Alkenes Reactions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
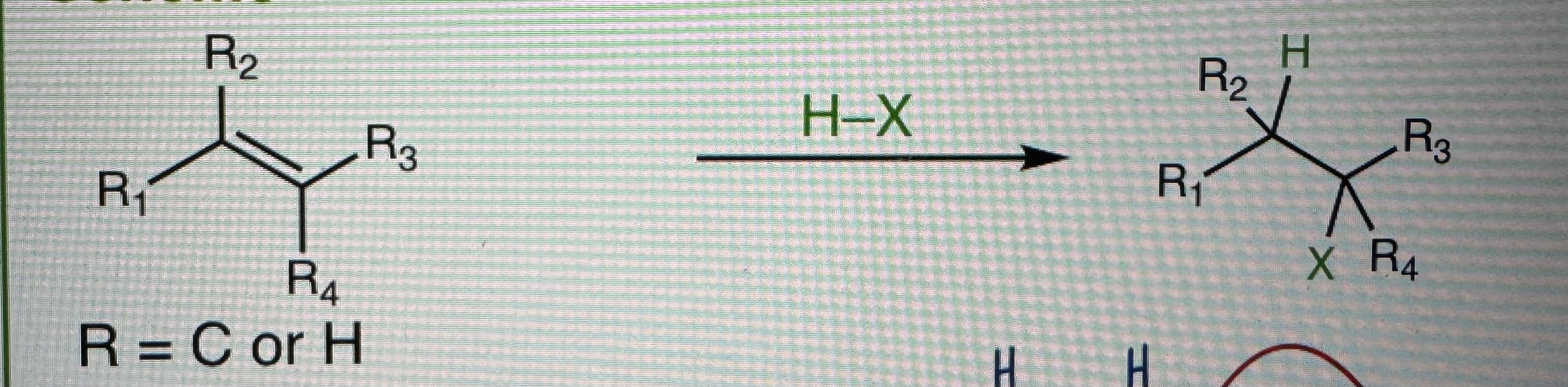
Hydrohalogenation (Electrophillic Addition of H-X)
H-X = HCI, HBr, HI, H3O+
Follows Marikovnikov’s Rule (X- adds to more substituted carbon)
Racemic Mixtures
Carbocation Intermediate
Front or backside attack
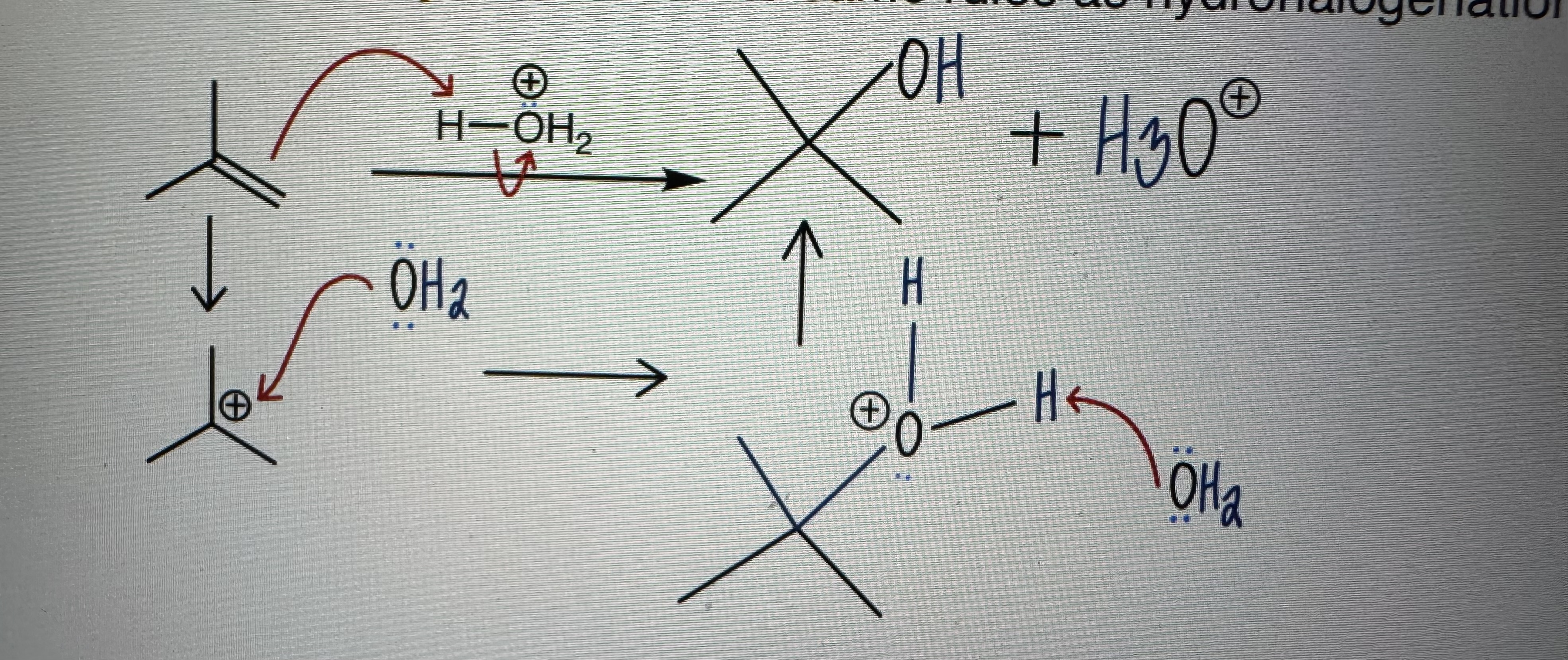
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration
Same as hydrogenation WITH a deprotonation step
Follows Marikovnikov’s Rule (X- adds to more substituted carbon)
Racemic mixtures
Catalytic amount of acid
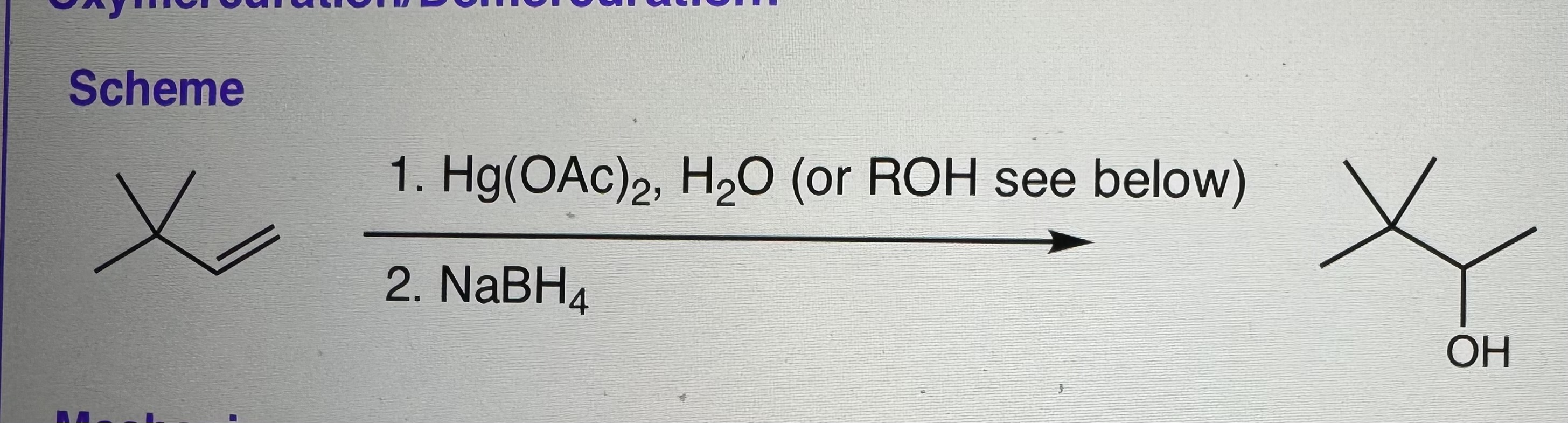
Oxymercuration/Demercuration
Uses:
Step 1) Hg(OAc)2 and H2O (or ROH to form ethers)
Step 2) NaBH4
-Markovnikov addition
-NO rearrangements
-NO mechanism needed for demercuration
-Racemic mixtures of products
