OPT 311 Tonic Pupil
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is a tonic pupil?
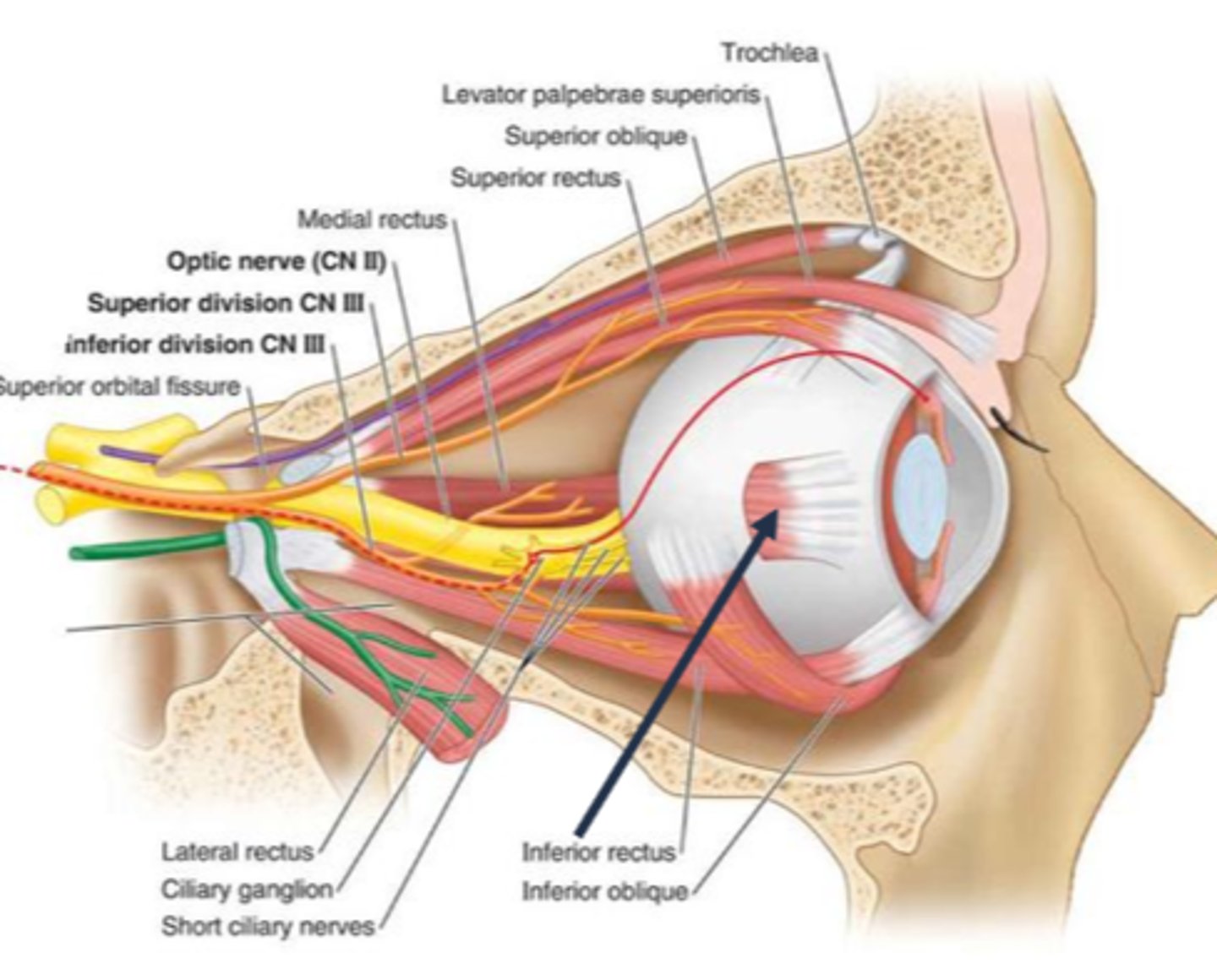
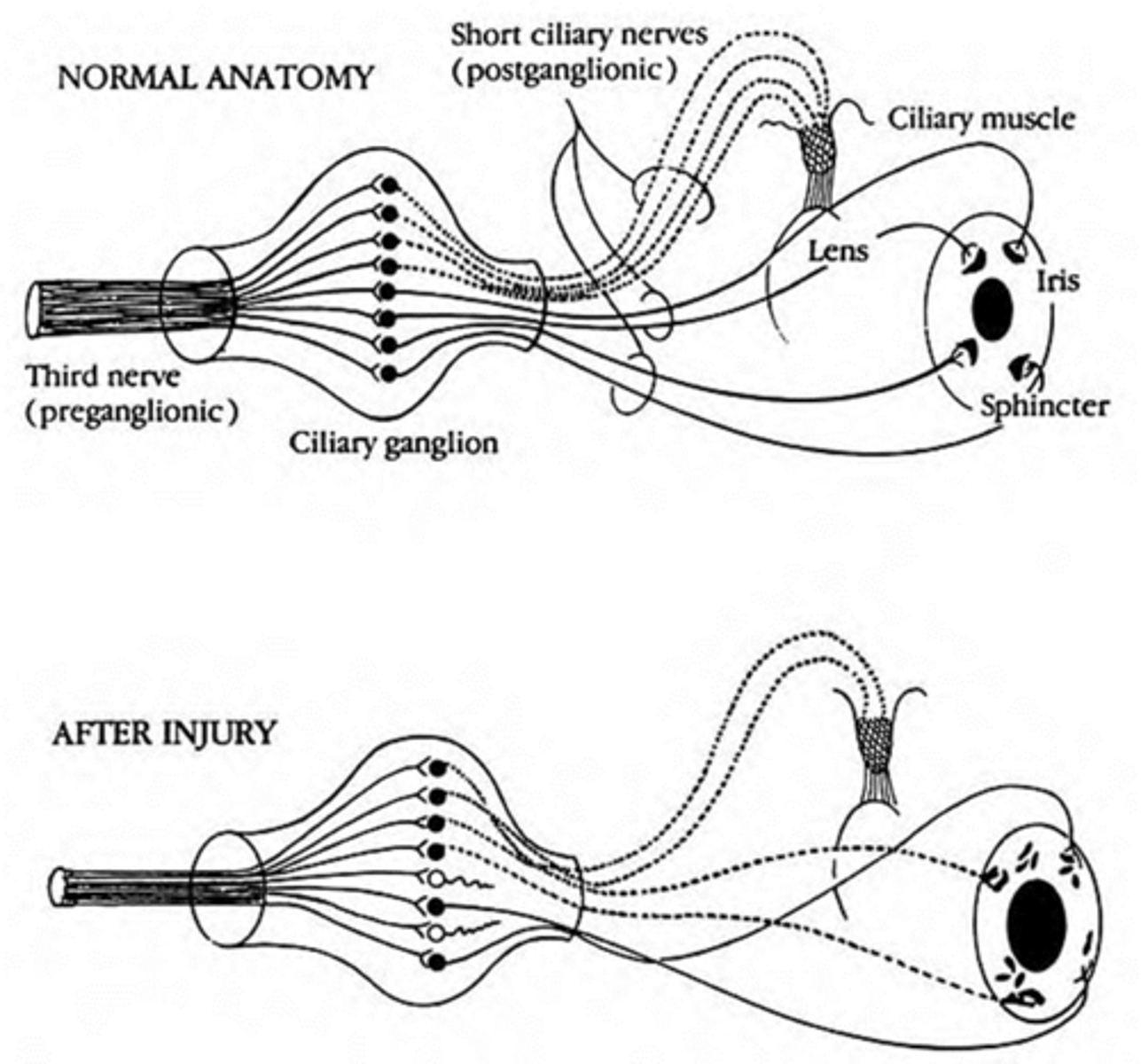
ciliary ganglion damage due to trauma, infection, demyelinated, inflamed = parasymp fibers affected = pupil responds to near, but does not respond to light (light-near dissociation pupils) = large pupil
