Diagram of Basics | Quizlet
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
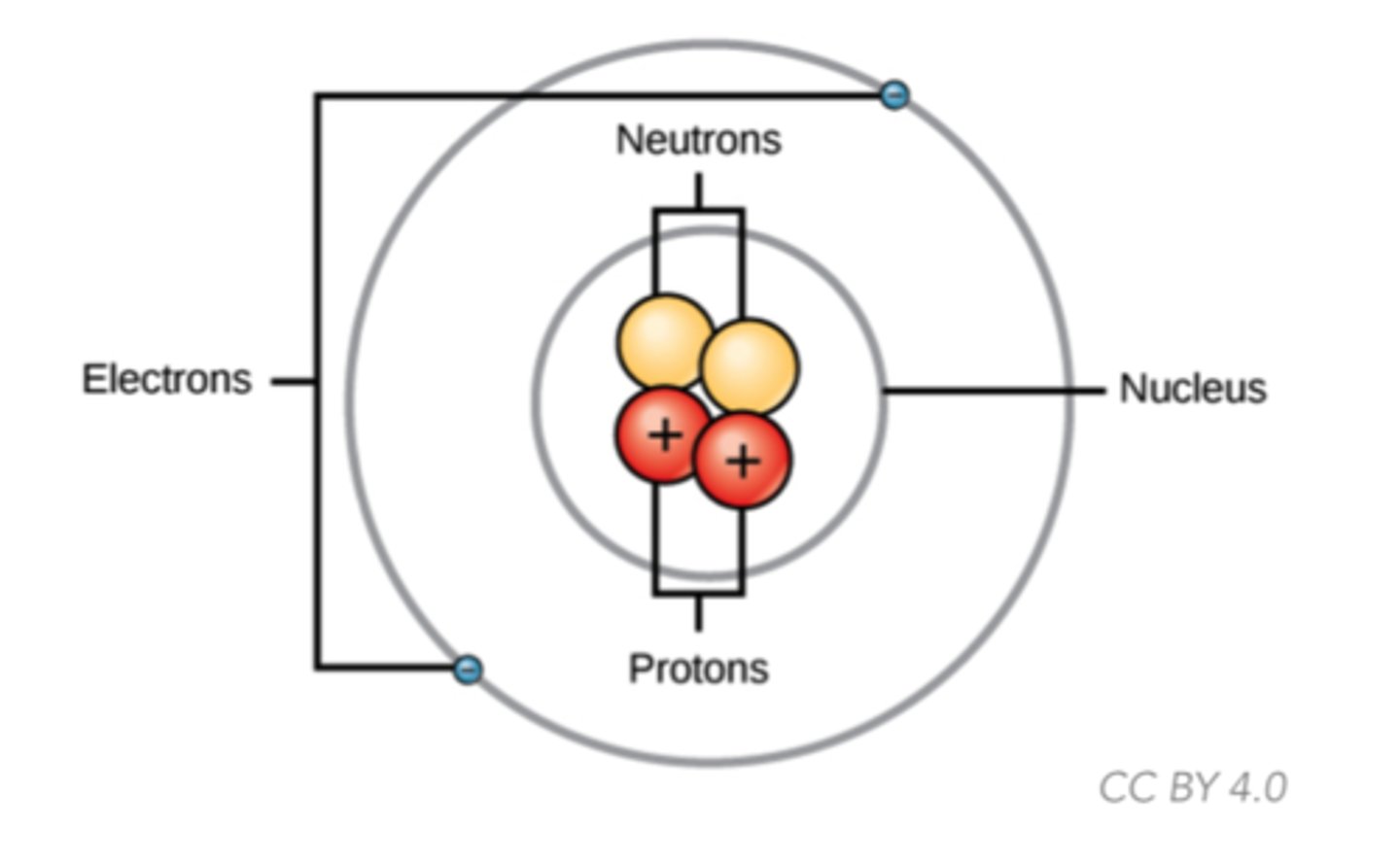
What is the fundamental building block of matter composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons?
atom
What is a group of 2 or more atoms held together by chemical bonds?
