4th Six-Weeks, Unit II: The Cold War
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Cold War
(1945-1991) The period after the Second World War marked by rivalry and tension between the two nuclear superpowers, the United States and the communist government of the Soviet Union. The Cold War ended when the Soviet government collapsed in 1991.

rivalry
A competition between two or more groups. During the Cold War the U.S. and the Soviet Union (U.S.S.R) competed for world power.
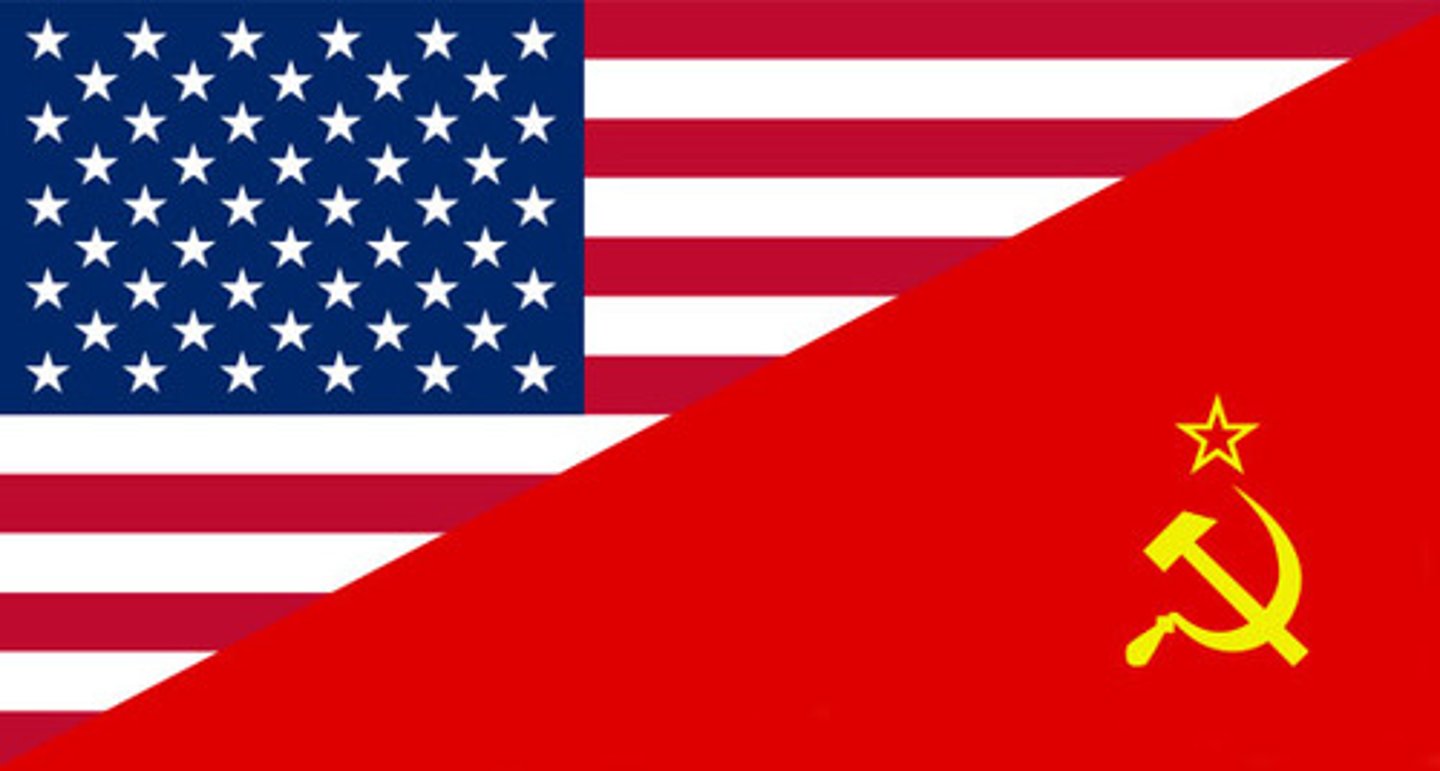
superpower
a huge powerful country (state)

communism
A political system characterized by a centrally planned economy with all economic and political power resting in the hands of the central government. A form of socialism that abolishes private ownership.

containment
A U.S. foreign policy adopted by President Harry Truman in the late 1940s, in which the United States tried to stop the spread of communism by creating alliances and helping weak countries to resist Soviet advances
Truman Doctrine
1947, President Truman's policy of providing economic and military aid to any country threatened by communism or totalitarian ideology, mainly helped Greece and Turkey

Marshall Plan
..., a United States program of economic aid for the reconstruction of Europe (1948-1952). Helped contain communism during the early years of the Cold War.

