Quiz 2: Cells
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TEM images: be familiar with recognizing organelles Organelles: recognize and/or draw them and know their purpose in the cell What’s the difference between free and bound ribosomes? Miller and Urey experiment what was it and why was it significant? Where did life likely originate and how do we know? What steps had to happen before the first cell was made? Endosymbiotic theory: what is it and what evidence is there for it? Life functions, of paramecium and Chlamydomonas Know how to calculate magnification and use scale bars to calculate the actual size of a cell in an image. Structure of prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes Be able to compare and contrast prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells What are some advantages of having compartments
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
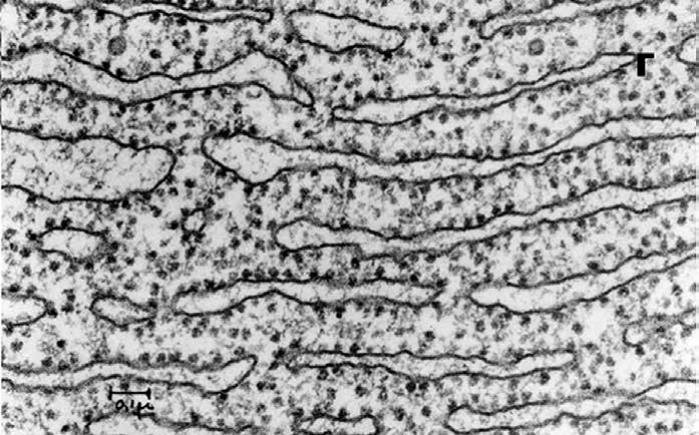
What organelle is this?
Rough ER
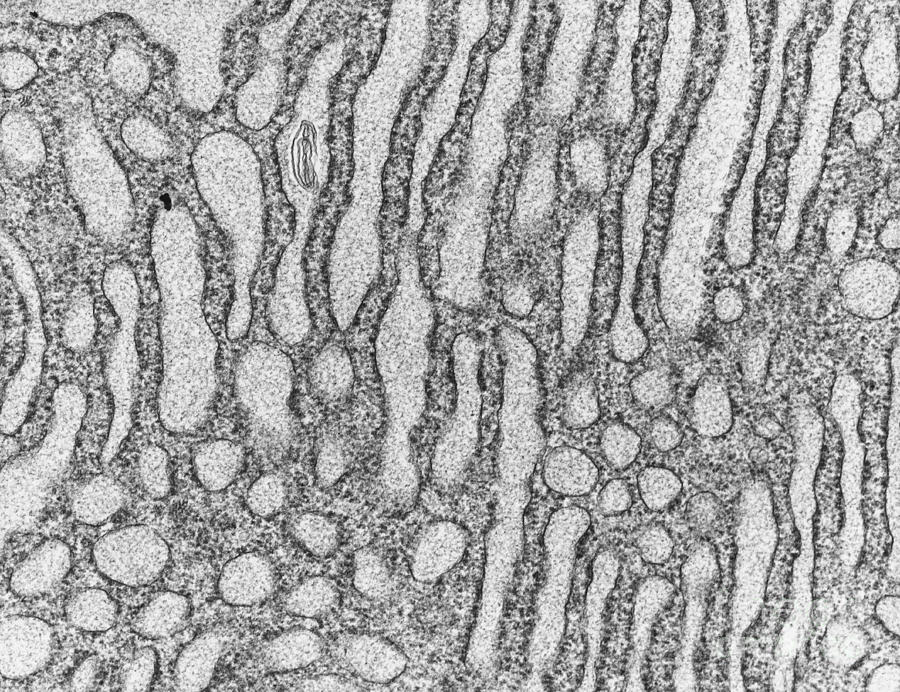
What organelle is this
Smooth er
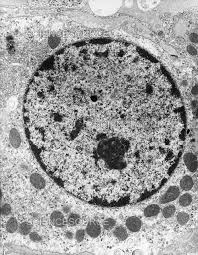
What organelle is this?
