developmental psychology ch10
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Long term romantic relationships: Theories
Similarity hypothesis - homogamy
Complementarity
Similarity theory:
Similarities in physical appearance, race/ethnicity, education, socioeconomic status, religion → provides basis for dating
More disclose about themselves, look for similarity in values, attitudes, beliefs, and personality traits → if compatible: relationship may survive
Influence of personality traits like stability and agreeableness.
Sternberg’s love triangle:
Three components of adult love relationships:
Passion (sexual arousal)
Intimacy (feeling of closeness)
Commitment (marriage/exclusivity)
Change across relationship: passion → intimacy → commitment
Keeping passion and intimacy takes work.
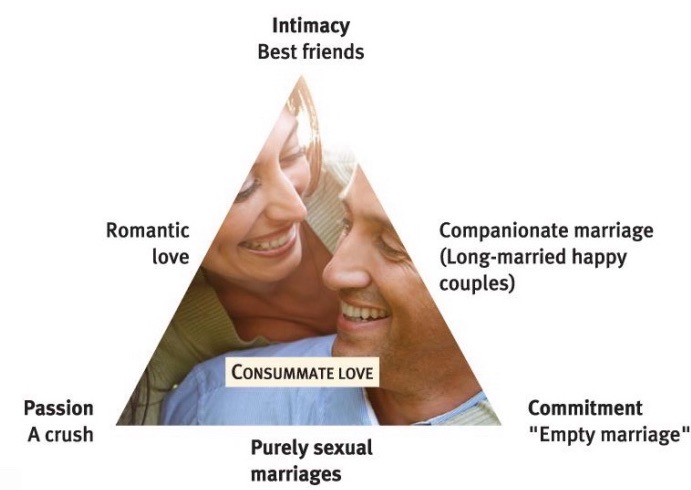
Attachment styles in terms od models:
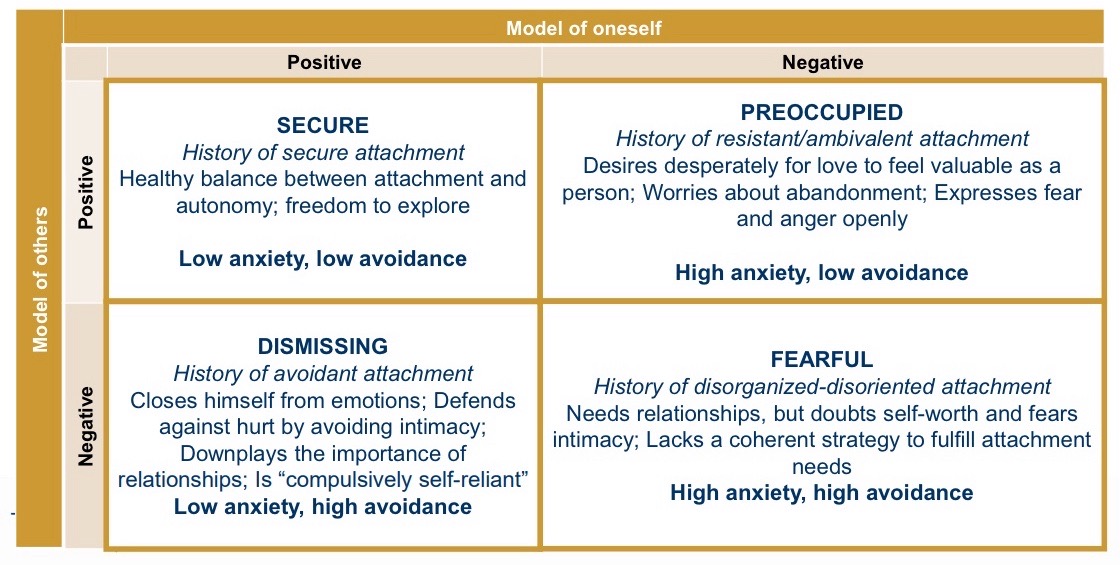
Influence of attachment on relations:
Secure: Positive emotions, longer relationships, can discuss various issues
Dismissing: fear of intimacy, shut-down, inhibition of feelings
Preoccupied: Obsessive/jealous, emotional during conflicts
What are internal working models shaped by:
Early parent-kid relations, but influenced by the quality of later relationships (sensitive parents).
