Drugs for Parasitic Infections
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
What are the two broad groups of endoparasites?
protozoa or helminths
Malaria
Amebiasis
Giardiasis
Trichomoniasis
Toxoplasmosis
Protozoa or helminths?
Protozoa
Nematodes (roundworms), Trematodes (flukes), Cestodes (tapeworms)
Protozoa or helminths?
Helminths
Ectoparasites live on
skin or hair shafts (lice, scabies)
What is the worlds most important parasitic disease
malaria
Most malaria cases are caused by
P. falciparum and P. vivax (Other species: P. ovale and P. malariae)
In malaria, there is periodic rupture of _____ from erythrocytes into the bloodstream along with other _____ which lead to symptoms
merozoites
pyrogens
What is the life cycle of malaria
1. mosquito infects human
2.injected sporozoites migrate to liver; sporozoites enter liver cells, multiply, and emerge as merozoites
3. merozoites enter red blood cells and destroy them
4. mosquito ingests gametocytes with blood meal
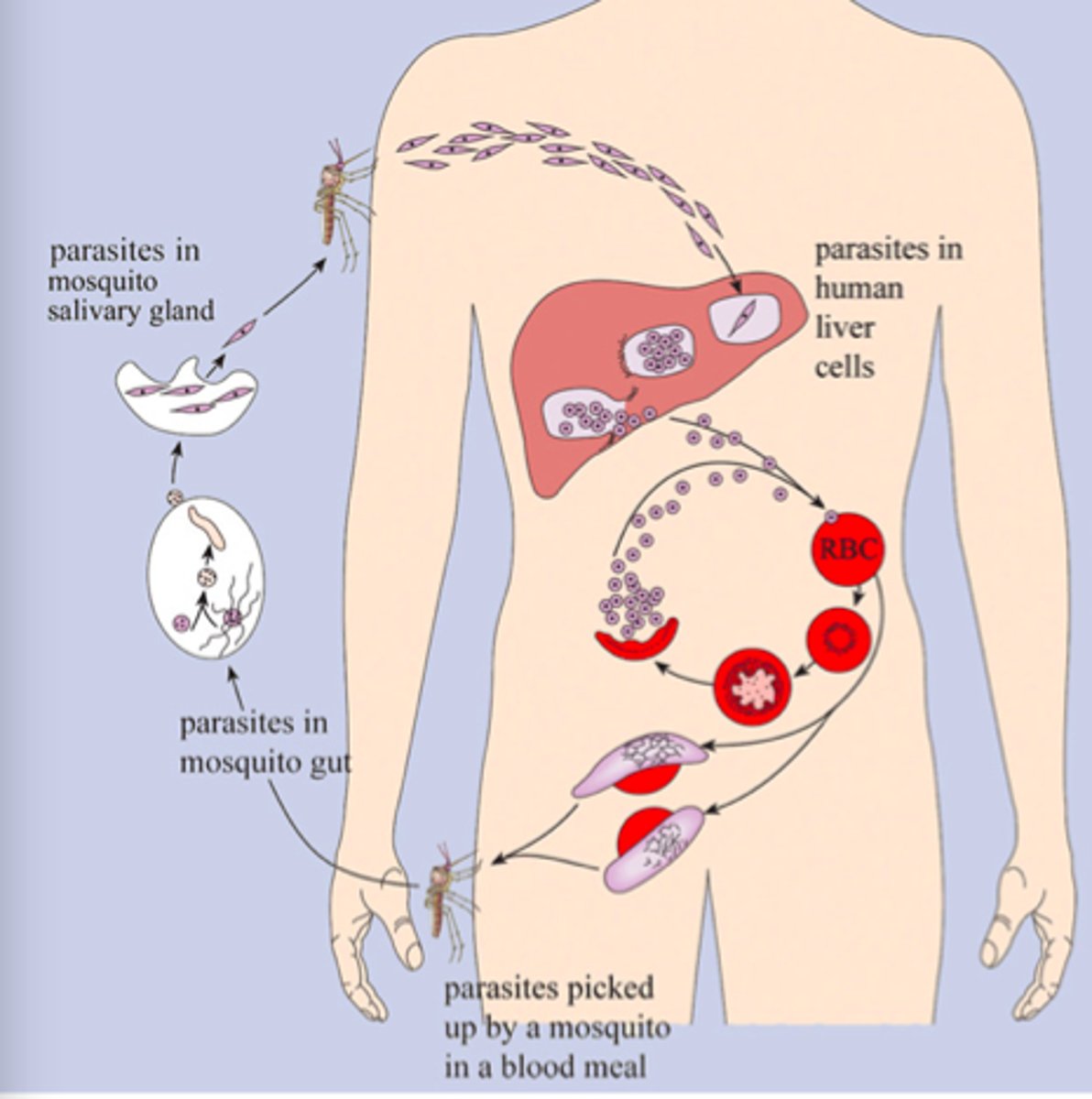
____ from mosquitos are not affected by drugs
sporozoites
What is the term for asexual multiplication that malaria undergoes in the liver
Exoerythrocytic schizogeny
Schizonts mature and release _____ into the blood
merozoites
Dormant schizonts must be treated with
primaquine
What is the term for the multiplication that malaria undergoes in the RBCs
erythrocytic schizogeny
Most antimalarial drugs prevent replication during what stage?