molecule
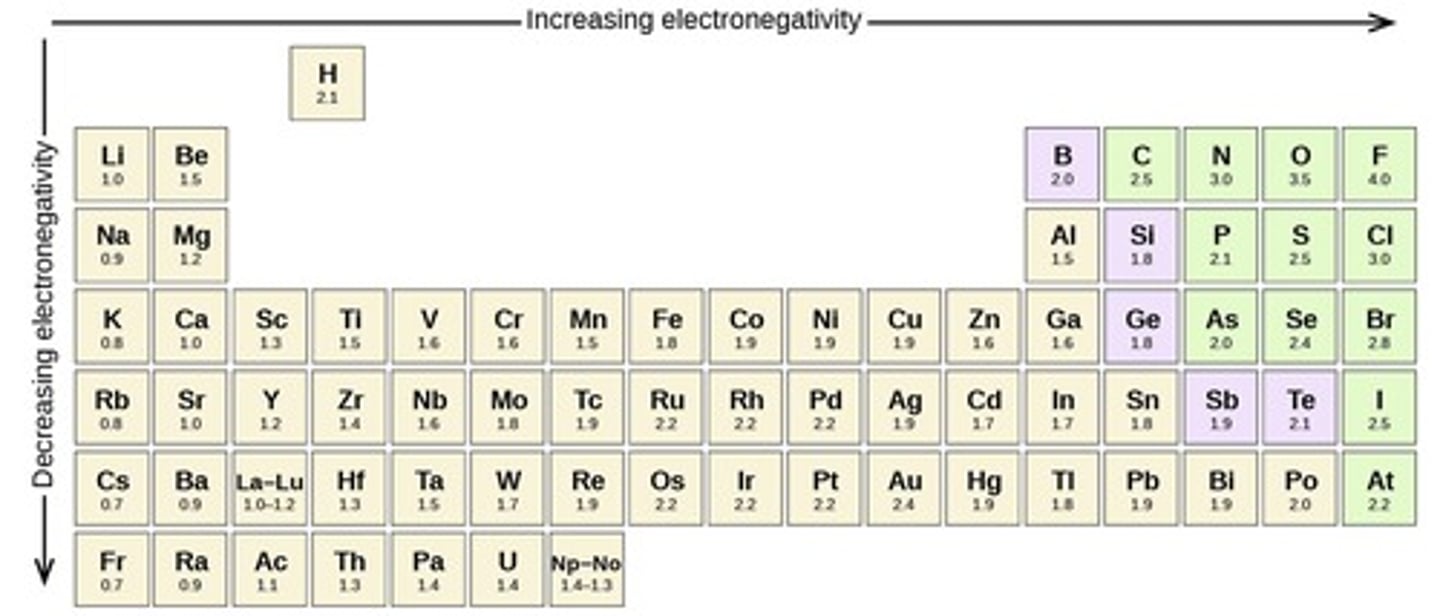
What term describes the ability of an atom to attract electrons?
electronegativity
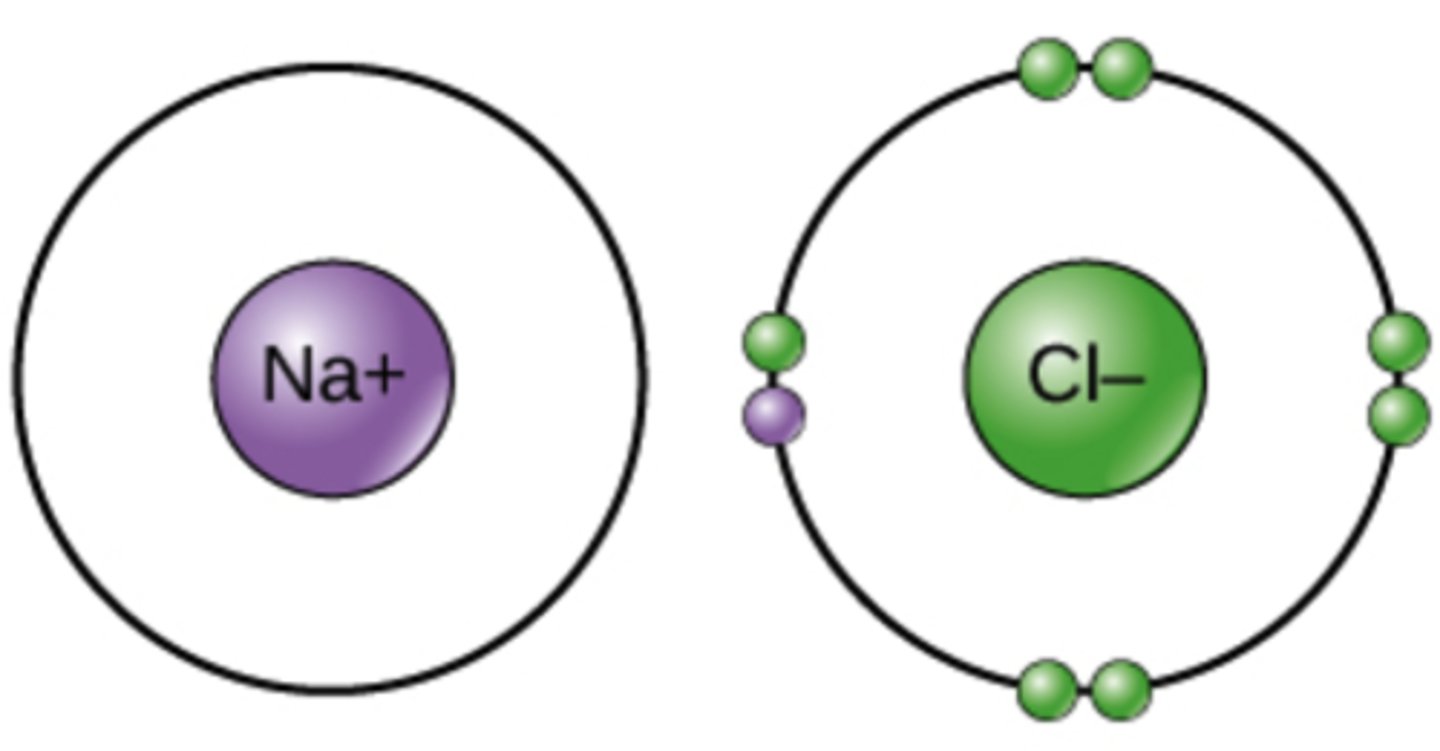
Which chemical bond involves the transfer of electrons from atom to atom where