-H2O (Nu) will attack MOST SUBSTITUTED C (most positively charged as electron density goes to Hg)
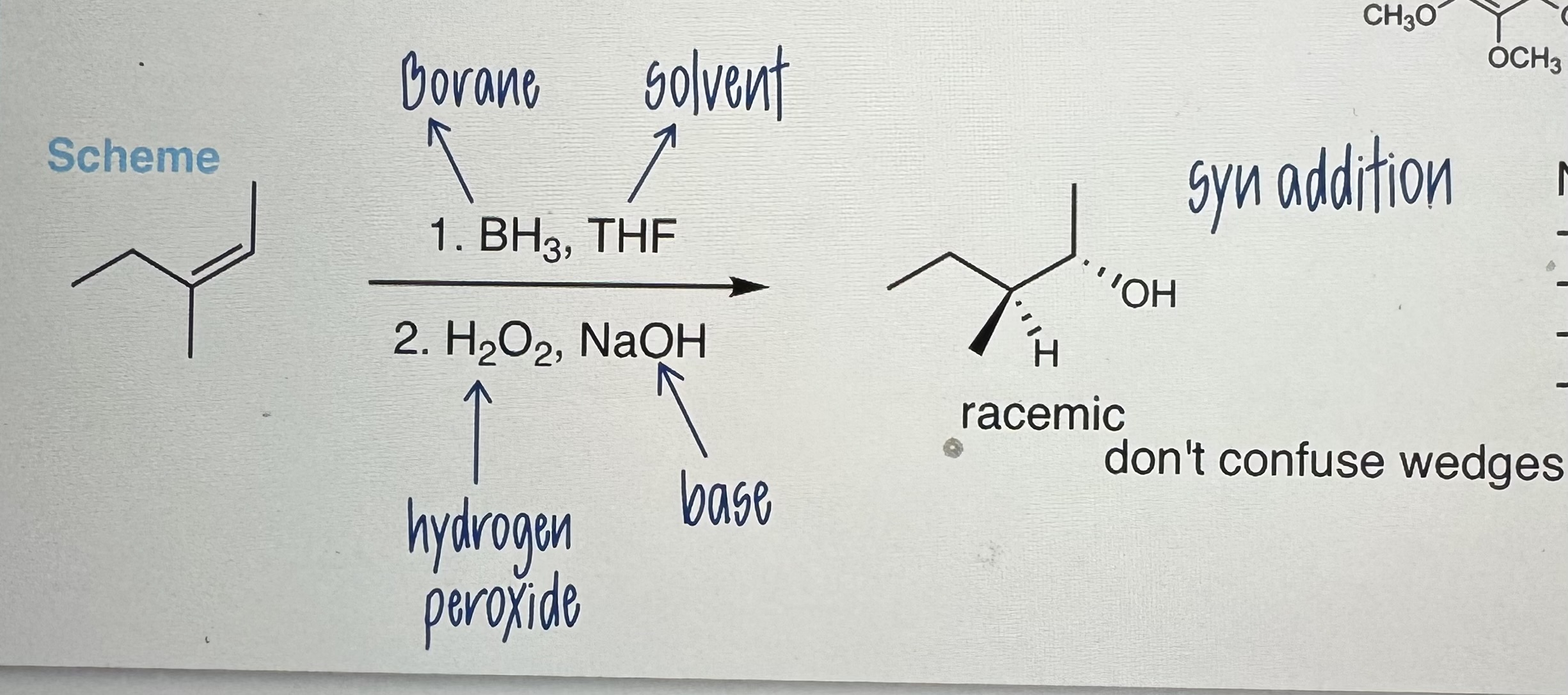
Hydroboration/Oxidation
Uses:
Step 1) BH3 (Borane), THF (solvent)
Step 2) H2O2 (H peroxide), NaOH (base)
-ANTI- Markovnikov Product (adds to LEAST substituted carbon) boron groups bond to less statically hindered Carbon and more electro + than H
-NO rearrangements