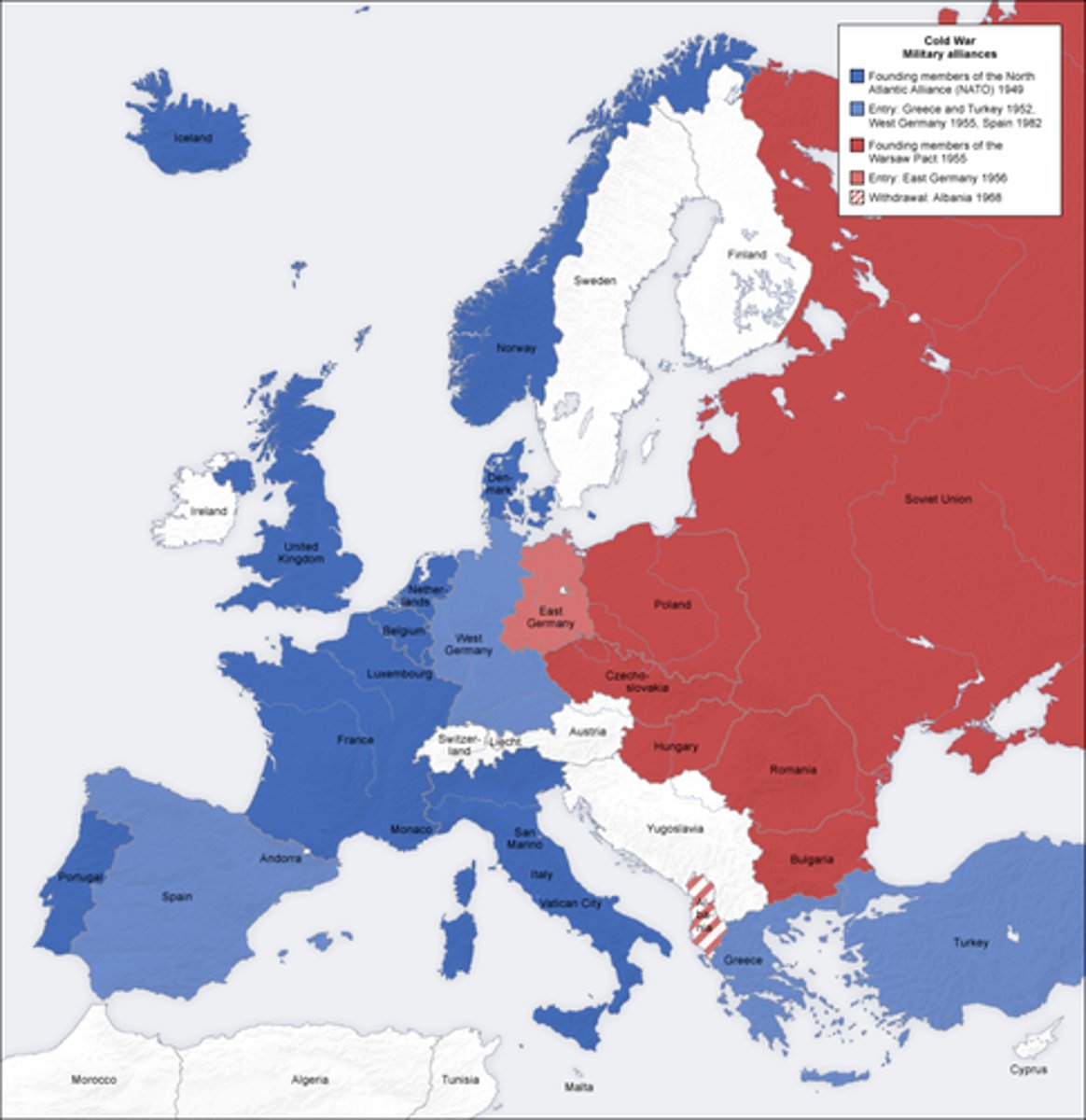
NATO
..., North Atlantic Treaty Organization; an alliance made to defend one another if they were attacked by any other country; US, England, France, Canada, Western European countries. A response to the threat of Soviet expansion.
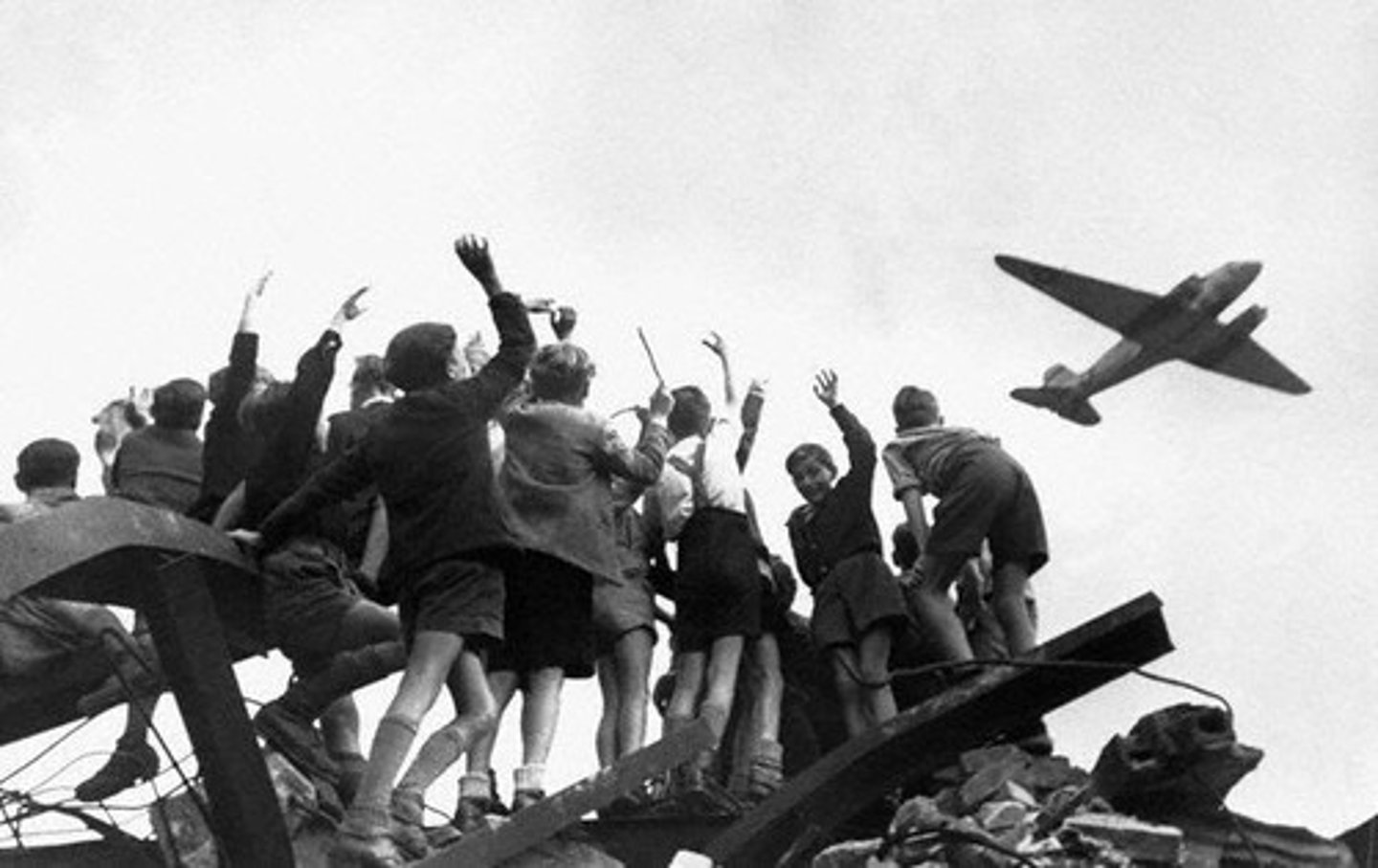
Berlin Airlift
n 1948, the US supplied food and fuel to citizens of west Berlin when the Russians closed off land access to Berlin

