Honers Chemistry Chapter Test (LAMP High School)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Atomic Radius
Decreases across a period (left to right) and increases down a group (top to bottom).
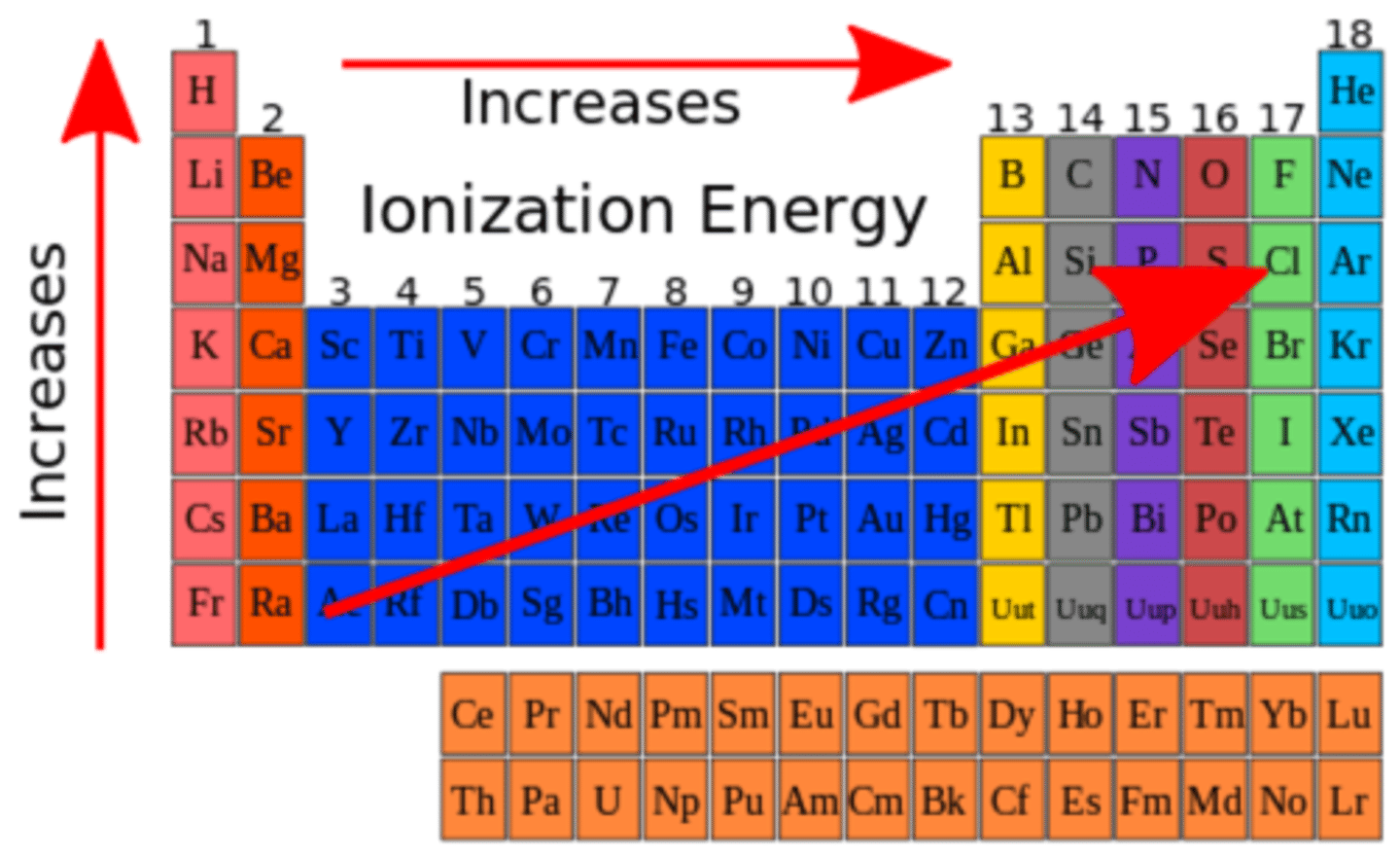
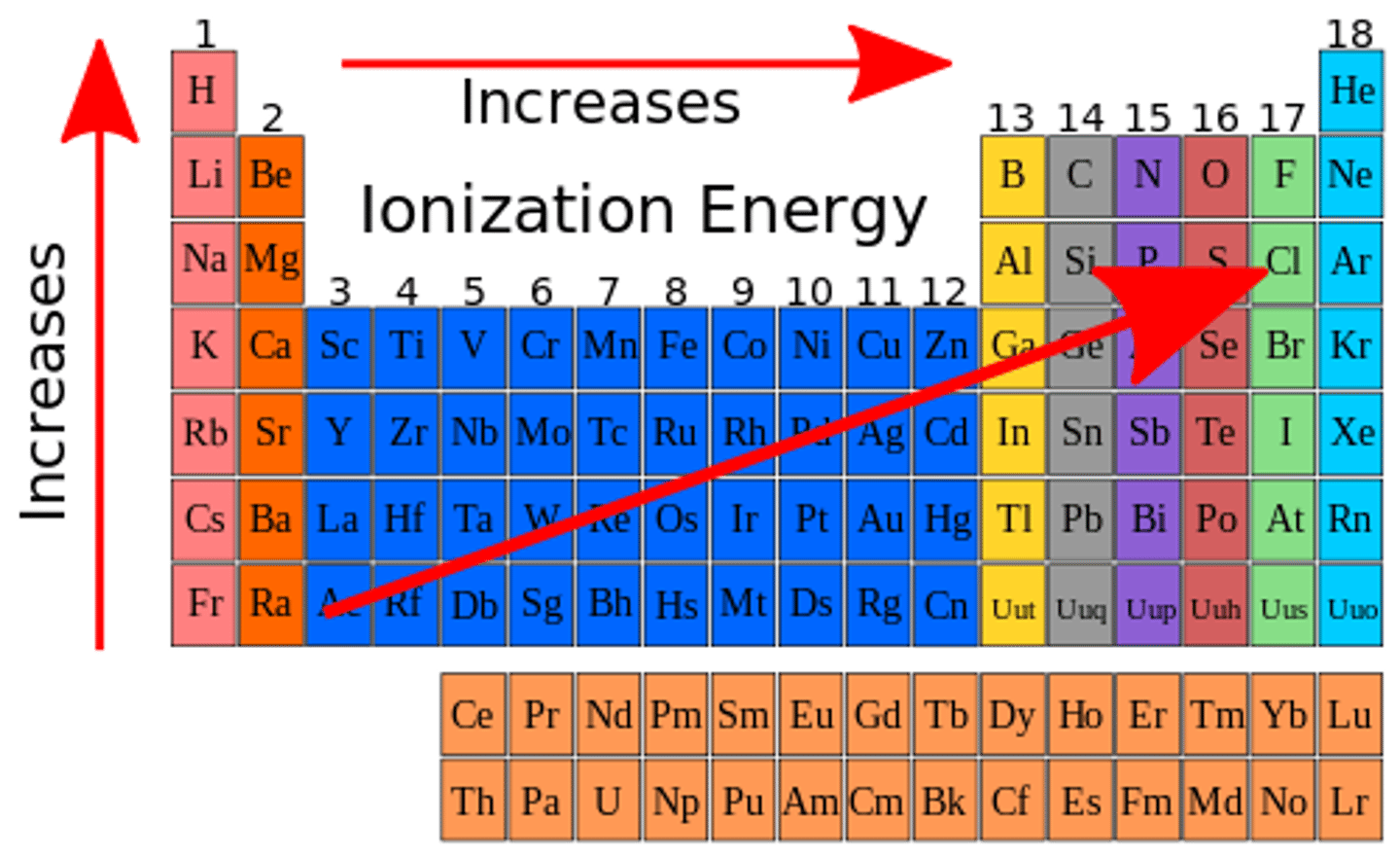
Ionization Energy/Electronegativity
Increases across a period (left to right) and decreases down a group (top to bottom).
Electron Affinity
Increases generally across a period (left to right), with some exceptions, and decreases generally down a group (top to bottom), with some exceptions.
What is the atomic radius?
The atomic radius is a measure of the size of an atom, defined as the distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost stable electron orbital.
How is atomic radius typically measured?
It is often measured as half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms that are bonded together (covalent radius).
What is the trend in atomic radius across a period & group
Atomic radius generally decreases across a period (left to right). Atomic radius generally increases down a group (top to bottom).
What is ionization energy?
Ionization energy is the minimum amount of energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous state.
What does a higher ionization energy indicate?
A higher ionization energy means the electron is harder to remove, indicating a stronger hold of the atom on its electrons.
What is the trend in ionization energy across a period & group?
Ionization energy generally increases across a period. Ionization energy generally decreases down a group.
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract a shared pair of electrons in a chemical bond.
Which elements have the most electronegativity?
Noble Gases
What does the difference in electronegativity between two bonded atoms determine?
It helps determine whether the bond is ionic or covalent.
What is the trend in electronegativity across a period & group?
Electronegativity generally increases across a period. Electronegativity generally decreases down a group.