-Racemic Mixtures
-Borane Reagents (BH3, B2H6, 9-BBN)
-Syn addition: wedges facing them same side (NOT / absolute configuration)
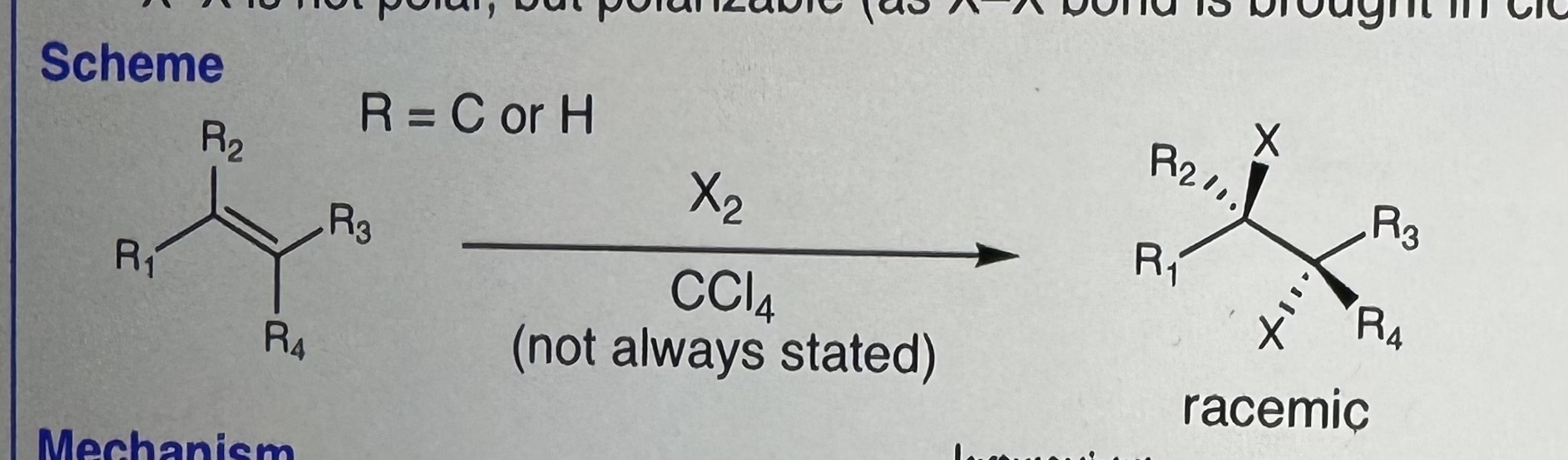
Halogenation
X-X is NOT polar (may be polarizable due to close pi bond or dipole)
Step 1) Replace X-X with Cl2, Br2, or I-Cl
Step 2) CCI4 = non nucleophillic solvent
-Products are racemic (both enantiomers should be drawn)
Anti addition of X2
