APWH Final Quiz 2022 - APUSH/USH Fundamental Term List
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
alien & sedition acts (1798)
date: 1798
key people: john adams
four internal security laws passed by the U.S. Congress, restricting aliens and curtailing the excesses of an unrestrained press, in anticipation of an expected war with France. After the XYZ Affair (1797), war with France had appeared inevitable.

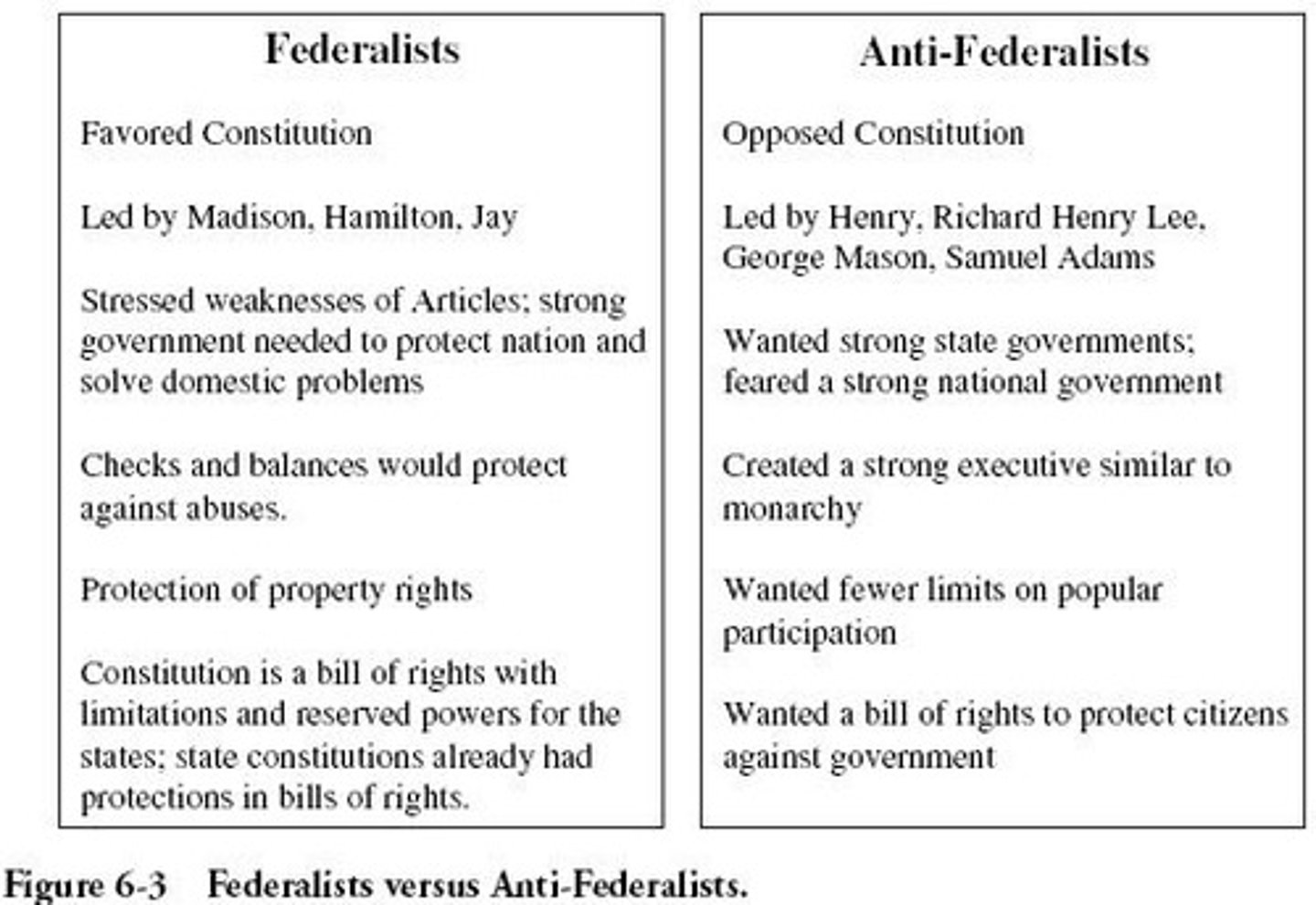
antifederalists
The Antifederalists were a diverse coalition of people who opposed ratification of the Constitution. Although less well organized than the Federalists, they also had an impressive group of leaders who were especially prominent in state politics.
articles of confederation
date: november 15, 1777
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 original states of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate by the Second Continental Congress on November 15, 1777, and sent to the states for ratification.

bacon's rebellion (1676)
date: 1676
Bacon's Rebellion was an armed rebellion held by Virginia settlers that took place from 1676 to 1677. It was led by Nathaniel Bacon against Colonial Governor William Berkeley. It was the first rebellion in the North American colonies in which discontented frontiersmen took part.

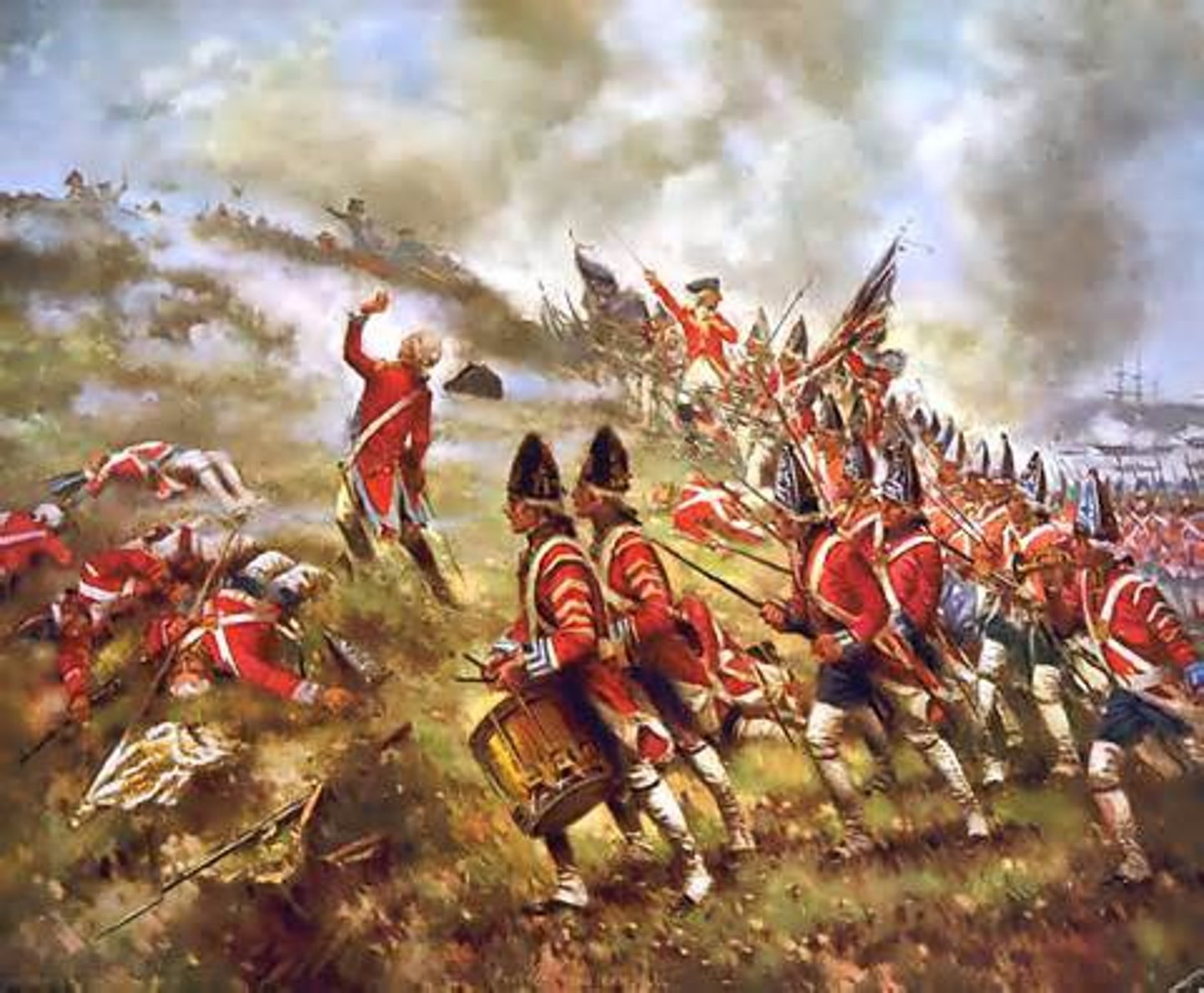
battle of breed's hill
date: june 17, 1775
Battle of Bunker Hill, also called Battle of Breed's Hill, (June 17, 1775), first major battle of the American Revolution, fought in Charlestown (now part of Boston) during the Siege of Boston.

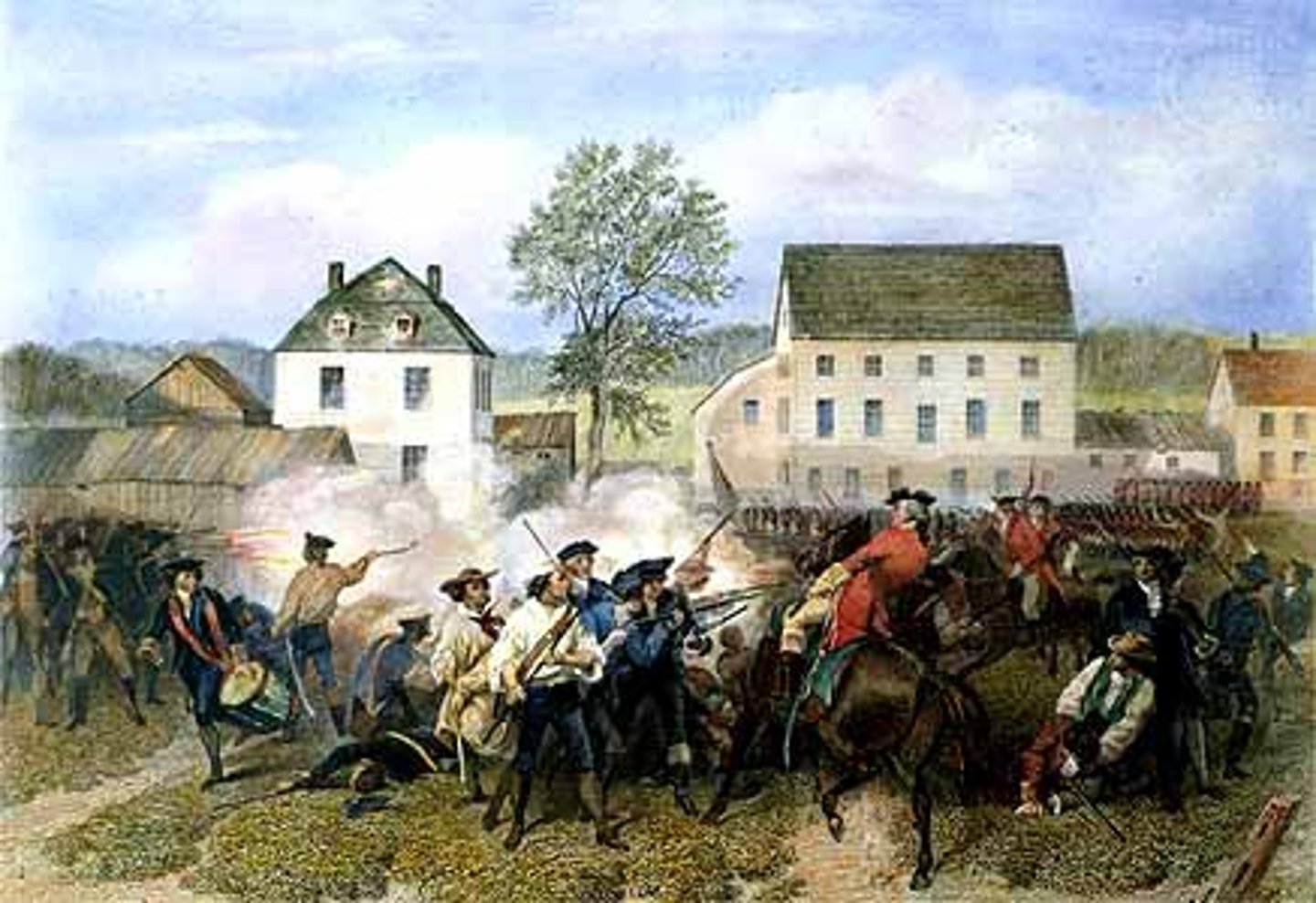
battle of concord
date: apriil 19, 1775
The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. The battles were fought on April 19, 1775 in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concord, Lincoln, Menotomy, and Cambridge.