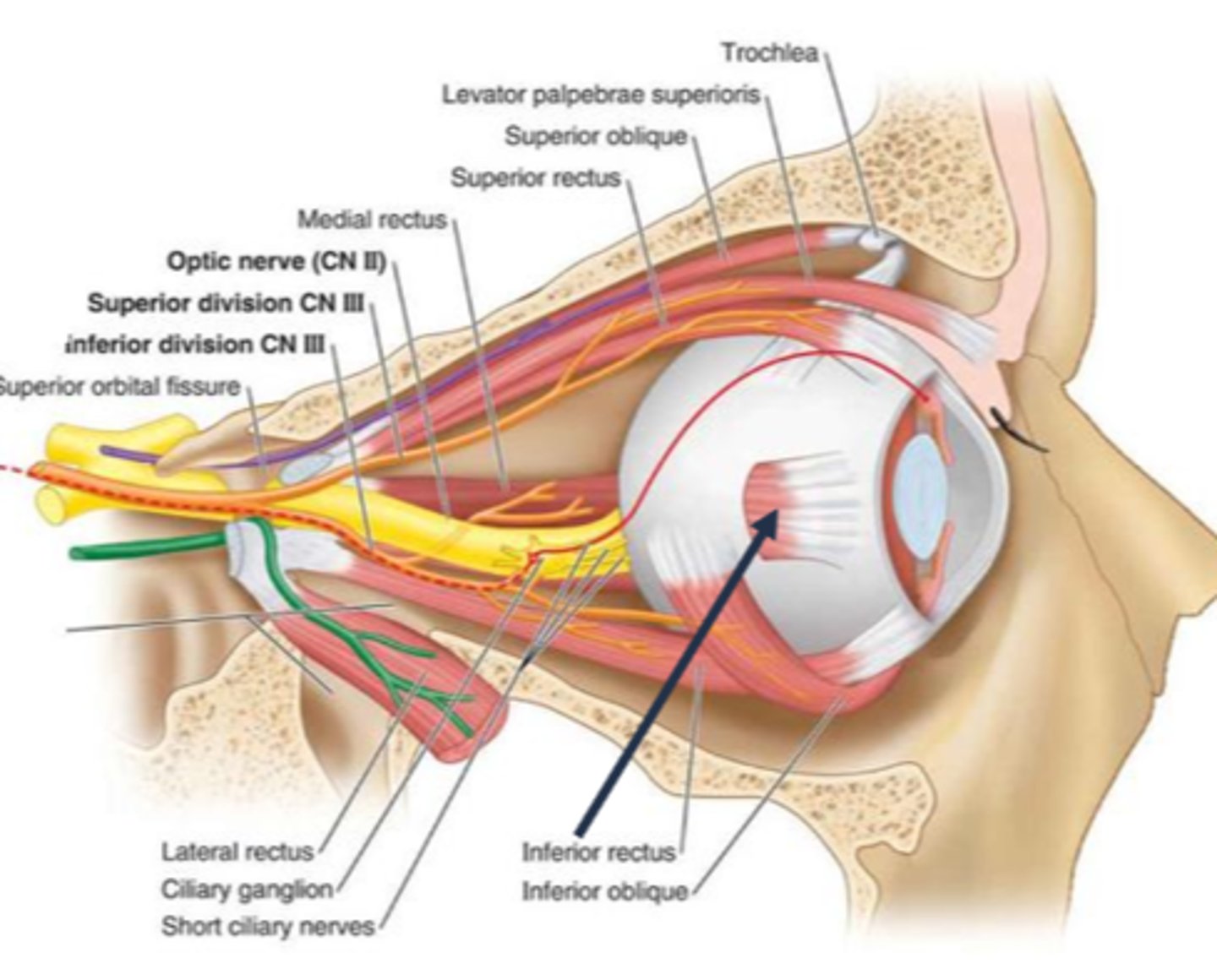
Ultimately, is a tonic pupil a large pupil caused by an issue with the muscle, NMJ, nerve, or brain?
nerve
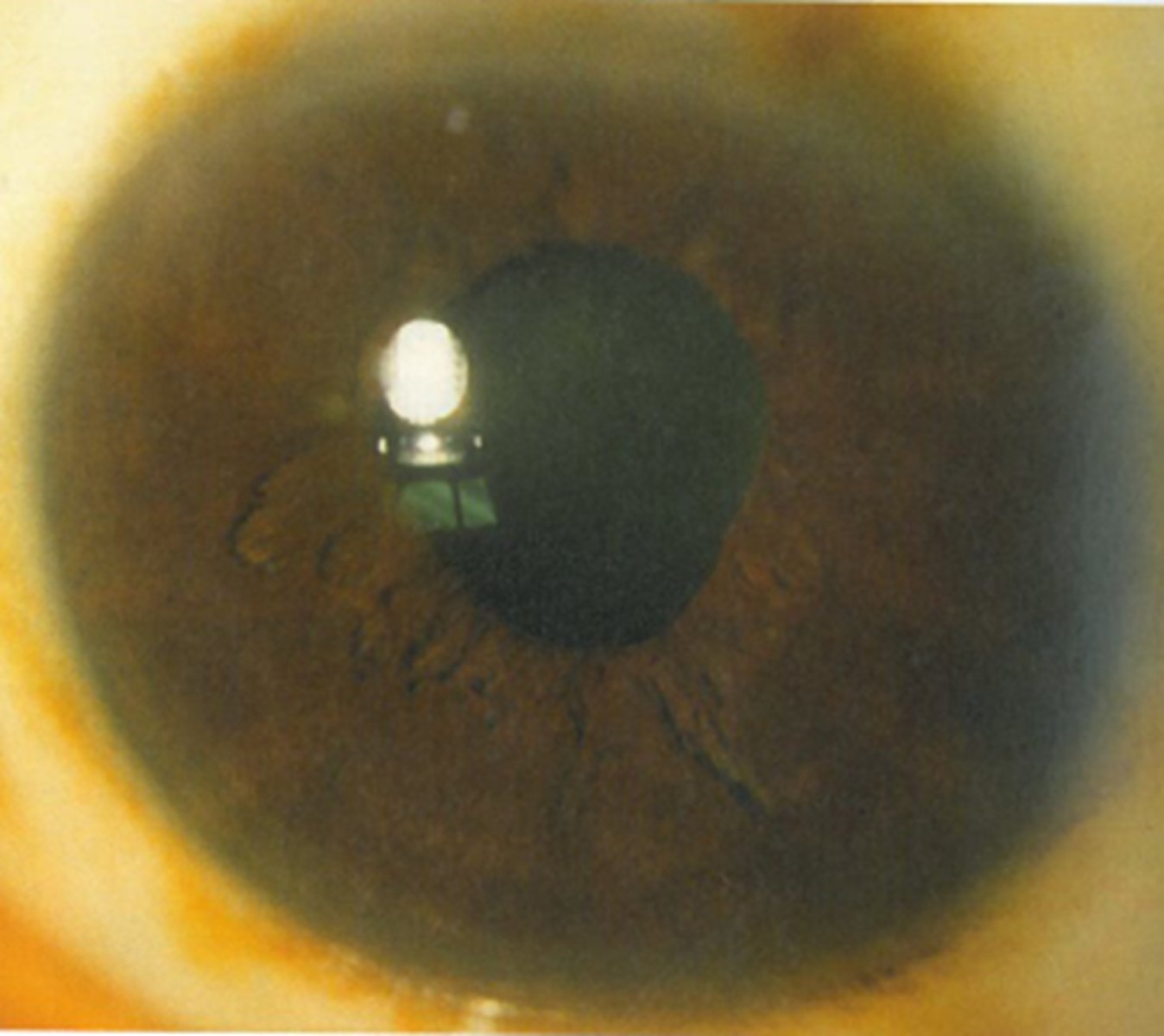
What are the 4 S's that we expect to see when looking at the size and shape of a tonic pupil?