Erythrocytic schizogeny
What are the three forms of malaria therapy?
Suppressive (prophylactic), treatment of acute attack, prevention of relapse
What must be confirmed before drug treatment of malaria?
diagnosis
Which malaria infections are most severe?
P. falciparum
___ and ___ are species of malaria that can persist in the liver and cause relapses
P. vivax and P. ovale
What is the prophylactic rx given pre-travel for malaria
Chloroquine 500 mg once per week started 1-2 weeks before travel
What is the adult dose of chloroquine given for active erythrocytic stage malaria
Treatment: 1 g once, then 500 mg at 6 h, 24 h and 48 h
What are the adverse effects of chloroquine
Nausea, abdominal pain, headache, visual disturbances
Quinine sulfate is derived from the bark of the
cinchona tree in south america

What is the 1st line agent used for malaria in chloroquine resistant straints
quinine sulfate
Does quinine sulfate have a short or long half life
short
What is the dose given for quinine sulfate
Quinine sulfate 650 mg TID x 3-7 days
Quinine sulfate can be used in combination with what abx depending on the region
Doxycycline, tetracycline, or clindamycin for 3 to 7 days
What are the adverse effects of quinine sulfate
•GI symptoms: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
•Cinchonism: tinnitus, vertigo, deafness, headache, and dysphoria
•Hypoglycemia
What is blackwater fever
QUININE SULFATE causes possible hypersensitivity reaction causing massive hemolysis, hemoglobinemia, and hemoglobinuria
What cocktail was originally developed in British colonial india to hide the bitter taste of quinine
Gin and tonic
Are quinine products still on the market?
Taken off market in 2007 and only used for malaria now
Quinidine gluconate is a _____ of quinine
stereoisomer
What drug is used for severe, life threatening malaria
quinidine gluconate
What form is quinidine gluconate administered in?
parenteral
What is quinidine gluconate given with (same as quinine sulfate)?
doxycycline, tetracycline, clindamycin
What is the risk of quinidine gluconate from a cardiac perspective
Class 1a antiarrhythmic agent: need cardiac monitoring because of proarrhythmias
Quinidine gluconate is a potent inhibitor of ____ enzyme
CYP 2D6 (many drug interactions)
What is the drug of choice for patients with malaria requiring parenteral therapy?