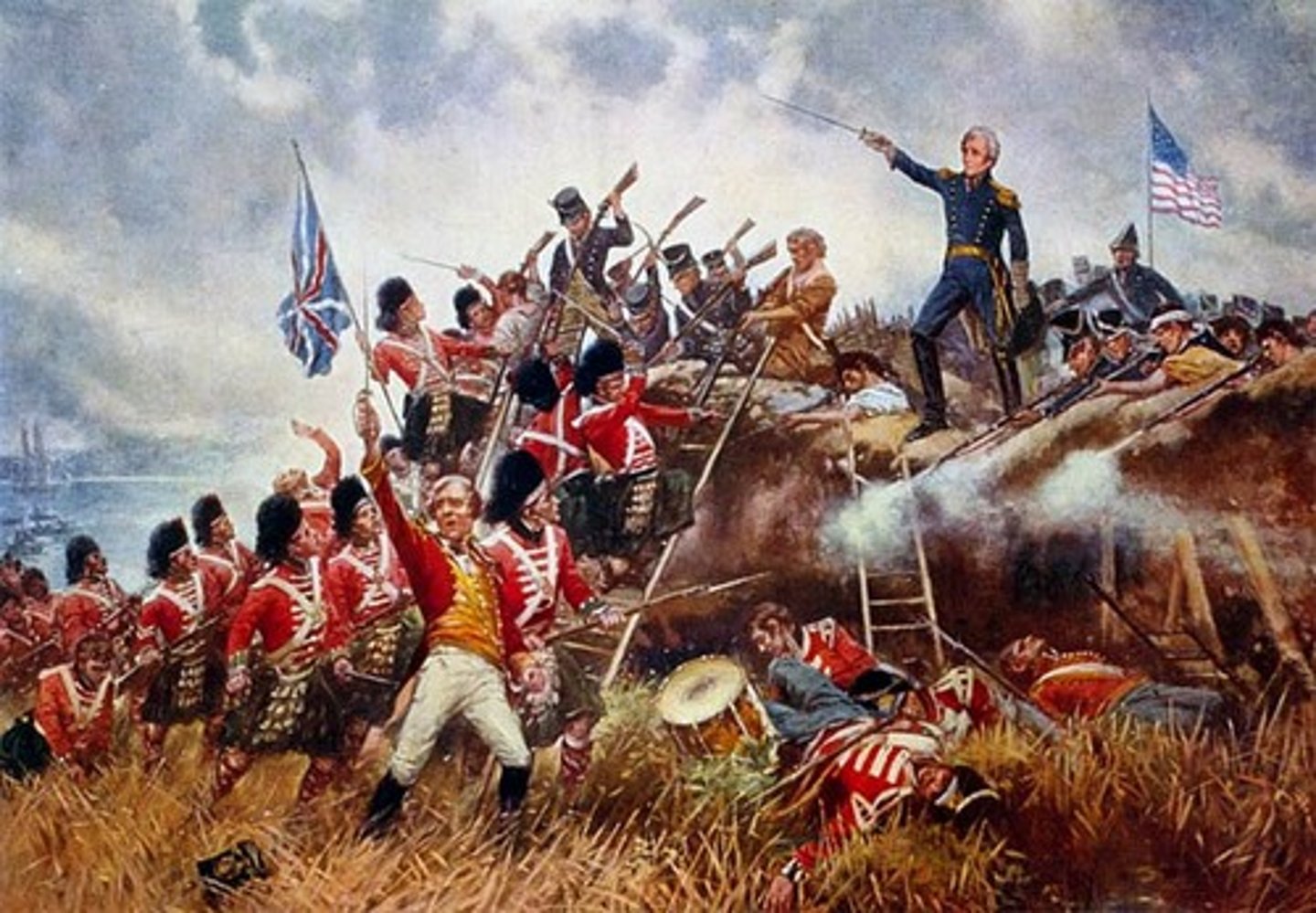
battle of new orleans
date: january 8, 1815
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815 between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles southeast of the French Quarter of New Orleans, in the current suburb of Chalmette, Louisiana.

battle of princeton
date: january 3, 1777
The Battle of Princeton was a battle of the American Revolutionary War, fought near Princeton, New Jersey on January 3, 1777, and ending in a small victory for the Colonials. General Lord Cornwallis had left 1,400 British troops under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Charles Mawhood in Princeton.

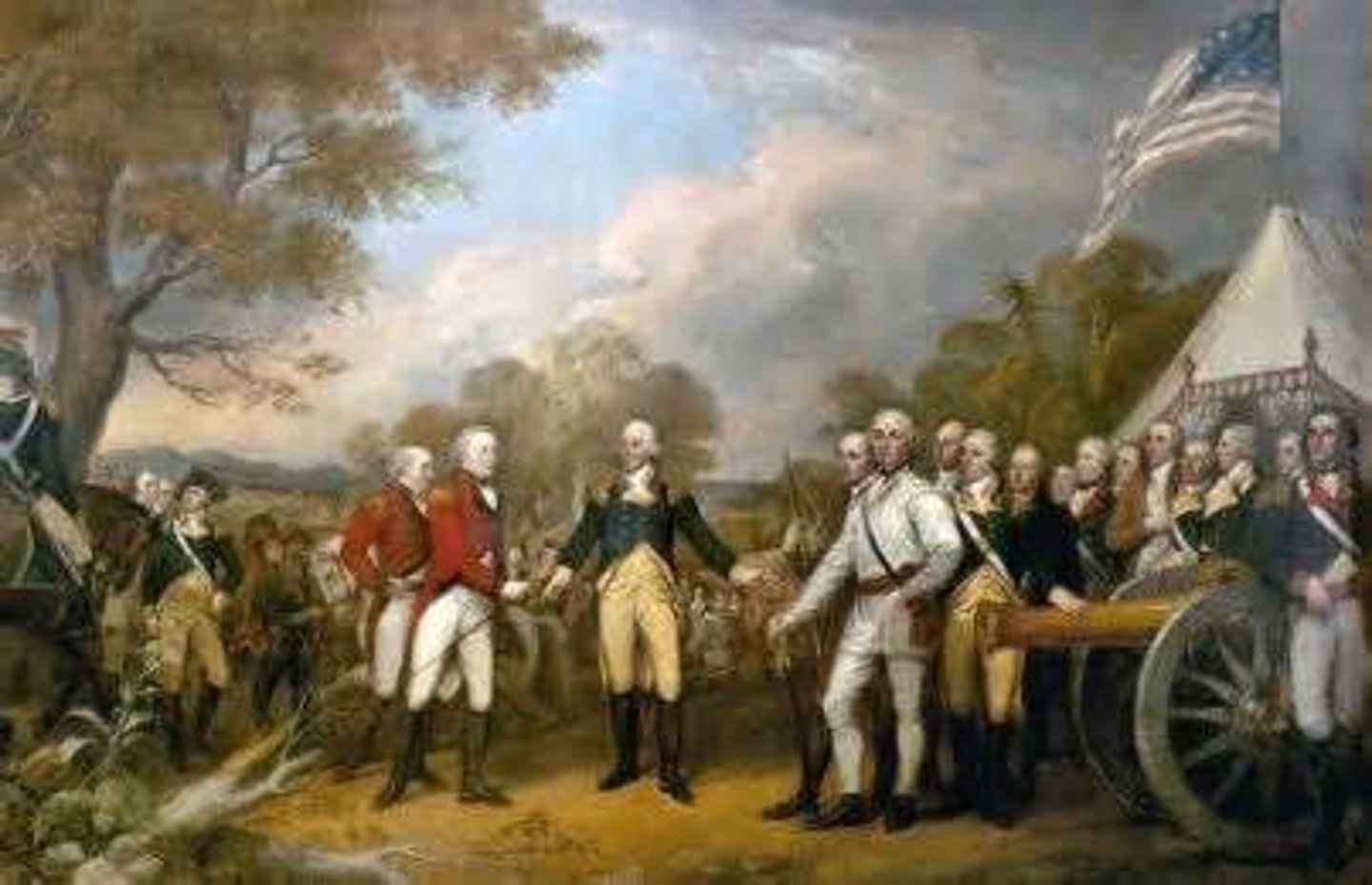
battle of saratoga (1777)
date: september 19, 1777 - october 19, 177
The Battles of Saratoga marked the climax of the Saratoga campaign, giving a decisive victory to the Americans over the British in the American Revolutionary War.

