2.Neurogenesis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What are the 4 kinds of typical model systems?
C. Elegans (302 neurons)
Drosophila (100k neurons)
Frog (16 million neurons)
Mouse and rat (75 and 56 million neurons, respectively)
What are the 3 layers of a germ plate?
ectoderm (outer layer)
mesoderm (middle layer)
endoderm (inner layer)
Endoderm germ layer gives rise to…
primitive gut
lung!
liver, pancreas, digestive tubes
yolk sac
Mesoderm germ layer gives rise to…
axial
paraaxial
sclerotome → skeleton
myotome → skeletal muscles
intermediate
lateral
visceral mesoderm → heart, blood vessels
head
Ectoderm germ layer gives rise to the ….
epidermis → skin
neural tubes → brain, spinal cord
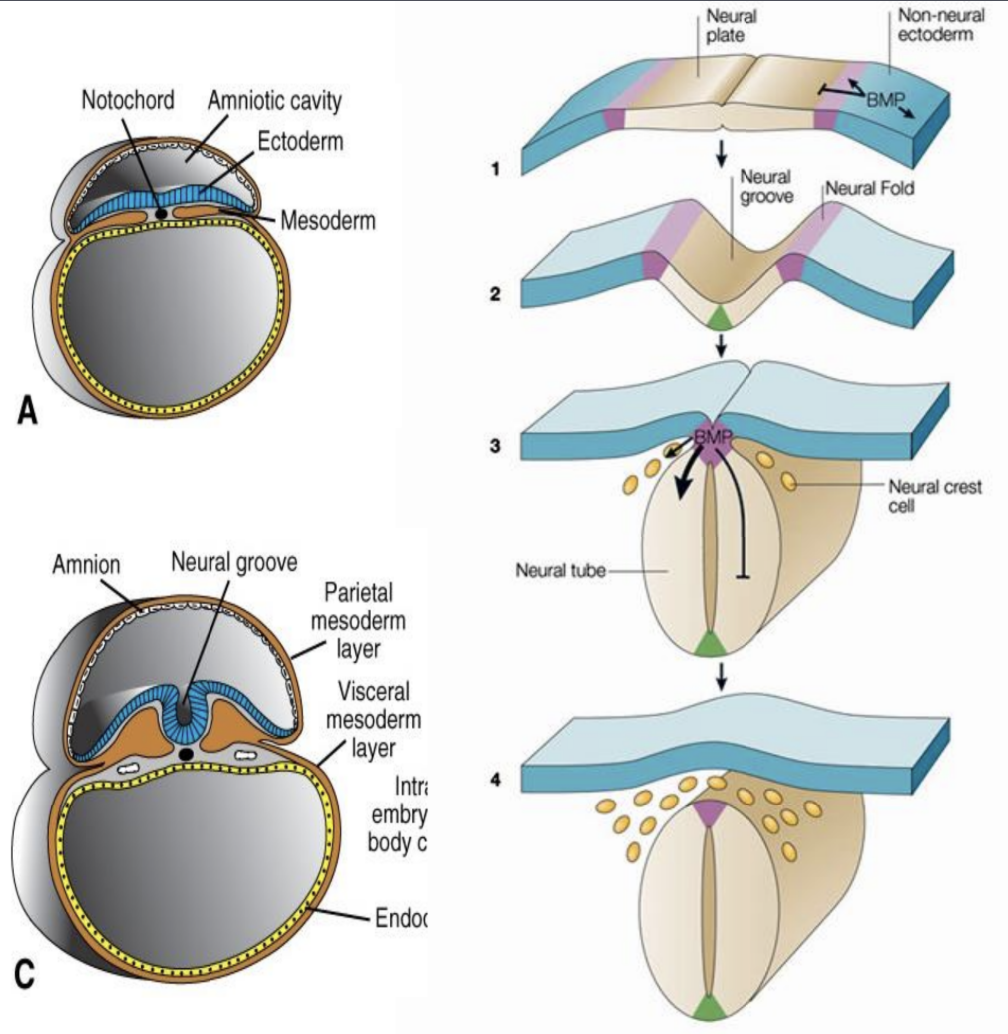
Central Nervous System (CNS) arises from specialized epithelium—the neural plate. This process relies on the inhibition of ___ signaling?
Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP)
Neural crest cells derive from the dorsal neural tube and migrate out to form the ___ and melanocytes and cartilage in the head.
Neural crest cells have been shown to form at an intermediate level of BMP signaling.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
What are the 3 early embryonic brain ventricles?
Forebrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain
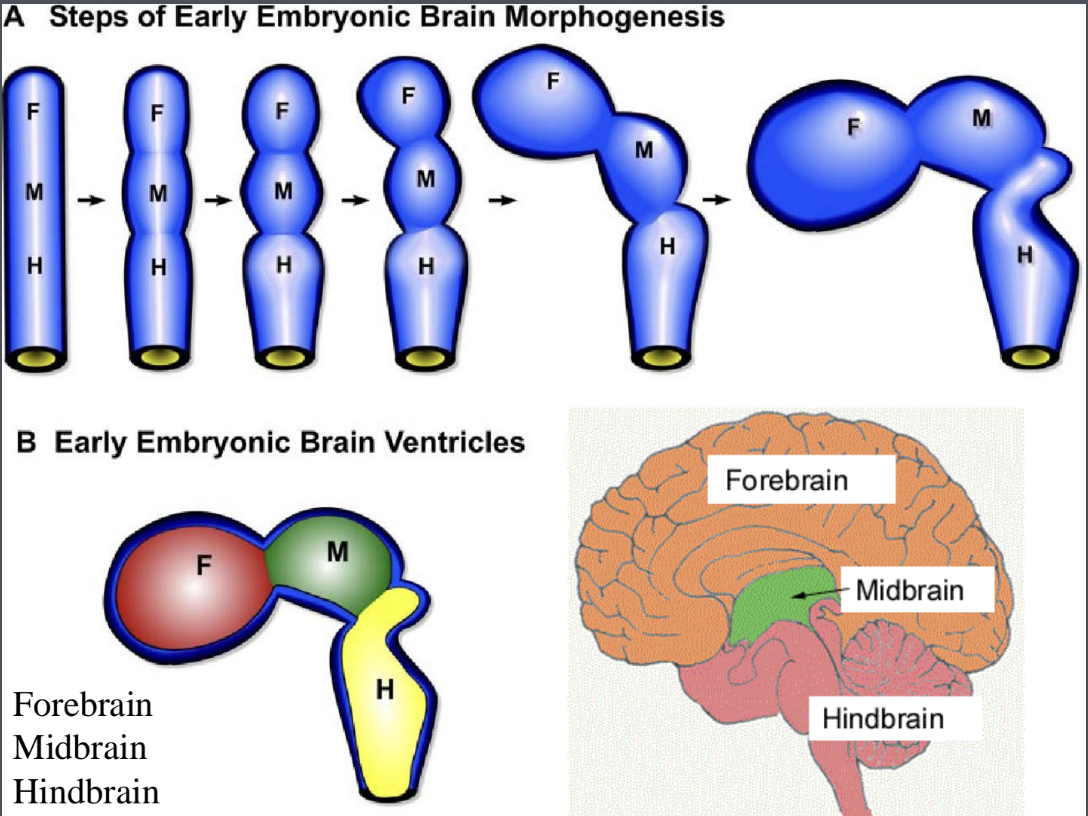
When developed, what are the 4 brain ventricles?