sector paralysis = abnormal shape due to sphincter/dilater paralysis
stromal spread = iris stroma spreads due to lack of innervation
pigment stream entropion = pupil border of iris is entropic adjacent to a part of the pupil border that is more flat
stromal streaming = stroma flows towards area that sphincter still works when light is turned on
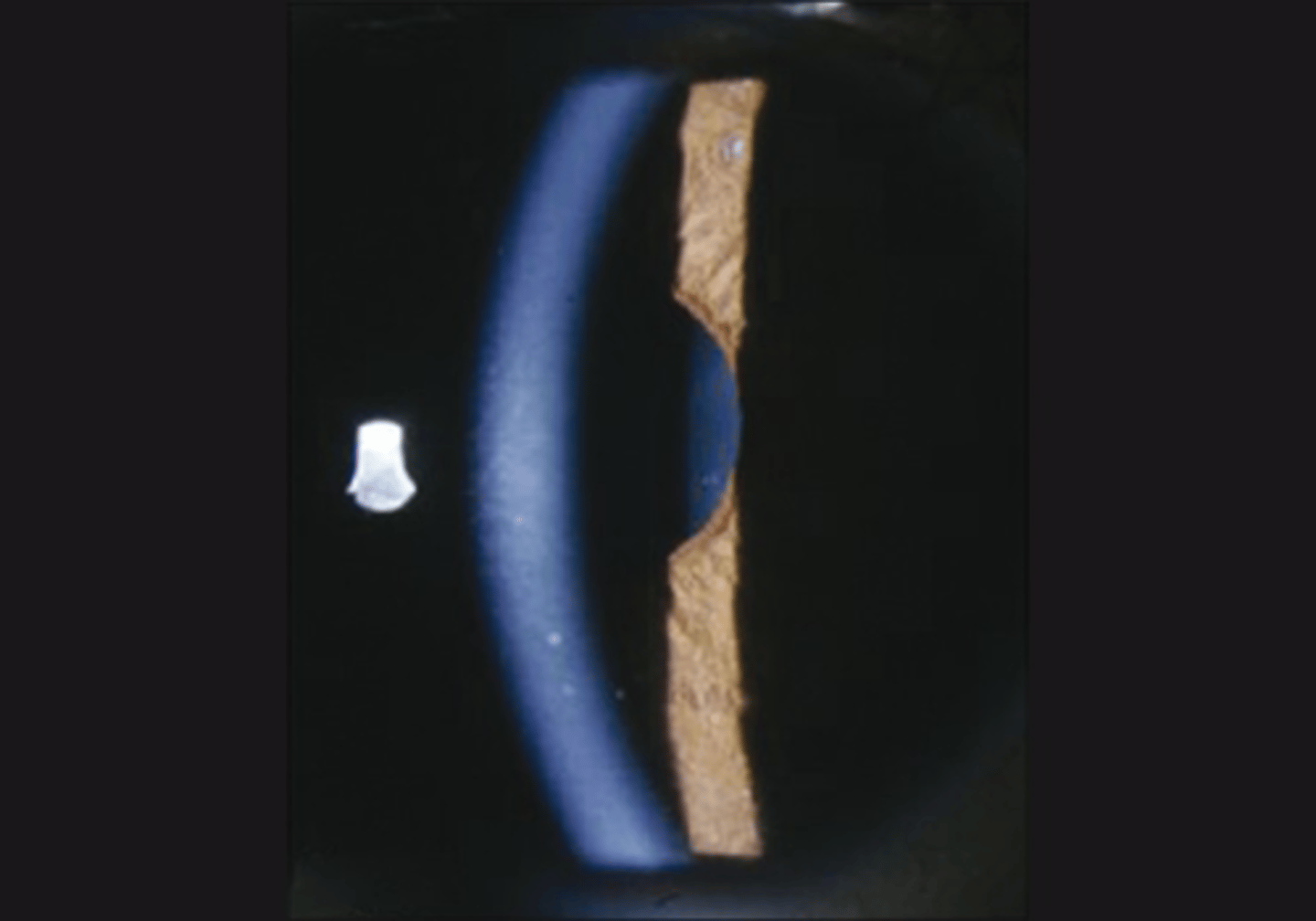
What do we expect to see when looking at the direct response of a tonic pupil?
