Chapter 10 Unemployment
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what is the long run type of unemployment called
Natural Rate of Unemployment
what is the short run type of unemployment called
Cyclical Unemployment
Natural Rate of Unemployment
baseline level of unemployment in an economy that it returns to in the long run
does the natural rate of unemployment vary
yes
what counts as employed
worked any part-time or full-time paid job in the last week
what counts as unemployed
MUST MEET ALL 3 CONDITIONS:
don’t have a paid job
are willing and able to work
looked for jobs in the past 4 weeks
if you are temporarily laid off, you are counted as ___
unemployed
if you are starting a new job soon, you are counted as __
unemployed
what counts “not in the labor force”
neither employed or unemployed
3 examples of “not in labor force”
retired
full-time student
stay at home parent
what might overstates the unemployment rate
well qualified job seekers take a few weeks to find a new job
what might understate the unemployment rate
Discouraged workers: willing to work but think no jobs are available, so they stop their search
Marginally attached workers: temporarily stopped searching (maybe starting work soon)
Underemployed workers: people working less than they want
in terms of hours (visible unemployment)
in roles their skills don’t match (invisible unemployment)
how do age, education, and regional differences affect unemployment
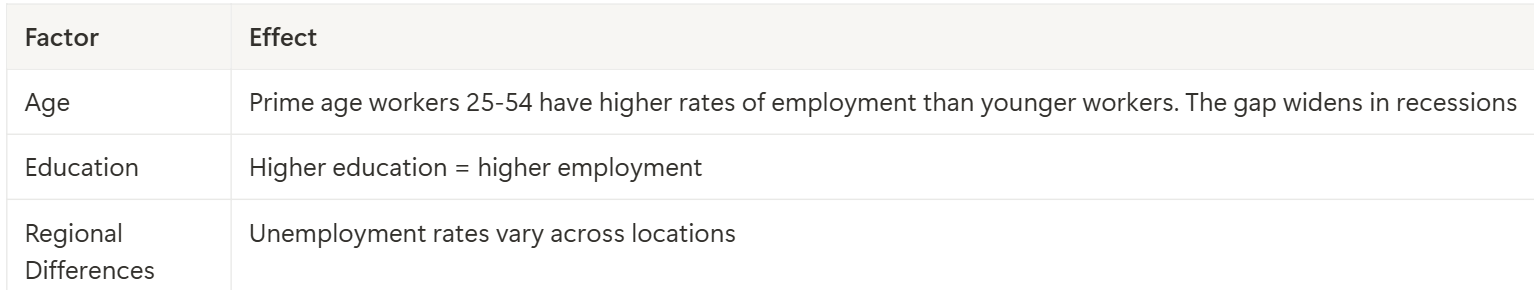
most unemployment periods are __
short
there is an ___ relationship between GDP growth and unemployment
inverse
name 2 causes of long run unemployment (don’t go into detail)
Frictional Unemployment
Structural Unemployment
Frictional Unemployment
The time spent looking for a job
unemployed university graduates
workers changing jobs, relocating, looking for their first job
allows better matching between workers and jobs → improves productivity and satisfaction
Structural Unemployment
Unemployment for long periods of time due to a surplus in labor - more workers than jobs
occurs when the wage is ABOVE the equilibrium wage
minimum wage ensures living standards, but causes unemployment for young and less skilled workers
effect, advantage and disadvantage of
Minimum wage
Unions
Efficiency Wages
Gov policies
Skills mismatch

In the labor market, __ are demanders and _ are the suppliers
businesses, workers
natural unemployment formula
Natural Unemployment = frictional unemployment + structural unemployment
Cyclical Unemployment
fluctuates with the economy’s ups and downs, often exceeding the natural rate during recessions and dipping below it during booms
the impact of expansions and recessions
Cyclical Unemployment formula
cyclical = actual unemployment rate - natural unemployment rate