What is electron affinity?
Electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when a neutral gaseous atom gains an electron to form a negative ion (anion).
What does a high (more negative) electron affinity value indicate?
It indicates a strong attraction for an extra electron, releasing energy when the atom gains one.
What is the trend in electron affinity across a period & group?
Electron affinity generally increases (becomes more negative) across a period. Electron affinity generally decreases down a group.
Practice with Atomic Radius:
Element has the highest Atomic Radius. Also which element has the lowest.
A. Francium and Helium
B. Flourine and Neon
C. 67
D. Potassium and Argon
A
Practice with Ionization Energy:
Element has the highest Ionization Energy. Also which element has the lowest.
A. Sodium and Magnesium
B. Helium and Cesium
C. Uranium and Neptunium
D. Argon and Mygone
B
Practice with Electronegativity:
Element has the highest electronegativity. Also which element has the lowest.
A. Boron and Sodium
B. Boron and potassium
C. Flourine and Cesium
D. IDK
C
What is a Lewis dot diagram?
A visual representation of the valence electrons in an atom or molecule.
Practice for Lewis Dot Diagram-
https://chemquiz.net/lew/
https://chemquiz.net/lew/
Practice for Periodic Trends-
https://chemquiz.net/ptr/
https://chemquiz.net/ptr/
What is an oxidation number?
A hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds to atoms of different elements were treated as purely ionic.
How do you find the oxidization #?
The combination of the 2 elements must have a net number of 0.
Ex: Na^+2 S^-2 = 0
Ionic Bond
Transfer of electrons
Covalent Bond
Sharing of electrons
Atoms Involved in Ionic Bond
Typically metal + non-metal
Atoms Involved in Covalent Bond
Typically non-metal + non-metal
Force of Attraction in Ionic Bond
Electrostatic attraction between ions
Force of Attraction in Covalent Bond
Mutual attraction to shared electrons
Typical State of Ionic Bond
Crystalline solids at room temp.