NO direct response (or may be extremely subtle)
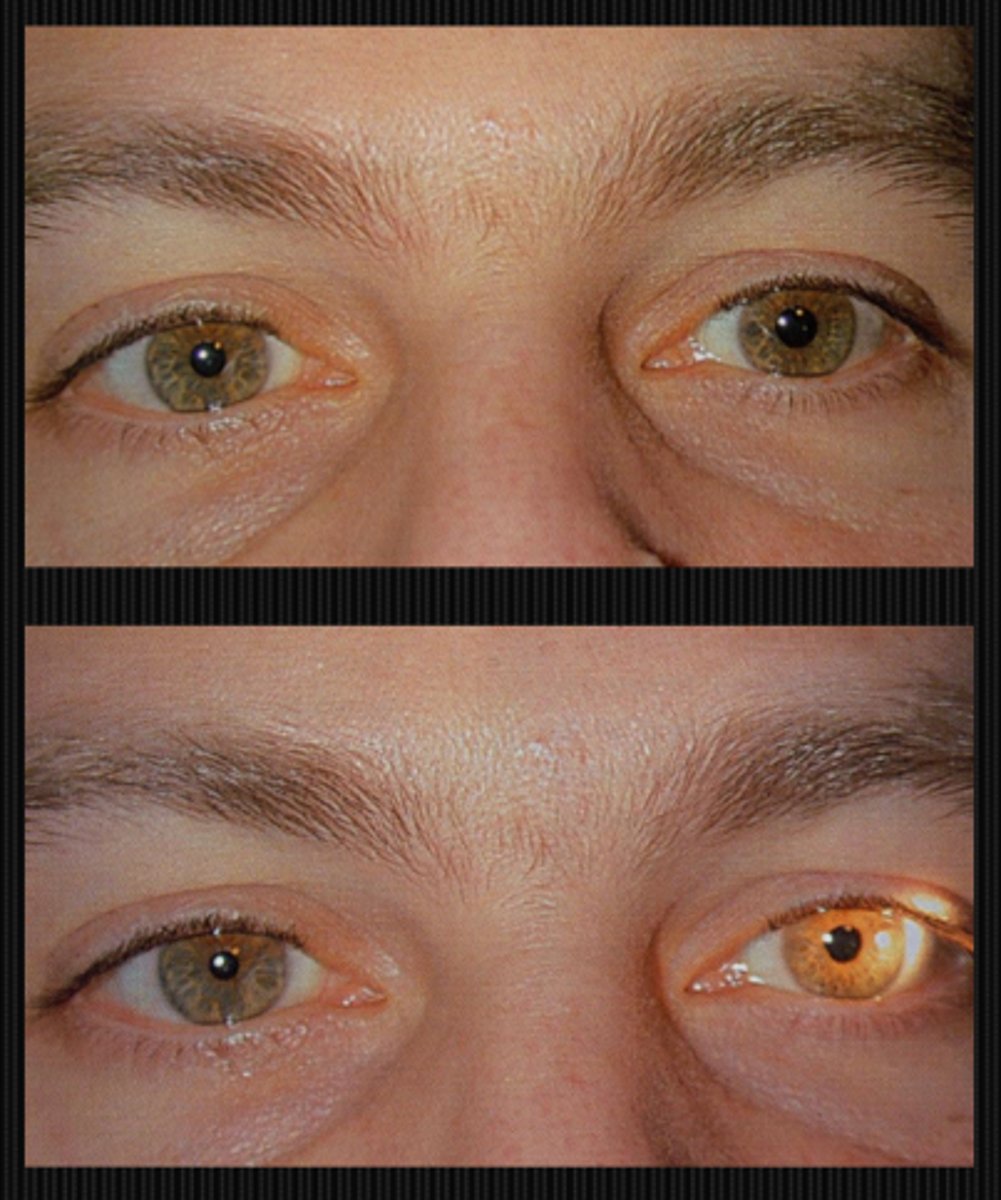
What do we expect to see when looking at the near response of a tonic pupil?
slow, tonic constriction to near
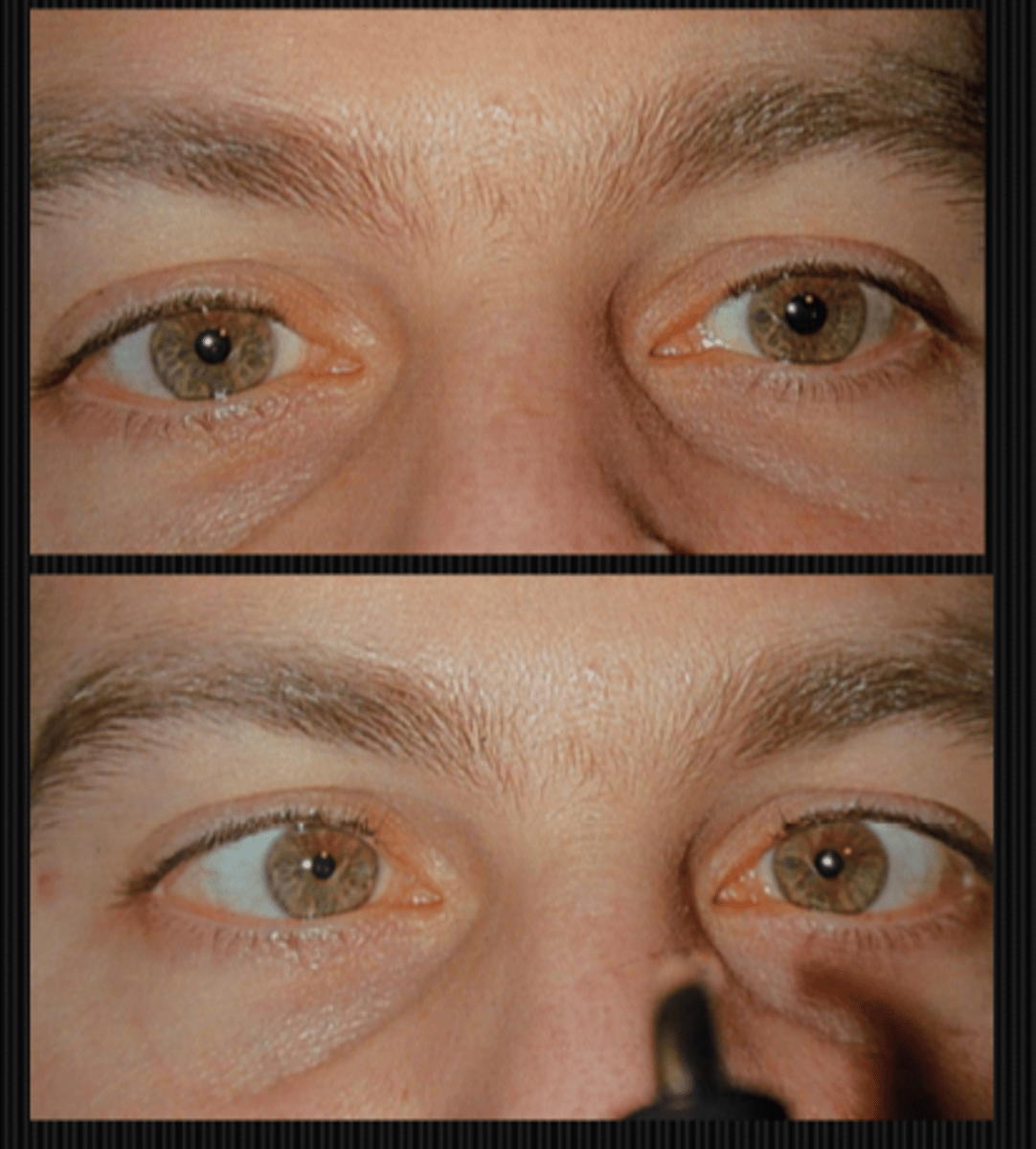
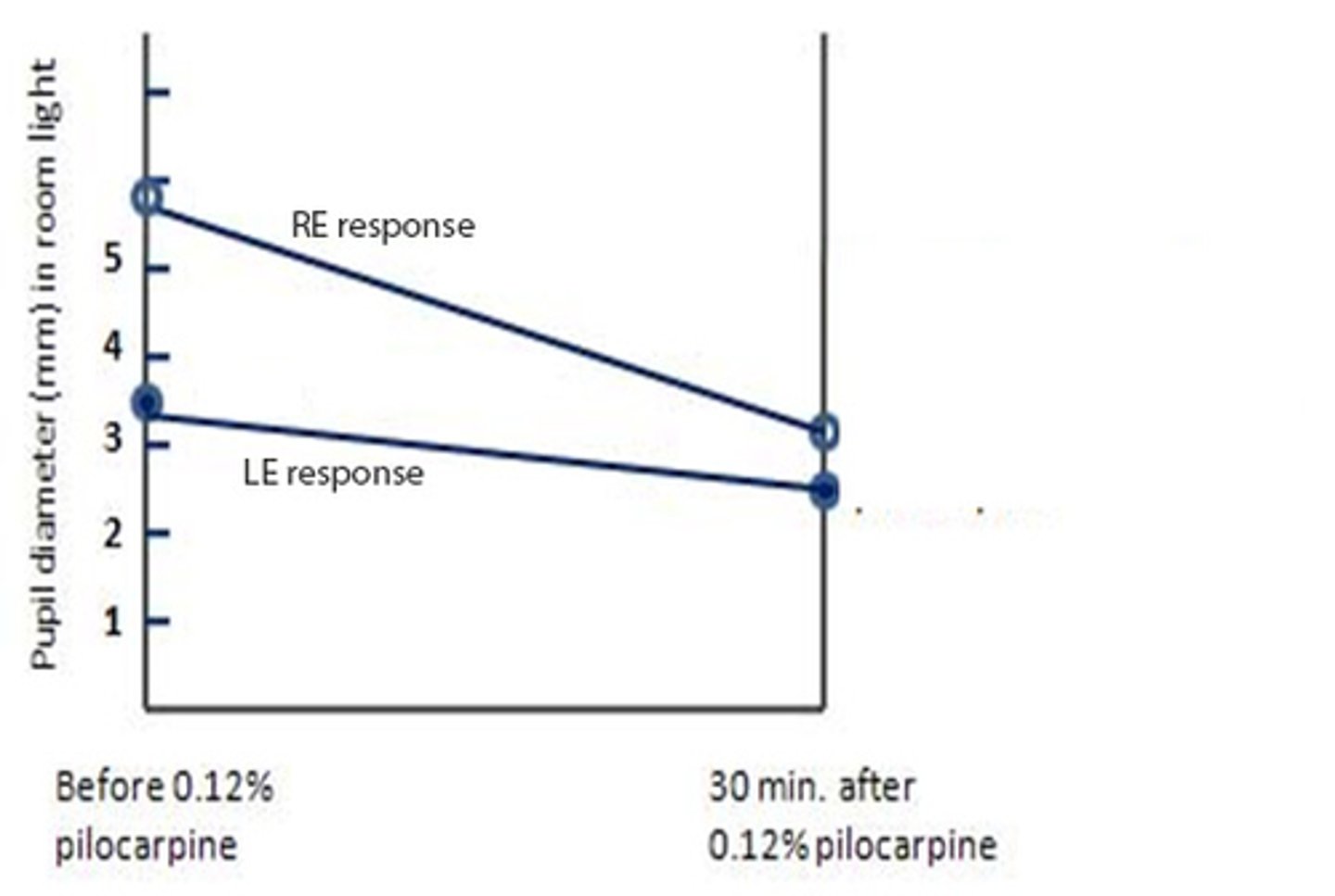