Does marriage make people happy?
Robust evidence: marriage status is linked to better health and subjective well-being - stronger effects for men, but benefits of marriage apply to happy marriages.
Also no differences in midlife happiness in married vs long-term cohabiting couples.
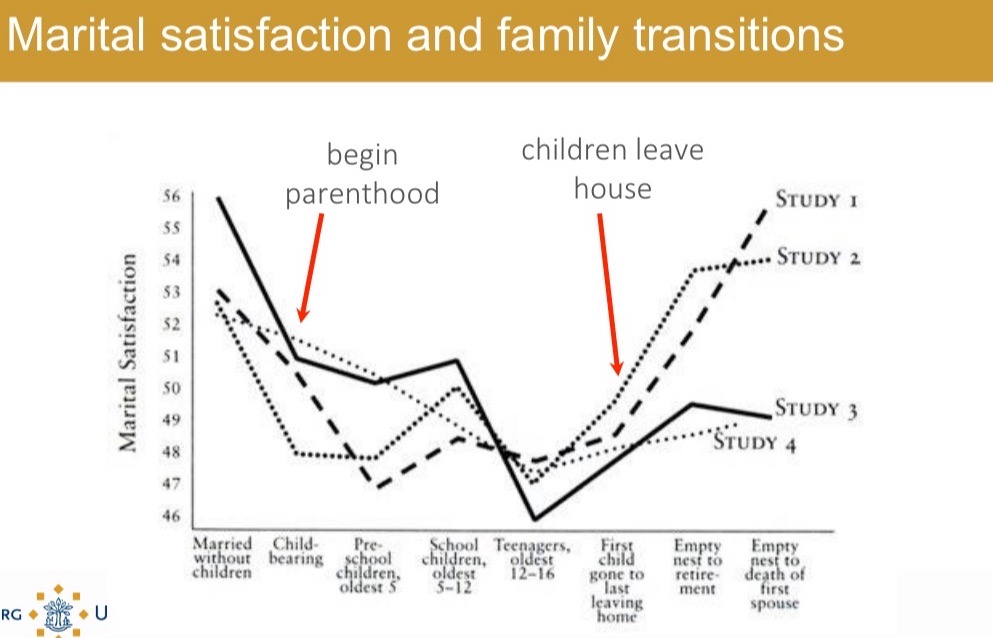
Marriage begins with high expectations, after which disenchantment sets in = happiness peaks in honeymoon phase.
Satisfaction goes down rapidly but goes a bit up after empty nest.
Divorce: Separation can cause…
Moving
Homework burden
Legal hassles
Financial problems
Divorce: Positive and Negative changes
Positive changes:
Production of emotional growth and feelings of self-sufficiency
Relief for some who were unhappy
Negative changes:
Disengagement of one parent through lack of contact/paying child support
Challenges with discipline or lack of connection to step children
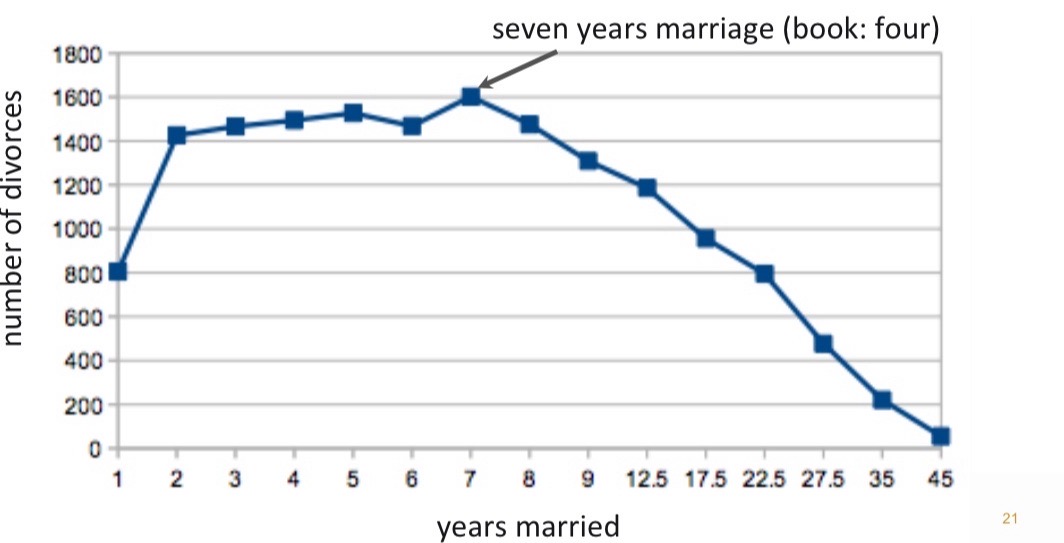
Divorce after a good or bad marriage:
Divorce after bad marriage: Increase in happiness
Divorce after good marriage: Decrease in happiness
Decline of marriage rates: Deinstitutionalization
Marriage no longer a fixed institution and emergence of alternative family forms during the last third of 20th century.