artesunate IV
Artesunate IV is a derivative of the herbal artemisinin which is extracted from the ____ plant
wormwood plant
Artesunate IV is more effective than ____ and safer than _____
>effective than quinine
>safer than quinidine
what is the adverse effect of artesunate IV
hemolytic anemia
Artesunate IV is followed by the oral combination drug
Coartem
What are the drugs used for the erythrocytic stage of malaria
Cloroquine
Quinine sulfate
Quinidine gluconate
Artesunate IV
Malarone
Coartem
Mefloquine
Malarone is a combination of
atovaquone and proguanil
What is the 1st line agent for both prophylaxis and tx against chloroquine resistant plasmodia
Malarone
What is the dosage for Malarone
single dose w/ meals x3 days
What are the adverse effects of malarone
nausea, vomiting, rash, and headache
Coartem is a combination of
artemether and lumenfantrine
What is the first line treatment of chloroquine resistant plasmodia
Coartem
What is the dosage info for Coartem
twice daily w/ meals for 3 days
What are the adverse SE's for Coartem
n/v, headache, dizziness, weakness
Coartem can cause what cardiac related SE
prolonged QT interval
What should you AVOID when taking Coartem
CYP 3A4 inhibitor drugs
What antibiotic can be an alternative for prophylactic treatment against chloroquine resistant plasmodia
Doxycycline (100 mg daily 1-2 days before travel)
Mefloquine can be used for
prophylaxis and treatment of chloroquine-resistant Plasmodia
What is the half life of mefloquine
20 days
What are the adverse SE's of mefloquine
neuropsychiatric syndrome (depression, psychosis, and seizures) makes this a 2nd line agent for treatment
What 2 drugs does mefloquine interact with
quinine and beta blockers (lead to cardiac arrest)
Which antimalarial drug is used very frequently in the military
Mefloquine
Primaquine is a drug that works during the ____ stage
extra-erythrocytic
What is the only drug that prevents relapse from P. vivax and P. ovale
Primaquine
What is the dose given for primaquine
15 mg/day x14 days
You should use primaquine with either ____ or ____
chloroquine or quinine
What are the adverse effects of primaquine
abdominal cramps, nausea, hemolytic anemia 2nd to G6PD deficiency
Before using primaquine you must screen for
G6PD deficiency
G6PD deficiency
X-linked recessive trait resulting in hemolytic anemia
Entamoeba histolytica is caused by
Ingestion of cysts in contaminated food and water
What systemic symptoms can amebiasis cause
•Ulceration of the bowel and amebic dysentery
•Liver abscesses from entry through the portal vein
What are the two broad categories of amebicides used
luminal and tissue
Luminal amebicides are
poorly absorbed drugs used to treat asymptomatic disease
What are the 2 luminal amebicides we should know
•Iodoquinol - take with meals to limit GI toxicity
•Paromomycin - an aminoglycoside
Tissue amebicides are drugs of choice for _____ disease
invasive
What are the 2 tissue amebicides we should know
•Metronidazole (Flagyl) 750mg po tid x 10 days
•Tinidazole (Tindamax) 2 gm po qd x 3 days
Metronidazole is well absorbed from the ____ and widely distributed to most tissues including the brain
GI tract
What is the half life of metronidazole
8 hours (excreted in urine)
Metronidazole undergoes an intracellular conversion to toxic _____ by process unique to _____ bacteria and protozoans. This results in cell death by destruction of _____.
nitro radical
anaerobic bacteria
DNA
Metronidazole is active against protozoa causing what 3 diseases we've learned about?
amebiasis, giardiasis, trichimoniasis
Metronidazole is also active against most anaerobic bacteria including:
Bacteroides fragilis, Clostridia difficile, and Peptostreptococcus
Metronidazole is contraindicated in what portion of pregnancy
during 1st trimester
Considered a category B drug in 2-3rd trimesters
What are the adverse effects of metronidazole
Nausea, headache, dry mouth, metallic taste
Metronidazole should be taken with
food to minimize GI effects
Name two drugs that metronidazole interacts with
Warfarin and ethanol
When warfarin is taken with metronidazole, what can occur?
increase in INR (bleeding risk)
When ethanol is taken with metronidazole, what can occur?
acetaldehyde poisoning resulting in flushing, nausea, vomiting, and throbbing headache (metronidazole inactivates aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme necessary for metab of acetaldehyde)
Tinidazole is a ____ generation nitroimidazole
2nd gen
What are 3 advantages of Tinidazole over metronidazole (hint: what is it active against, half-life, Giardia use)
•Active against some metronidazole-resistant strains of Trichomonas
•Longer half-life allows single daily dosing
•Can use single dose against Giardia
Tinidazole has the same adverse effect profile as
metronidazole
Tinidazole is a category ____ drug in pregnancy
C
What are the two treatments used for Giardiasis
•Metronidazole 250mg tid x 7days
•Tinidazole - single dose of 2 gm
What is the treatment used for Trichomoniasis
Metronidazole or tinidazole 2 gm x 1 dose
What is the treatment for Toxoplasmosis
pyrimethamine + sulfadiazine
Pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine are potent inhibitors of _____ reductase and can induce ____ deficiency
dihydrofolate, folate
Nematodes are also called
round worms
Ascariasis
giant round worm
Trematodes are
flukes
what is the 2nd leading cause of morbidity from parasitic diseases
Schistosomiasis (snail vector)
Cestodes are
tapeworms
How does one acquire tapeworms
pork, beef, fish tapeworms
What is the drug of choice for nematode infections
albendazole
Albendazole inhibits _____ function and depletes ____ stores leading to worm death
microtubules, glycogen
albendazole should be avoided during the ___ trimester
1st