissolve freely in one another in any proportion
46
New cards
ion-dipole
- ionic compounds dissolve in polar solvents
47
New cards
dispersion forces
- non-polar solids dissolve in non-polar solvents
48
New cards
hydration of ionic compounds
- positive ends of H2O attract to anions; negative ends of H2O attract to cations
- hydation of ions causes salt to fall apart in water
- hydation of ions causes salt to fall apart in water
49
New cards
electrolyte
a substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that conducts electric current
50
New cards
nonelectrolyte
a substance that dissolves in water to give a solution that does not conduct an electric current
51
New cards
saturated solution
contains the maximum amount of solute for a given quantity of solvent at a constant temperature and pressure
52
New cards
unsaturated solution
a mixture that contains less dissolved solute than is possible at a given temperature
53
New cards
supersaturated solution
contains more dissolved solute than a saturated solution at the same temperature
54
New cards
molarity
the number of moles of solute per liter of solution (changes with temp)
55
New cards
dilution
- the process of adding solvent to lower the concentration of solute in a solution
- M1V1=M2V2
- M1V1=M2V2
56
New cards
three interactions in solution process
- solute-solute interaction (separate solute)
- solvent-solvent interaction (overcome IMFs)
- solvent-solute interaction
- solvent-solvent interaction (overcome IMFs)
- solvent-solute interaction
57
New cards
chromatography
separates chemical species using differing strengths of IMFs between and among solution and surface of stationary phase
58
New cards
mobile phase of chromatography
solvent
59
New cards
stationary phase of chromatography
solid, chromatography paper
60
New cards
fractional distillation
separation of liquid mixture by vaporization and then condensing vapor into liquid
61
New cards
light equation
c = λv
62
New cards
Planck's equation
E=hv
63
New cards
photoelectric effect
the emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
64
New cards
electromagnetic spectrum
the range of wavelengths or frequencies over which electromagnetic radiation extends.
65
New cards
spectroscopy
the study of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter
66
New cards
absorption spectroscopy
measures the amount of light absorbed by the sample as a function of wavelength
67
New cards
UV and visible light cause
- electronic transitions within atoms
- can be used to gather information about electronic configurations
- can be used to gather information about electronic configurations
68
New cards
infrared radiations cause covalent bonds to
- bend, stretch, and vibrate (depending on bond type and functional group)
- can be used to distinguish between compounds having different types of bonds
- can be used to distinguish between compounds having different types of bonds
69
New cards
microwaves cause
- molecular rotations
- can determine location of different atoms in a molecule
- give information about the chemical composition and structure of molecules
- can determine location of different atoms in a molecule
- give information about the chemical composition and structure of molecules
70
New cards
spectrophotometer
an instrument that measures the absorbance or transmittance of light, as a function of wavelength
71
New cards
colorimeter
a device that measures the color of foods in terms of value, hue, and chroma
72
New cards
cuvette
a straight-sided, optically clear container for holding liquid samples in a spectrophotometer or other instrument. (1 cm thick)
73
New cards
absorbance
the amount of light absorbed by the sample
74
New cards
transmittance
the amount of light that passes through the sample
75
New cards
Beer's Law
- explains the relationship between absorbance at a given wavelength and concentration
- A = εbc
- A = εbc