BSCI222 - Mendelian Genetics
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
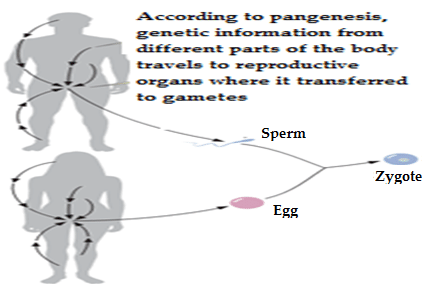
What is pangenesis?
Model of inheritance of genetic information proposed by Darwin
All parts of the body produce small bits “gemmules” that go through the blood system and collect reproductive organs to be transferred to gametes
What was Gregor Mendel’s role in Mendelian Genetics?
1860’s sweet pea hybridization
Applied mathematical analysis (frequencies of trait segregation in crosses)
Predicted existence of traits encoded in discrete units
What is a gene?
A basic unit of biological information (encodes a protein)
What is an allele?
An alternative form of a single gene
What is a locus?
A designated location on a chromosome (ex. to find a gene)
What is a genotype?
The actual genetic makeup of an individual (ex. sequence variation at a gene)
What is the phenotype?
An observable characteristic or trait due to a sequence variation at a gene
What is heterozygous?
A genotype in which the two alleles are different (ex. Aa)
What is homozygous?
A genotype in which the two alleles are the same (ex. AA or aa)
What are reciprocal crosses?
Crosses in which the phenotype of each sex in the parents is reversed as compared with the original cross (tests role of sex on inheritance)
What is a test cross?
Means of determining the genotype of individual with a dominant phenotype (is it AA or Aa) by crossing it with a homozygous recessive (aa)
A? x aa
if get 4/4 dominant then AA
if get 2/4 dominant then Aa
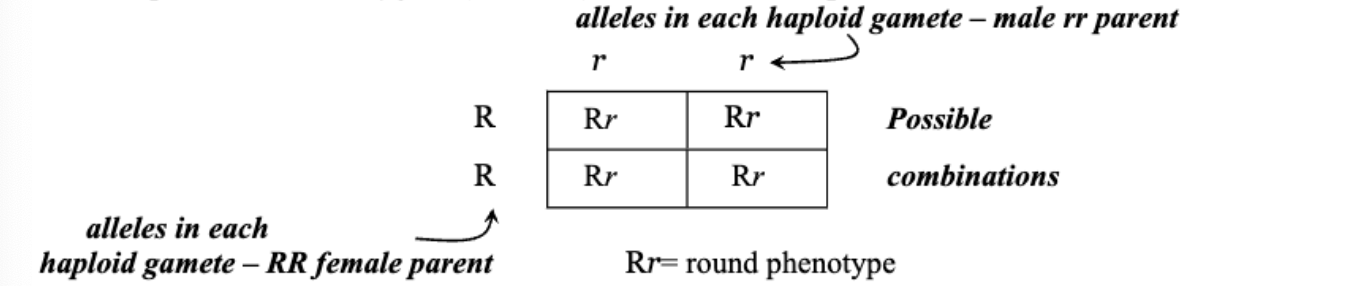
What is a monohybrid cross?
A cross involving a single trait
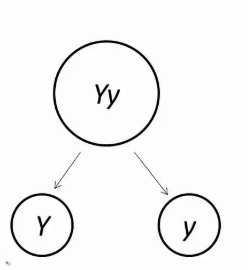
What is the law of segregation?
Two alleles coding the same trait in an individual (ex. YY, Yy, yy) separate during gamete formation so that a gamete only gets one from each parent
What is a dihybrid cross?
Cross involving two traits!
What is the law of independent assortment?
Different pairs of alleles separate independently of each other during gamete formation.
What is the multiplication rule?
P(A) AND P(B) = P(A) x P(B)
What is the addition rule?
As long as both event are mutually exclusive: P(A) OR P(B) = P(A) + P(B)
What are chi-square tests?
x² = ∑ [(observed # - expected #)2/ (expected #)]
How do you derive expected #?
# of offspring x fraction with phenotype (from punnett)
How do you calculate degrees of freedom?
df = # phenotypes - 1
Use this to find the critical value at 0.05
How do you use the x2?
If x2 > critical value
data fits the model within statistical variation (ACCEPT VALUES AS LIKELY)
If x2 < critical value
data does not fit the model (REJECT VALUES)