Chapter 21: The Lymphoid and Immune Systems
1/141
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merged flashcards from Chapter 21, McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
Microbiome
Microorganisms that reside on and in the human body; most are beneficial but some are harmful
Immune system
Cell population that inhabits all organs and defends the body from disease agents
Lymphoid system
System for immune cells that recover fluid, inspect for disease, activate responses, and return fluid
Lymphedema
Swelling due to impaired lymphoid drainage
Immune surveillance
Filtering fluid through the lymph nodes for immune responses
Lipid absorption
Absorption of lipids by the lymphoid system in the small intestine
Lymphoid system components
Lymph
Lymphatic vessels
Lymphoid tissue
Lymphoid organs
Lymph
A clear, colorless fluid similar to plasma but low in protein that serves as tissue fluid in the lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic vessels (lymphatics)
Transport lymphoid system’s lymph
Lymphoid tissue
Aggregates of lymphocytes and macrophages within the organs
Lymphoid organs
Organs where lymphoid cells are concentrated; surrounded by connective tissue capsules
Lymphatic capillaries
Microscopic vessels that allow bacteria and cells to enter via intercellular clefts
Intercellular clefts
Gaps between lymphatic capillary cells to allow bacteria and cells to enter
Lymphatic drainage
Done through collecting vessels that converge to larger lymphatic trunks
Collecting ducts (lymphoid ducts)
Where the lymphatic trunks converge (thoracic and right)
Right lymphatic duct
Recieves lymph from the right arm, right side of head and thorax; empties into right subclavian vein
Thoracic duct
Larger than right lymphatic duct; recieves lymph from below diaphragm, left arm, left side fo head, neck, and thorax; empties into left subclavian vein
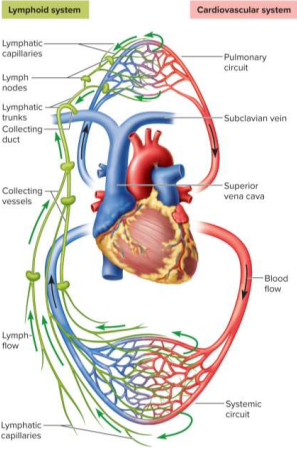
Subclavian veins
Veins below the clavicle that collect from the collecting ducts, passes through lymph nodes
Glymphatic system
Lymphatic-resembling vessels associated with neuroglia to deliver nutrients and drain wastes
Neutrophil
White blood cell type associated with the lymphoid system
Natural killer cells (NK cells)
Lymphocytes that attack and destroy infected host cells, cancerous cells
T lymphocytes (T cells)
Lymphoid system cells that mature within the thymus
B lymphocytes (B cells)
Lymphoid cells that activate to proliferate and differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells
Macrophages
Large phagocytic cells that present antigens to alert other immune cells
Dendritic cells
Antigen-presenting cells found in the skin, mucous membranes, and lymphoid organs
Diffuse lymphoid tissue
Tissue with scattered lymphocytes; prevalent in exterior-facing body passages (respiratory, digestive, urinary, reproductive)
Aggregated lymph nodes
Clusters of lymphoid nodules in the small intestine
Primary lymphoid organs
Includes the red bone marrow and thymus; are sites where T and B cells become immunocompetent
Secondary lymphoid organs
Include lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen; are sites where immuncompetent cells migrate and populate
Red bone marrow
Soft and loosely organized material separated from bone tissue for hematpoiesis and immunity
Thymus
A bilobed organ in the superior mediastinum; houses developing T cells and secretes hormones regulating activity
Involution
Degeneration and shrinkage; happens with age to the thymus
Lymph nodes
Bean-shaped structures that cleanse lymph and are sites of lymphocyte activation; ~450 in young adult