Nucleus
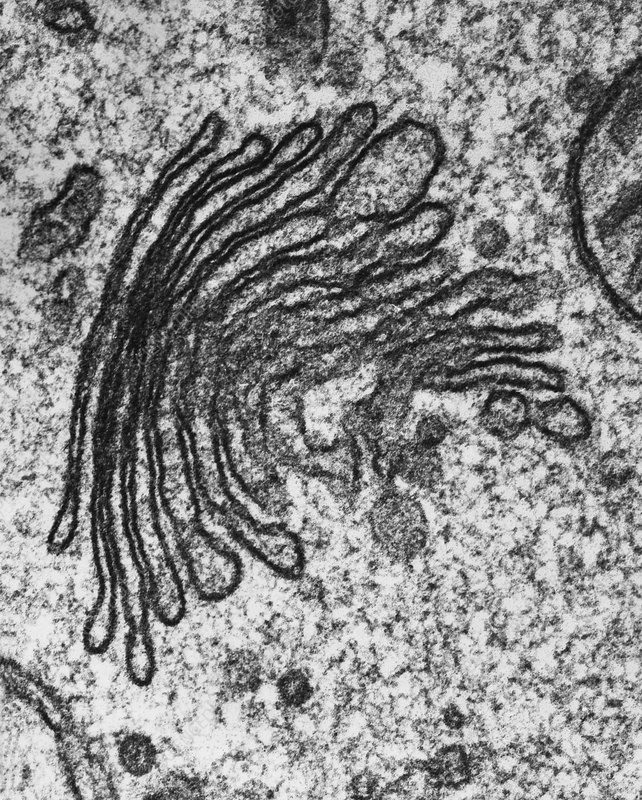
What organelle is this
Golgi apparatus
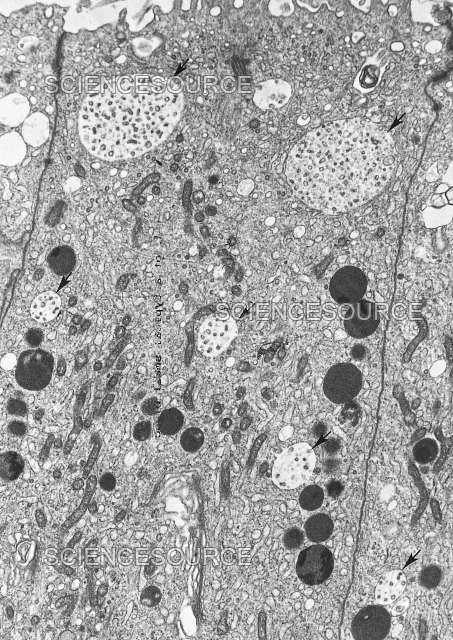
What organelle are the dark spots?
Lysosomes
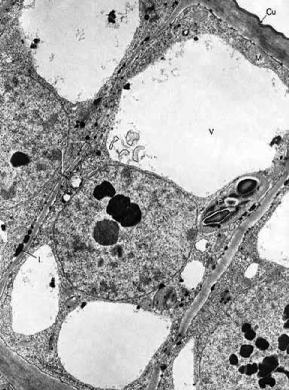
What organelle is the large white space?
Vacuole
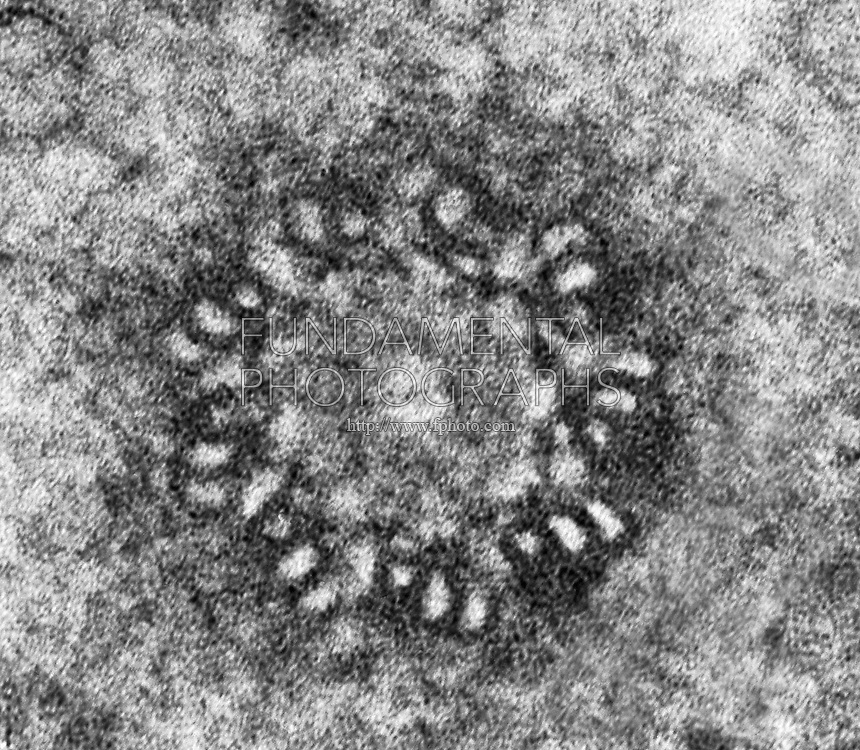
What organelle is this?