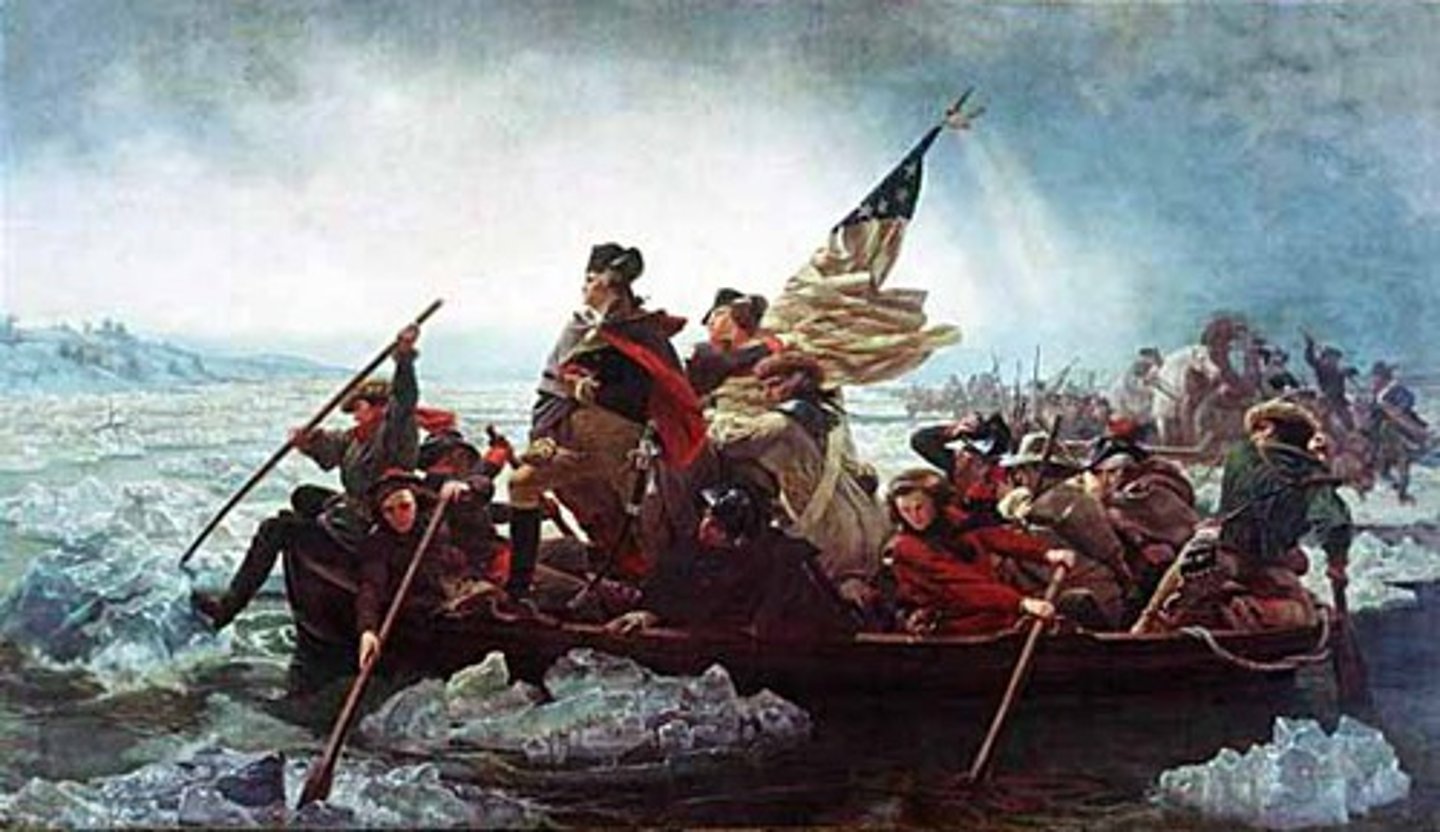
battle of trenton
date: december 26, 1776
The Battle of Trenton was a small but pivotal American Revolutionary War battle that took place on the morning of December 26, 1776, in Trenton, New Jersey.

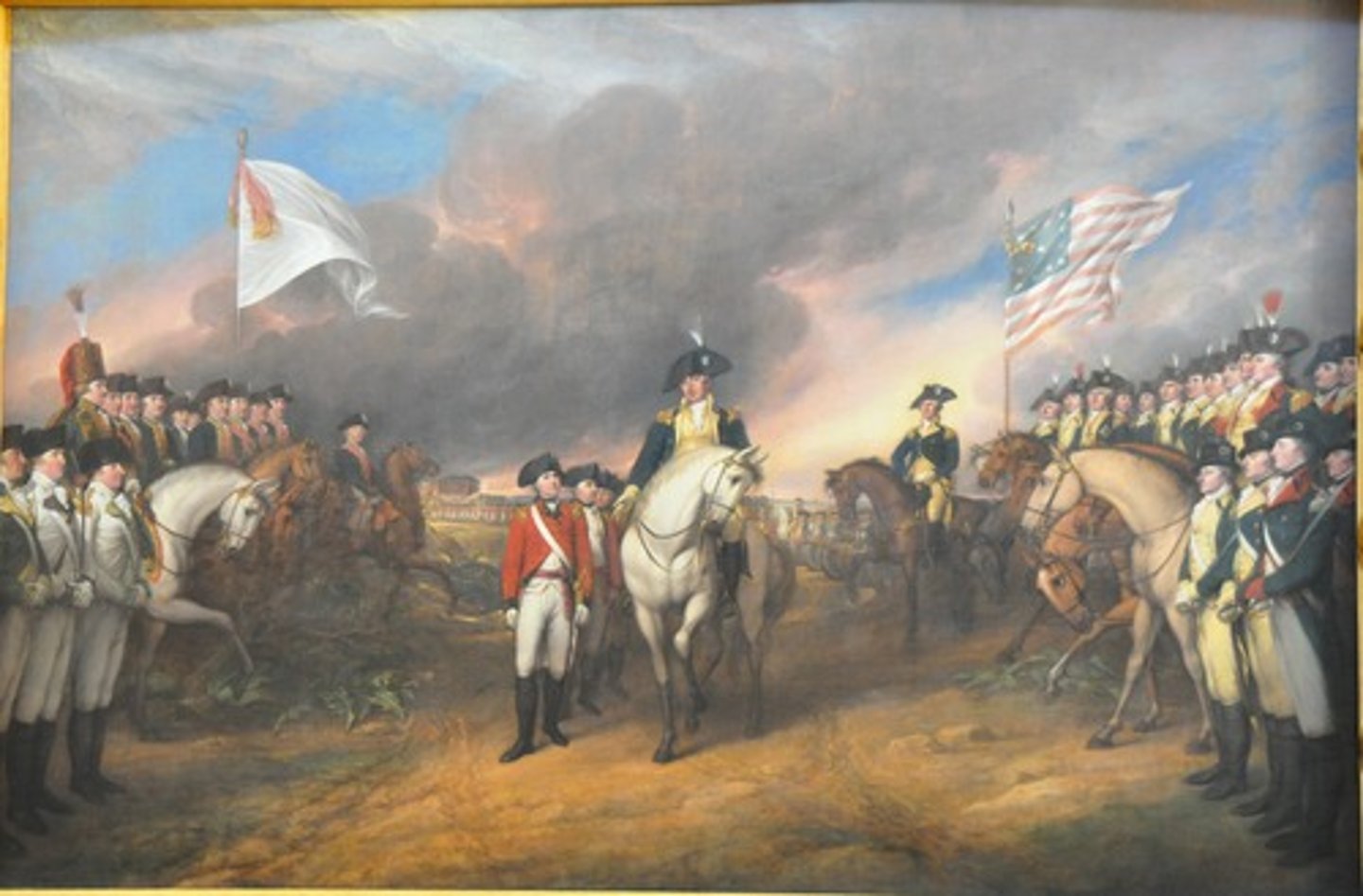
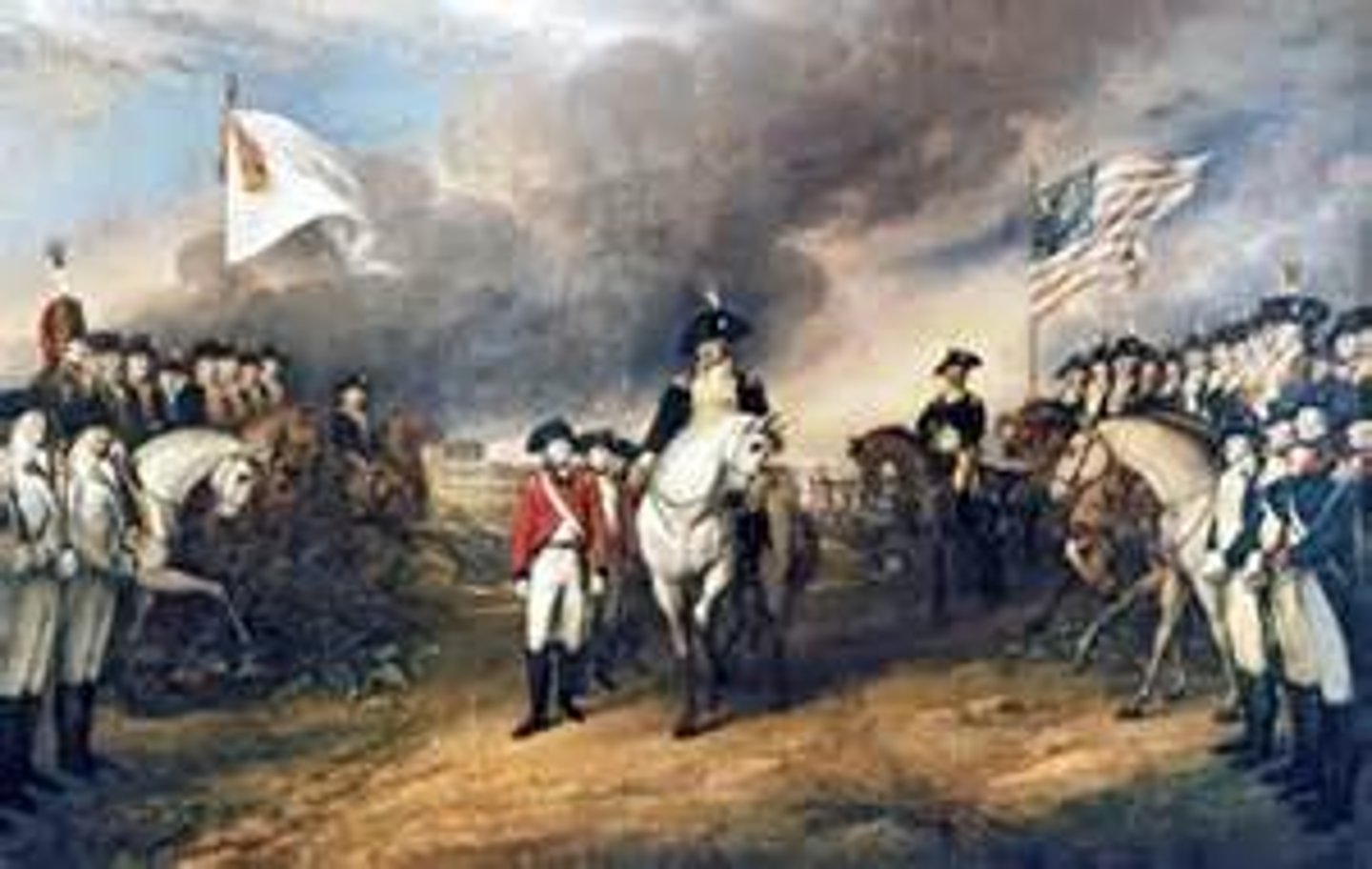
battle of yorktown
date: september 28, 1781 - october 19, 1781
Siege of Yorktown, (September 28-October 19, 1781), joint Franco-American land and sea campaign that entrapped a major British army on a peninsula at Yorktown, Virginia, and forced its surrender. The siege virtually ended military operations in the American Revolution.

bill of rights
date ratified: december 15, 1791
The United States Bill of Rights comprises the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution.