Examples:
More childbirth outside marriage
Probability of divorce higher
Percentage of married couples lower
More children living with one parent
More people living alone
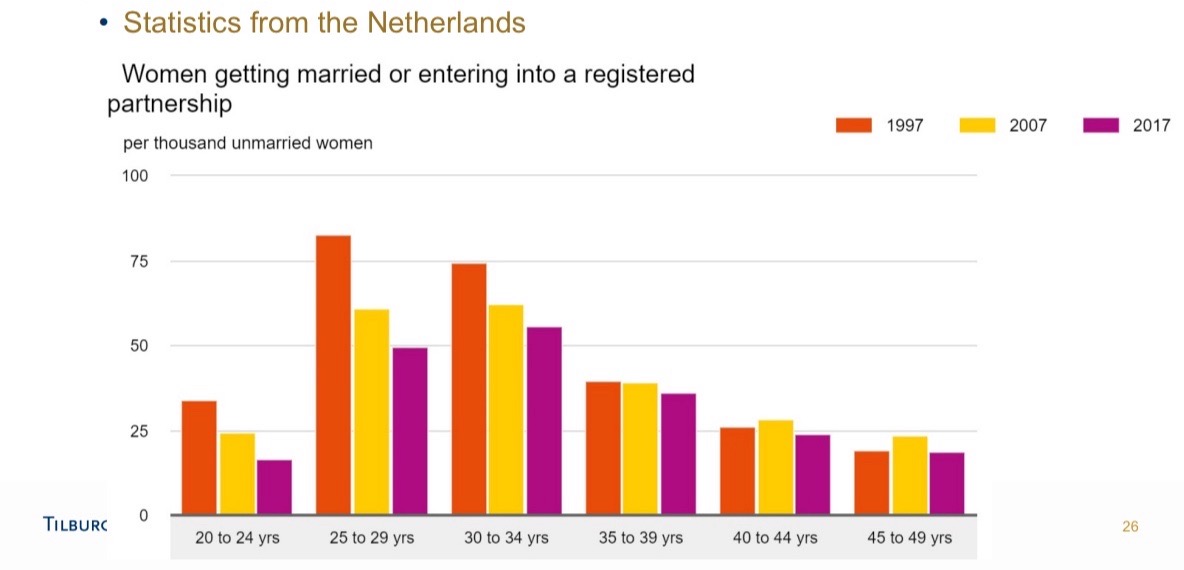
Living together before marriage - Netherlands:
More normal to live together for some time first before getting married or continue as unmarried couples → larger share 35 year olds who cohabit without being married.
Diverse lifestyles - Single;
In 2009 in US, 25-35 year olds as many single as married - 46-46%.
Stereotypes: swinging single vs desperately lonely, suicidal
Indeed: diversity, various reasons for being single - chosen/not
Often deep bonds with siblings, friends, younger adults
Diverse lifestyles - Non-heterosexual marriage
In NL: same-sex marriage legalised 2001.