-Trans product
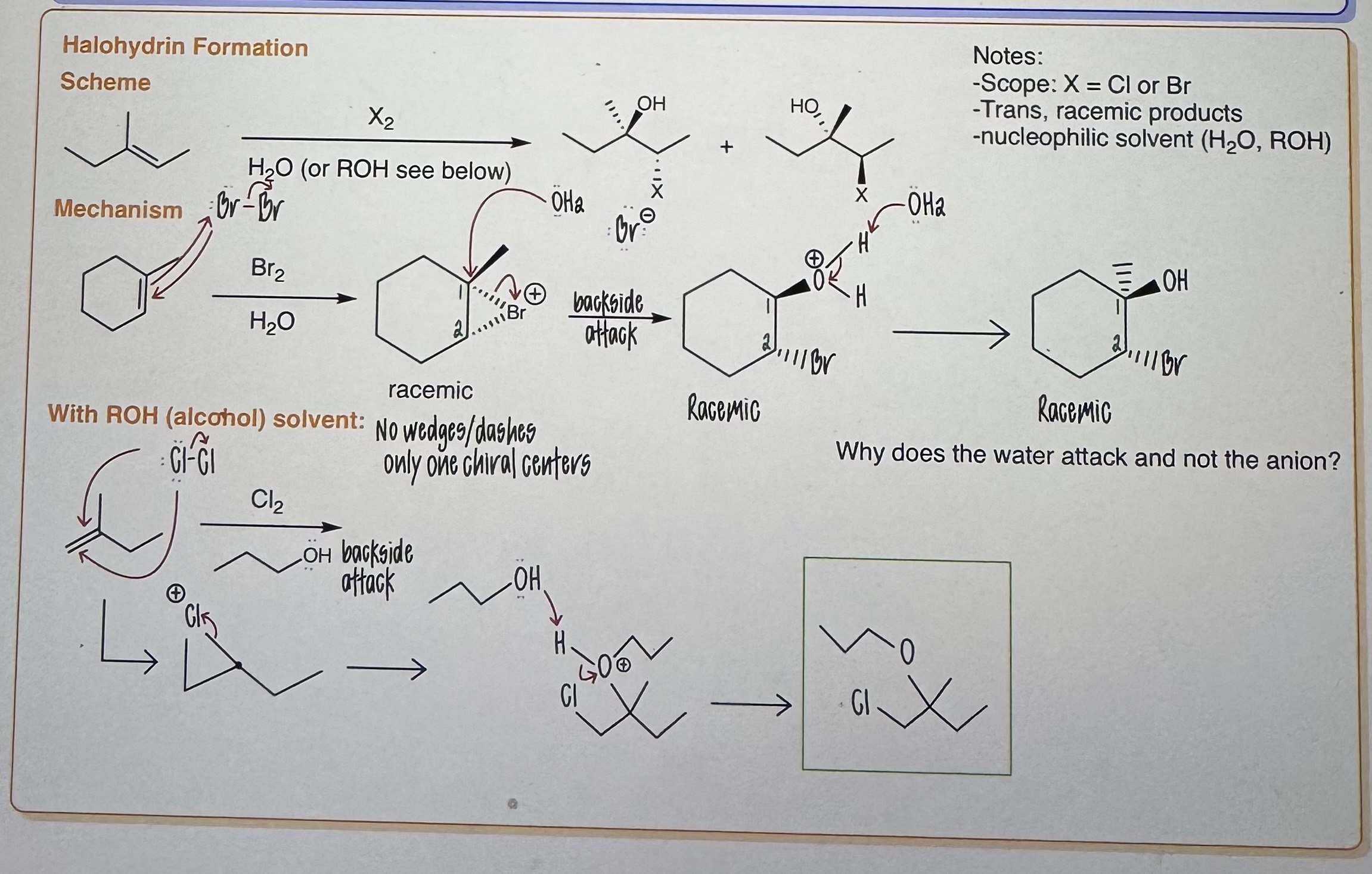
Halohydrin Formation
Step 1) X2 = Cl or Br
Step 2) H2O, ROH (nucleophillic solvent)
-Trans, racemic products
-Witb ROH (alcohol) solvent: No wedges/dashes only ONE chiral center
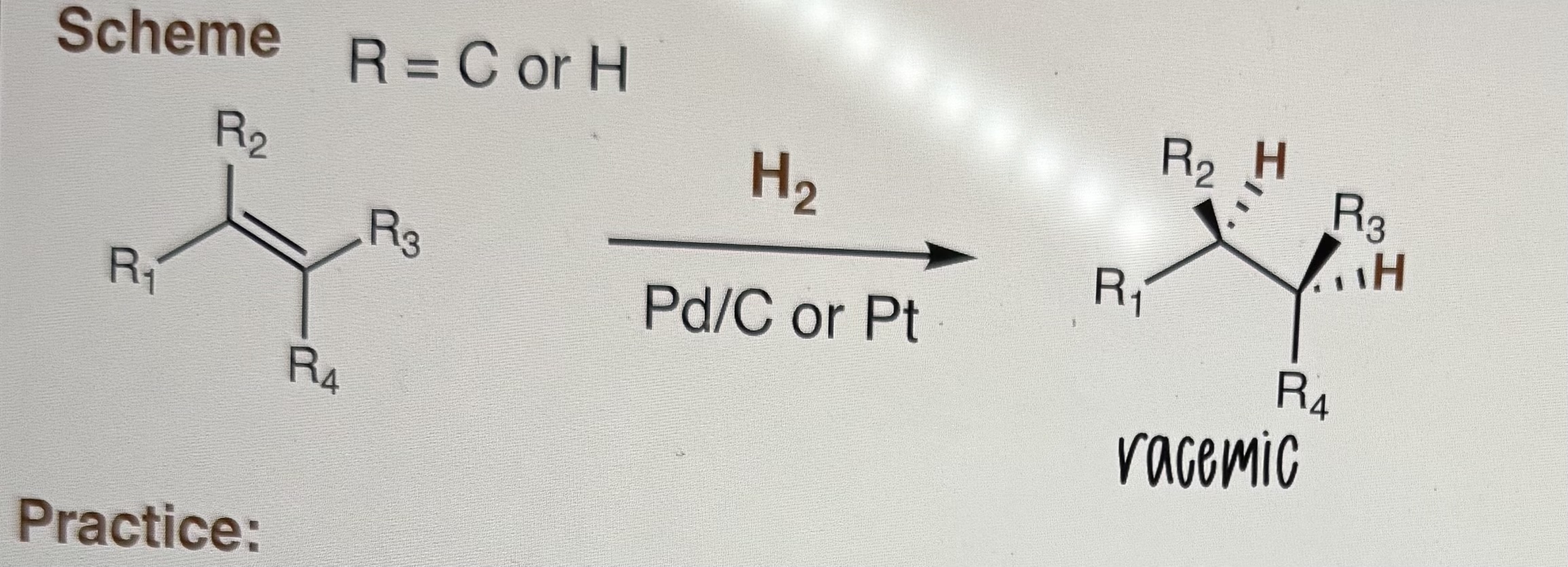
Hydrogenation of ALKENES
R = C or H
Step 1) H2
Step 2) Pd/C or Pt
-Syn addition of hydrogen
-Racemic products
-NO mechanisms