Centrosome
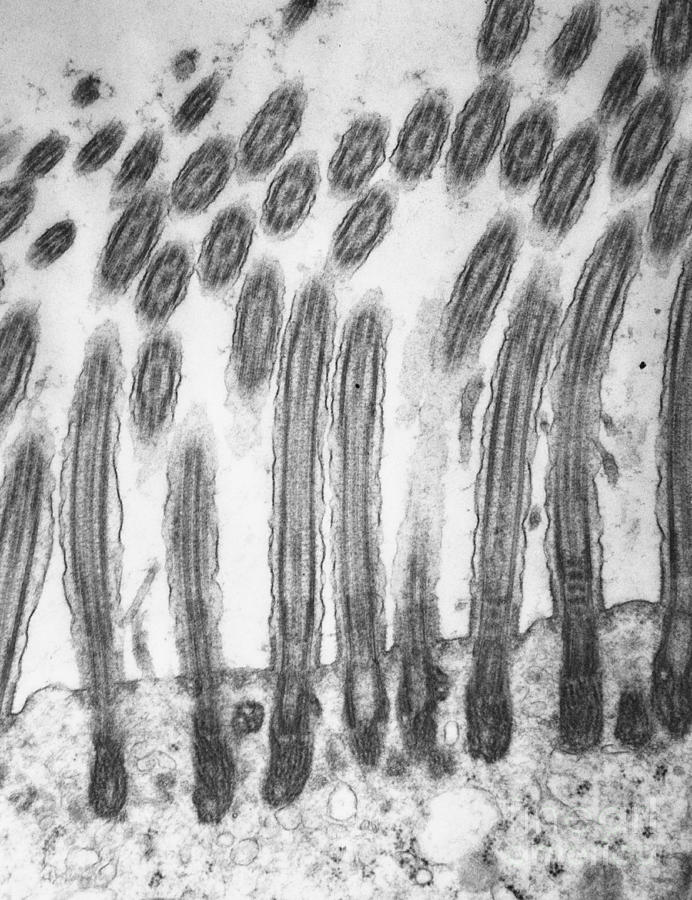
What is this?
Cilia
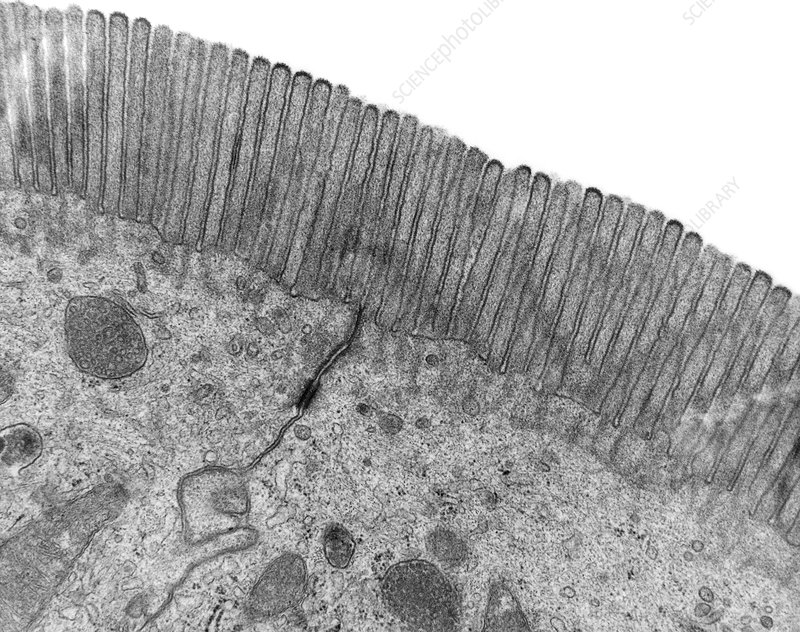
What is this?
Microvilli
What’s the difference between cilia and microvilli?
Cilia are longer and thicker than microvilli. Cilia can move while microvilli cannot. Cilia look more like hairs, while microvilli are folded cell membranes.