both atoms have different electronegativities?
ionic
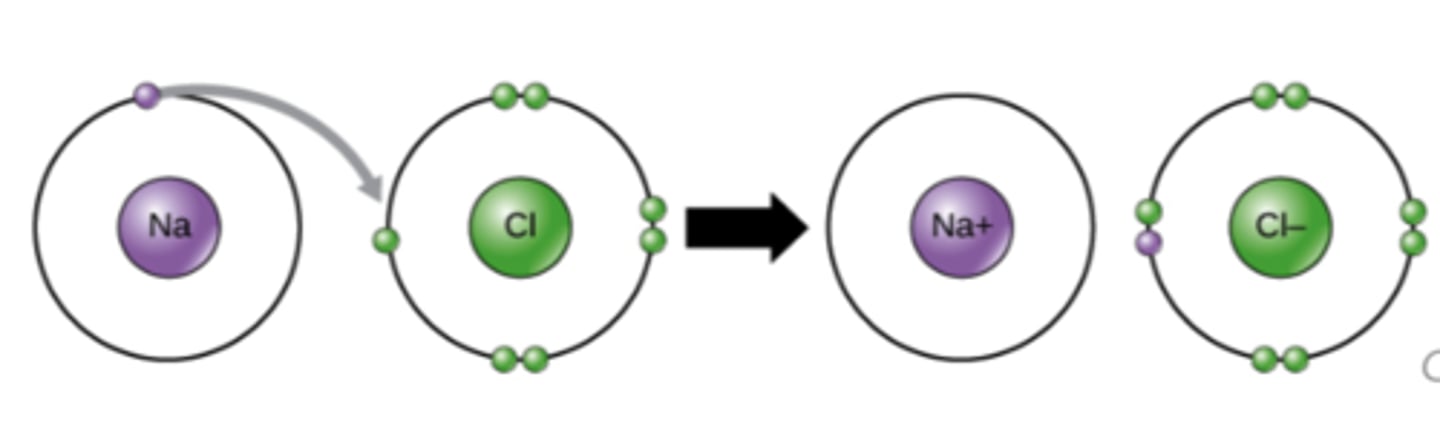
Which chemical bond involves electrons shared between atoms of similar electronegativities?
covalent
What number of covalent bonds can form between two atoms?