-Assume excess is H2
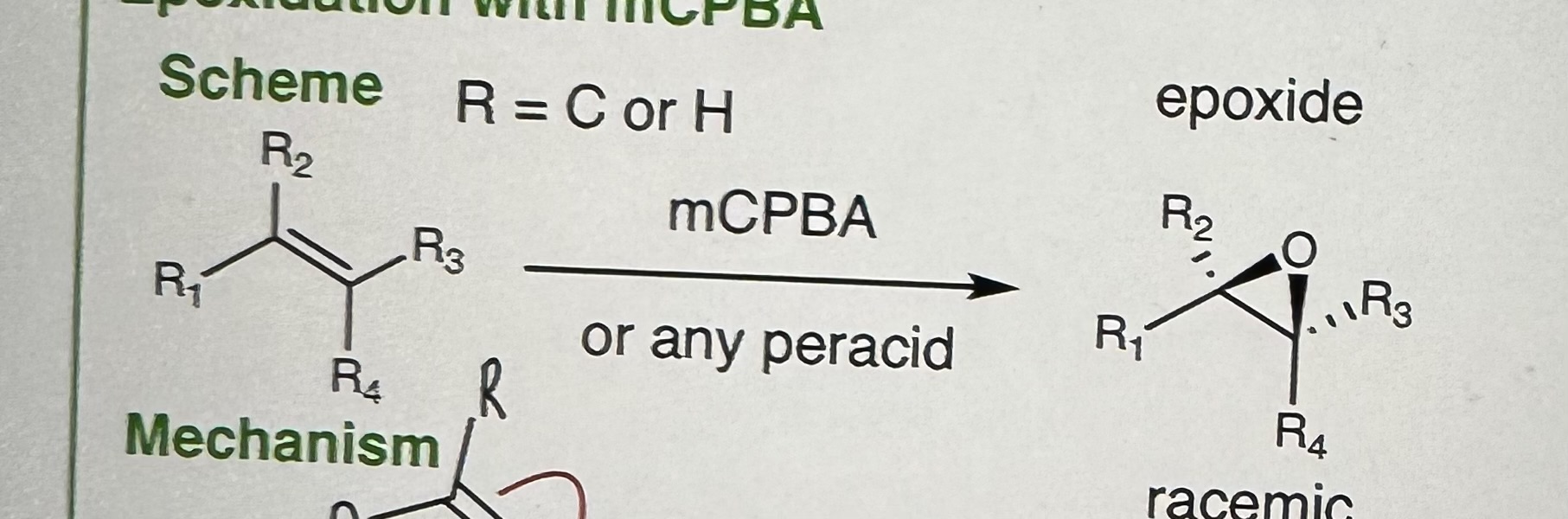
Exploitation with mCPBA
R = C or H
Step 1) mCPBA
Step 2) Any peracid
Expoxide: 3 ring structure
Mechanism NOT be asked on exam
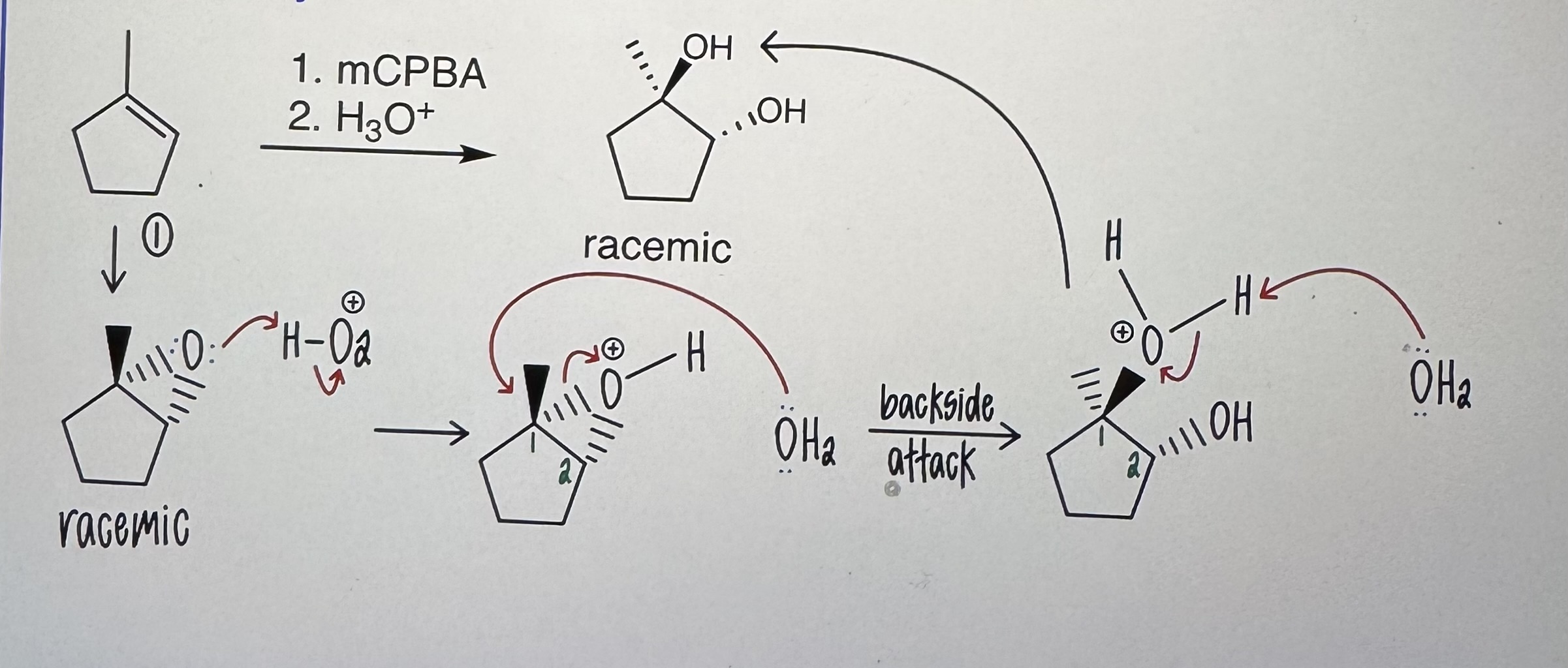
Anti Dihydroxylation
Step 1) mCPBA
Step 2) H3O+
Trans, racemic
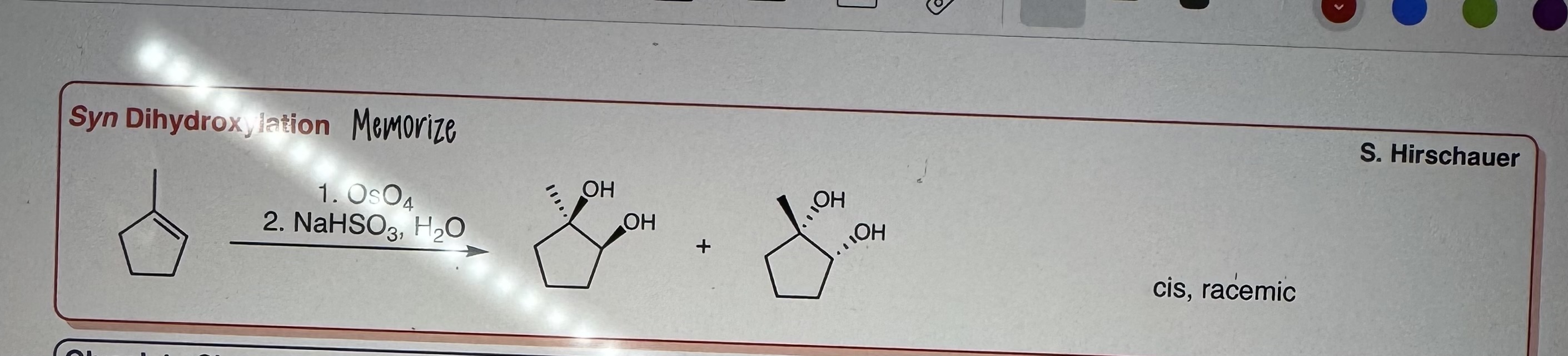
Syn Dihydroxylation
Step 1) OsO4
Step 2) NaHSO3, H2O
cis, racemic
MEMORIZE.