In US: 2015. In Germany: 2017
Stigma, prejudice, discrimination still highly prevalent
Characteristics - similar to heterosexual, balance of everything - flexible gender roles, higher quality
Challenges for new parents
Altercations in hormones
Neurobiology
Physical health
Self-concept
Perceived efficacy
Emotional health
Relationships
Social networks
Unrealistic expectations
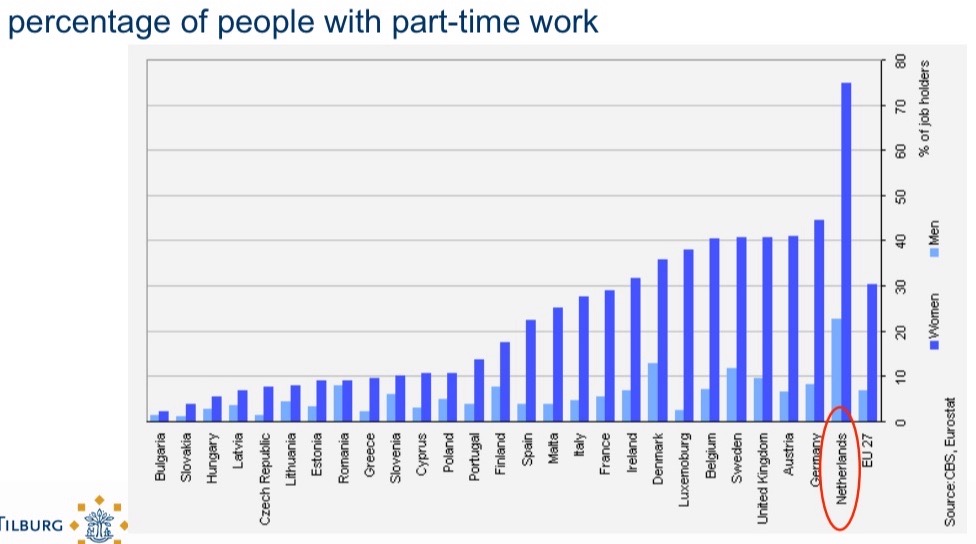
Relationships threat
Less time for intimacy, division of labor
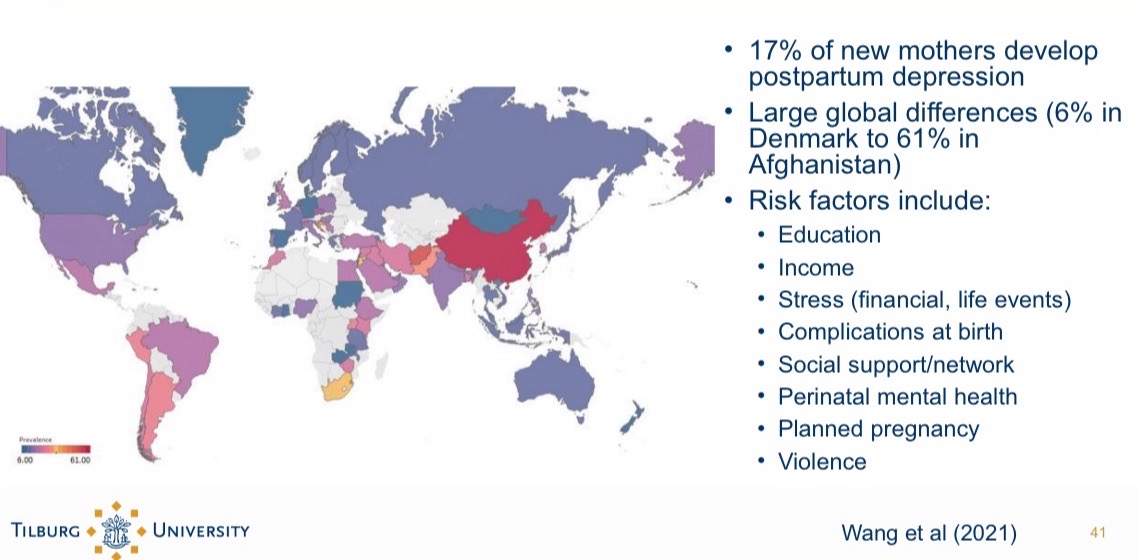
Postpartum depresion
Diverse lifestyles - Single
Challenges - forming intimate relationships, loneliness, marriage-oriented society, social and financial prejudice.
Advantages - more time for life decisions, autonomous decisions, time to develop personal resources, explore places and things, privacy.
Older adults who never married - easier to cope with loneliness in old age.