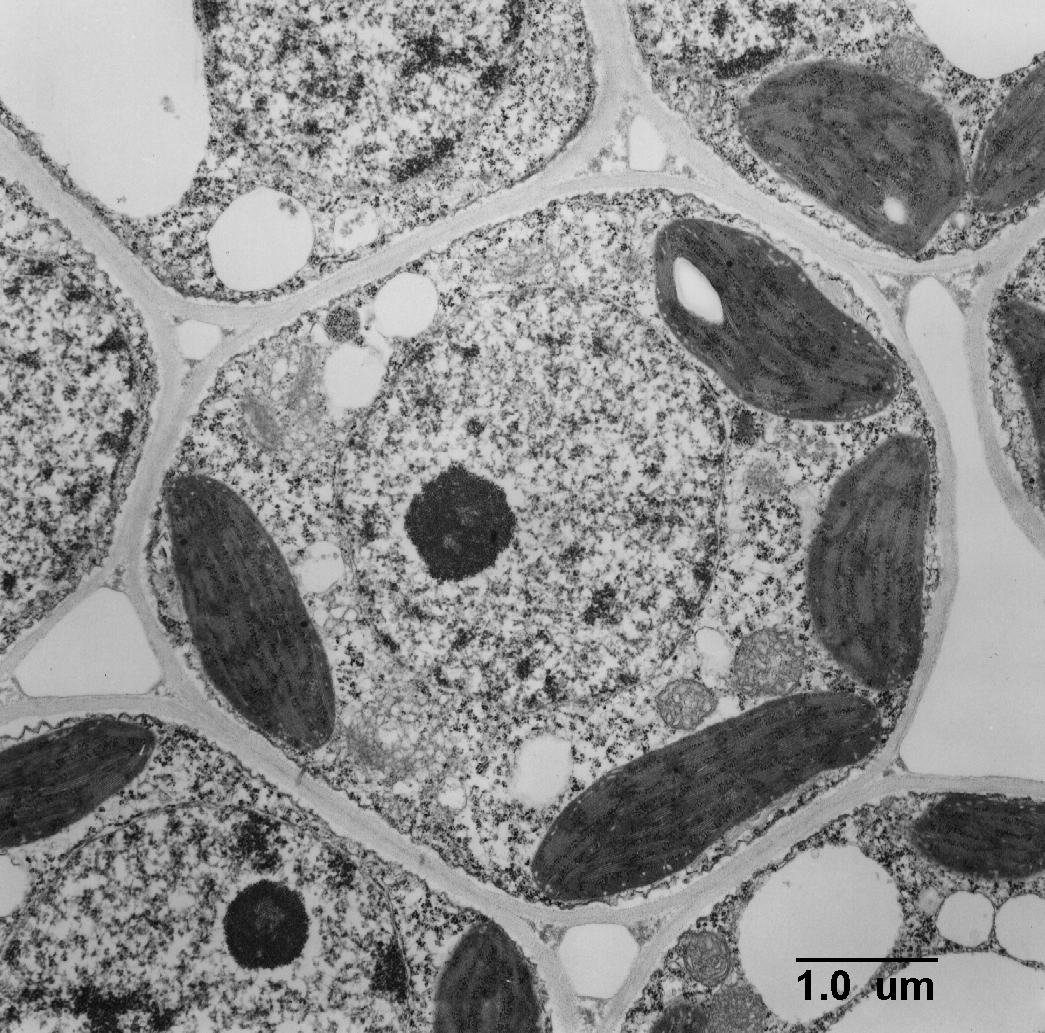
Prokaryote, plant or animal cell?