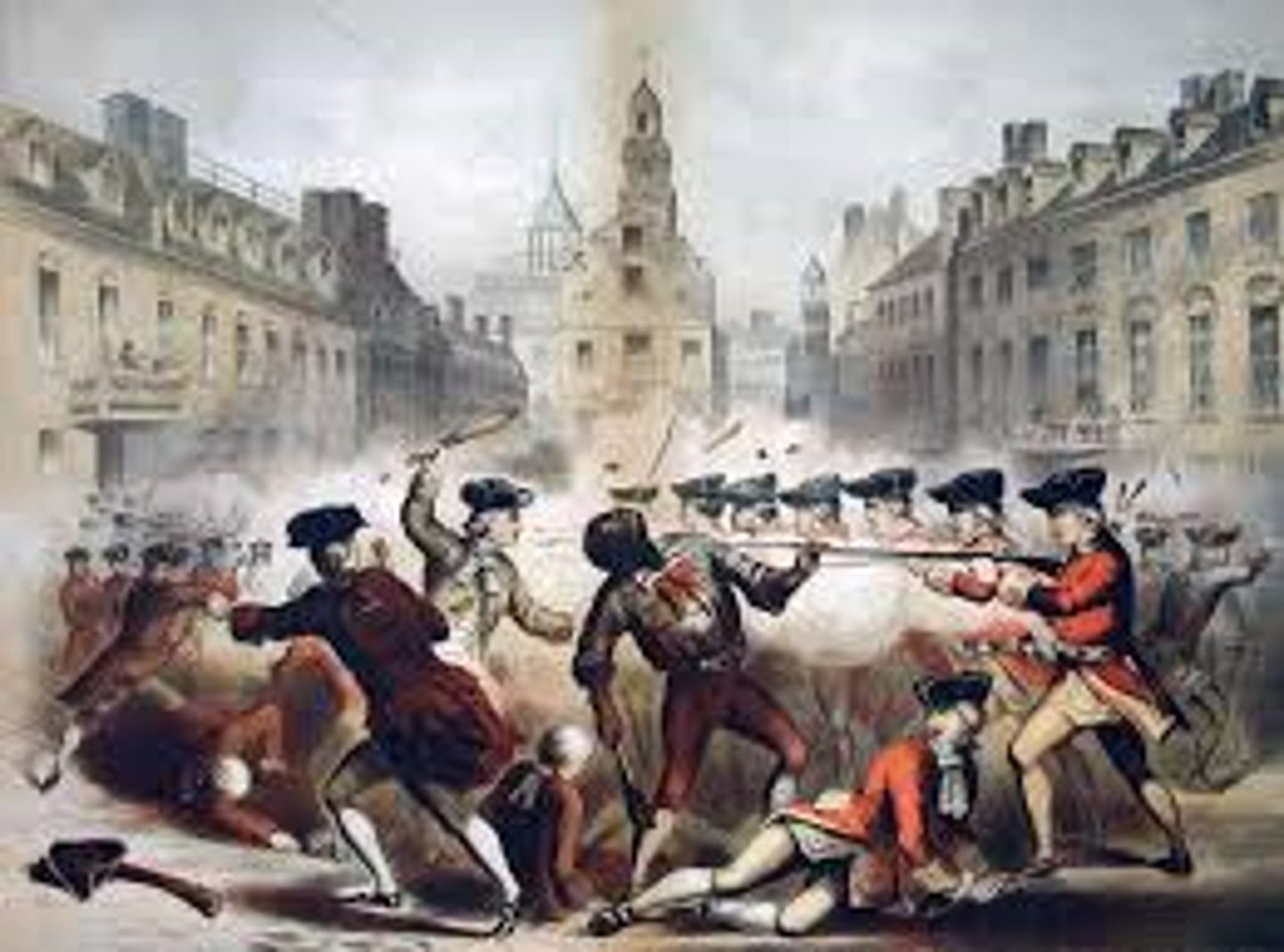
boston massacre
date: march 5, 1770
The Boston Massacre was a confrontation in Boston on March 5, 1770, in which a group of nine British soldiers shot five people out of a crowd of three or four hundred who were abusing them verbally and throwing various missiles.

broad constructionism
Broad construction, sometimes called "loose construction," is an approach to constitutional interpretation emphasizing a permissive and flexible reading of the Constitution, and especially of the powers of the federal government.

checks and balances
counterbalancing influences by which an organization or system is regulated, typically those ensuring that political power is not concentrated in the hands of individuals or groups.
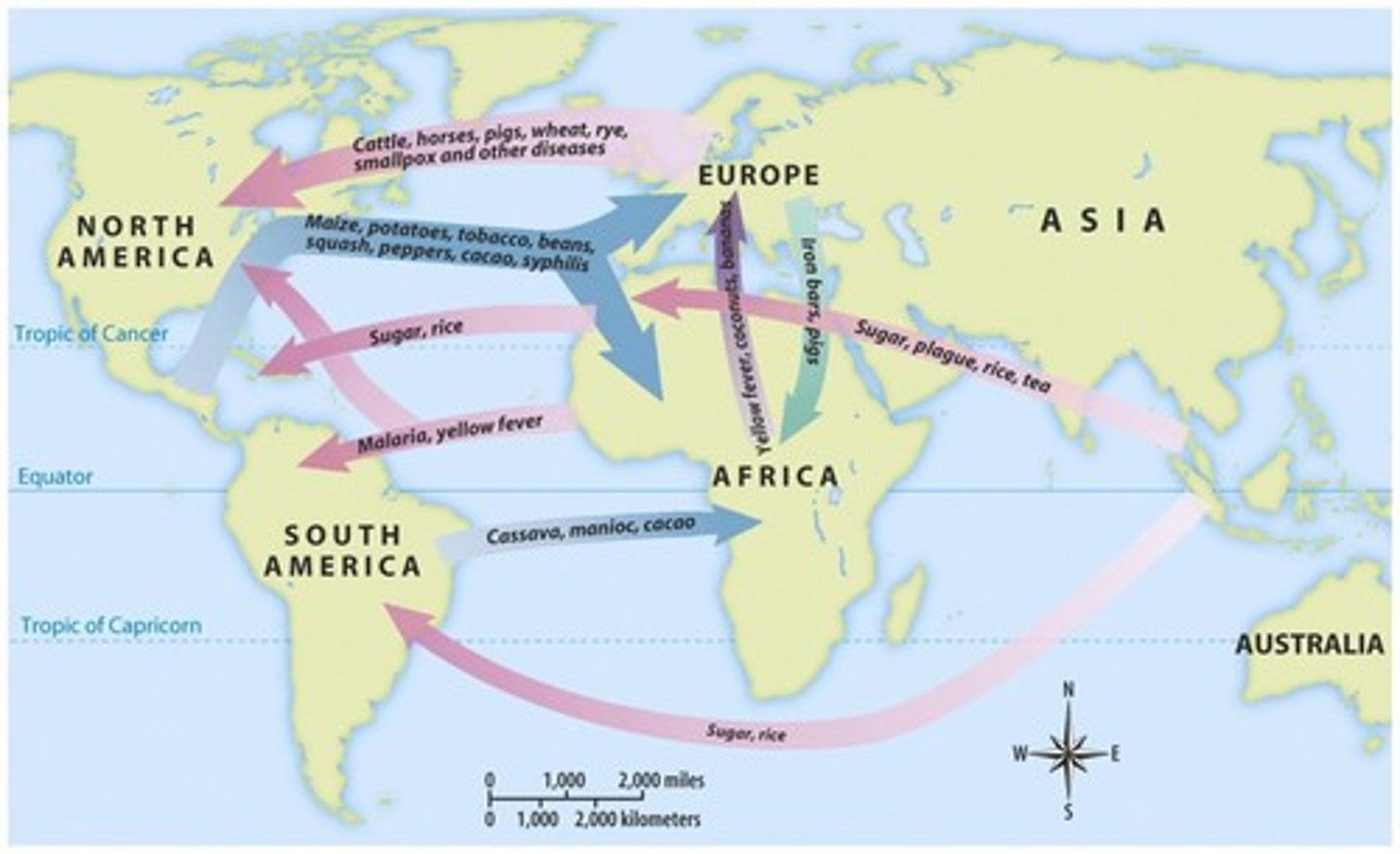
columbian exchange
date: 1942
The Columbian Exchange refers to the exchange of diseases, ideas, food. crops, and populations between the New World and the Old World following the voyage to the Americas by Christo pher Columbus in 1492.
daniel shay
born: 1747
died: september 29, 1825
Description
Capt. Daniel Ogden Shays was an American soldier, revolutionary and farmer famous for being one of the leaders and namesake of Shays' Rebellion, a populist uprising against controversial debt collection and tax policies in Massachusetts in 1786-1787.

doctrine of nullification
nullification, in U.S. history, a doctrine expounded by the advocates of extreme states' rights. It held that states have the right to declare null and void any federal law that they deem unconstitutional.

doctrine of predestination
Predestination, in Christian theology, is the doctrine that all events have been willed by God, usually with reference to the eventual fate of the individual soul. Explanations of predestination often seek to address the paradox of free will, whereby God's omniscience seems incompatible with human free will.

election of 1800
Jefferson and Burr each received 73 votes in the Electoral College, so the House of Representatives had to decide the outcome. The House chose Jefferson as President and Burr as Vice President.

eli whitney
born: december 8, 1765
died: january 8, 1825
Eli Whitney Jr. was an American inventor, widely known for inventing the cotton gin, one of the key inventions of the Industrial Revolution that shaped the economy of the Antebellum South.

elizabeth cady stanton
born: november 12, 1815
died: october 26, 1902
Elizabeth Cady Stanton was an American writer and activist who was a leader of the women's rights movement in the U.S. during the mid- to late-19th century

federalists
The Federalist Papers is a collection of 85 articles and essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay under the collective pseudonym "Publius" to promote the ratification of the United States Constitution.

frederick douglass
born: february 1818
died: february 20, 1895
Frederick Douglass was an African-American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman. After escaping from slavery in Maryland, he became a national leader of the abolitionist movement in Massachusetts and New York, becoming famous for his oratory and incisive antislavery writings.

horace mann
born: may 4, 1796
died: august 2, 1859
Horace Mann was an American educational reformer, slavery abolitionist and Whig politician known for his commitment to promoting public education. In 1848, after public service as Secretary of the Massachusetts State Board of Education, Mann was elected to the United States House of Representatives
indentured servitude
Indentured servitude refers to a contract between two individuals, in which one person worked not for money but to repay an indenture, or loan, within a set time period.

james madison
born: march 16, 1751
died: june 28, 1836
party: democratic-republican party
James Madison Jr. was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the 4th president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. He is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for his pivotal role in drafting and promoting the Constitution of the United States and the Bill of Rights

john marshall
born: september 24, 1755
died: july 6, 1835
party: federalist party
John Marshall was an American politician and lawyer who served as the fourth chief justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835.