How will a tonic pupil present after the 0.125% pilocarpine denervation supersensitivity test?
tonic pupil will constrict more in response to dilute pilocarpine (bc the eye was starved)
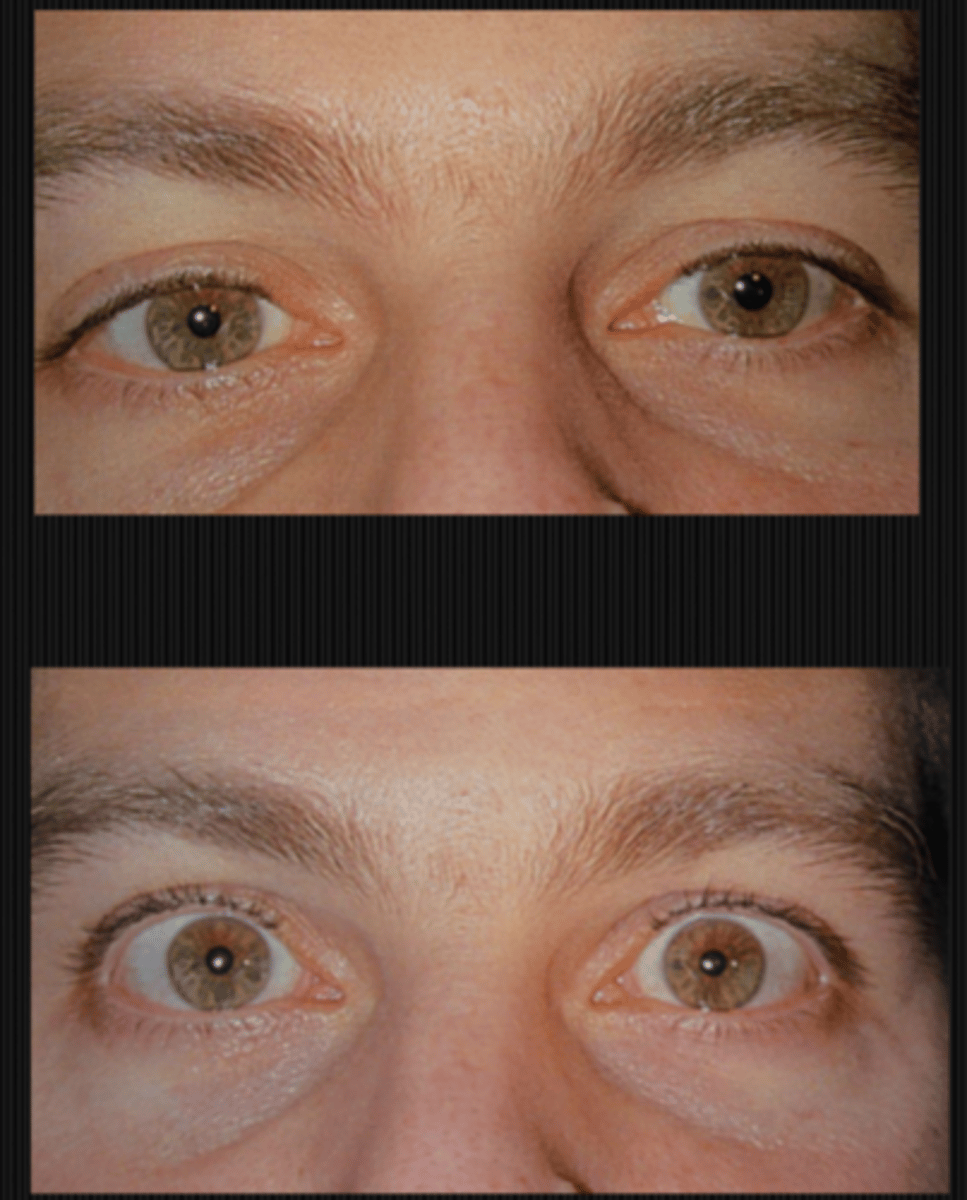
Ex) Based on the result of this 0.125% pilocarpine denervation supersensitivity test, which eye has the tonic pupil?