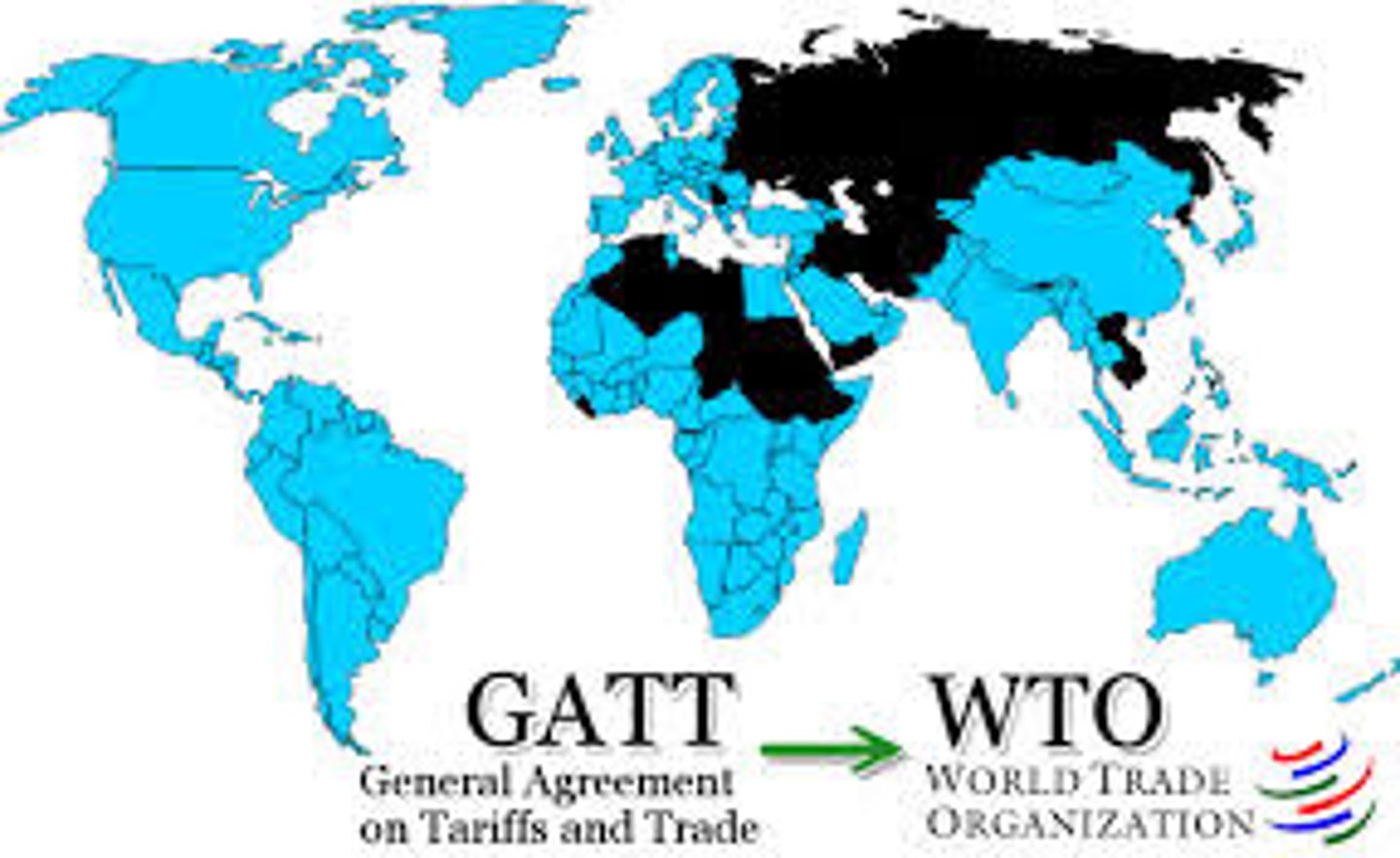
GATT (General Agreement of Tariffs and Trade)
1947 - to promote unrestricted trade, particularly reduction of tariff
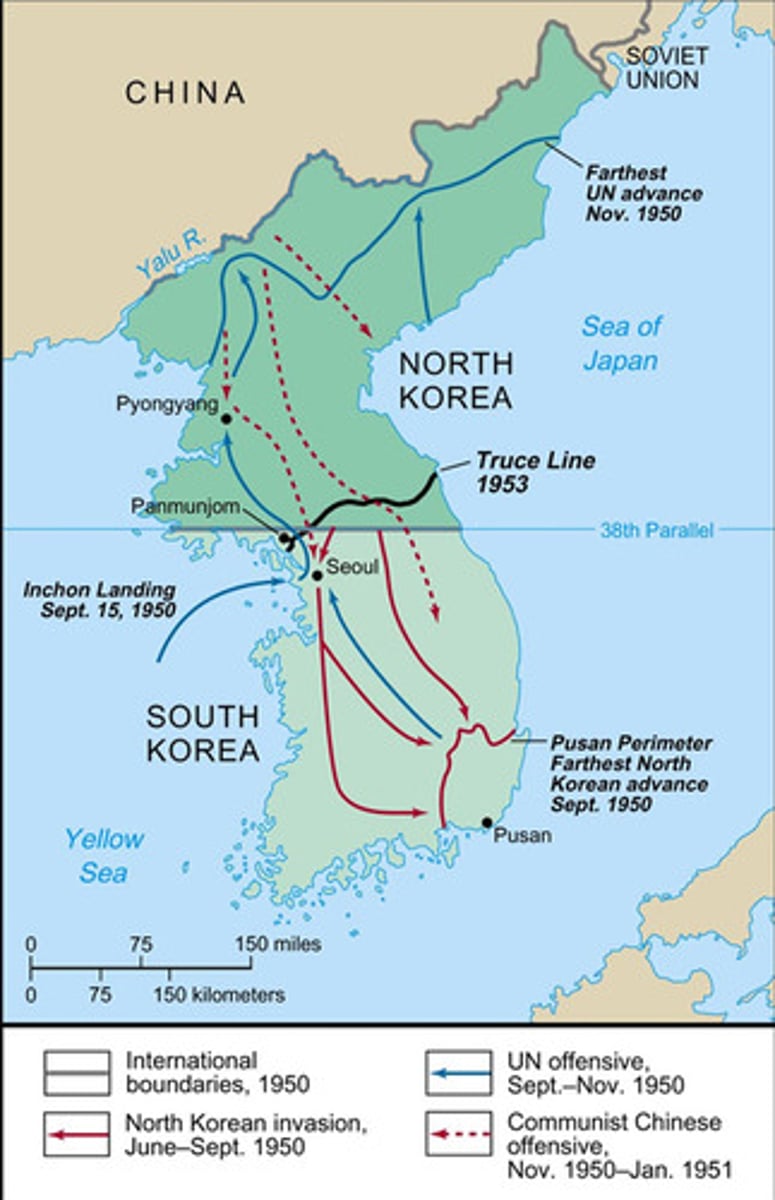
Korean War
(1950-3) A conflict between UN forces (primarily US and S Korea) against North Korea, and later China; Gen. Douglas Macarthur led UN forces and was later replaced by Gen. Ridgeway; Resulted in Korea remaining divided at the 38th parallel.
defense spending
government spending for military armaments, equipment, and personnel

