Health and Well-Being Ch. 11
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Health psychology
A field that involves the application of psychological principles to promote health and well-being
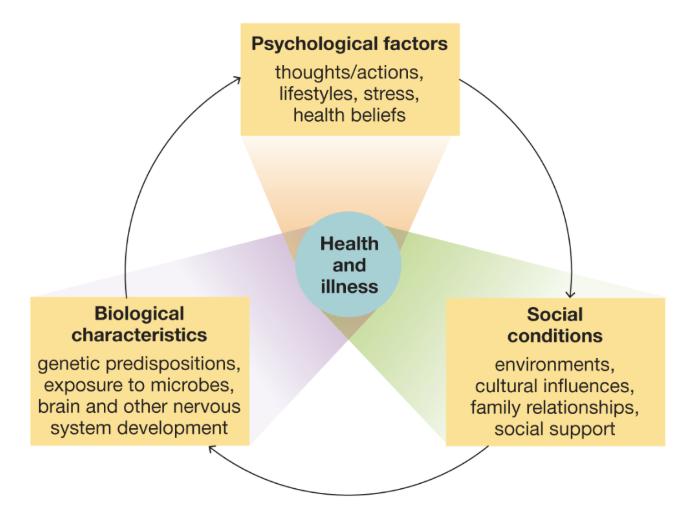
Biopsychosocial Model
An approach to psychological science that integrates biological factors, psychological processes, and social-contextual influences in shaping human mental life and behavior
(Contrasts with the traditional medical model that views the individual as passive recipient of both disease and treatment)
Stressor
Something in the environment that is perceived as threatening/demanding
Eustress
The stress of positive event
Distress
The stress of negative events
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
body system involved in stress response and regulation
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Adrenal Glands:
Cortisol
Circulates throughout the body to various brain areas (Hypothalamus, Pituitary Gland, and Adrenal Glands)
It triggers a negative-feedback look to turn off the HPA Axis (stress response regulation)
Signals the hypothalamus and amygdala to encode memory and process emotions related to stress
SLOWS THE STRESS RESPONSE
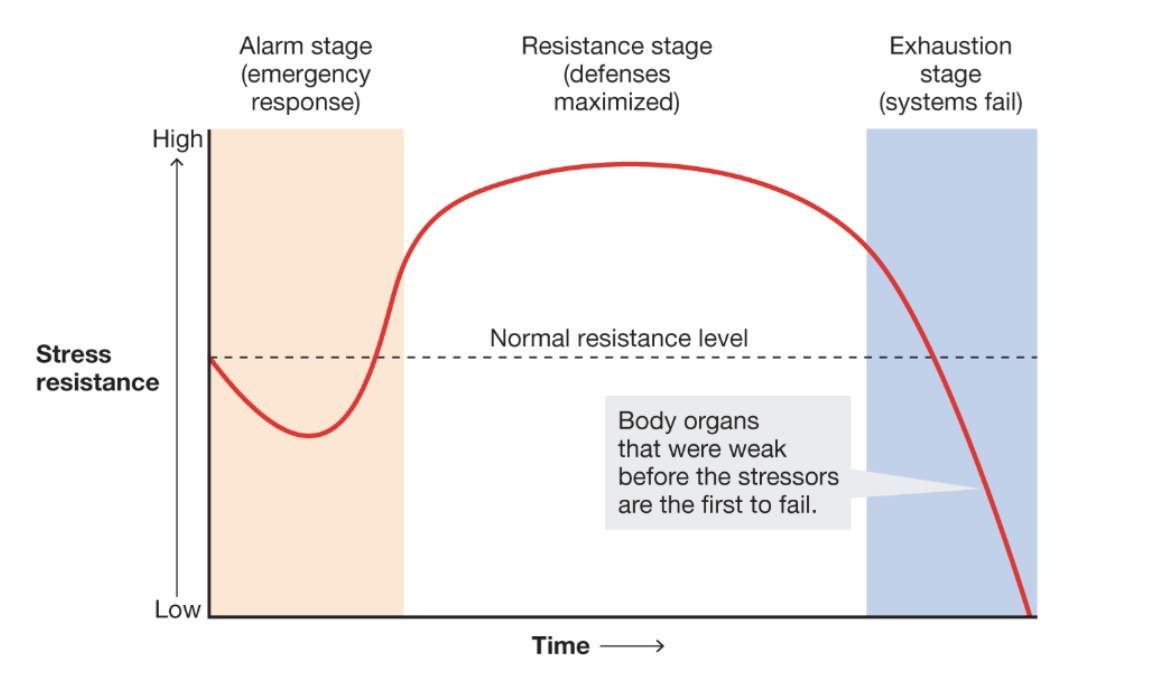
The General Adaptation Syndrome
Three stages of psychological response to stress
Alarm Stage
Resistance Stage
Exhaustion Stage (systems fail)
Allostatic Load
The cumulative “wear and tear” on biological systems including the stress, digestive, immune, cardiovascular, and hormonal systems, after repeated or chronic stressful events.
Psychoneuroimmunology
a field of study that explores the complex interactions between the brain, nervous system, immune system, and behavior
Ex - how chronic stress can trigger or worsen inflammatory conditions like psoriasis
Types of coping
Emotion focused coping
Try to prevent having an emotional response to a stressor
Problem-focused coping
Confront or minimize stressor
Buffering Hypothesis
When others provide emotional support, the recipient is better able to cope with stressful events