Typical State of Covalent Bond
Gases, liquids, or soft solids
What is a polyatomic ion?
A charged chemical species composed of two or more atoms covalently bonded together that functions as a single, discrete unit in chemical reactions.
What is lattice energy?
A quantitative measure of the strength of the electrostatic forces of attraction between ions in a solid ionic compound.
What does high lattice energy indicate about the stability of an ionic solid?
It indicates a very stable ionic solid, as a significant amount of energy was released during its formation.
How does lattice energy affect the melting and boiling points of ionic compounds?
Compounds with high lattice energies generally have high melting and boiling points because more thermal energy is needed to overcome the strong forces holding the ions together.
What is the relationship between lattice energy and the hardness of ionic materials?
High lattice energy contributes to the hardness of ionic materials because the ions are held in place very strongly.
How does lattice energy influence the solubility of ionic compounds in water?
Compounds with higher lattice energies are generally less soluble in water because the strong inter-ionic forces are difficult for water molecules to overcome.
What does Coulomb's Law describe?
The electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two charged particles.
What is the formula for Coulomb's Law?
F = k (q^1q^2)/r^2
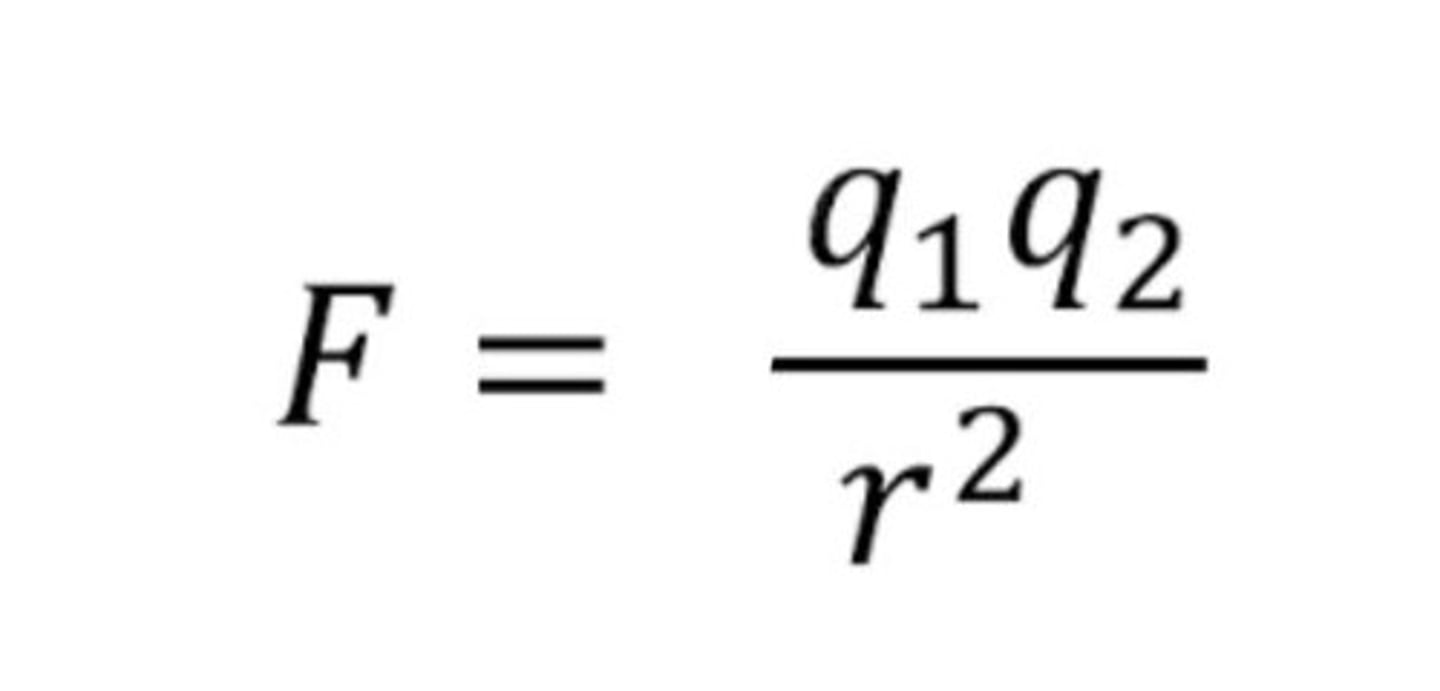
What is a chemical bond?
A lasting attraction between atoms, ions, or molecules that enables the formation of chemical compounds.
Why do chemical bonds form?
Because the resulting compound or molecule is more stable and has a lower potential energy than the individual, separated atoms.
What is the result of forming a chemical bond?
The formation of a compound or molecule that is more stable.
What happens to potential energy when atoms bond?
It decreases, leading to a more stable arrangement.
