BIO 1010 Unit 3 Exam
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Cell
The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism; capable of preforming all processes neccesary for life
Robert Hooke
Who discovered cells in plant cell walls in 1665?
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
Who first observed single celled organisms in 1675?
Cells are the most basic unit of life
What is the first rule of cell theory?
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
What is the second rule of cell theory?
All cells arise from pre-existing cells
What is the third rule of cell theory?
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
Who proposed cells are the basic unit of life and co-founded cell theory in 1838?
Rudolf Virchow
Who proved that cells replicate through division in 1885?
Light microscopy
A type of microscopy that uses visible light and lenses to magnify the details of an object
Electron microscopy (TEM and SEM)
A type of microscopy that uses electron beams to provide detailed imaging of cell structure and organelles
Cell fractionation and centrifugation
Techniques used to separate cellular components based on size, density, and solubility
Surface area to volume ratio
Aspect of cells that influences cell metabolism, nutrient exchange, and waste removal; As cells grow larger, their volume increases more rapidly than their surface area
Prokaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Does not contain a nucleus
Prokaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Lacks membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
typically smaller; 1-10 micrometers
Prokaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Contains 70s ribosomes
Prokaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Reproduces through binary fission
Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Contains membrane bound organelles and linear DNA inside a nucleus
Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Has a complex structure with cytoskeleton
Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Typically larger in size; 10-100 micrometers
Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Contains 80s ribosomes
Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic?
Reproduces through mitosis and meiosis
Stem cells
Undifferentiated cells with the ability to differentiate into specialized cell types; important for development, tissue repair, and regenertion
Embryonic stem cells
Stem cells found in embryos that are capable of developing into any cell type
Adult stem cells
Multipotent stem cells found in various tissues, important for repair and regeneration
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Electron microscopy that captures detailed surface structures.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Electron microscopy that focuses on internal structures
Plasma membrane
Cell structure that is selectively permeable and controls what goes in and out of the cell; made up of a phospholipid bilayer
Cytoplasm
Gel like structure within the cell that contains organelles, cytoskeleton, and various molecules
Ribosomes
Cell structure composed of rRNA and proteins; site of protein synthesis
Free in the cytoplasm or bound to the ER
Where are the ribosomes found?
Nucleus
Organelle with a double membrane structure (nuclear envelope) and nuclear pores; contains chromatin; houses genetic material + regulates gene expression
Nucleolus
Organelle within the nucleus; site of ribosome assembly (rRNA synthesis and ribosomal subunit assembly)
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
An extensive network of membranes found in Eukaryotic cells; involved in the synthesis, folding and modification of proteins, calcium storage and release, and drug metabolism and detoxification
Rough ER
ER studded with ribosomes; involved in protein synthesis
Smooth ER
ER without ribosomes; involved in lipid synthesis, metabolic processes, and detoxification
Golgi Apparatus
Organelle made up of a stack of vesicles; involved in processing, packaging, and shipping of cellular products
Cisternae
The flattened sacs that make up the golgi apparatus
Glycosylation
One way that the golgi modifies molecules
Vesicles
Small membrane bound stack that transport substances within the cell
Vacuoles
Large membrane bound sacs in plant and fungi cells; Store water, ions, nutrients, pigments, and contribute to cell structure
Central vacuole
A type of vacuole in plant cells that helps keep turgor preassure
Mitochondria
Double membrane bound organelle with an outer membrane and an inner crista; participates in cellular respiration and ATP production
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The process through which mitochondria produces ATP
Peroxisomes
Membrane bound organelles that break down acids
Endomembrane system
A collection of membrane bound organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport proteins/lipids
Rough and Smooth ER, Golgi, and Vesicles
What organelles are part of the endomembrane system?
A, C, E, B, D
Put the following sequence of Endomembrane functions in order:
A) Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes on the rough ER synthesize proteins.
B) Processing in the Golgi: Proteins are further modified and sorted.
C) Folding and Modification: Newly synthesized proteins undergo initial modifications in the ER.
D) Vesicle Transport: Processed proteins are packaged into new vesicles for transport to their final destinations.
E) Vesicle Formation: Vesicles bud off from the ER carrying these proteins to the Golgi.
