Physics - 13 Electromagnetic Waves - 13.3 Communications & 13.4 Ultraviolet Waves, X-Rays, and Gamma Rays
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Carrier wave
waves used to carry any type of signal
How shorter wavelength of carrier wave affects properties [3]:
- more information
- shorter range (due to higher absorption)
- less dispersion
Radio wave transmission [3]:
- long wavelength (LW)
- medium wavelength (AM)
- short wavelength (FM)
Radio wave transmission: long wavelength (LW) [4]
- ground waves
- long range
- follows curvature of Earth and diffracts around objects
- national and international radio stations
Radio wave transmission: medium wavelength (AM) [4]
- sky waves
- limited range
- reflect off ionosphere and Earth's surface
- local radio stations
AM stands for:
Amplitude Modulation
Radio wave transmission: short wavelength (FM) [5]
- space waves
- must be in 'line of sight'; cannot penetrate objects
- can penetrate atmosphere (satellite)
- TV broadcasting
- carry more information
FM stands for:
Frequency Modulation
Microwave transmission
communication to and from satellites as they penetrate the atmosphere
Microwaves penetrate the atmosphere without [4]:
- reflection
- refraction
- diffraction
- absorption
Modulation
to change a signal
Oscillator
device that supplies carrier waves in the form of an alternating current
Transmitter
device that sends out signals in the form of radio waves
Audio signal
alternating current representing a sound wave
Total internal reflection
the complete reflection of light by the inside surface of a medium
Optical fibre communication
- light transmits through glass over long distances with very little absorption
- light reflects off internal surfaces of glass when it bends
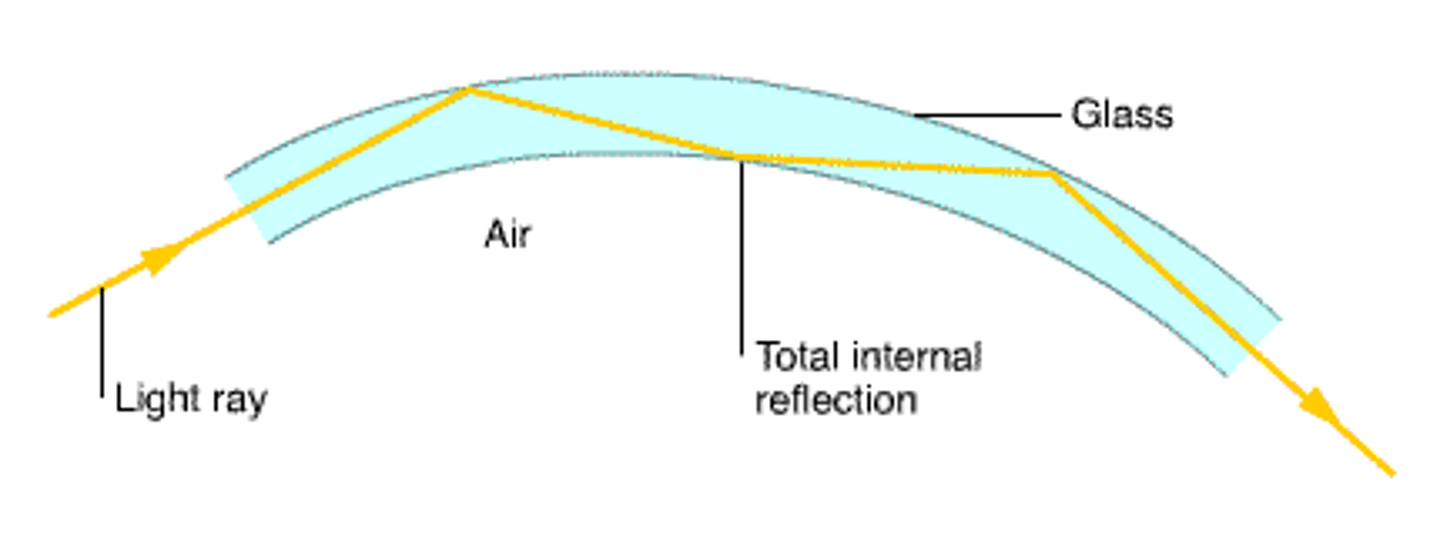
Advantages of optical fibres [2]:
- carries more information as visible light and infrared have short wavelengths
- less susceptible to interception
UV waves have a (longer/shorter) wavelength than visible light and carry (more/less) energy
shorter, more
Uses of ultraviolet waves [2]:
- inks that glow under ultraviolet light
- security markers
Dangers of ultraviolet waves [2]:
- harmful to eyes and may cause blindness
- harmful to skin and may age prematurely, cause sunburn or skin cancer
Protection against ultraviolet waves [2]:
- wear sun cream and sunglasses when outside to block UV
- don't go over recommended time in a sun bed
Why are x-rays and gamma rays similar?
they have a similar wavelength
X-rays and gamma rays have a (long/short) wavelength and carry (more/less) energy than the rest of the spectrum
short, more
What stops x-rays and gamma rays?
thick lead plate
X-ray production:
produced in x-ray tubes when fast-moving electrons or other particles strike a metal target
Gamma ray production:
produced when unstable nuclei decay
(Gamma rays/x-rays) have a shorter wavelength
gamma rays
Uses of x-rays [2]:
- detecting internal cracks in metal objects
- creating images of broken bones
Uses of gamma rays [3]:
- irradiation of food
- sterilisation of medical equipment
- chemotherapy (killing cancer cells)
Dangers of x-rays and gamma rays [3]:
- both are ionising, causing atoms to become charged by dislodging electrons
- high doses will kill living cells
- low doses cause cell damage, gene mutation and cancer
Film badge
device that measures the approximate amount of radiation received in a given period