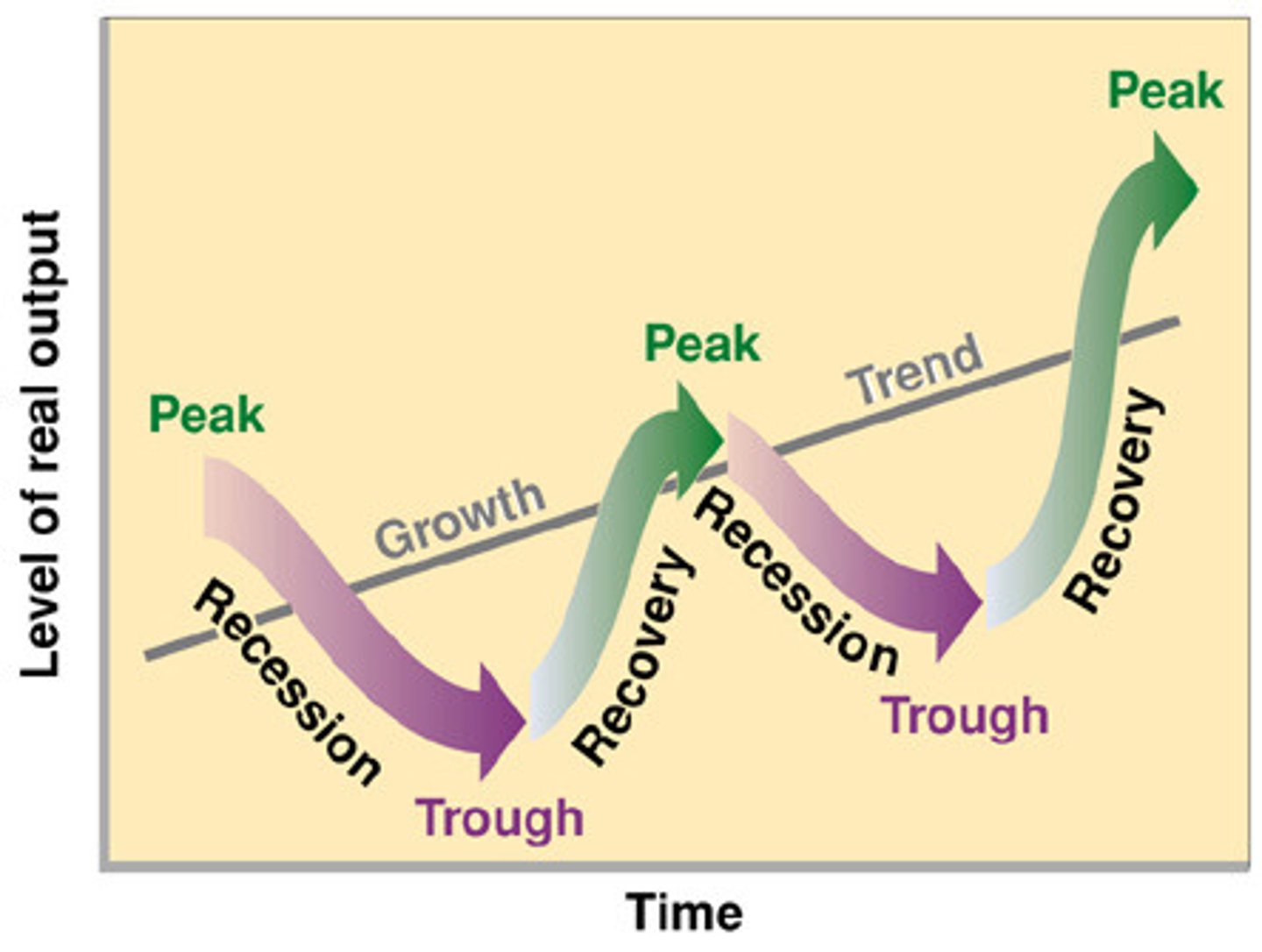
business cycle
Recurring fluctuations in economic activity consisting of recession and recovery and growth and decline
military-industrial complex
Eisenhower's term for the close ties between the defense industry and the military that might influence government policy.

Cuban Missle Crisis
(1962) crisis that arose between the United States and the Soviet Union over a Soviet attempt to deploy nuclear missles in Cuba

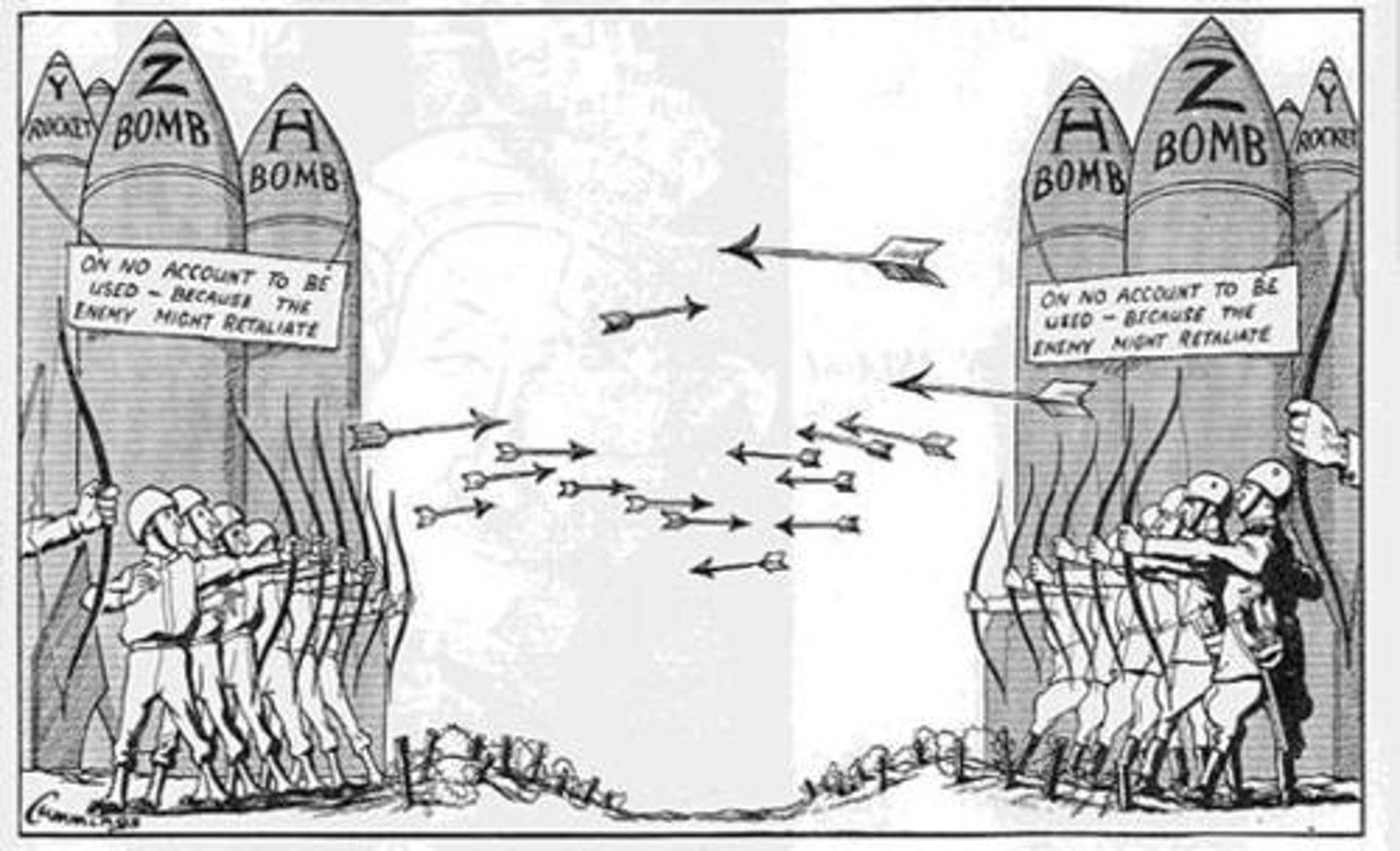
Arms Race
Cold war competition between the U.S. and Soviet Union to build up their respective armed forces and weapons
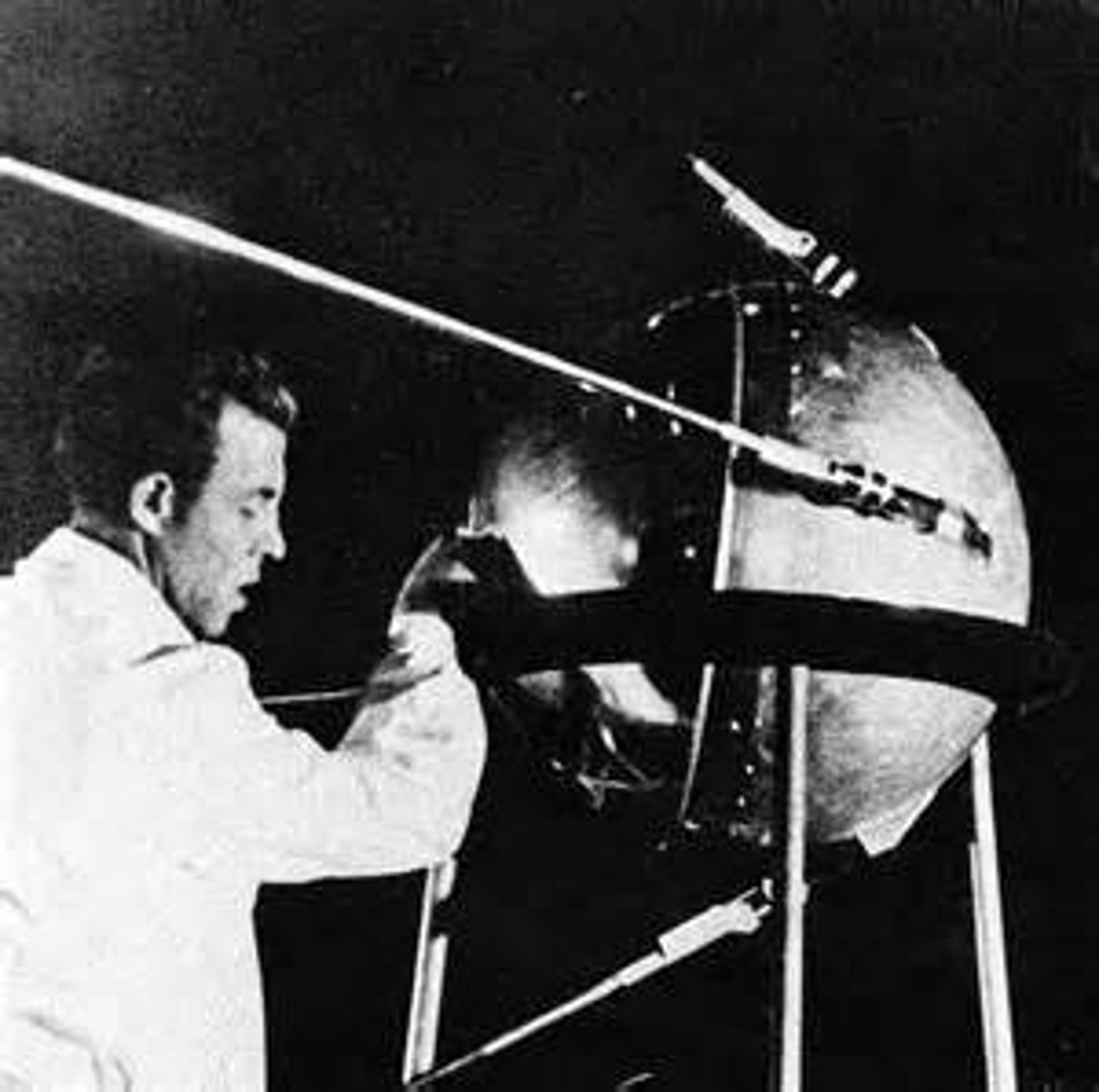
Sputnik
First artificial Earth satellite, it was launched by Moscow in 1957 and sparked U.S. fears of Soviet dominance in technology and outer space. It led to the creation of NASA and the space race.