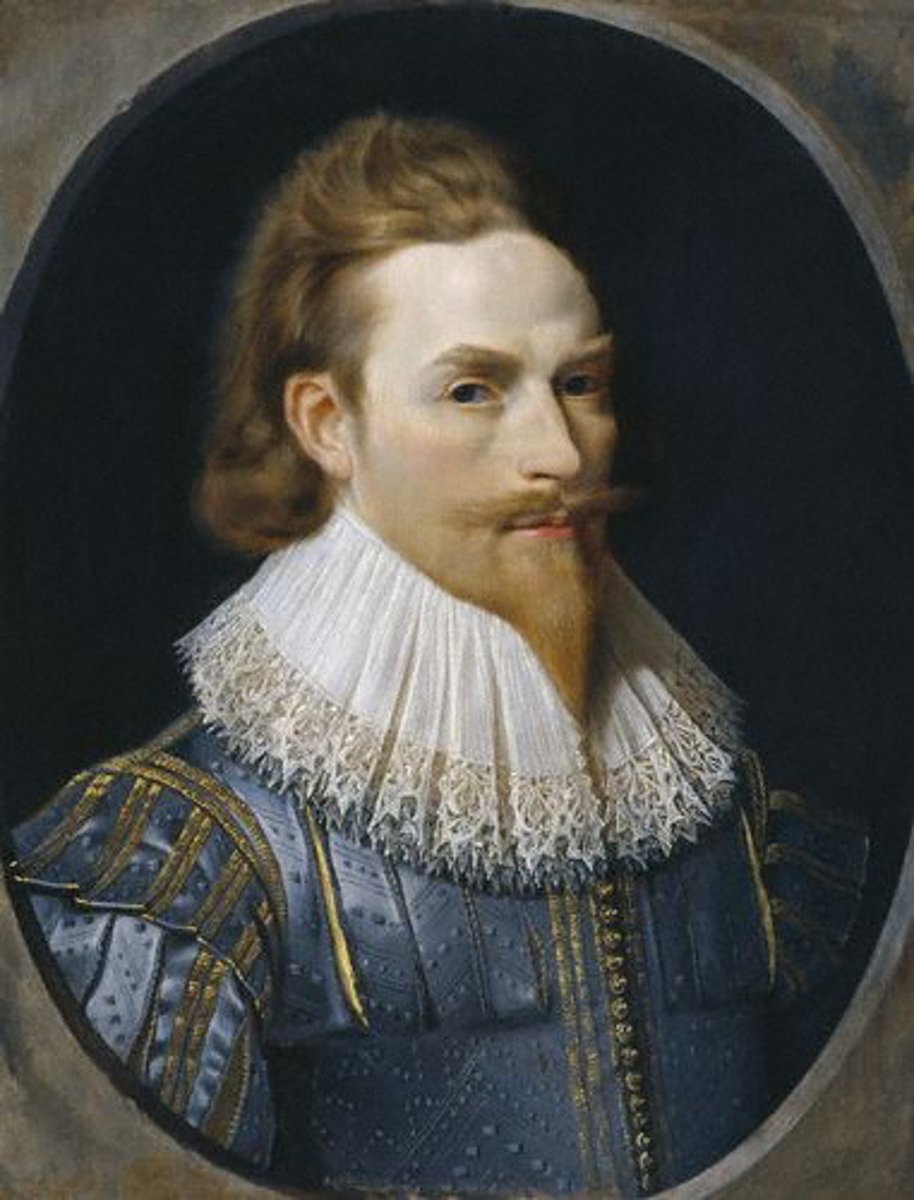
john winthrop
born: january 1588
died: march 26, 1649
John Winthrop was an English Puritan lawyer and one of the leading figures in founding the Massachusetts Bay Colony, the second major settlement in New England following Plymouth Colony. Winthrop led the first large wave of colonists from England in 1630 and served as governor for 12 of the colony's first 20 years

jonathon edwards
born: october 5, 1703
died: march 22, 1758
Jonathan Edwards was an American revivalist preacher, philosopher, and Congregationalist theologian. Edwards is widely regarded as one of America's most important and original philosophical theologians.

lexington & concord 1775
date:: april 19, 1775 - 1783
The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. The battles were fought on April 19, 1775, in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concord, Lincoln, Menotomy, and Cambridge.

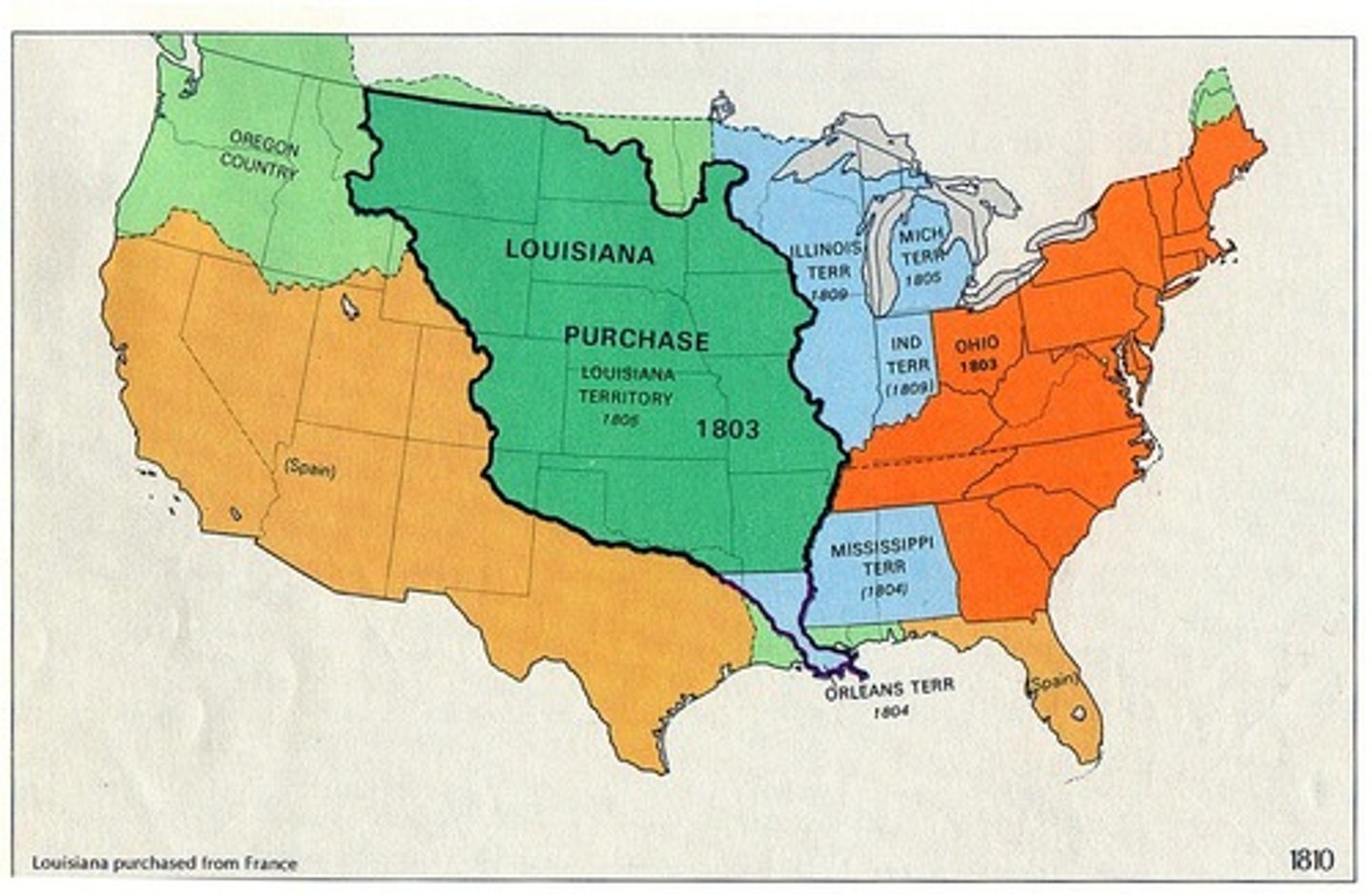
louisiana purchase 1803
date: 1803
The Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or approximately eighteen dollars per square mile, the United States nominally acquired a total of 828,000 sq mi.
marbury v. madison 1803
date decided: 1803
Marbury v. Madison, 5 U.S. 137, was a landmark U.S. Supreme Court case that established the principle of judicial review in the United States, meaning that American courts have the power to strike down laws and statutes that they find to violate the Constitution of the United States.