OD bc this is the diseased eye that is starved for ACh, so it will respond to dilute pilocarpine
What are the 3 types of tonic pupil?
local
neuropathic
Adies (idiopathic)
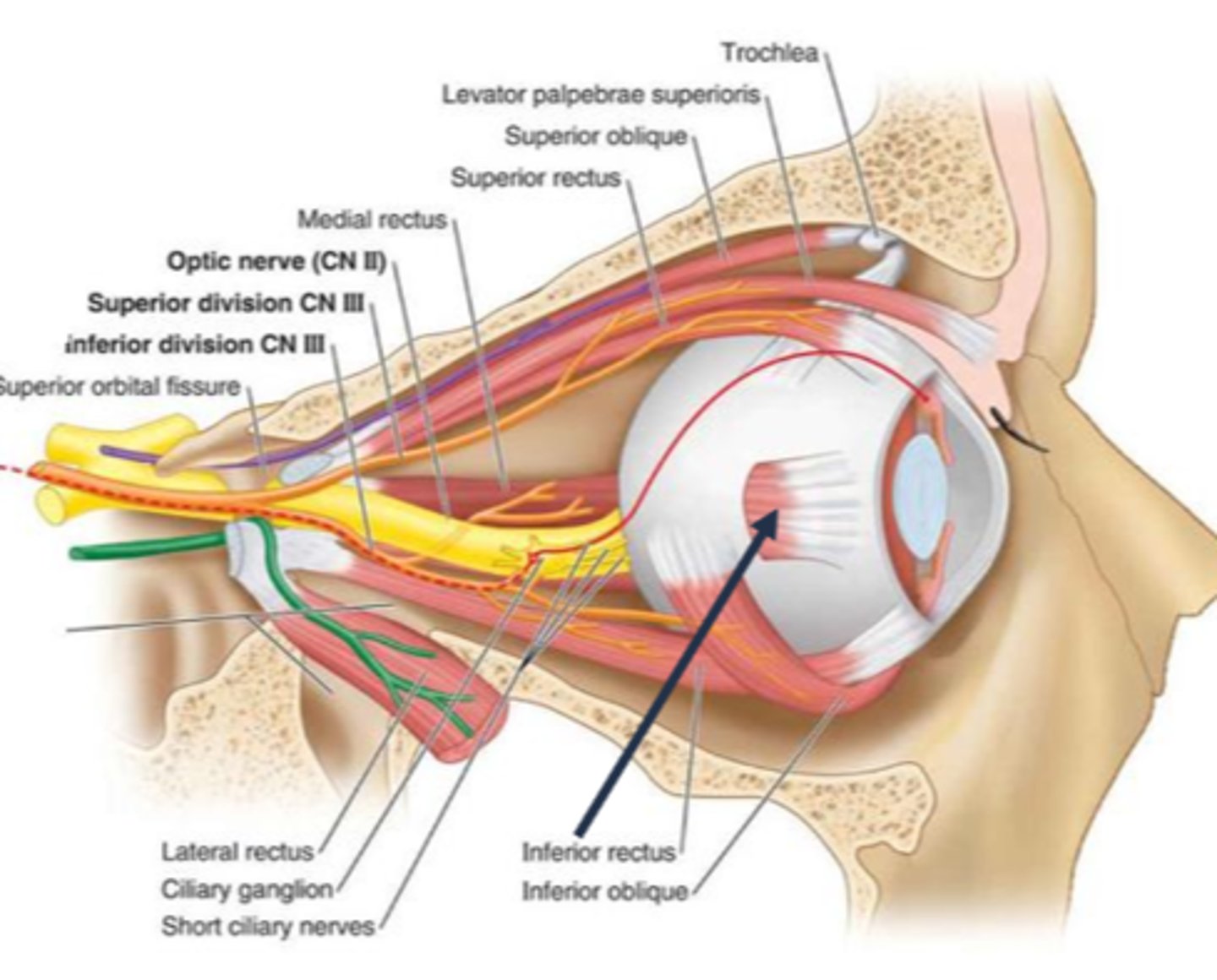
What are some causes of a local tonic pupil?
damage to ciliary ganglion via...
varicella
retrobulbar injection
orbital tumor
orbital surgery
traumatic iridoplegia = SPCN damage
post-ganglionic denervation
pre-ganglionic CN III palsy
abberrant regeneration of CN III
What are some causes of a neuropathic tonic pupil?
usually when pt's already have a known systemic disease such as...
DM
syphillis
Sarcoid
dysautonomia
Charcot-marie-Tooth syndrome
Ross' syndrome
NOTE: all are rare!
What are some causes of an Adie's tonic pupil?
idiopathic by definition
In which populations do we see Adie's tonic pupil?
females >>> males
age 20-40
THINK: Ladies get Aide's
What is the laterality of Adie's tonic pupil?
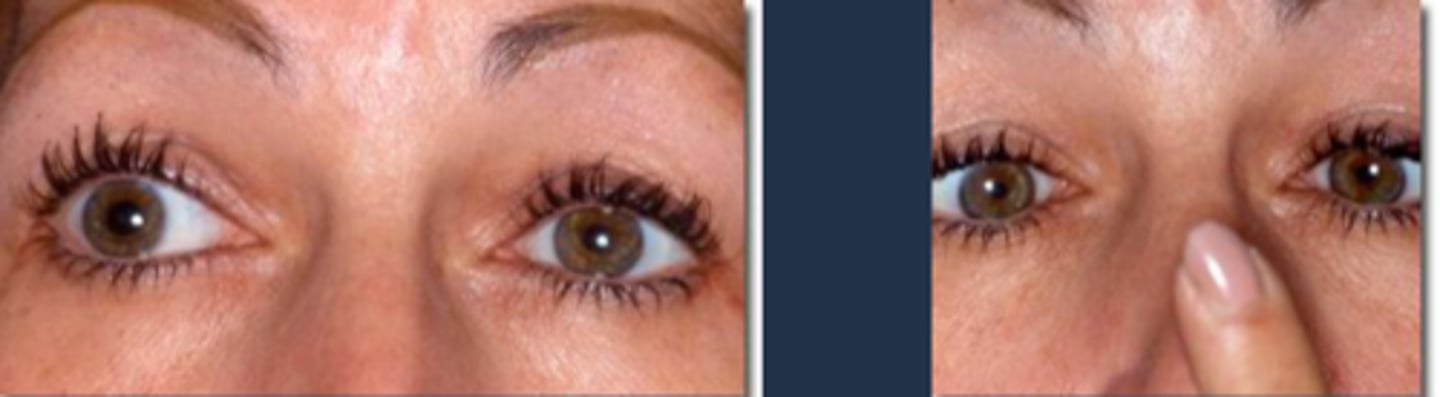
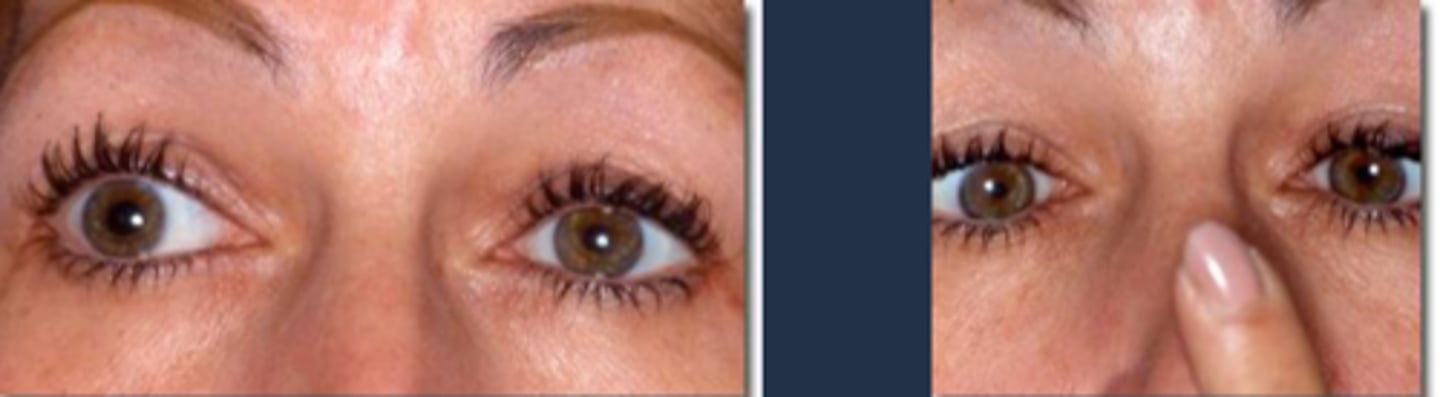
unilateral at first, then fellow eye can become involved
Why does the pupil react to near, but not to light in Adie's tonic pupil?