Afferent lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic vessels that lead into the lymph node
Efferent lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic vessels that lead out of the lymph node
Lymphadenitis
Swollen lymph nodes in response to antigens
Lymphadenopathy
Term for all lymph node diseases
Metastasis
Condition where cancerous cells travel to other sites for reestablishment; easy in lymphatic vessels
Tonsils
Patches of lymphoid tissue at the entrance to the pharynx; guards against ingested or inhaled pathogens
Tonsillitis
Inflammation of the palatine tonsils
Pharengeal tonsil
Tonsil on the wall of the pharynx
Palatine tonsils
Two tonsils on the posterior margin of the oral cavity
Lingual tonsils
Numerous tonsils on the base of the tongue
Spleen
The largest lymphoid organ
Purposes include:
RBC recyclation
Fetal blood production
Blood volume stabilization via plasma transfers
Splenectomy
Removal of the spleen in response to rupture; increases chances of future infections and premature death
Pathogens
Agents capable of producing disease
Viruses
Bacteria
Fungi
Other microbes
First line of defense
Skin and mucous membranes, which serve as barriers to pathogens — keratin, lysozymes, and hyaluronic acids
Second line of defense
Protections against pathogens that break the skin or mucous barriers, such as leukocytes, antimicrobial proteins, fevers, inflammation, and NK cells
Third line of defense
Adaptive immunity to specific pathogens that leave a memory
Immune system
Population of cells, chemicals, physical barriers, and physiological responses broken up into innate and adaptive immunity
Innate immunity
Defenses one is born with that protect one from a broad spectrum of disease agents; defends at point of invasion, is nonspecific, and lacks memory to pathogens
Adaptive immunity
Defenses against specific pathogens, developed only upon exposure while maintaining a memory
Keratin
Hard and easily replaced protein on skin that maintains a dry and nutrient-poor surface
Acid mantle
Thin film of lactic and fatty acids from sweat and sebum that inhibits bacterial growth
Mucous membranes
Covers the digestive, urinary, respiratory, and reproductive tracts to trap microbes
Lysozyme
Enzymes in the mucous membrane that destroys bacterial cell walls in the first line of defense
Hyaluronic acid
Acid that serves as a barrier to prevent bacterial growth in the first line of defense
Phagocytes
Cells that engulf foreign matter
Leukocyte types
Neutrophils (bacterial)
Eosinophils (parasitic)
Basophils (dilation)
Monocytes (macrophages)
Lymphocytes (memory)
Neutrophils
Type of leukocyte that wanders in connective tissue, killing bacteria either through phagocytization or chemicals
Eosinophils
Type of leukocyte found in mucous membranes to guard against parasites (tapeworms, roundworms) and allergens
Basophils
Type of leukocyte that secretes chemicals aiding mobility and action, such as histamine (vasodilation) and heparin (stops blocking clots)
Lymphocytes
Type of leukocyte that includes T and B cells for adaptive immunity and NK cells for innate immunity
Monocytes
Type of leukocyte that emigrates from the blood into connective tissue to transform into macrophages
Macrophage system
Includes all phagocytic cells except leukocytes — includes monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and others
Interferons
Proteins secreted by virally infected cells and immune cells to “alarm” nearby cells, which bind to nearby receptors for antiviral protein production and NK cell/macrophage stimulation