Centrosome
Organelle composed of two centrioles arranged perpendicularly; Organizes microtubules during cell division (found in animal cells)
Centrioles
Pair of cylindrical structures within the centrosomes; organize the mitotic spindle (found in animal cells)
Lysosomes
Membrane bound organelles that recycle and clean cellular waste, macromolecules, and pectin (found in animal cells); digest damaged organelles and engulfed pathogens, such as bacteria, within vesicles
Cell wall
Cellular structure made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin; provides structural support and protection against stress (found in plant cells)
Chloroplasts
Double membrane bound organelles containing chlorophyll; site of photosynthesis (found in plant cells)
Cytoskeleton
A structure of protein fibers within the cytoplasm that provides structural support, facilitates cell movement, and maintains cell shape
Microtubules
Hollow tubes made of tubulin that provide rigidity and serve as tracks for organelle movement
Intermediate filaments
Fibrous proteins that provide mechanical strength and support to the cell
Microfilaments
Thin solid rods made of actin proteins involved in cell movement and that support cell shape (ex. muscles)
Flagella
Long whiplike structures that propel entire cells
ex. Sperm or algae movement
Cilia
Hairlike projections that help propel fluids across cell surfaces (ex. trachea) or help with the reception of signals (ex. sensory olfactory neurons)
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
A complex network of proteins and carbohydrates that surround cells in tissues (ex. collagen); provide structure, regulate function, and aid in cell signalling
Cell adhesion, cell migration, and cell differentiation
List 3 examples of activities of the extracellular matrix
Cell Junctions
Specialized structures that facilitate communication and adhesion between adjacent cell or between cells and the ECM
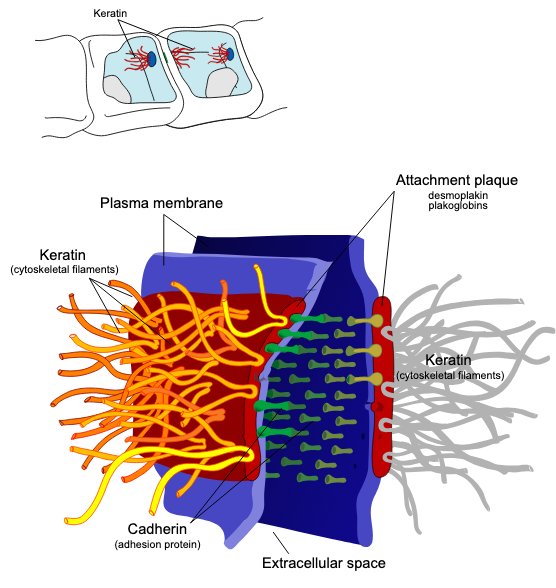
Desmosomes
A type of cell junction
Anchors cells together using intermediate filaments, especially in tissues subject to mechanical stress (ex. skin)
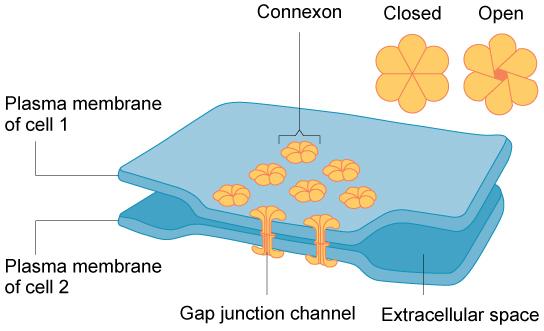
Gap junctions
A type of cell junction
Channels that allow direct communication and the exchange of small particles between adjacent cells to coordinate cell activities (ex. cardiac muscle contraction)
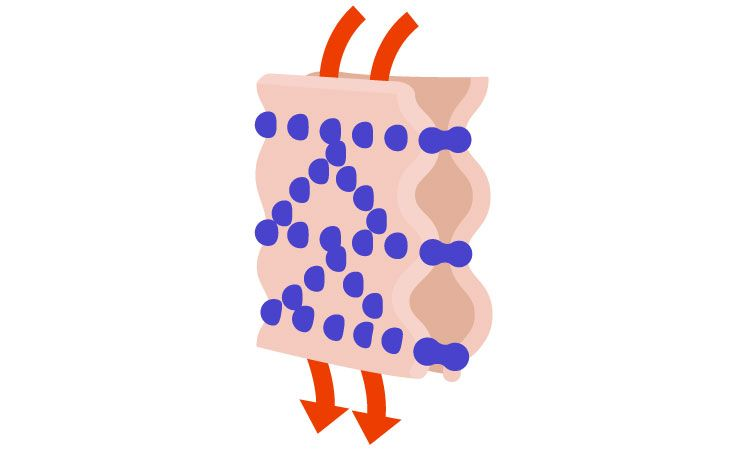
Tight junctions
A type of cell junction
Forms a continuous barrier between cells sealing off the intercellular space to maintain tissue integrity and reliable transport
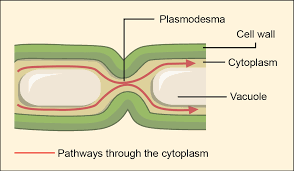
Plasmodesmata
A type of cell junction in plant cells
Cytoplasmic channels that traverse the cells walls of plant cells, connecting the cytoplasm of adjacent cells
Desmosome
What cell junction is this?