ciliary ganglion damage and recovery = nerve axoplasm that once went to accom now goes to pupil = pupillomotor fibers innervated by accom fibers = pupil still reacts to near
What are 3 ways that accom can be affected by Adie's tonic pupil?
normal
OR
accom paresis only in affected eye = unequal accom, HA
OR
CB spastic tonicity due to accom knocked out = denervation supersensitivity of ACh receptors = accom spasm, excess accom
Why is it that induced astig can show up in Adie's tonic pupil?
CB segmental paralysis = CB tugs on different parts of lens differently
What are some S/S of Adie's tonic pupil?
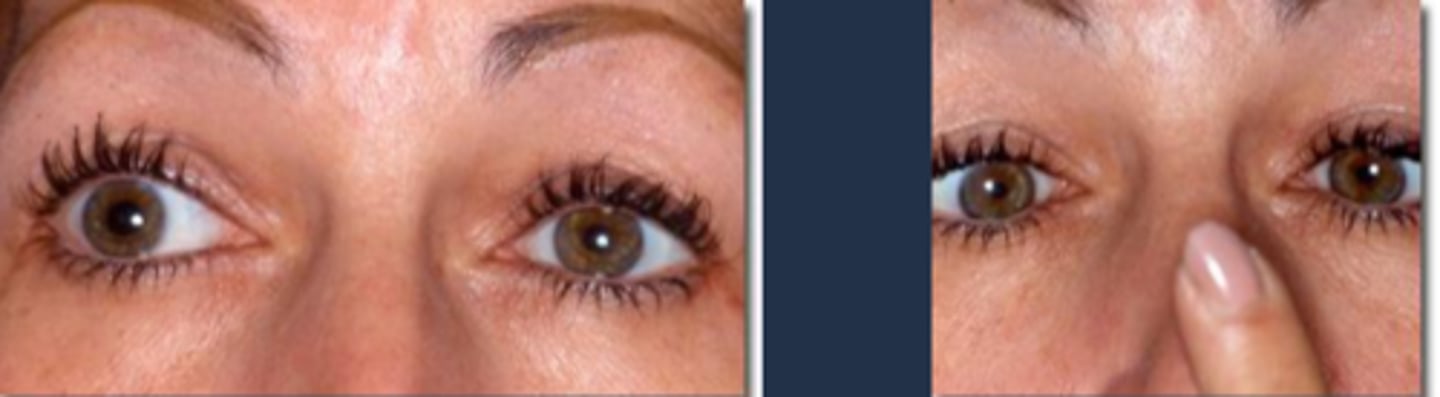
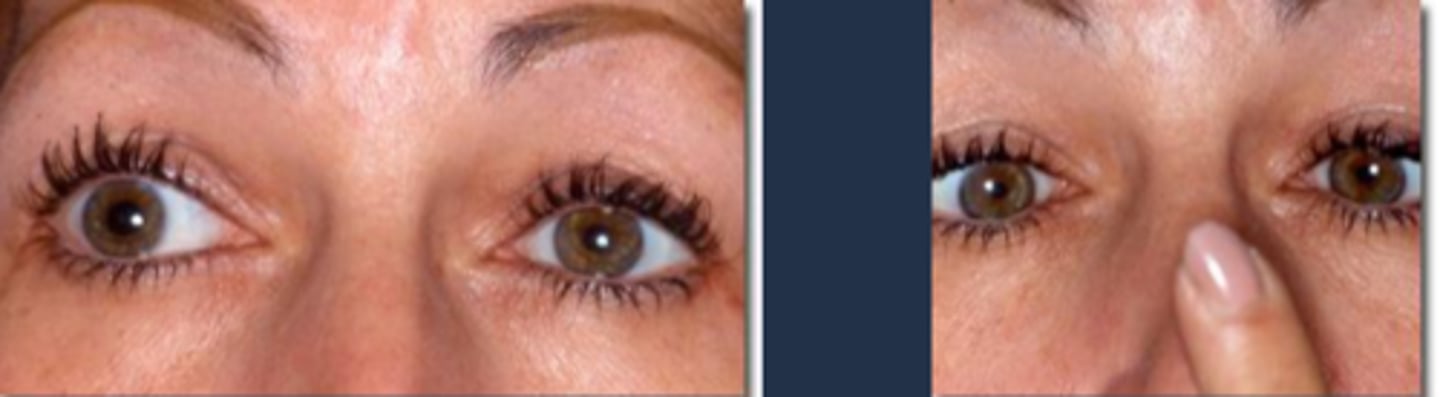
anisocoria
blurred vision
brow ache from accom issue
photophobia
dark adaptation issues
Pulfrich stereo phenomenon
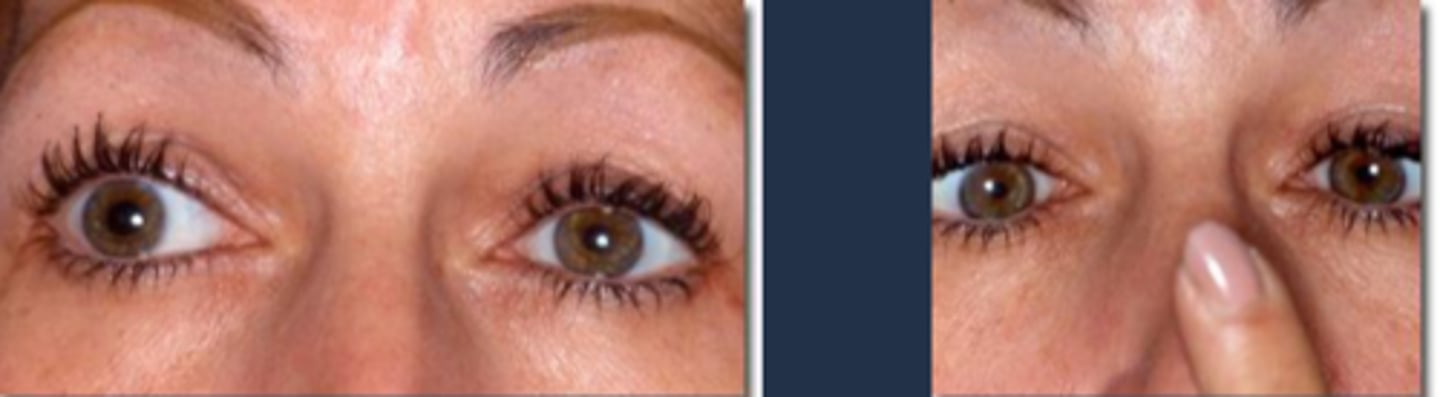
What is the Pulfrich stereo phenomenon sometimes seen in Adie's tonic pupil?