first and second lateral ventricles
one in each cerebral hemisphere
interventricular foramen
third ventricle
one in diencephalon
cerebral aqueduct
fourth ventricle
one in hindbrain (pons and medulla)
central canal
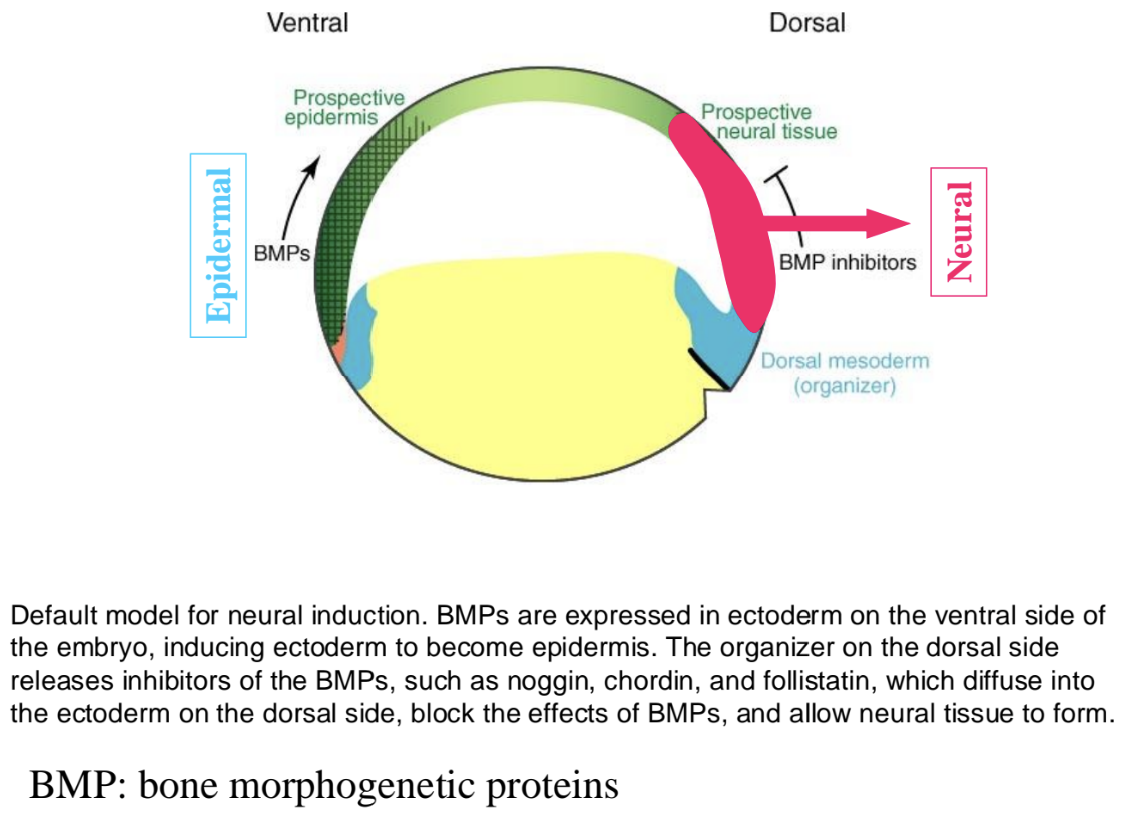
About Neural induction, most work was performed in amphibian embryos and the key molecule is BMP. What is neural induction?
process by which embryonic cells in the ectoderm make a decision to acquire a neural fate (to form the neural plate) rather than give rise to other structures such as epidermis or mesoderm
What is the default model for neural induction?
BMPs are expressed in ectoderm on embryo’s ventral side, inducing ectoderm to become epidermis
organizer on dorsal side releases inhibitors of BMPs like noggin, chordin, follistatin, which diffuse into ectoderm on dorsal side, block the effects of BMPs, and allow neural tissue to form
What is a Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP)?