Electron Config Practice:
https://chemquiz.net/ele/
https://chemquiz.net/ele/
Ion
A charged atom or molecule
Cation
A positively charged ion
Anion
A negatively charged ion
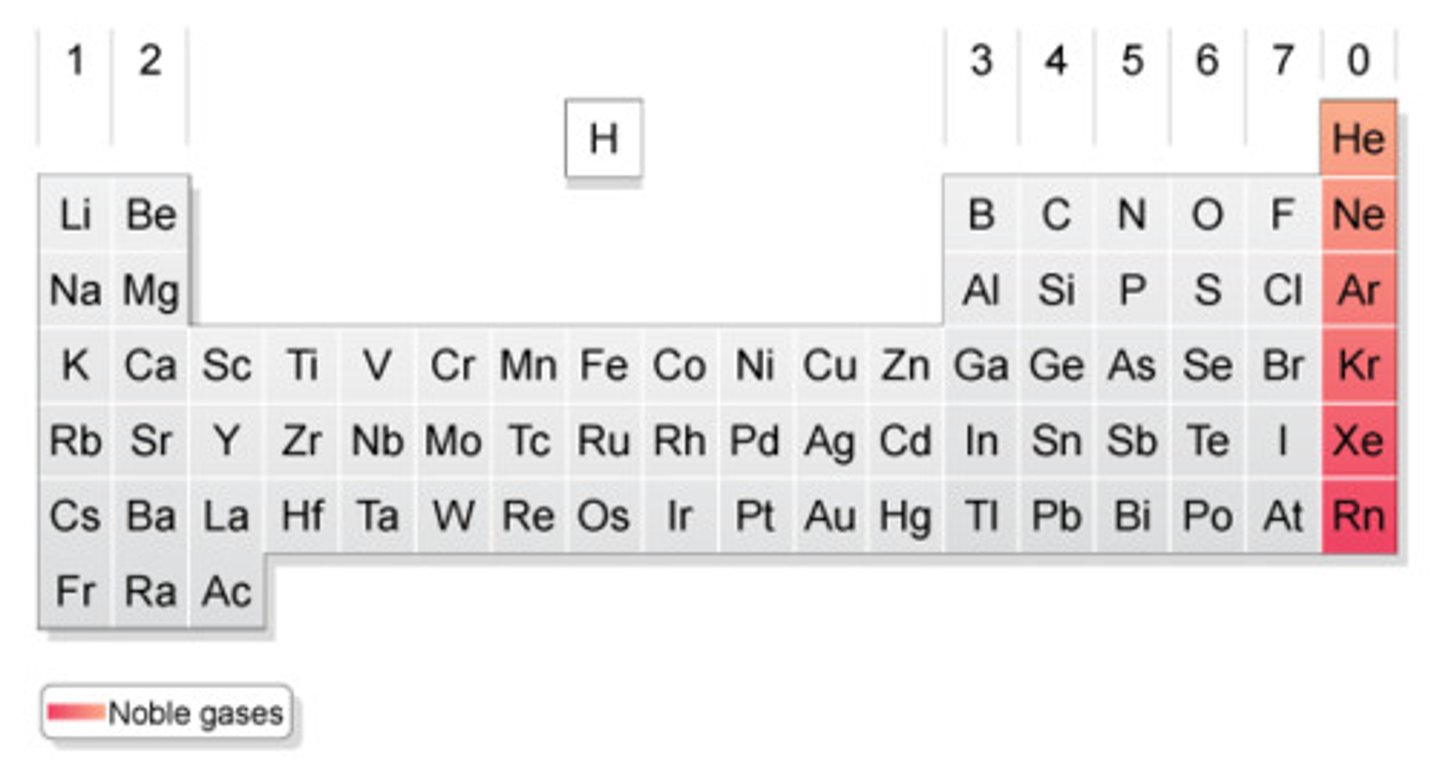
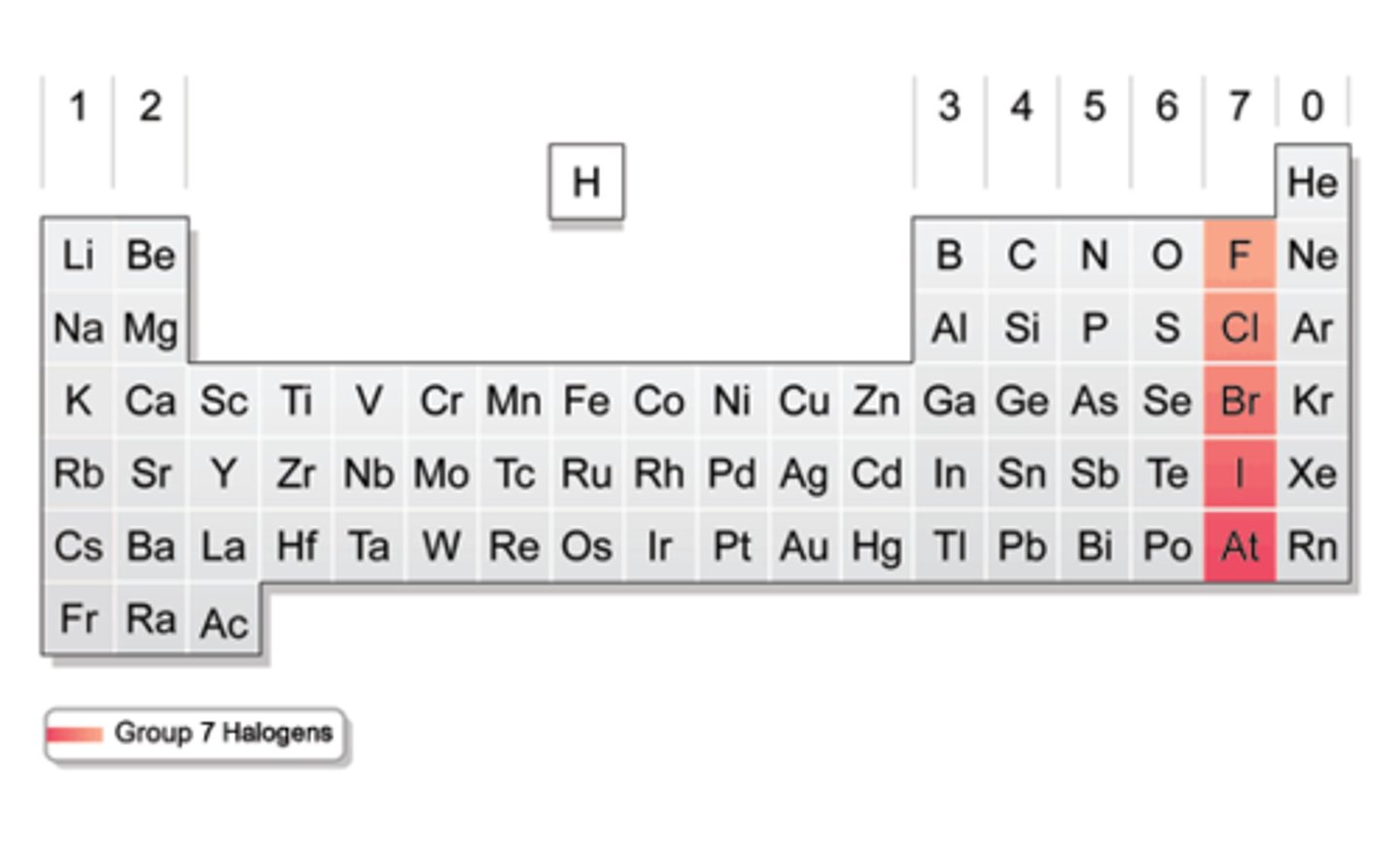
What on the table?
Halogens
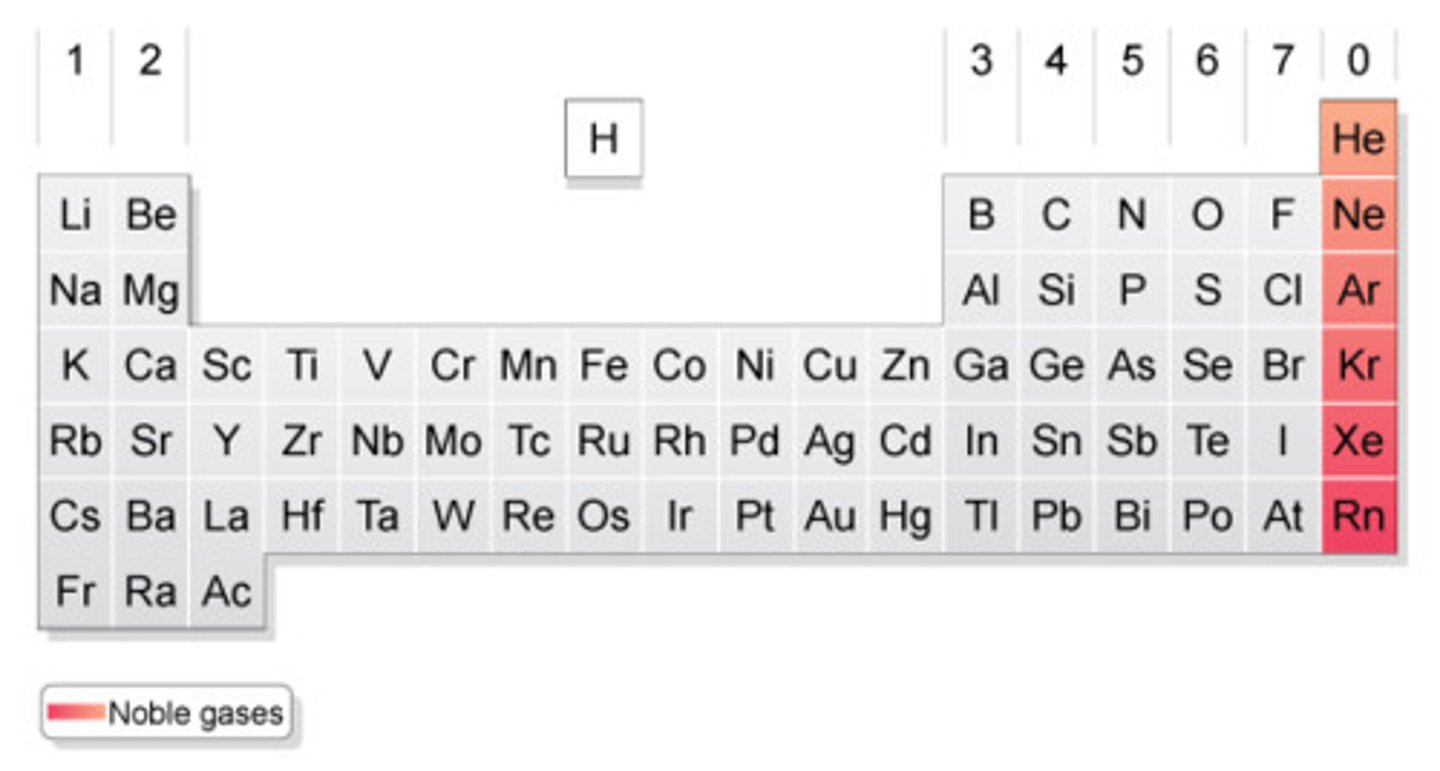
What is this on the table?