satellite
An object that revolves around another object in space

McCarthyism
The term associated with Senator Joseph McCarthy who led the search for communists in America during the early 1950s through his leadership in the House Un-American Activities Committee. Eventually McCarthy was discredited for these "red scare" communist witch-hunts.

Venona Papers
deciphered messages from the Soviets that revealed the names of Soviet spies. Led to Julius Rosenberg's execution and the trial of Alger Hiss. It showed 359 individuals who were involved in espionage for Soviets

HUAC (House Un-American Activities Committee)
~ Beginning in 1947, this committee investigated possible Communist infiltration of the entertainment industry and the government.

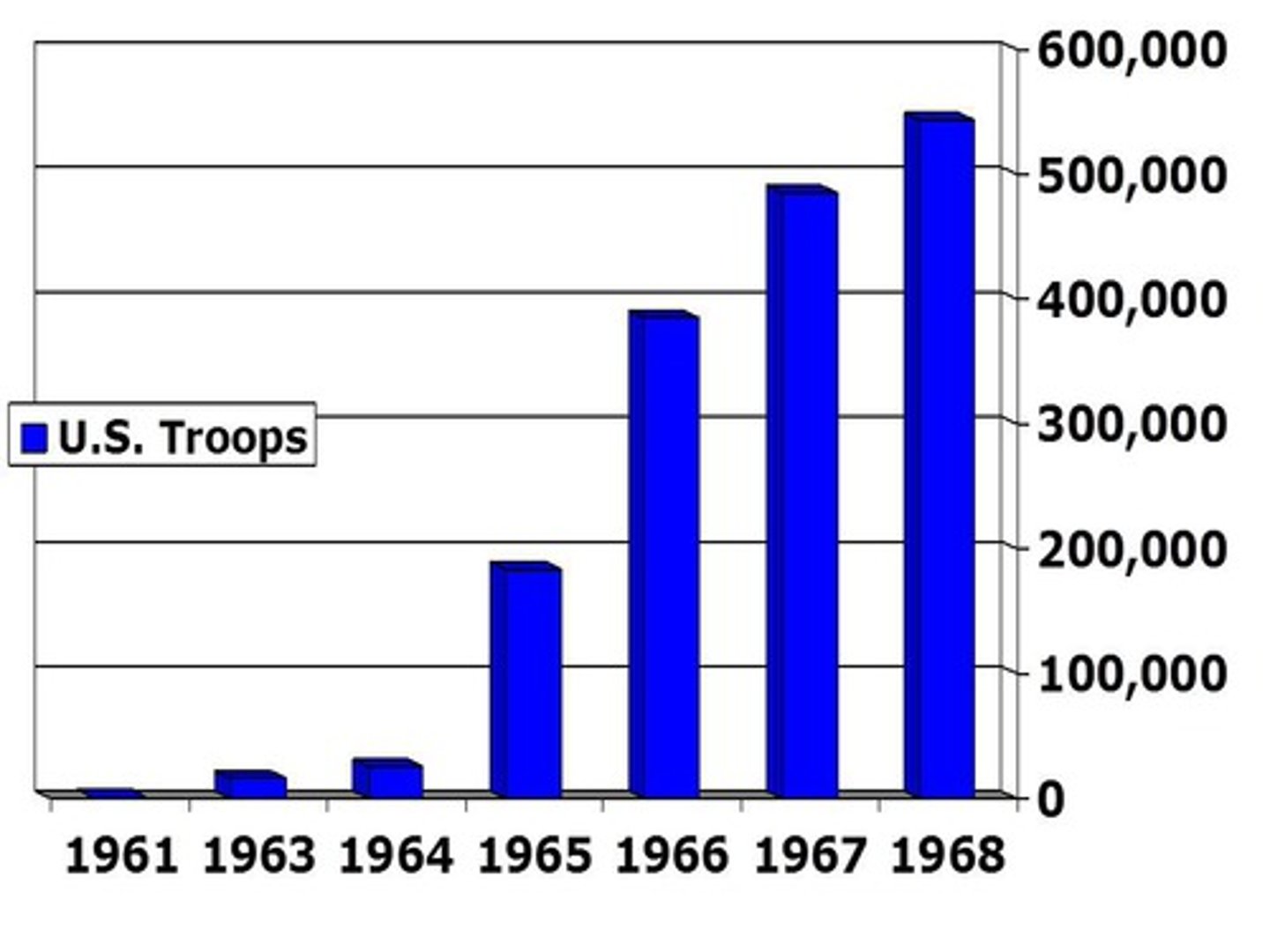
Vietnam War
58,000 Americans would lose their lives in the first televised war. The United States wanted to prevent communism from spreading to South Vietnam, while North Vietnamese forces were fighting for independence from foreign occupation.

