1.4 Carbohydrates
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
Carbohydrates
includes sugars and polymers of sugar
contain a carbonyl group and many hydroxyl groups
C, H, and O
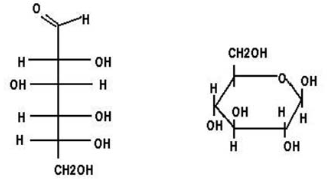
Monosaccharides
monomers of carbohydrates
simple sugars
1:2:1 ratio, starting with CH2O
most common is glucose
nutrients and fuel for cells
used in cellular respiration
can serve as building blocks for amino acids, or as monomers for di- and polysaccharides
Disaccharides
two monosaccharides joined together by covalent bonds
most common is sucrose
monomers of sucrose are glucose and fructose
plants transfer carbohydrates from roots to leaves in the form of sucrose
Polysaccharides
polymers of carbohydrates
complex carbohydrates
polymers with many sugars joined via dehydration reaction
The storage polysaccharides are starch and glycogen
plants store starch(polymers of glucose monomers) to store excess glucose
animals store glycogen(polymer of glucose), stored in liver and muscle cells
structural polysaccharides are cellulose and chitin
cellulose is a tough substance that forms plant cell walls
chitin forms the exoskeleton of arthropods