Noble Gases
Why does the Atomic Radius increase as you go up the group, Why does it go down?
increases cuz of more energy levels as you go down.

Why does the Atomic Radius decrease as you go across the period, Why does it go down?
it decreases as cuz as you go across, more protons pull the electron closer that causes the radius to decrease.

Why does the Ionization energy decrease as you go down the group?
Cuz the valence electrons are farther from, the nucleus and also that the atomic radius is bigger as you go down.
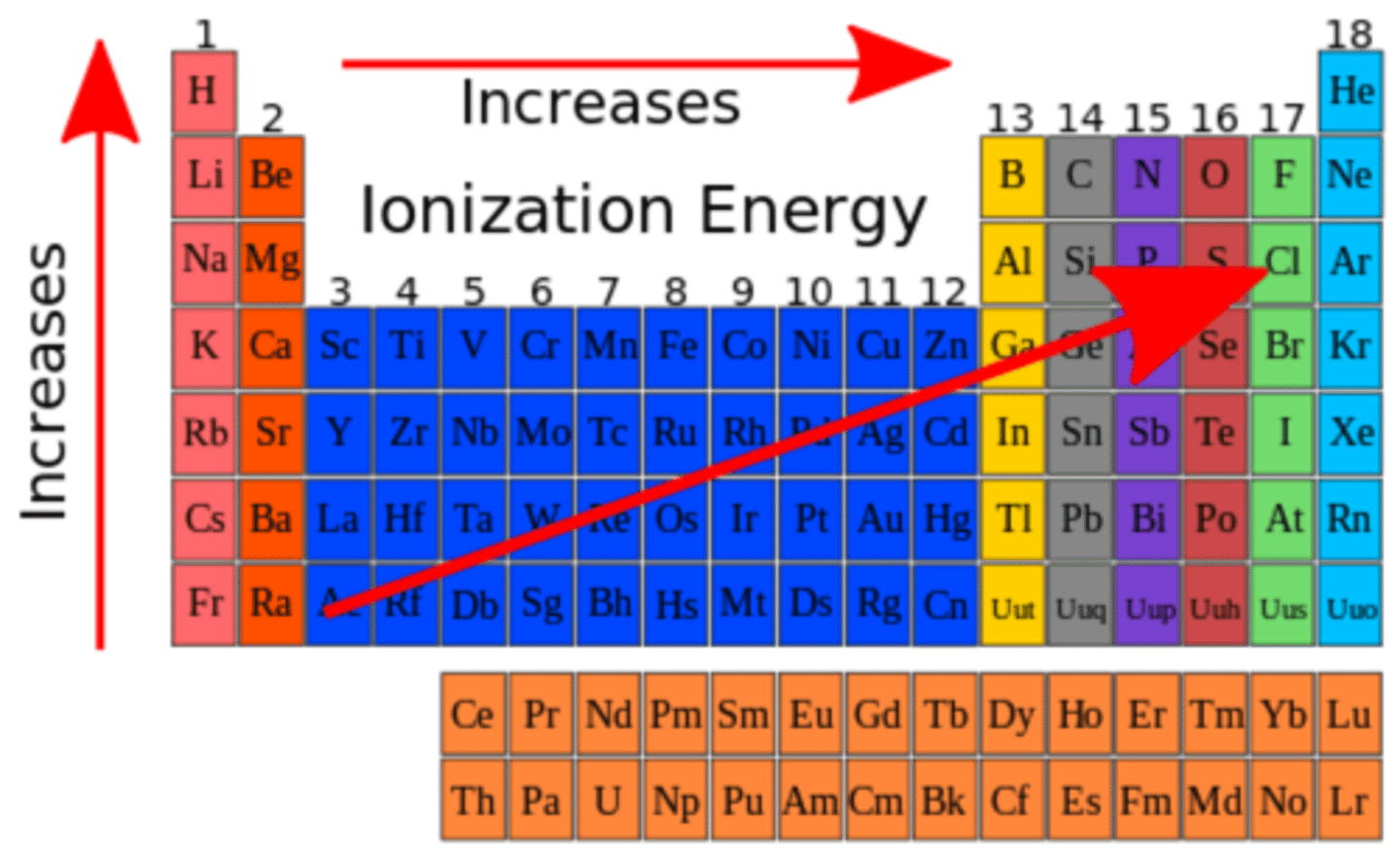
Why does the Ionization increase as you go across the period?
cuz atoms valence electrons are farher from the nucleaus, therefore less columbic attraction (force between particles) holds protons and electrons.