Plant, because it has chloroplast and large vacuoles
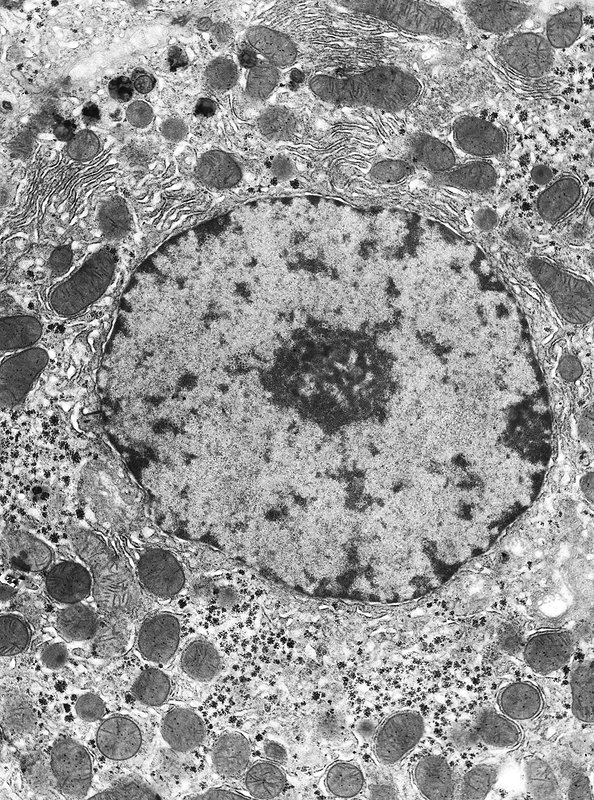
Prokaryote, plant or animal cell?
Animal cell, no cell wall, no large vacuole (only small ones, you can see little lysosomes
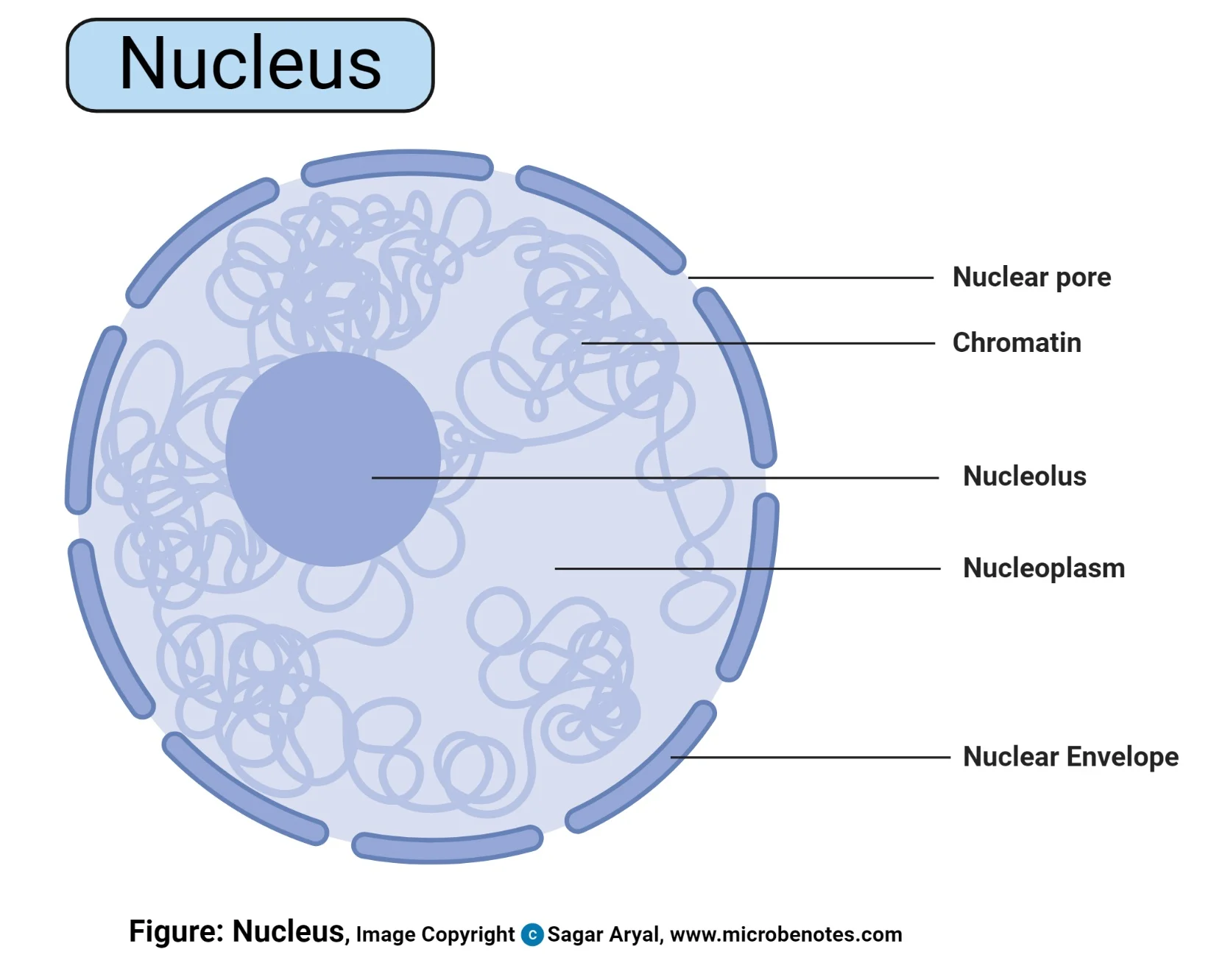
What is the location, and function of a nuclues
DNA replication, transcription, and RNA processing all take place within the nucleus.