anisocoria = one eye receives more light than the other = visual pigments more bleached in one eye = difference in signal transmission time from each eye = 2D objects appear to be 3D

Aside from the pupil not constricting to light, what are 2 other possible clinical findings seen in tonic pupil?
reduced corneal sensitivity bc sensory fibers from CN V1 travel through the damaged ciliary ganglion
decreased deep tendon reflexes for unknown reasons (called Holmes-Adie syndrome)
What is Holmes-Adie syndrome?
idiopathic tonic pupil
reduced deep tendon reflex
What is Ross's syndrome?
idiopathic tonic pupil
reduced deep tendon reflex
excess sweating
How do we perform supersensitivity testing of accom when accom is affected in a tonic pupil?
instil 0.25% pilocarpine OU = CB contracts = increased accom = re-refract pt = affected eye will have an increase in myopia with the pilocarpine (compared to the normal eye)
How do we treat the issue of CB spastic tonicity (tonic accom / accom spasm) sometimes seen in tonic pupil? 2 options
tropicamide or other atropine-like drug to relax the CB (but increases anisocoria)
OR
occlude/frost bottom part of glasses lens to prevent binocular vision at near (induce monovision)
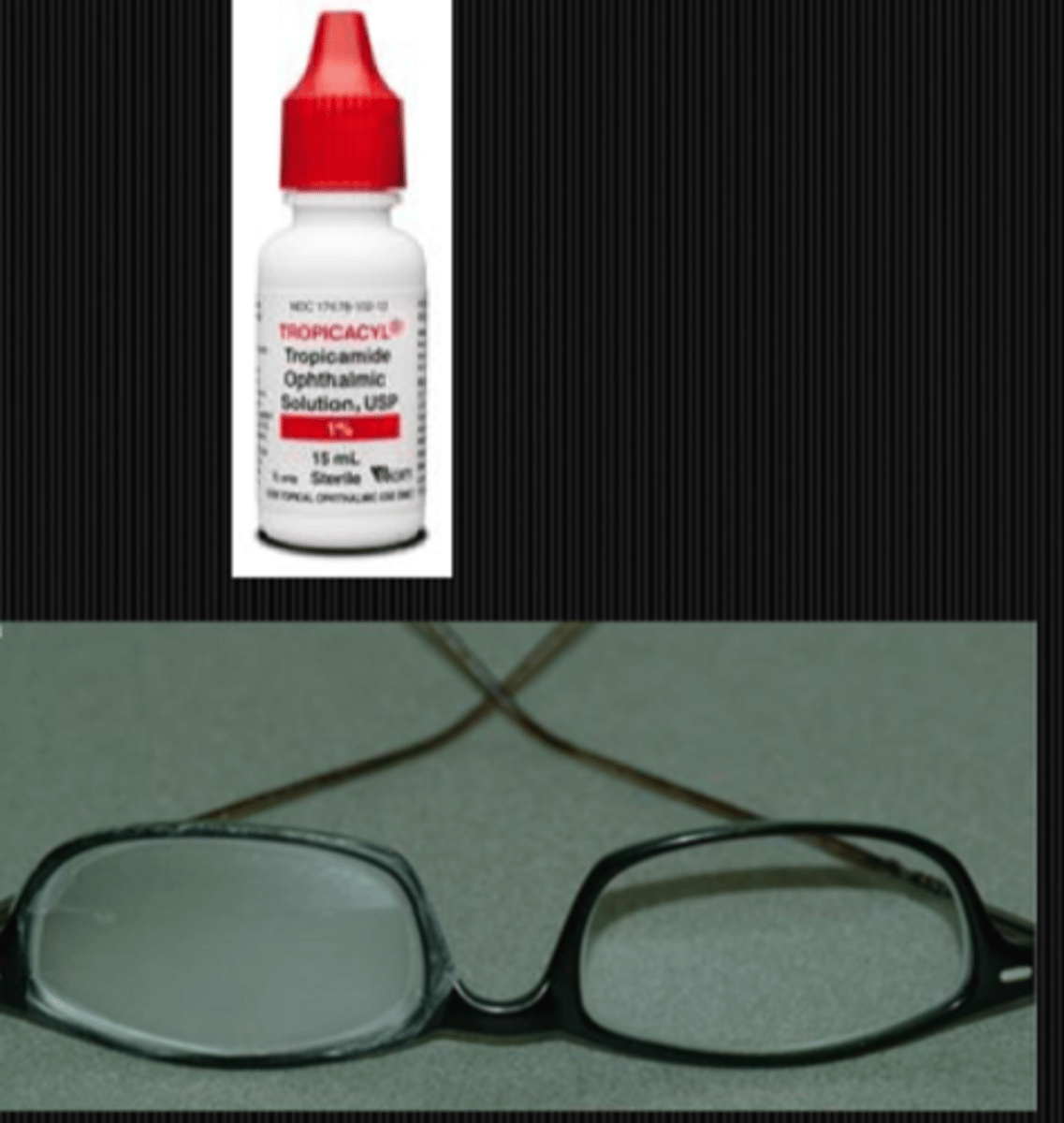

How do we treat the issue of accom paresis (reduced accom) sometimes seen in tonic pupil? 3 options.
eserine or pilocarpine to stimulate the CB mm (but side effects of CB spasm, HA, myopia)
OR
MF CL in affected eye
OR
occlude/frost bottom part of glasses lens to prevent binocular vision at near (induce monovision)

How do we treat the issue of anisocoria seen in tonic pupil? 3 options.
eye is super-sensitive to ACh and ACh-like molcules = prescribe 0.125% or 0.25% pilocarpine or Vuity = reduce pupil size (for cosmesis)
photochromic lenses for photophobia
cosmetic CL with a certain pupil size for cosmesis, photophobia

How long does it take for the pt to heal from a tonic pupil?
1-6 years, more on the longer end if accom is involved