a member of the TGF-Beta (Transforming Growth Factors) family
binding to their receptors (BMPR) activates the Smad pathway (transcription factor)
inhibition of BMP (by inhibitors like noggin, chordin) induces neural differentiation
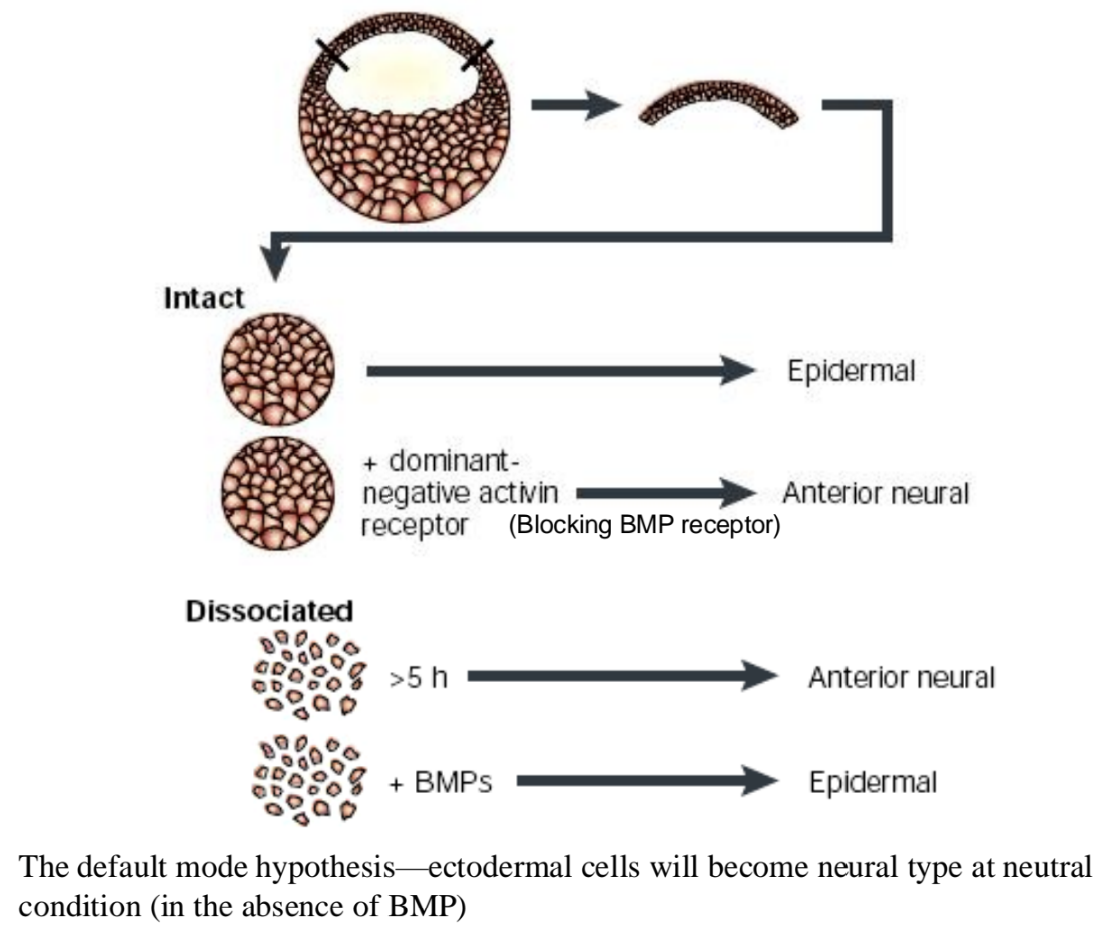
What is the default mode hypothesis?