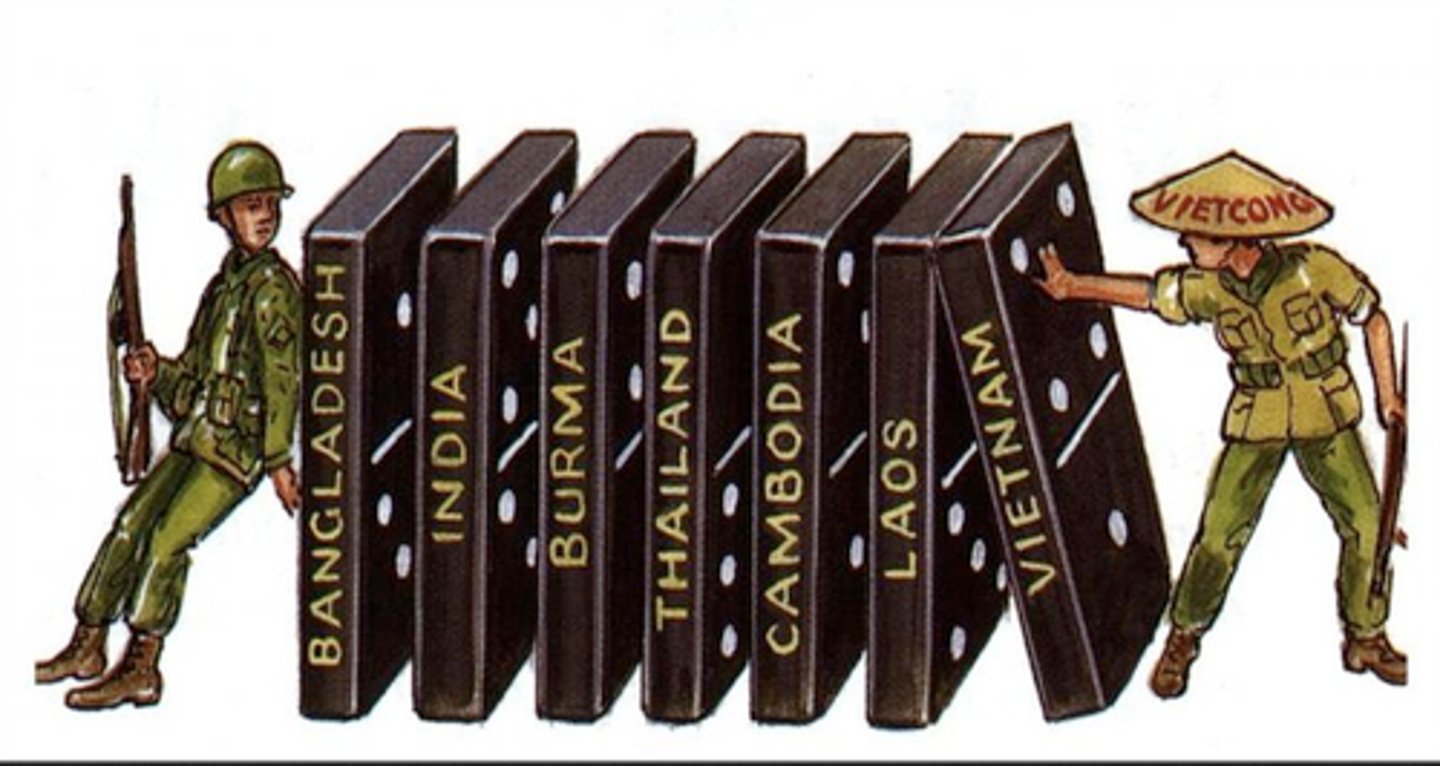
domino theory
A theory that if one nation comes under Communist control, then neighboring nations will also come under Communist control. Leading to American involvement in several conflicts, such as Korea and Vietnam.