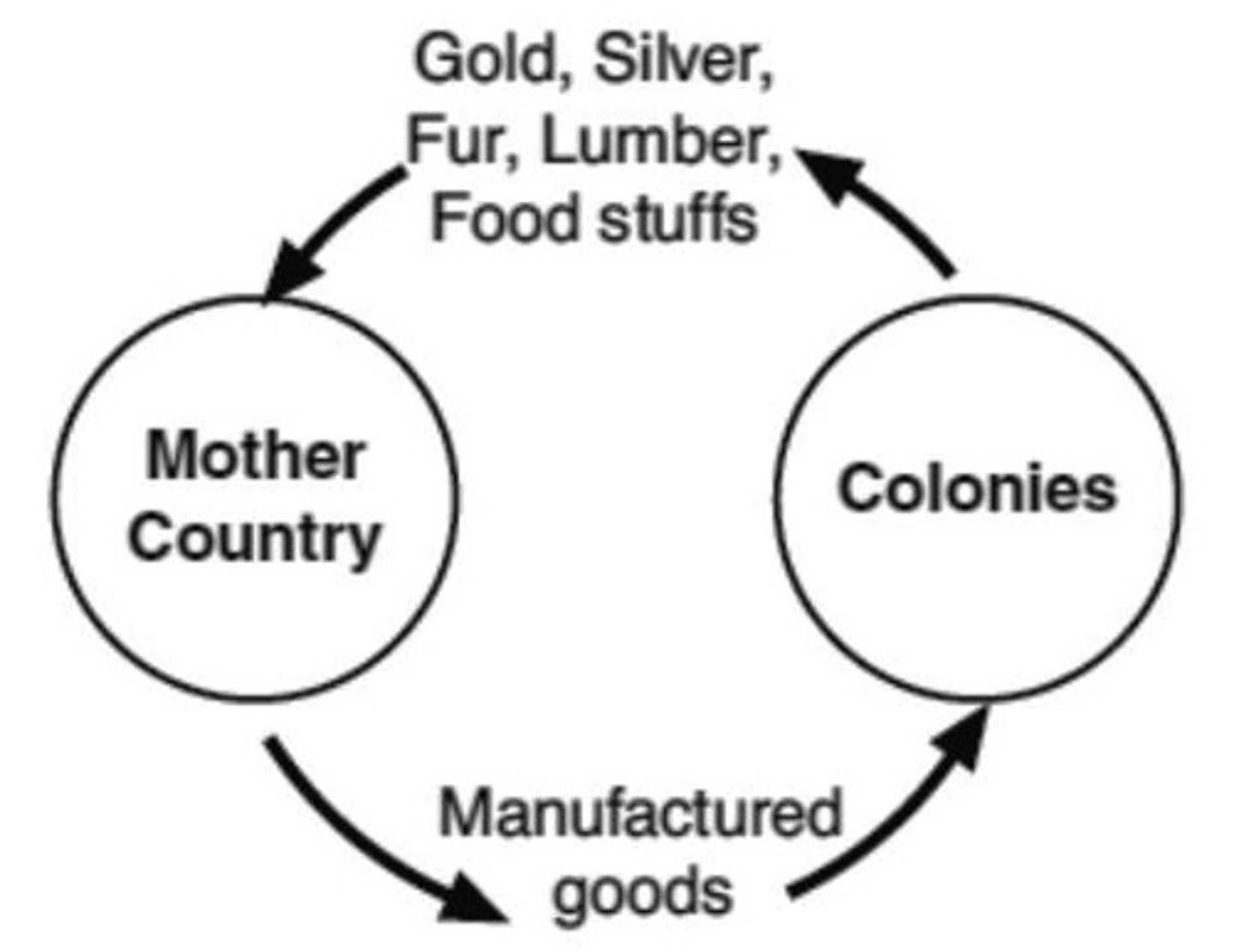
mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
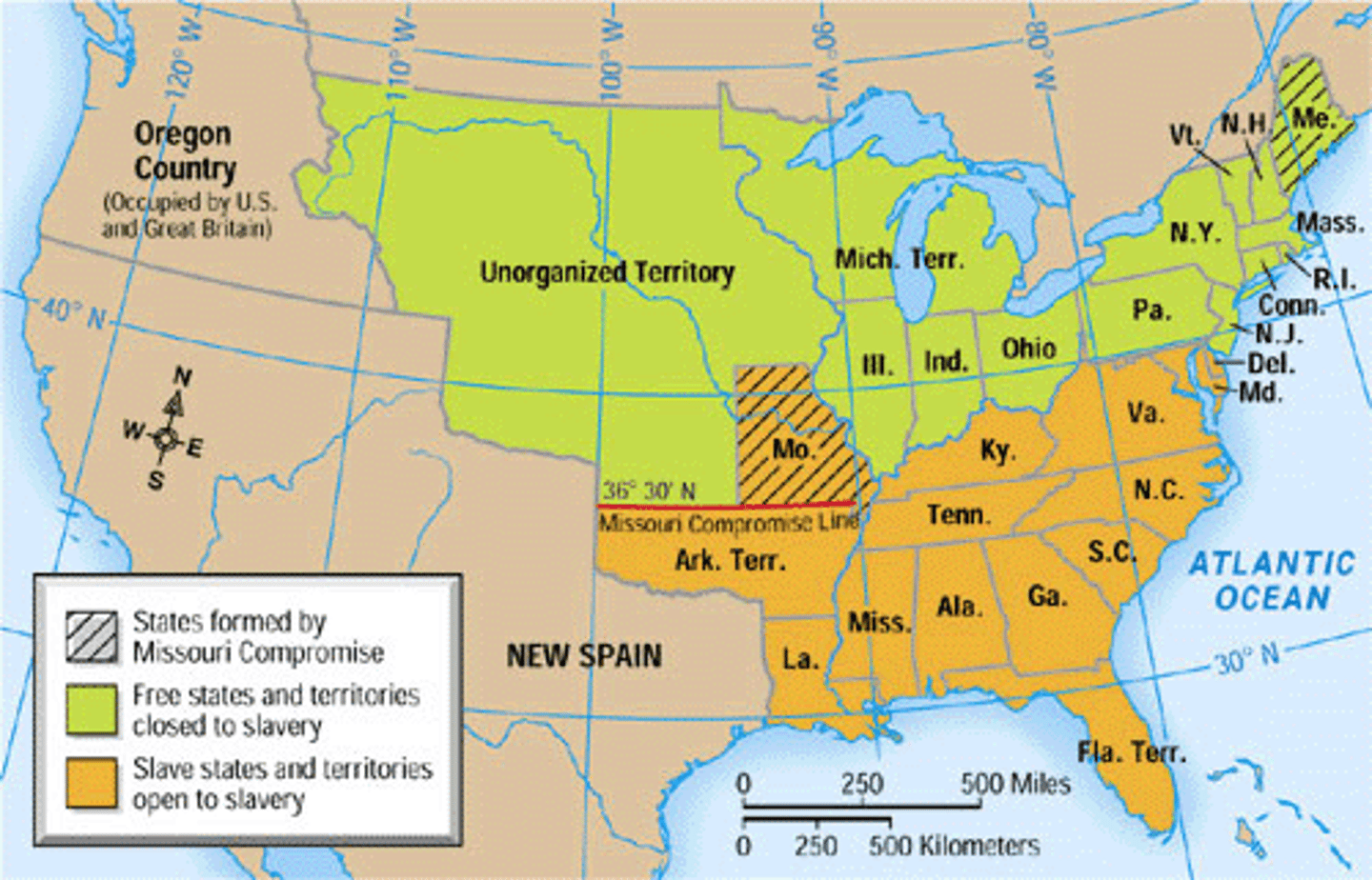
missouri compromise 1820
Missouri Compromise, (1820), in U.S. history, measure worked out between the North and the South and passed by the U.S. Congress that allowed for admission of Missouri as the 24th state (1821). It marked the beginning of the prolonged sectional conflict over the extension of slavery that led to the American Civil War.
nathaniel bacon
born: january 2, 1647
died: october 26, 1676
Colonist of the Virginia Colony, famous as the instigator of Bacon's Rebellion of 1676, which collapsed when himself died from dysentery.

new jersey plan
The New Jersey Plan was designed to protect the security and power of the small states by limiting each state to one vote in Congress, as under the Articles of Confederation. Its acceptance would have doomed plans for a strong national government and minimally altered the Articles of Confederation.

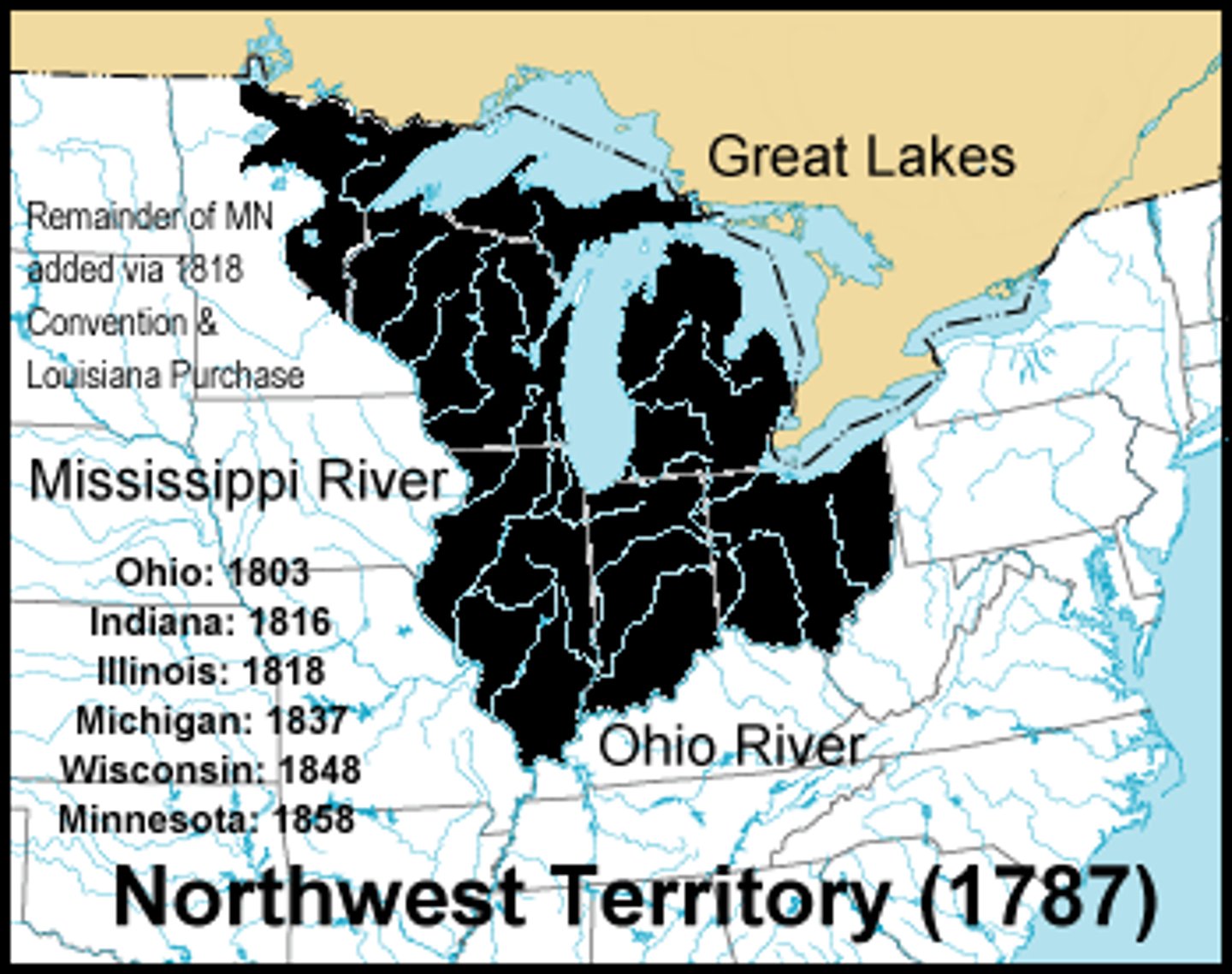
northwest ordiances
date: july 13, 1787
Also known as the Ordinance of 1787, the Northwest Ordinance established a government for the Northwest Territory, outlined the process for admitting a new state to the Union, and guaranteed that newly created states would be equal to the original thirteen states.
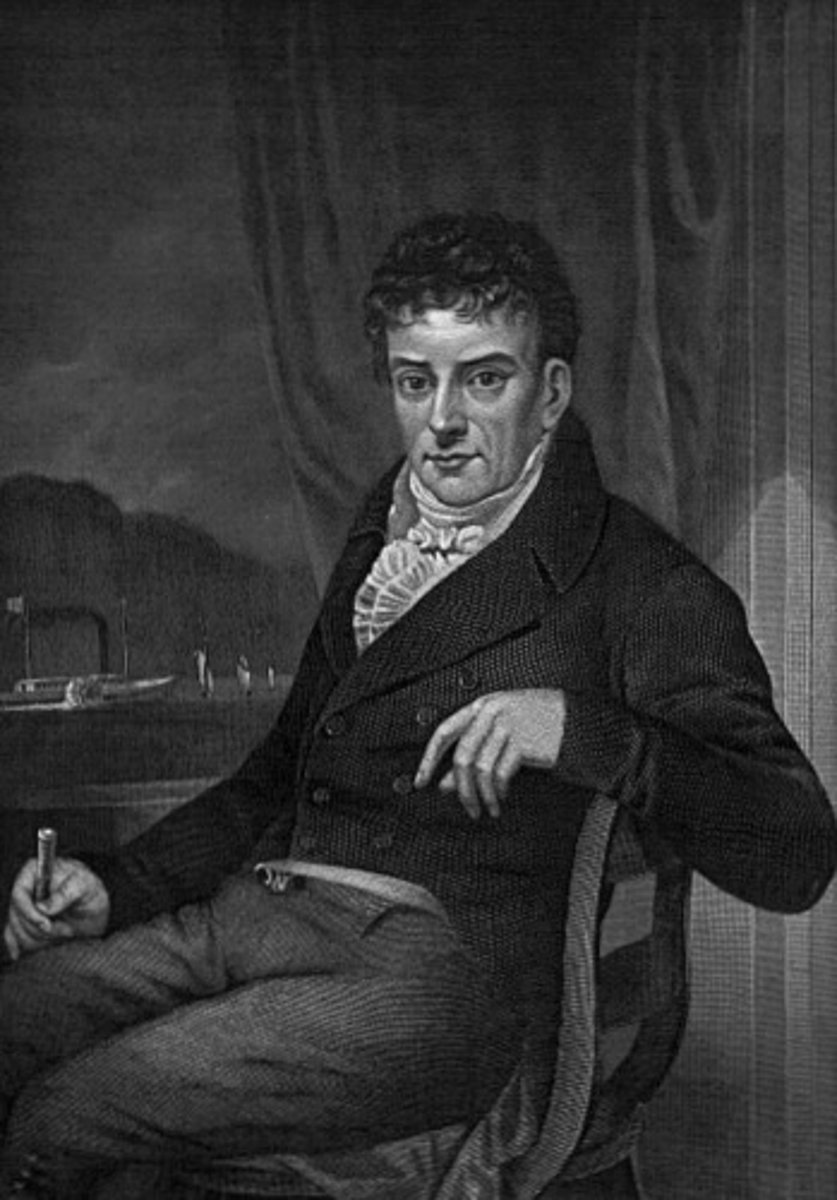
robert fulton
born: november 14, 1765
died: february 24, 1815
Robert Fulton was an American engineer and inventor who is widely credited with developing the world's first commercially successful steamboat, the North River Steamboat.