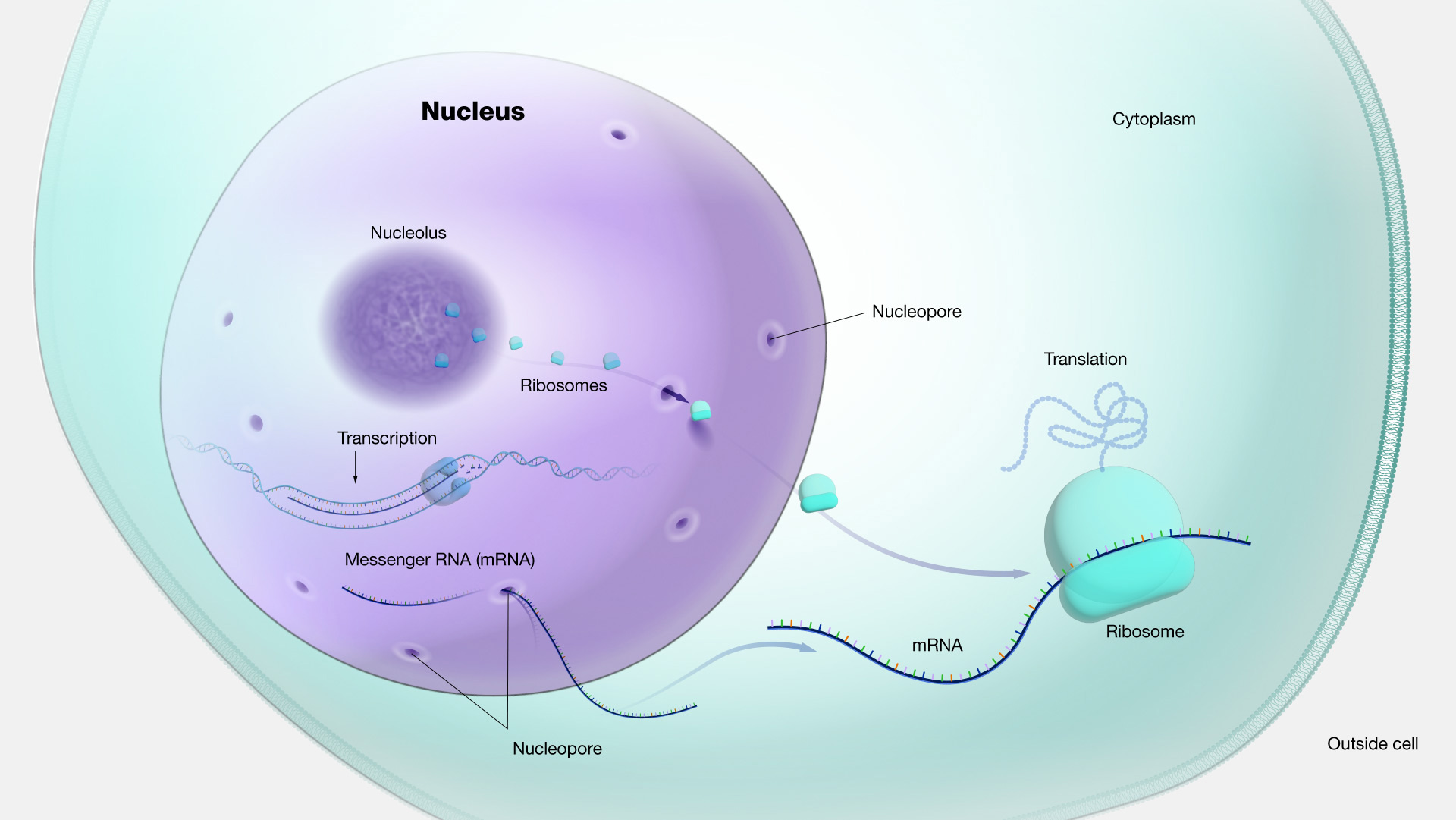
What is the structure of a nucleus
Structure can be generally divided into two distinct compartments: (i) The nuclear envelope, consisting of the inner and outer nuclear membrane, the nuclear pores, and the nuclear lamina, and (ii) the nuclear interior
What’s the difference between free and bound ribosomes?