Ectodermal cells will become neural type at neutral condition (in the absence of BMP)
All neurons and glia in the brain come from neural tube. Meanwhile, the number of cells is regulated at several levels:
by intrinsic limits of the number of progenitor cell division (ex: always 302 neurons in adult C. elegans)
by extracellular signals (mitogen and mitogen inhibitors)
by rate of cell death (programmed cell death = apoptosis)
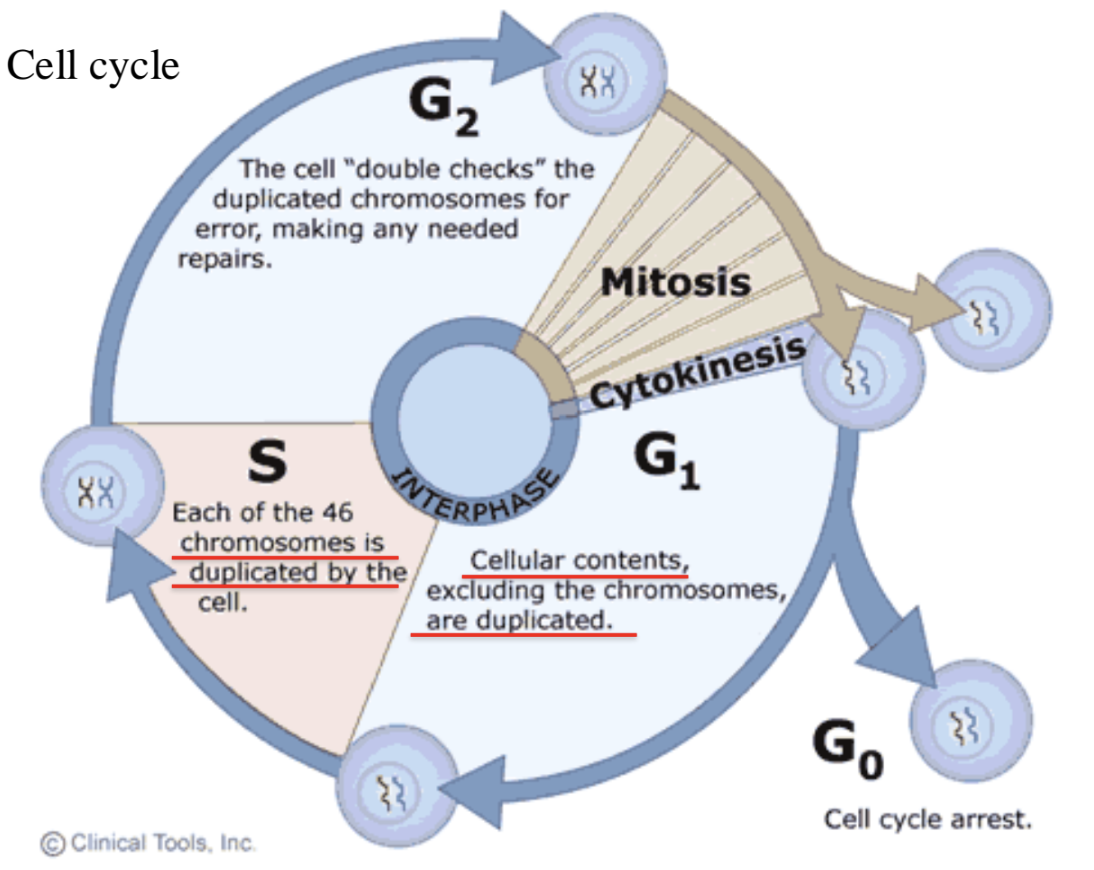
Cell Cycle
cytokinesis
interphase (below are subphases)
G1
cellular contents, not chromosomes, are DUPLICATED
S
each of 46 chromosomes are DUPLICATED by cell
During S phase, all of the DNA in a cell is replicated, thereby doubling the amount of DNA in the cell
G2
cell “double checks” duplicated chromosomes for error, making any needed repairs
Mitosis
division of one nucleus into two genetically-identical daughter nuclei (ex: mitosis of a somatic cell nucleus containing four chromosomes will produce two daughter nuclei containing four chromosomes each)
1st phase: prophase
During prophase, chromatin in the cell's nucleus becomes condensed into discrete chromosomes
also
G1 → G1 goes to cell cycle arrest aka STOPS
During interphase, the cell’s genetic content, or DNA, is dispersed within the nucleus as chromatin
During development,…
length of the cell cycle increases
increase is mainly at G1 phase
by the end of neurogenesis, nearly all cells leave the cell cycle and very few remain to generate new neurons (remember, neurons are postmitotic cells)
Neuron birthdating
technique used to determine when neurons were born
The developmental age at which a neuronal precursor cell exits the cell cycle
reliable method for classifying neurons in different nervous systems
early progenitor cell generates two distinct daughter cells after a mitotic division. This event is referred to as the neuronal birthdate of the daughter cell that is committed to a neuronal fate