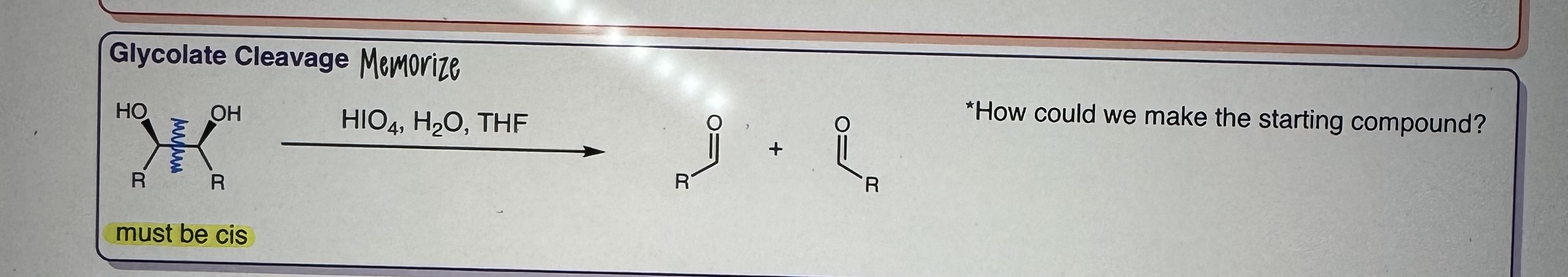
Glycolate Cleavage
Step 1) HIO4, H2O, THF
must be cis
MEMORIZE
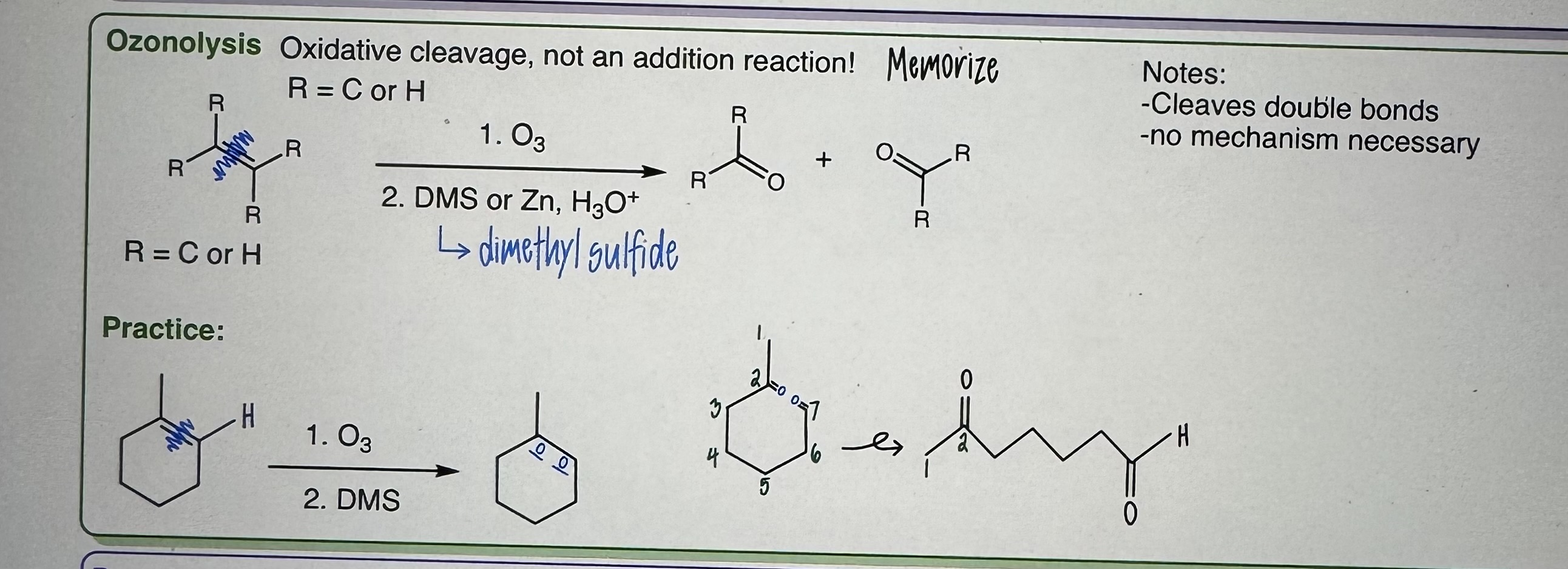
Ozonolysis
R = C or H
Step 1) O3
Step 2) DMS (dimethyl sulfide) or Zn, H3O+
Oxidative cleavage, NOT an addition reaction
Cleaves double bonds
No mechanism
MEMORIZE
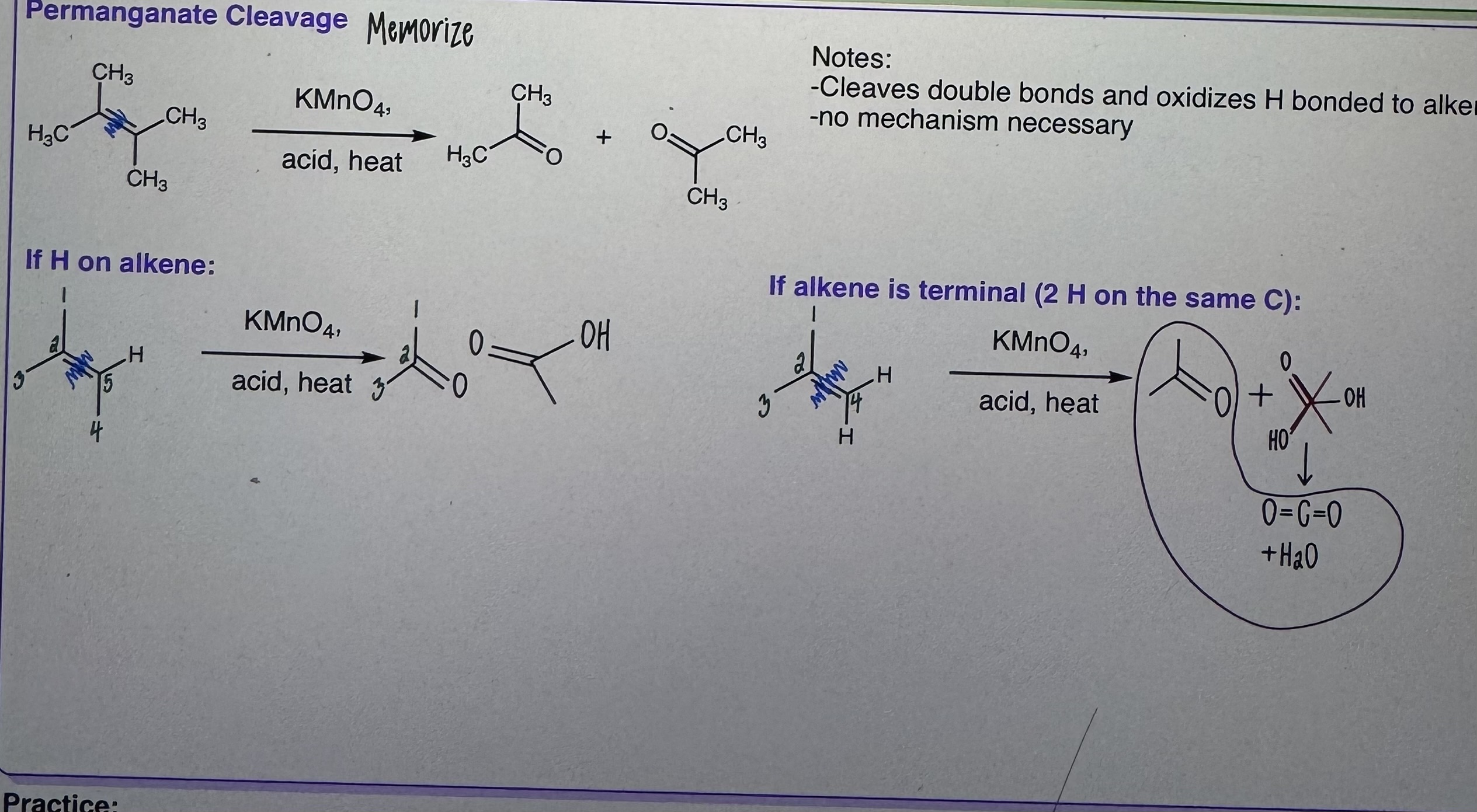