Free ribosomes produce proteins for the cell, they just float around the cytoplasm. Bound synthesizes polypeptides that are secreted from the cell or become integral proteins in the cell membrane, attached to rough ER.
What was the Miller-Urey experiment?
An experiement that simulated the conditions thought at the time to be present in the atmosphere of the early, prebiotic Earth.
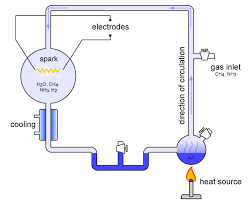
Why was the Millery-Urey experiment significant?
Provided the first evidence that organic molecules could be spontaneously produced from only inorganic molecules (supported Oparin and Haldane’s hypothesis).
Where did life likely originate and how do we know?
No “standard model” for the the origin of life on early Earth
What steps had to happen before the first cell was made?
The synthesis of simple organic molecules from inorganic compounds.
The assembly of these organic molecules into polymers.
The formation of a polymer that can self replicate (enabling inheritance).
Packaging of molecules into membranes with an internal chemistry different from the surroundings.
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
Eukaryotic cells are believed to have evolved via endosymbiosis – whereby one cell was engulfed by another and became assimilated into its cellular structure
Current evidence says that all eukaryotes evolved from a common unicellular prokaryote
This prokaryotic ancestor engulfed another aerobic bacterium, which over time lost its independent utility and developed into the mitochondria
What evidence is there for endosymbiotic theory?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are believed to have became due to endosymbiosis.
both have a double membrane (the outer membrane may have been vesicular in origin)
both have their own DNA, which is naked and circular (like in prokaryotes)
both have 70S ribosomes, which are also found in prokaryotic cells
Life functions of chlamydomonas (eukaryotic, lives in soil, fresh water, oceans, snow, etc.)
nutrition: photosynthesis
metabolism: both cytoplasm and chloroplast contain dissolved enzymes that catalyze metabolic reactions
move: A light sensitive “eyespot” allows Chlamydomonas to sense light and move to it using its two flagella,
also shows the organism's ability to respond to changes in the environment.
grow: until it reaches a maximum surface area to volume ratio, at which point it will divide.
reproduction: asexually via mitosis
The nucleus of the cell divides via mitosis to make another nuclei before the cell reproduces asexually. The nuclei can also fuse and divide to carry out a form of sexual reproduction .
excretion: oxygen byproduct of photosynthesis diffuses out through the cell membrane
homeostasis: excess water within the cell is collected into a pair of “contractile vacuoles” that swell and expel water through an opening in the cell membrane.
Life functions of parameciums (lives in freshwater, eukaryotic)
nutrition: eats smaller organisms
metabolism: cytoplasm contains dissolved enzymes that catalyze metabolic reactions
movement: with its cilia
response: in regards to its environment moves
grows until it reaches a maximum surface area to width and then divides
reproduction: does it asexually using mitosis, but can do it sexually by fusing two parameciums together
excretion: excretes waste out of an anal pore
homeostasis: contractile vacuole will swell and expel water to reach homeostasis (balance in inner workings)
contrast prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic cells containing membrane-bound organelles and are the basis for both unicellular and multicellular organisms. Prokaryotic cells do not have any membrane-bound organelles and are always part of unicellular organisms.
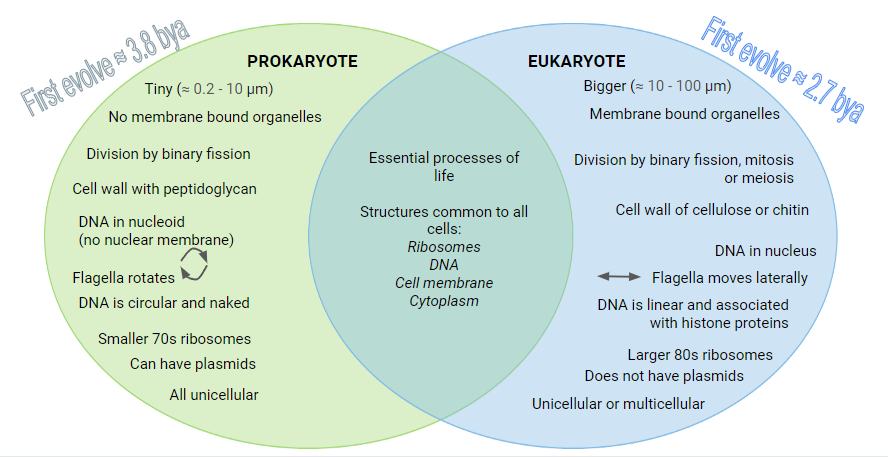
Compare and contrast the organelles within prokaryotes and eukaryotes. What do they have in common?