US survey - 2012 -
39% of singles uncertain about getting married
34% wants to get married
27% doe not want to get married
Division of labour
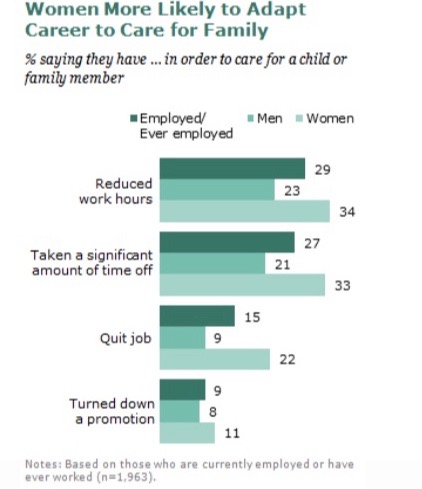
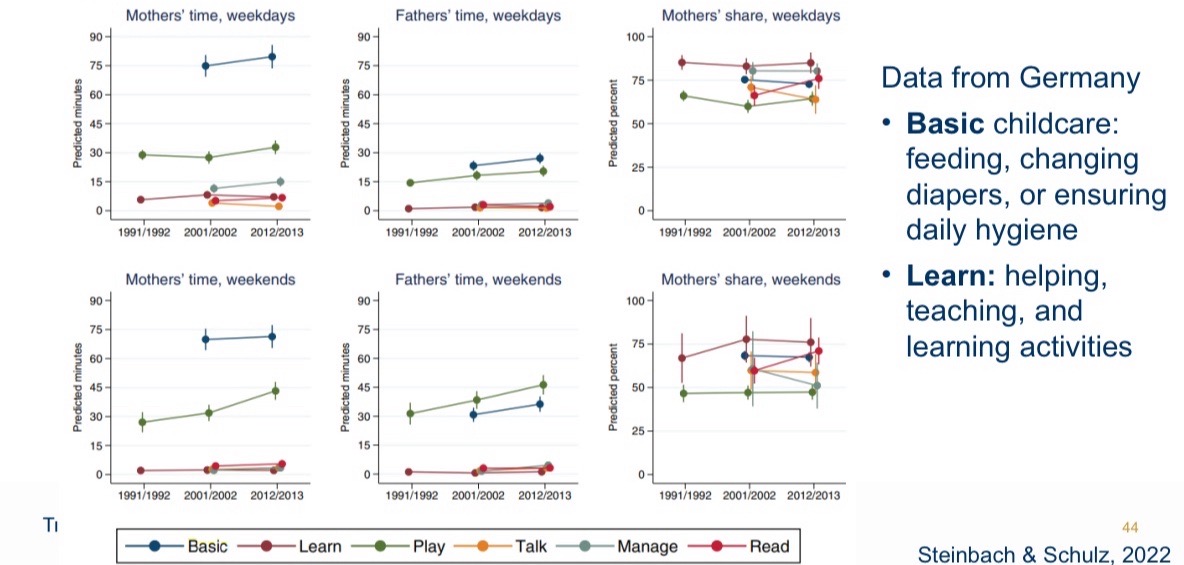
Fathers are starting to pitch in to do hands on childcare, their involvement is still skewed towards play activities.
Women provide 2x hands on childcare.
Significant variability in father involvement - related to views on women.
Parenting is a major transition in adulthood, characterised by growth and loss.
Parents use compensatory processes to minimise the impact of loss.
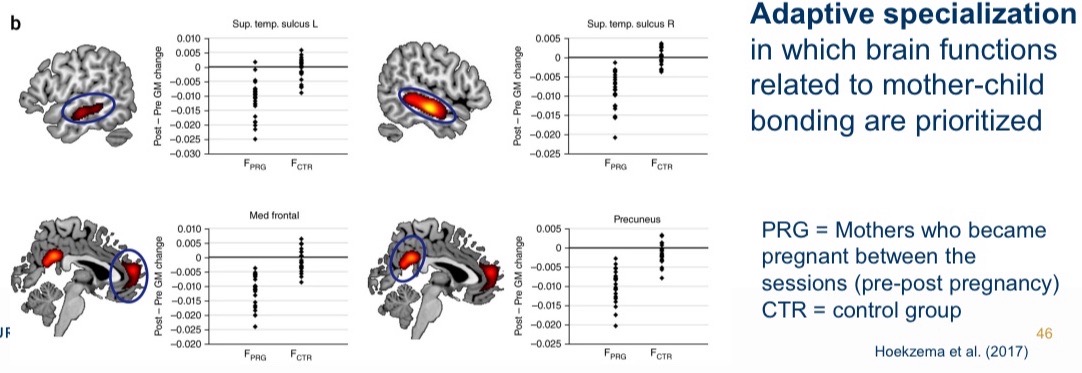
Parenthood and the brain
Transition to parenthood leads to decrease in cognitive functions and brain volume during pregnancy - persists for at least 2 years.