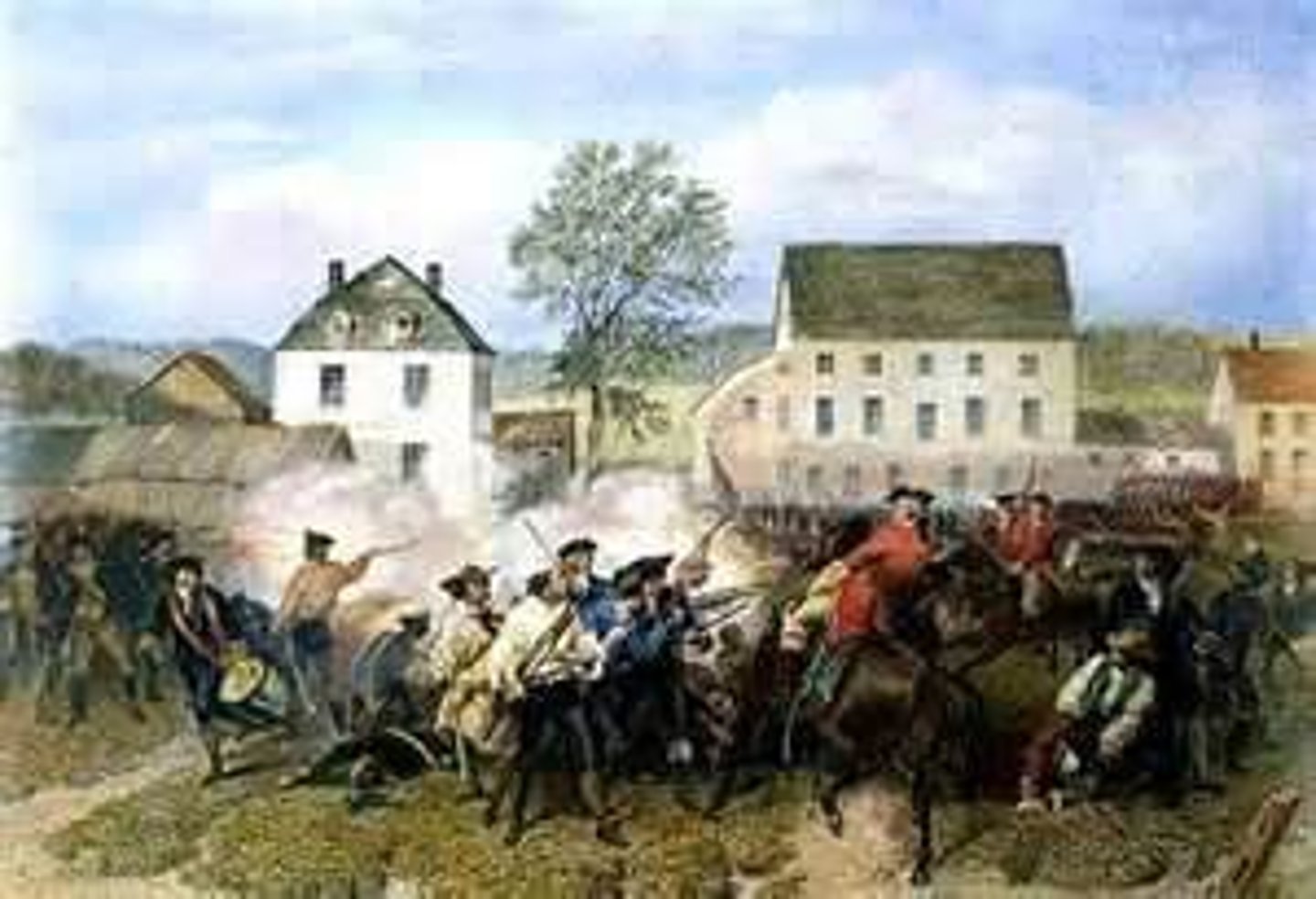
shay's rebellion
date: august 29, 1786
location: massachusetts
Shays' Rebellion was a series of violent attacks on courthouses and other government properties in Massachusetts that began in 1786 and led to a full-blown military confrontation in 1787.
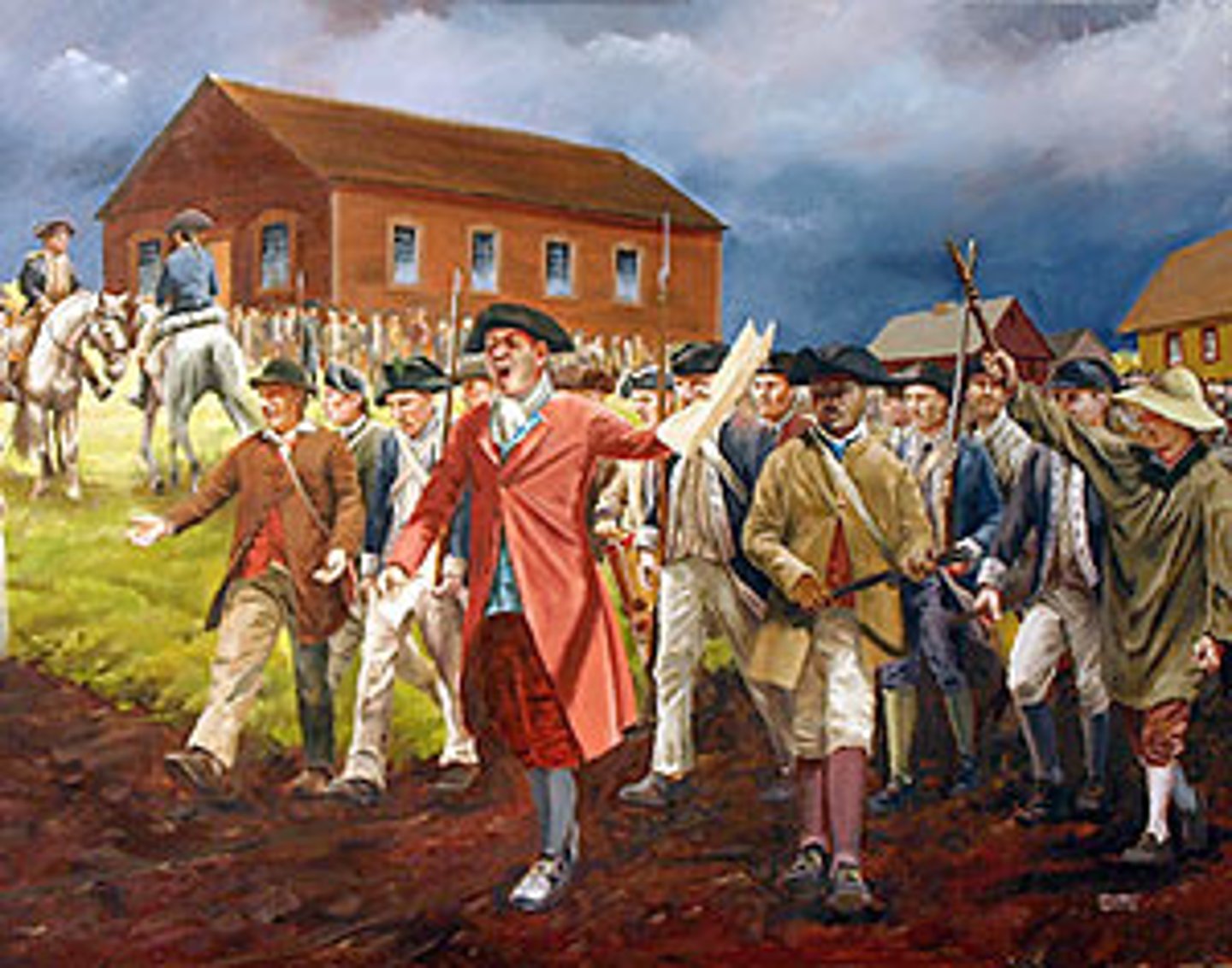

stamp act 1765
date: march 22, 1786
repealed: march 18, 1766
The Stamp Act of 1765 was an act of the Parliament of Great Britain which imposed a direct tax on the British colonies in America and required that many printed materials in the colonies be produced on stamped paper produced in London, carrying an embossed revenue stamp.

stono rebellion
date: september 9, 1739
Stono rebellion, large slave uprising on September 9, 1739, near the Stono River, 20 miles (30 km) southwest of Charleston, South Carolina. Slaves gathered, raided a firearms shop, and headed south, killing more than 20 white people as they went.
strict constructionism
Strict constructionisim, or original intent, is a theory limiting interpretation of legal and constitutional language to the literal meaning of this language at the time of passage. This theory contrasts with a loose construction of laws, which allows broader discretion by judges to determine intent in legal language.

temperance movement
temperance movement, movement dedicated to promoting moderation and, more often, complete abstinence in the use of intoxicating liquor (see alcohol consumption). In the early 1800s, many Americans believed that drinking was immoral and that alcohol was a threat to the nation's success. These beliefs led to widespread support for temperance, which means not drinking alcohol.

three-fifths compromise
Three-fifths compromise, compromise agreement between delegates from the Northern and the Southern states at the United States Constitutional Convention (1787) that three-fifths of the slave population would be counted for determining direct taxation and representation in the House of Representatives.

