ANSC 315 Lyme Disease
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Cause of Lyme Disease
Bacteria: Borrelia burgodorferi
spirochete
Vector: 3-host ticks
Reservoir Hosts: small mammals, birds
Transmission: bacteria multiply rapidly in midgut of tick once attached to host — takes about 48 hours until transmission becomes efficient
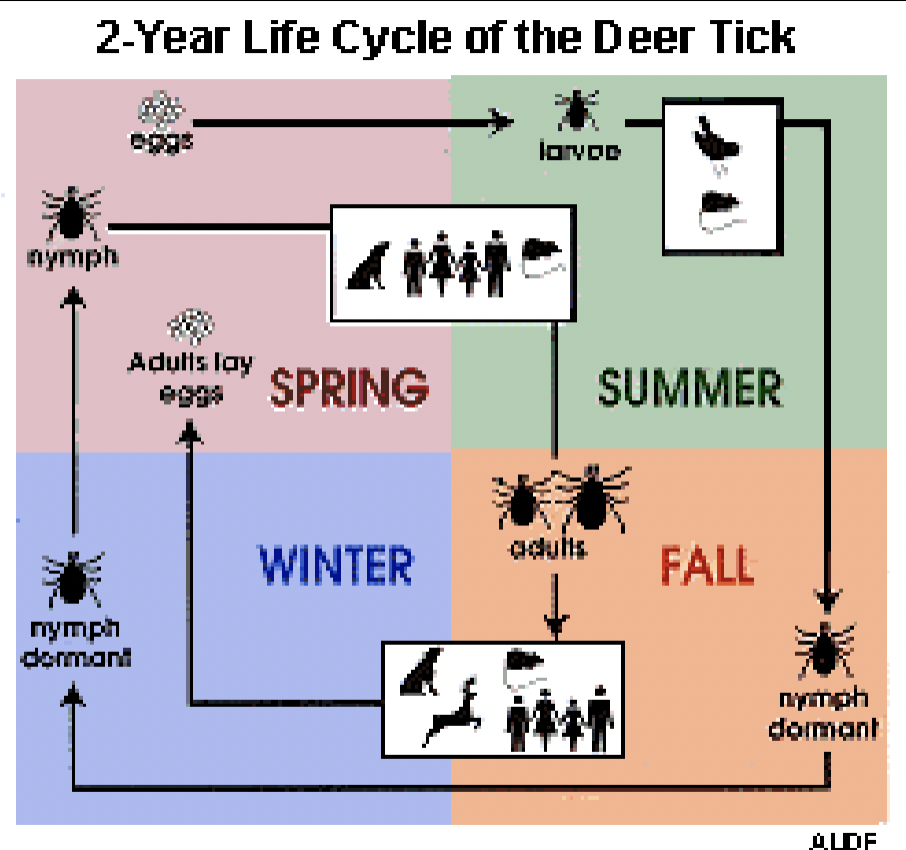
2 Year Life Cycle of the Deer Tick
Eggs → Larvae → Nymph Dominant → Nymph → Adults
Epidemiology
typically northeast, upper central states — 90% of cases
Risk of Infection
Opportunity of being bitten by an infected tick
Density of vector ticks
Proportion of ticks infected
Duration and nature of susceptible host’s activities in affected area
Signs & Symptoms in Dogs
lameness, fever, anorexia (2 months after infection) — arthritis
renal disease
CNS disorders
myocarditis
Diagnosis of Lyme Disease
History: exposure to tick
Antibody tests
EIA, IFA: high sensitivity, low specificity
New SNAP test (IDEXX): synthetic peptide that is highly conserved and is more specific
Can’t distinguish exposure from infection
Treatment for Dogs
antibiotics
clinical signs
not necessarily a good idea to use if serologically positive but not clinically affected animals
Vaccination
to vaccinate or not to vaccinate… that is the question!
Prevention of Lyme Disease
***Reduce exposure to ticks***
environmental control
individual animal collars (amitraz, permethrin), topicals
thorough inspection of animals
rapid removal of ticks
vaccination of unexposed animals — controversial
Public Health
Are Dogs a Source of Infection for Humans?
NO
BUT dogs can bring ticks into household