Gap junction
What cell junction is this?
Tight junction
What cell junction is this?
Plasmodesmata
What cell junction is this?
Fluid mosaic model
Model proposed by S.G. Singer and Garth Nicolson in 1972; depicts the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components that can move laterally within the membrane
Phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and charbohydrates
What are the main 4 components of the plasma membrane?
Phospholipids
Provide the structural component forming a lipid bilayer in the plasma membrane
Head
Part of a phospholipid that is hydrophilic; made up of a phosphate group attached to a glycerol molecule; oriented towards the outside of the membrane
Tail
Part of a phospholipid that is hydrophobic; consists of two saturated or unsaturated fatty acid chains; oriented towards the inside of the membrane
Saturation of phospholipid tails and presence of cholesterol
The fluidity of the plasma membrane depends on ________ and __________
Integral proteins
proteins that span the lipid bilayer and function in transport and signaling.
Peripheral proteins
proteins that are attached to the surface of the lipid bilayer and provide structural support and participate in signaling.
Channel and Transport proteins
List two types of integral proteins
In the outer surface
Where are carbohydrates found in the phospholipid bilayer?
Cell Recognition, Immune Response, and Cell-Cell communication
List the three functions of carbohydrates in the plasma membrane
Inside the phospholipid bilayer
Where is Cholesterol found in the cell membrane?
Regulates the fluidity of the cell membrane
Why is cholesterol important
Receptors
Integral proteins that bind specific molecules (ligands) such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or antigens and trigger cellular responses by initiating signal transduction pathways
Recognition sites
Carbohydrate chains on glycoprotiens and glycolipids that allow cells to recognize and adhere to each other
Viruses
_____ exploit specific glycoprotiens and receptors on host cell membranes for attachment and entry
Viral evolution
Rapid changes in surface markers (antigens) that allow viruses to evade immune detection and adapt to host defenses
Diffusion
Passive transport where substances move from high to low concentration
Passive transport
Molecule transport that does not require energy
Concentration gradient, Molecular size, Temperature, Solvent density
List the 4 factors that affect diffusion
Greater
Greater or less?
The ____ the difference in the concentration of two solutions the faster diffusion
Smaller
Bigger or smaller?
The ____ the molecules the faster the rate of diffusion
Higher
Higher or Lower?
The ____ the temp the faster the rate of diffusion
low
High or low?
Solvents with ___ densities dissolve faster
Facilitated diffusion/transport
Diffusion that utilizes transport proteins (channels or carriers) to move substances too large to diffuse through the membrane; does not use energy and moves with the concentration gradient
Osmosis
Diffusion specific to water molecules; moves water from low solute concentration to high solute concentration
Hypotonic
What type of solution is the cell in?
Water enters the cell because its concentration of solutes is higher than that of the solution causing lysis
Hypotonic
The solution or cell in reference has less solutes than that it is being compared to
Hypertonic
The solution or cell in reference has more solutes than that it is being compared to