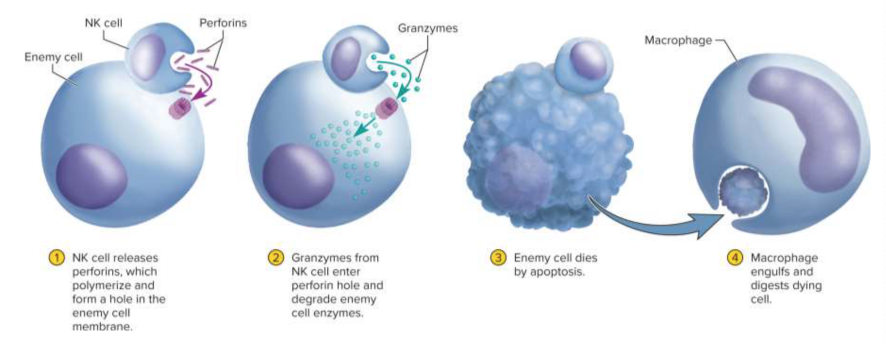
Natural killer cells (NK cells)
Type of cell on continuous patrol for pathogens, diseased host cells for destruction through binding
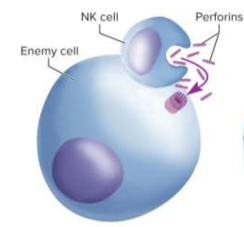
Perforins
Proteins released by NK cells to created holes in an infected cell’s plasma membrane
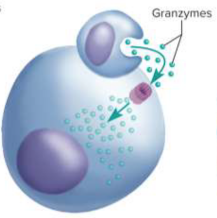
Granzymes
Protein-degrading enzymes that degrade cellular enzymes and induce apoptosis
Fever (pyrexia)
An abnormal elevation of body temperature caused from trauma, infections, and drug reactions to promote interferon activity, metabolic rate
Febrile
Pertaining to fever
Antipyretics
Fever-reducing medications; may slow down recovery
Exogenous pyrogens
Fever-producing agents originating outside the body, such as glycolipids on bacteria and viruses
Endogenous pyrogens
Fever-producing agents originating from within the body, increasing the set point
Fever stages
Onset
Stadium
Defervescence
Onset
The first stage of a fever where the body temperature rises
Stadium
The second stage of a fever where the body temperature oscillates around a higher set point
Defervescence
The third and last stage of a fever where body temperature returns to normal
Reye syndrome
Disorder in children younger than 15 following an acute viral infection like chickenpox or influenza
Involves swelling of neurons, fatty liver, and swelling brain pressure triggered by aspirin usage
Inflammation
Local defensive response to tissue injury, including trauma and infection for pathogen spread limitation and debris removal
Inflammation signs
Redness
Swelling
Heat
Pain
Hypermia
Increase of blood flow during inflammation, causing increased redness and heat
Swelling (edema)
Accumulation and enlargement of body due to increased fluid filtration from capillaries during inflammation
Inflammation pain
Caused by nerve injury, pressure, and stimulation by toxins
Pus
Yellow accumulation of dead neutrophils, bacteria, cellular debris, and tissue fluid
Abscess
Accumulation of pus in a tissue cavity
Adaptive immunity
The third line of defense in the body with a systemic effect, specificity, and memory to distinguish it from innate immunity
Systemic effect
Property of active immunity meaning that it acts throughout the body
Specificity
Property of adaptive immunity meaning that it creates protection to pathogens individually
Memory
Property of adaptive immunity meaning that it recognizes previous pathogens for quick reactions
Active immunity
The body does work to create antibodies
Natural active immunity
The body produces its own antibodies or T cells as a result of infection or exposure to antigen
Artificial active immunity
The body produces antibodies or T cells a result of vaccination against disease
Vaccine
Injection consisting of dead or weakened to stimulate immune responses for antibodies without causing disease
Booster shots
Additional injections on top of vaccinations to restimulate immune memory
Passive immunity
Something outside the body produces and transfers antibodies or T cells
Natural passive immunity
Temporary immunity from antibodies from another person; most common example is through antibody transfer in placenta and breast-feeding
Artificial passive immunity
Temporary immunity from injection of immune serum from another person or animal; emergency treatment for bites, botulism, tetanus, rabies, and other diseases
Antigen (Ag)
Any molecule that can bind an antibody; helps distinguish bodily from foreign cells
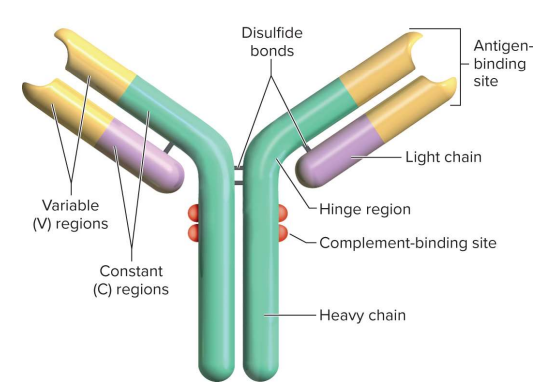
Antibodies (immunoglobulins)
Proteins that play defensive roles, some on immune cell membranes