Tet Offensive
1968, during Tet, the Vietnam lunar new year - Viet Cong and North Vietnamese Army raiding forces attacked provincial capitals throughout Vietnam, even seizing the U.S. embassy for a time. U.S. opinion began turning against the war.
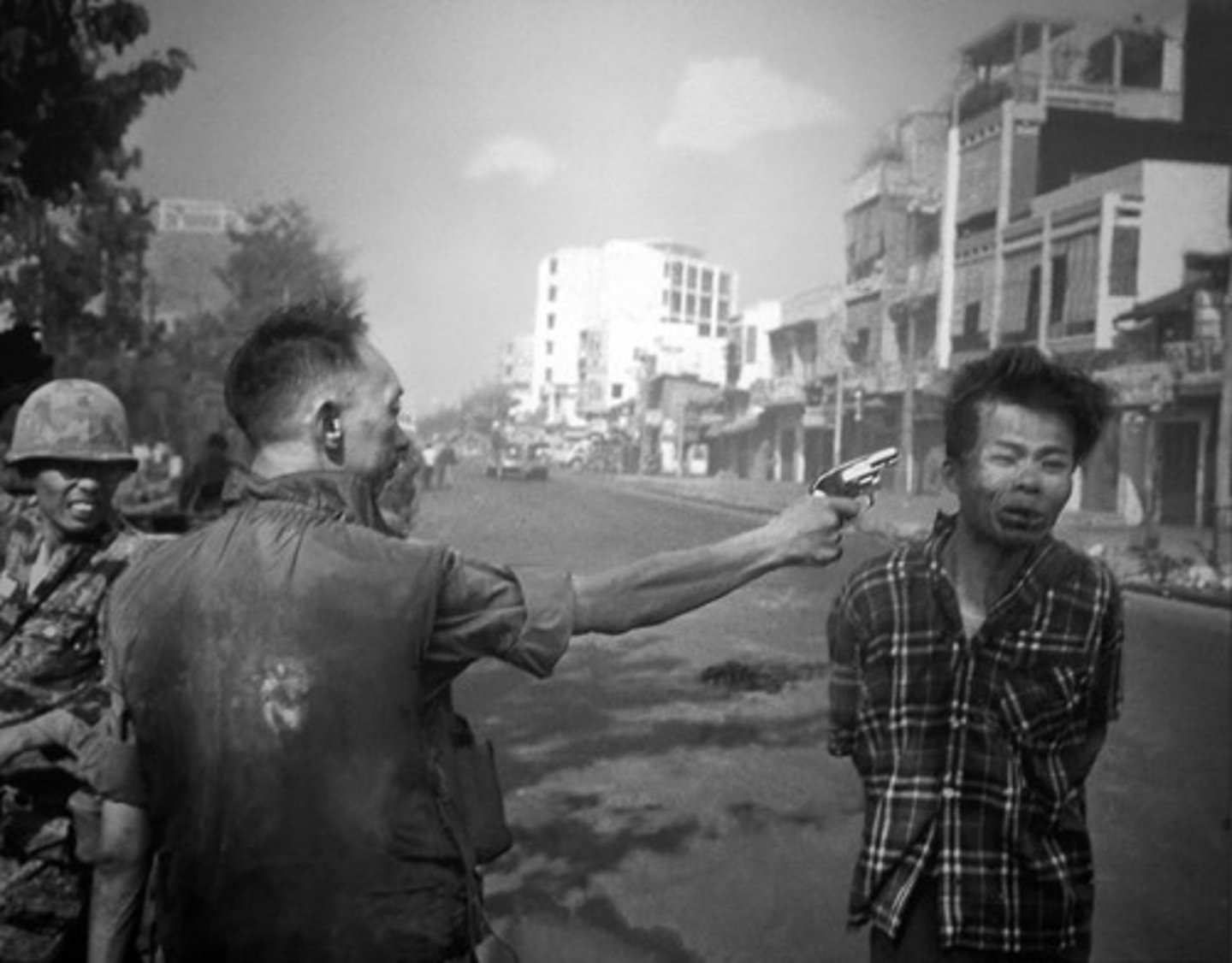

Gulf of Tonkin Resolution
was a joint resolution of the U.S. Congress passed on August 7, 1964 in direct response to a minor naval engagement known as the Gulf of Tonkin Incident. It is of historical significance because it gave U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson authorization, without a formal declaration of war by Congress, for the use of military force in Southeast Asia.
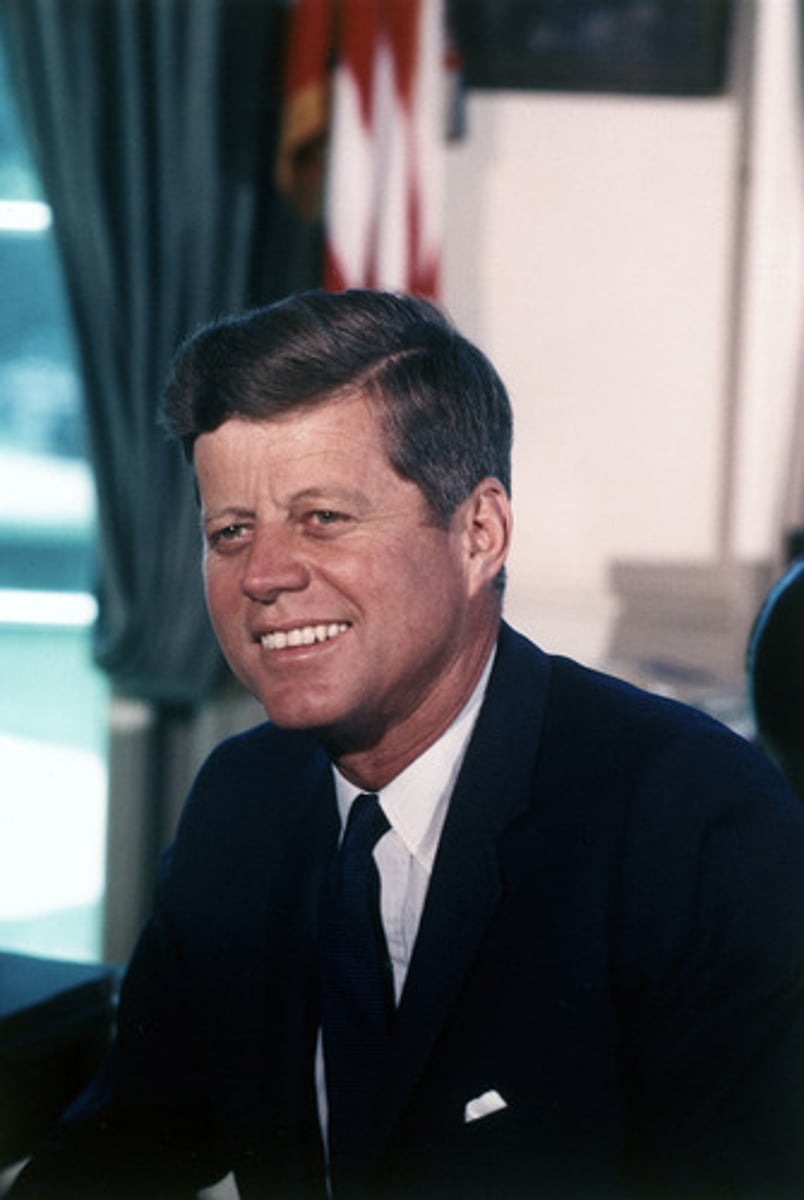
John F. Kennedy
35th President of the United States 35th President of the United States; only president to have won a Pulitzer Prize; events during his administration include the Bay of Pigs Invasion, the Cuban Missile Crisis, the building of the Berlin Wall, the Space Race, the African American Civil Rights Movement and early events of the Vietnam War; assassinated in Dallas, TX in 1963