Changes in brain volume positively related to maternal attachment after birth.
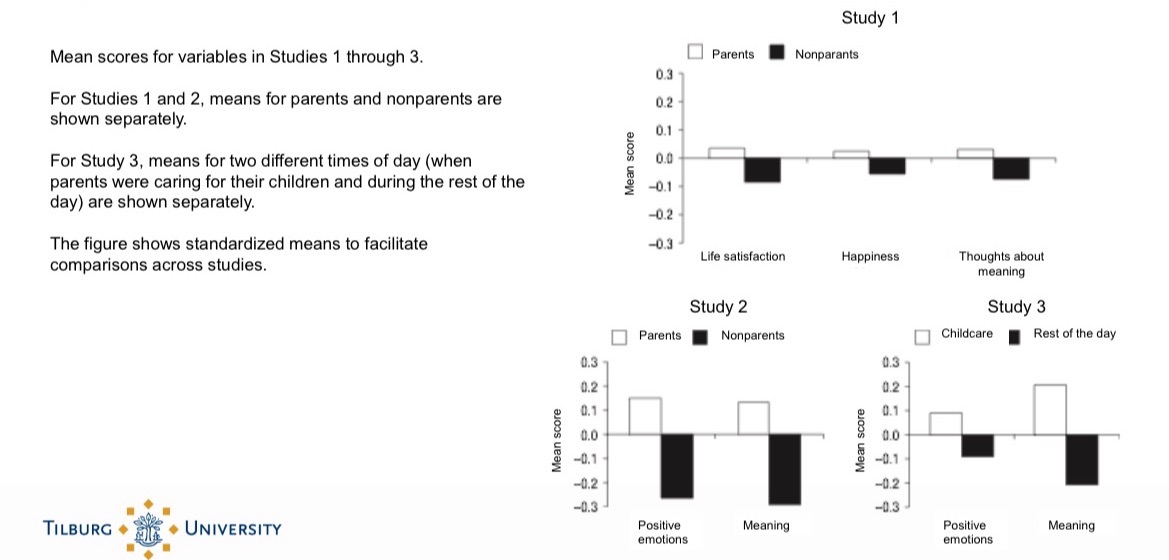
Effects of childbirth and parenthood
Initial positive effect only on Life satisfaction LS - increases before birth and decreases after birth and continues to decrease after second child.
LS and relationship satisfaction RS decrease
RS permanently below pre-birth level
Effects on affective well-being are small but positive
Decrease in self-esteem too, a bit less after second pregnancy
Parenthood makes couples less intimate and happy and produces traditional conflict-ridden marital roles
Big variability - good relationship prior is key
Insecurity - am I a good parent?
Time spent with children
Mothers spend more time with their children than previous generations.
Midlife
Those in midlife are often involved in caregiving and support for their kids and their parents.
In 2012, 47% of middle aged adults with kids have a parent over 65 years.
Subjective well-being of middle aged adults is often linked to the perception if their children have successfully adjusted after leaving home.
Empty nest
When child becomes adult - new adjustment phase for parents
Empty nest syndrome
Not the majority, decline in marital satisfaction.
For most, increase in marital satisfaction and quality time together.
Boomerang kids/back to bedroom
Financial and emotional support - can be positive experience for both, but also…
For parents - loss of privacy, conflicting schedules, relationship with partner is invaded
For children - loss of privacy and independence, feel like being treated as a child
Grandparenthood
First time grandparents mostly during middle age.
Increase in longevity -
1900 4% of 10 year olds have grandparents
2000 40%
Different meanings - source of biological reward and. continuity, emotional self-fulfilment or remote role
Grandmothers have more contact
Cultural - Mexican vs non-Latino, African Americans
Grandparenthood - changing profile
Increase in number of children who live with at least one grandparent
Divorce, adolescent pregnancies, drug use by parents
Full-time caregiving grandparents - elevated risk for health problems, depression & stress compared to part-time caregiving grandparents (Silverstein, 2009; Hadfield, 2014)|
→ Full-time caregiving grandparents are often from low-income minority groups, and not married