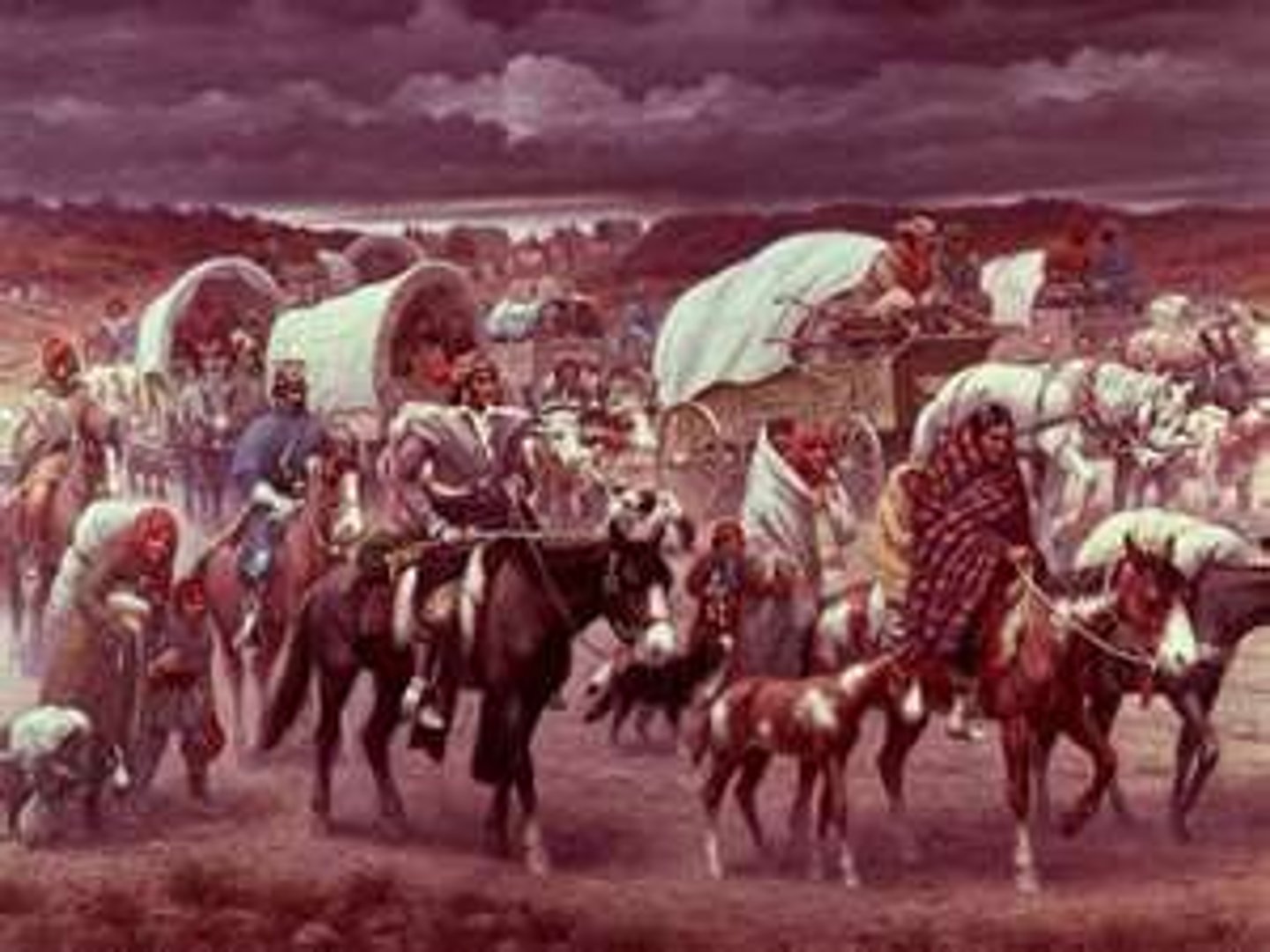
trail of tears
date: 1831
location: southeastern united states
The Trail of Tears was a series of forced displacements of approximately 60,000 American Indians of the "Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. Part of the Indian removal, the ethnic cleansing was gradual, occurring over a period of nearly two decades.

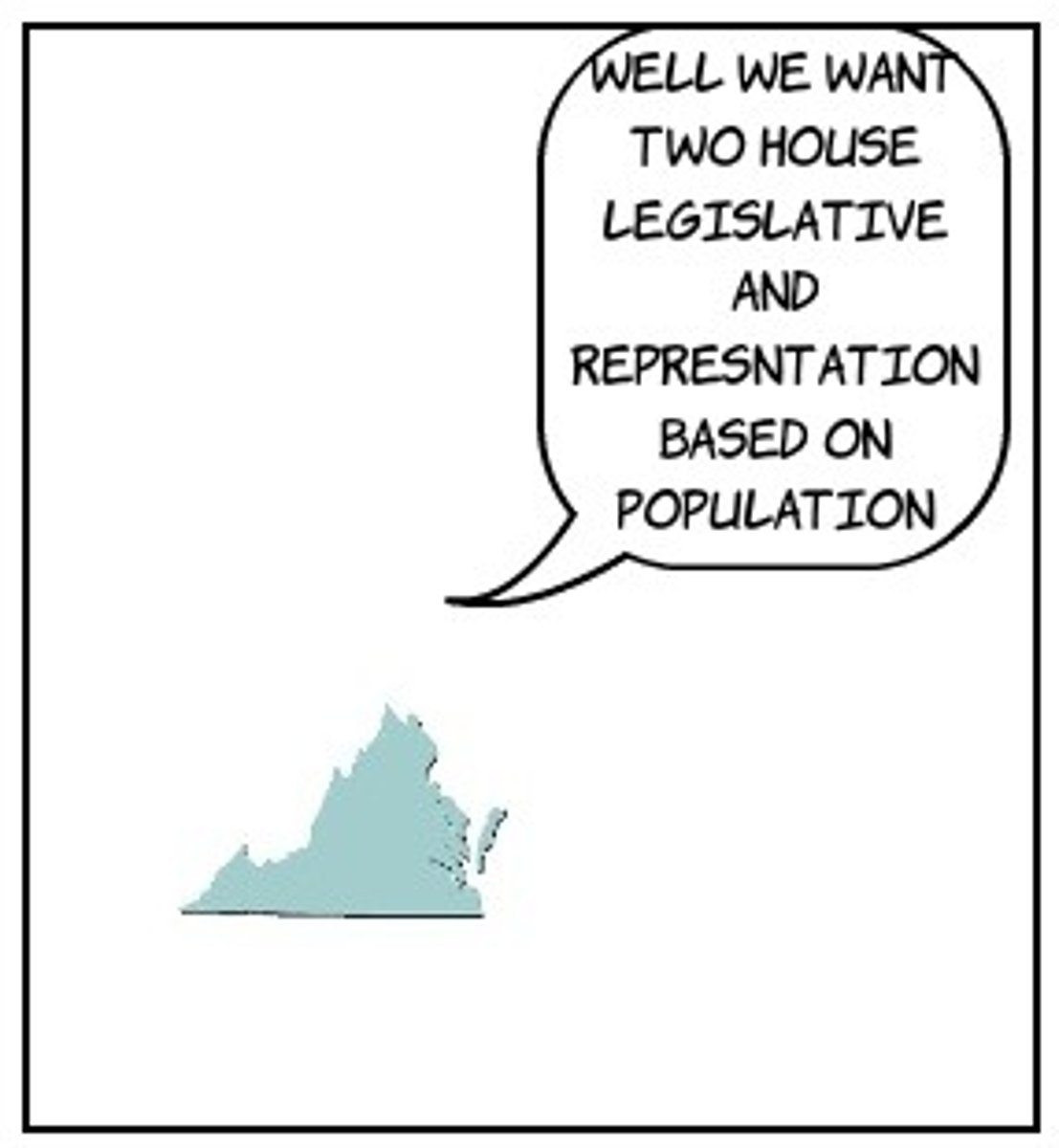
virginia plan
Introduced to the Constitutional Convention in 1787, James Madison's Virginia Plan outlined a strong national government with three branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. The plan called for a legislature divided into two bodies (the Senate and the House of Representatives) with proportional representation.
war of 1812
date(s): june 18, 1812 - february 18, 1815
The War of 1812 was a conflict fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida.

washington's farewell address
Washington's Farewell Address is a letter written by American President George Washington as a valedictory to "friends and fellow-citizens" after 20 years of public service to the United States. He wrote it near the end of his second term of presidency before retiring to his home at Mount Vernon in Virginia.

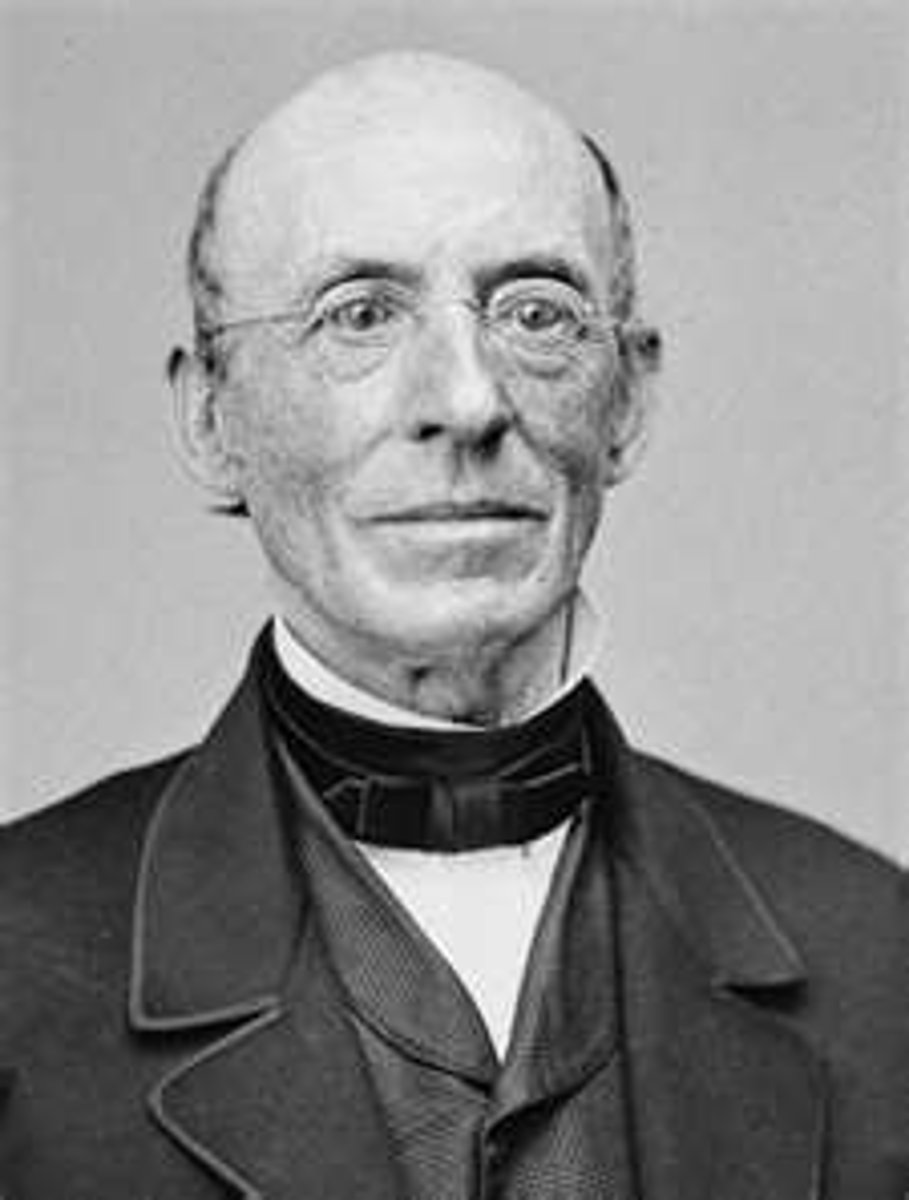
william lloyd garrison
born: december 10, 1805
died: may 24, 1879
William Lloyd Garrison was a prominent American Christian, abolitionist, journalist, suffragist, and social reformer. William Lloyd Garrison, (born December 10, 1805, Newburyport, Massachusetts, U.S.—died May 24, 1879, New York, New York), American journalistic crusader who published a newspaper, The Liberator (1831-65), and helped lead the successful abolitionist campaign against slavery in the United States.