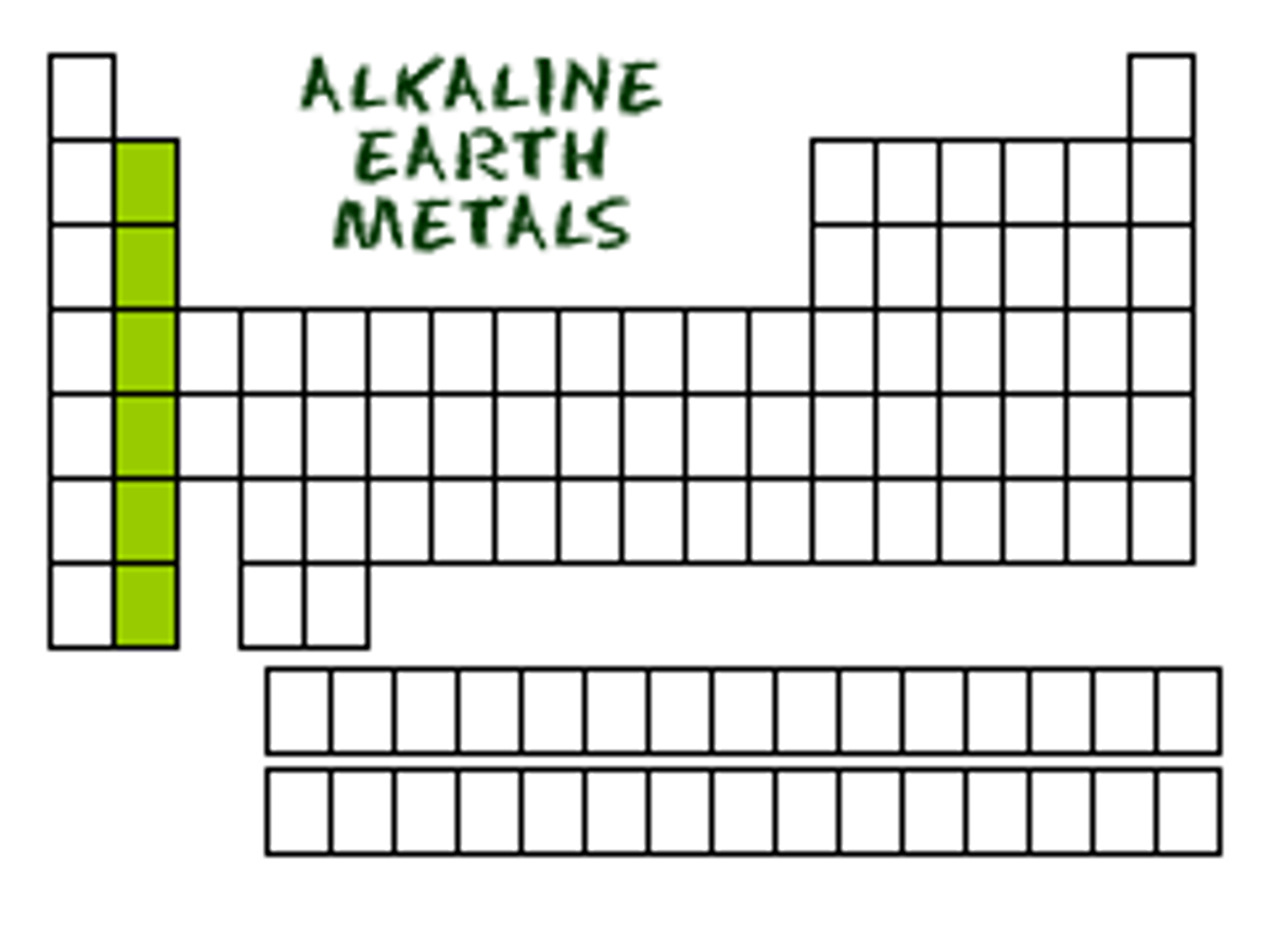
What is on the table?
Alkaline Earth metal
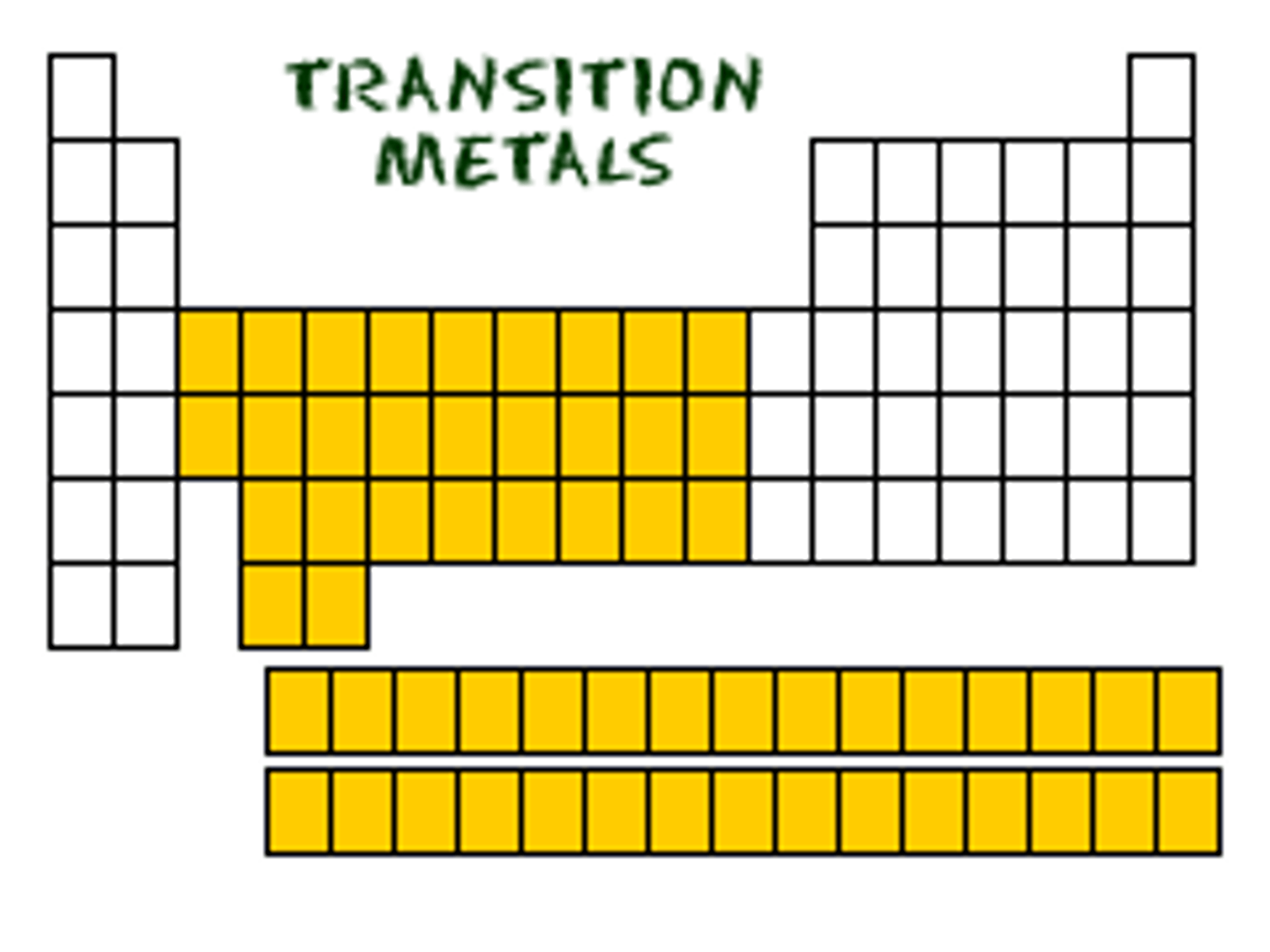
What on the table?