1(single), 2(double), or 3(triple)
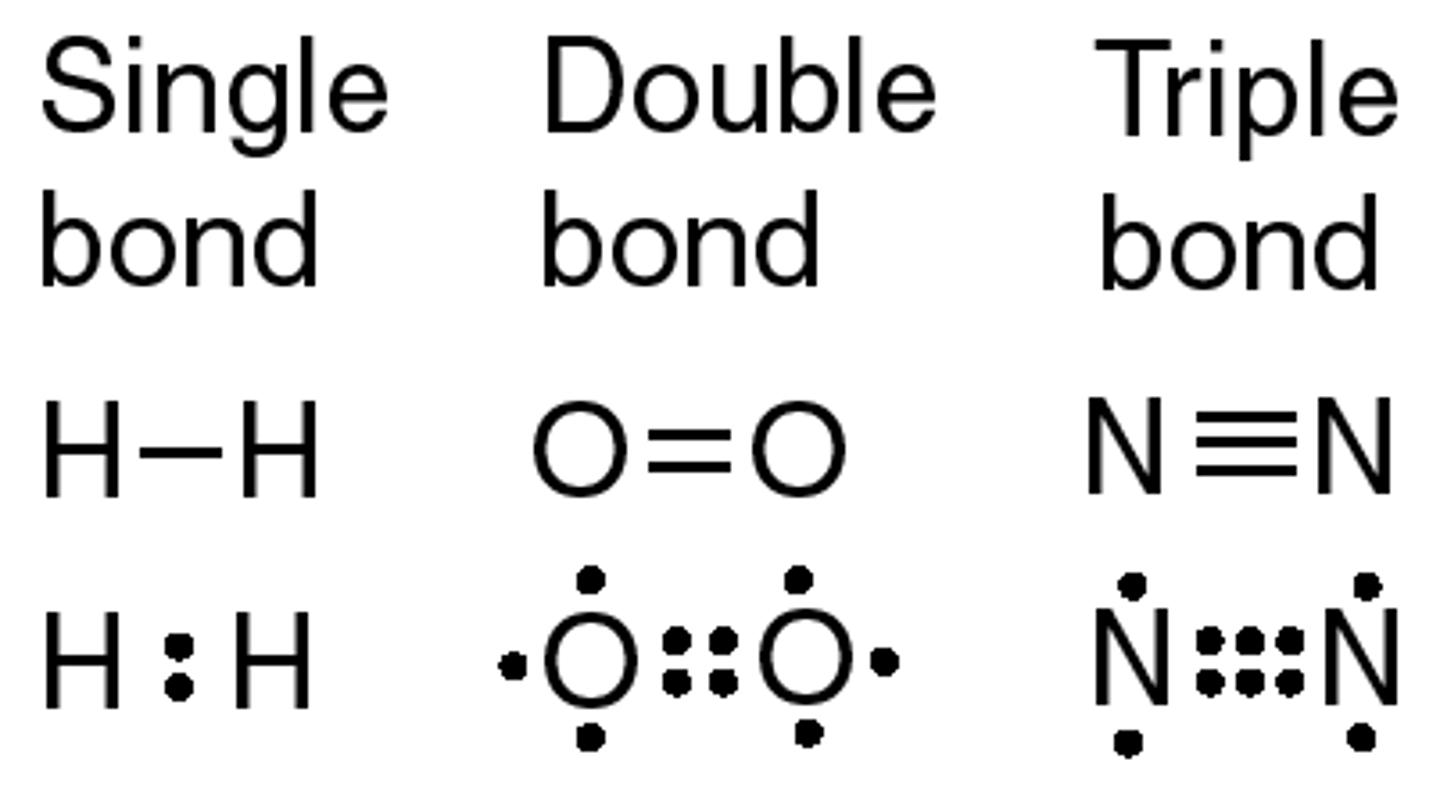
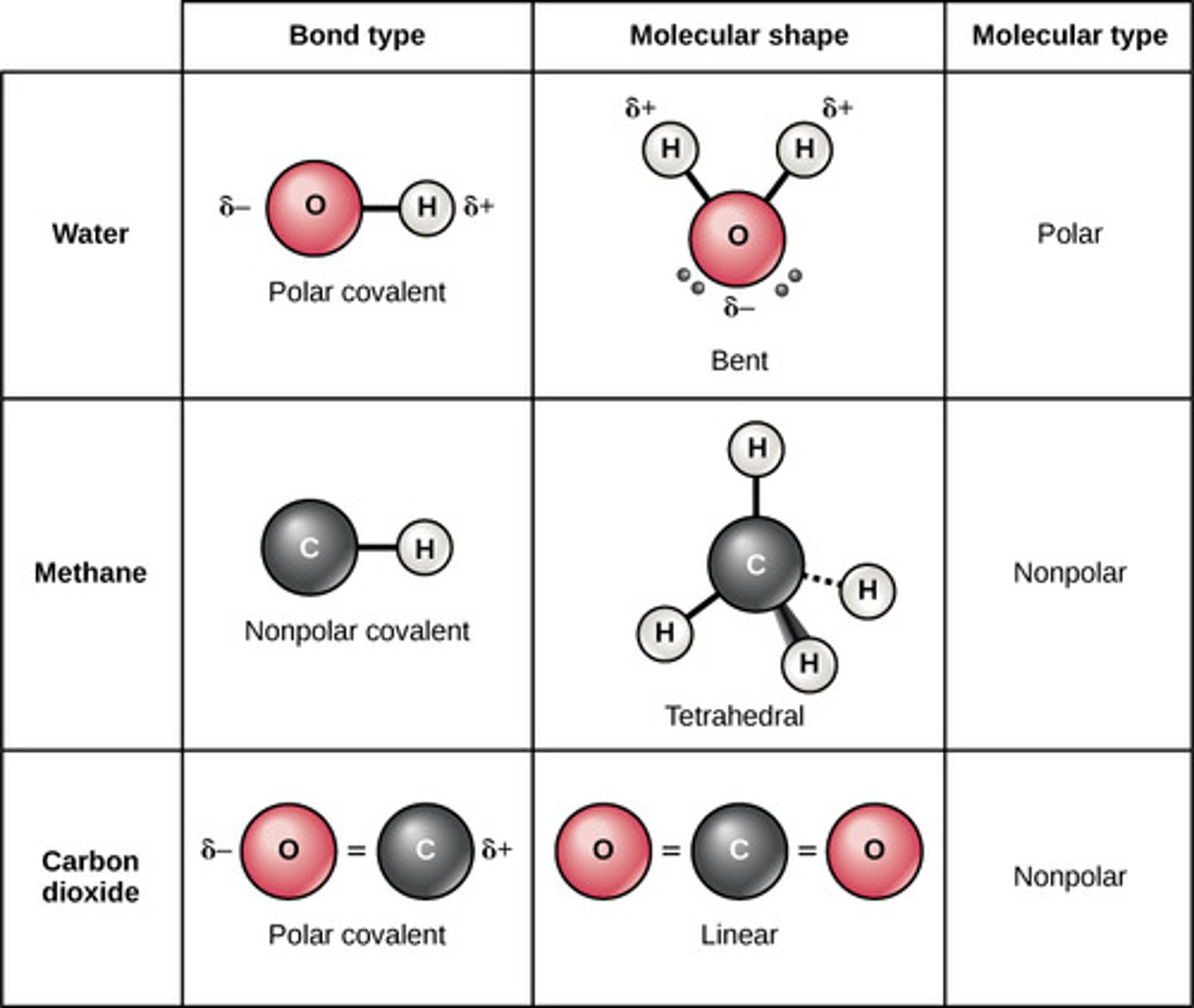
Which covalent bond involves equal sharing of
electrons between two atoms of identical electronegativity?