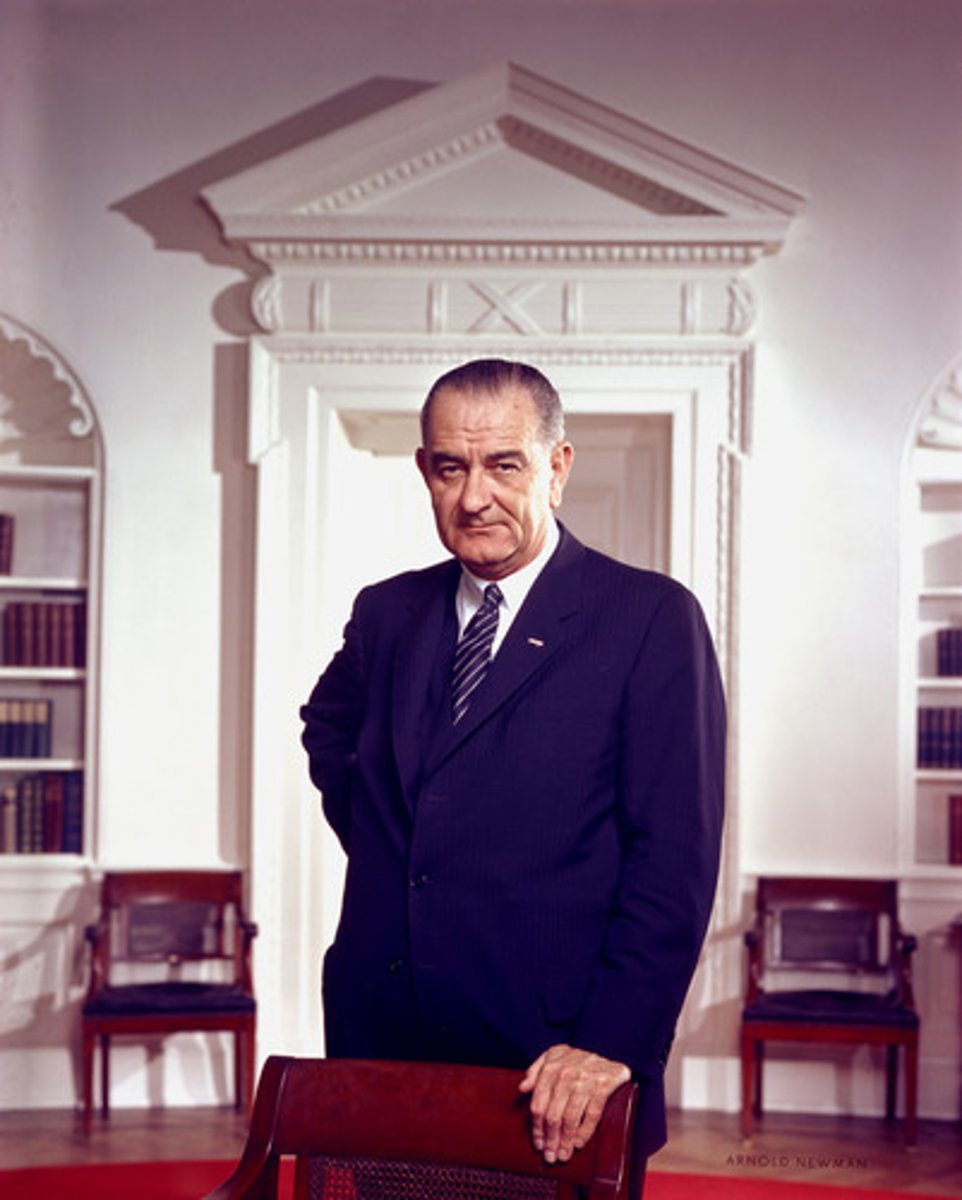
Lyndon Johnson
1963-1969, Democrat , signed the Civil Rights Act of 1964 into law and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. He had a War on Poverty in his agenda, including the Great Society, the Economic Opportunity Act, and other programs that provided food stamps and welfare to families in need. He also created a Department of Housing and Urban Development. His most important legislation was Medicare and Medicaid.

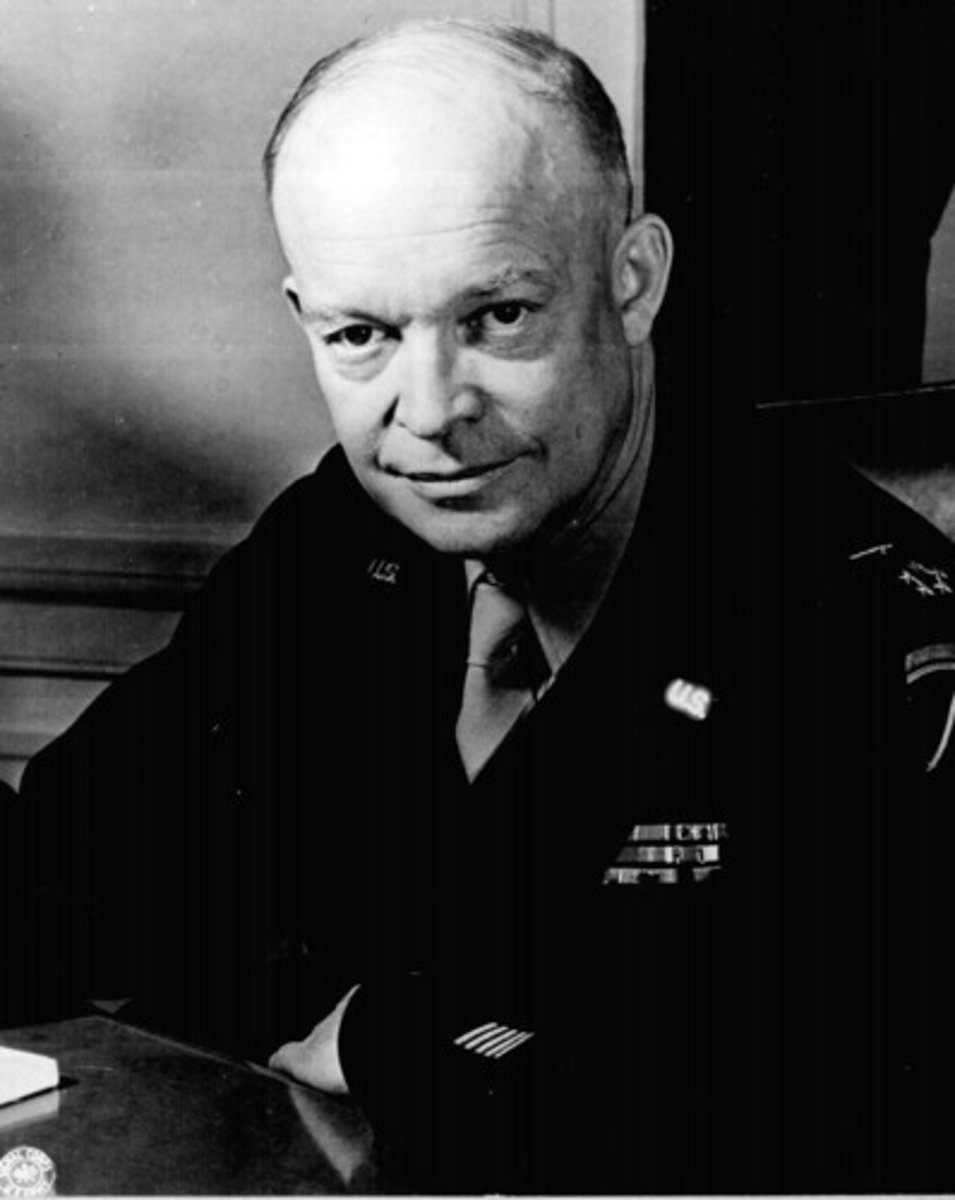
Dwight Eisenhower
"Ike" was the 34th President of the United States from 1953 until 1961. He was a five-star general in the United States Army during World War II and served as Supreme Commander.

Harry Truman
33rd President of the United States. Led the U.S. to victory in WWII making the ultimate decision to use atomic weapons for the first time. Shaped U.S. foreign policy regarding the Soviet Union after the war.