transition metal
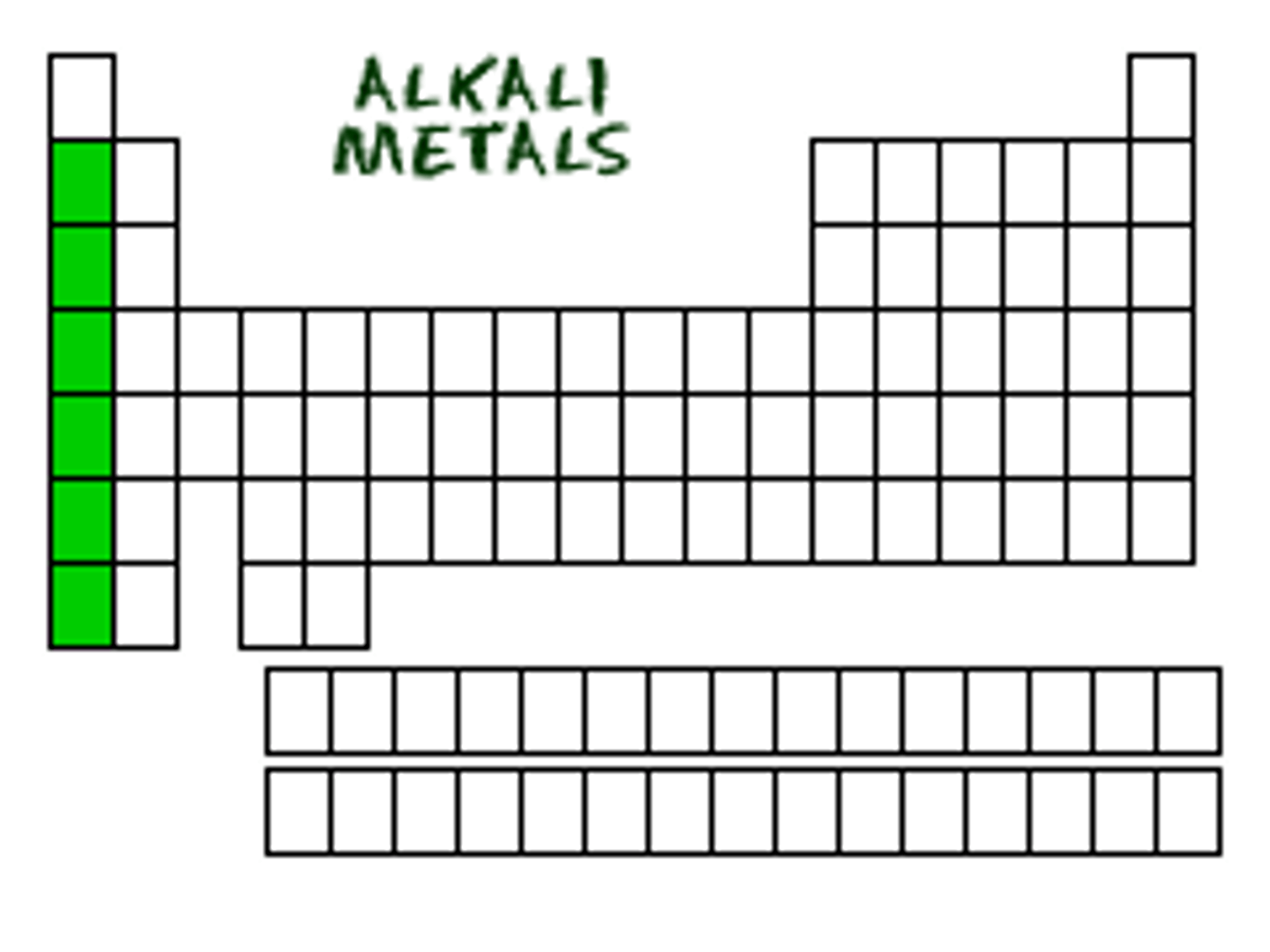
What on table?
alkali metal