DNA
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
What are some advantages of having compartments?
The compartments are distinct from the environment of the surrounding cytosol and are tailored to the specific functions of the organelle. Allows for more complex stuff to happen simultaneously.
What are some advantages of having compartments in the cytoplasm?
Enzymes and metabolites can be concentrated in a small space, increasing the chance for collision between active site and substrate
Substances that can damage cells can be isolated within a membrane, protecting remaining structures from degradation
Conditions, such as pH, can be maintained at an optimal value for a particular reaction
Large areas of membrane can become dense with proteins for a specific process
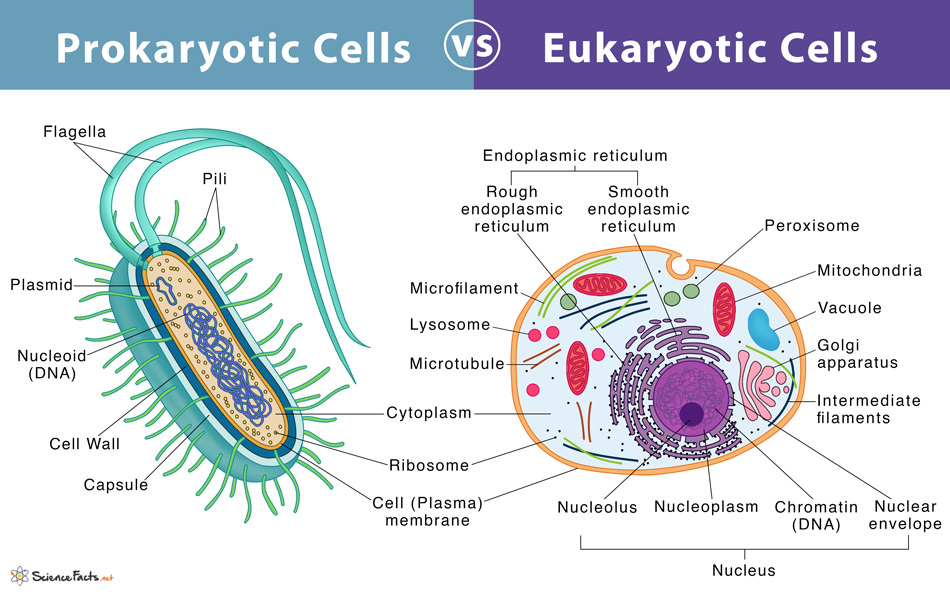
Structures in a prokaryotic?
Cell (plasma) membrane: responsible for regulating what materials move into and out of the cell
Cytoplasm (cytosol): gel-like fluid substance (mostly water with many dissolved molecules), site of metabolic reactions
Ribosome: build proteins during translation
Cell wall: provides shape and allows the cell to withstand turgor pressure without bursting
Pili*: enable the cell attach to surfaces, swap DNA with other cells and may be used to harpoon DNA in the environment
Capsule*: helps the cell keep from dehydrating and adhere to surfaces
Flagellum*: Long extensions used in cell locomotion
Prokaryotic cell data
naked (not associated with proteins)
Found in
Plasmid (extra pieces of DNA)
Nucleoid (main DNA of the cell)
DNA is a single loop, not enclosed in a membrane, it is found freely in the cytoplasm
Common structures between plant and animal cells
Nucleus
Free and bound 80s ribosomes
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Vesicles
Lysosome
Mitochondria
Chloroplast
Vacuole
Microtubules and Centrioles
Cytoskeleton
Cilia and Flagella
What is life?
made of cells
textbook says
Physical structures of life such as cells and DNA.
Physiological processes of life like growth and reproduction
Implication of early cells
Proof for LUCA
LUCA would have been a small, single-celled prokaryotic cell .
was an obligate anaerobe (did not use oxygen)
was a chemoautotroph, obtaining energy from hydrogen and converting
carbon dioxide and nitrogen into essential organic compounds
was able to live in extreme heat