Permanganate Cleavage
Step 1) KMnO4
Step 2) Acid, heat
-Cleaves double bonds and oxidizes H bonded to alkene
-NO mechanism
-MEMORIZE
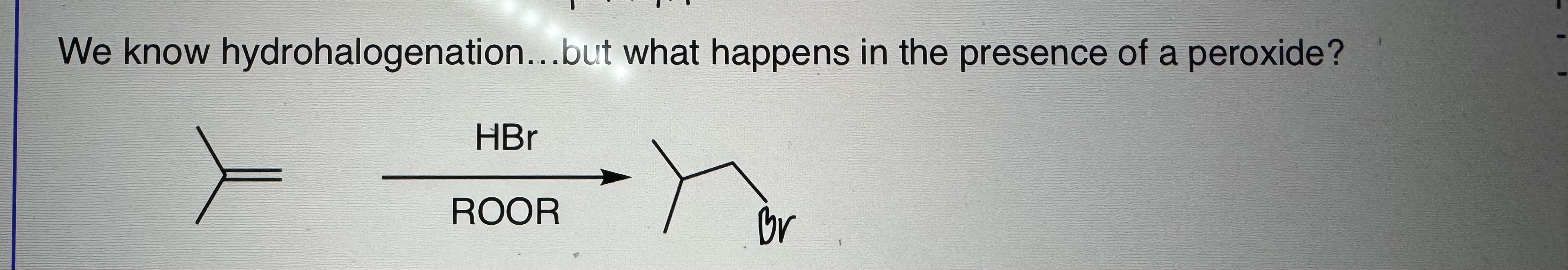
Free Radical Addition of HBr
Step 1) HBr
Step 2) ROOR
-Anti Markovnikov addition
-limited to HBR/peroxides
Initiation, Propagation, Termination