non-polar
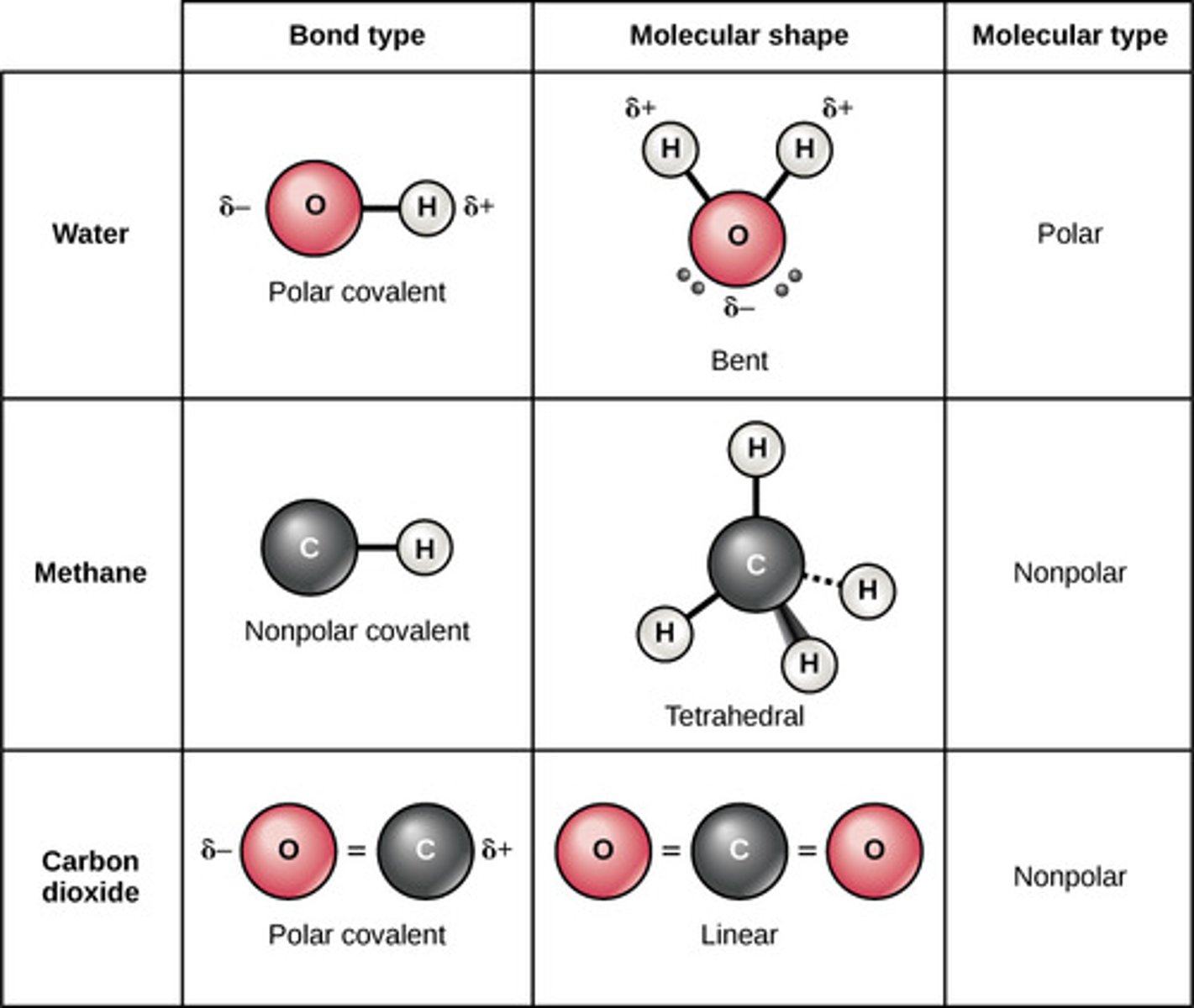
Which covalent bond involves unequal sharing of electrons
between two atoms of different electronegativities?
polar
(Note: leads to the
formation of a dipole)
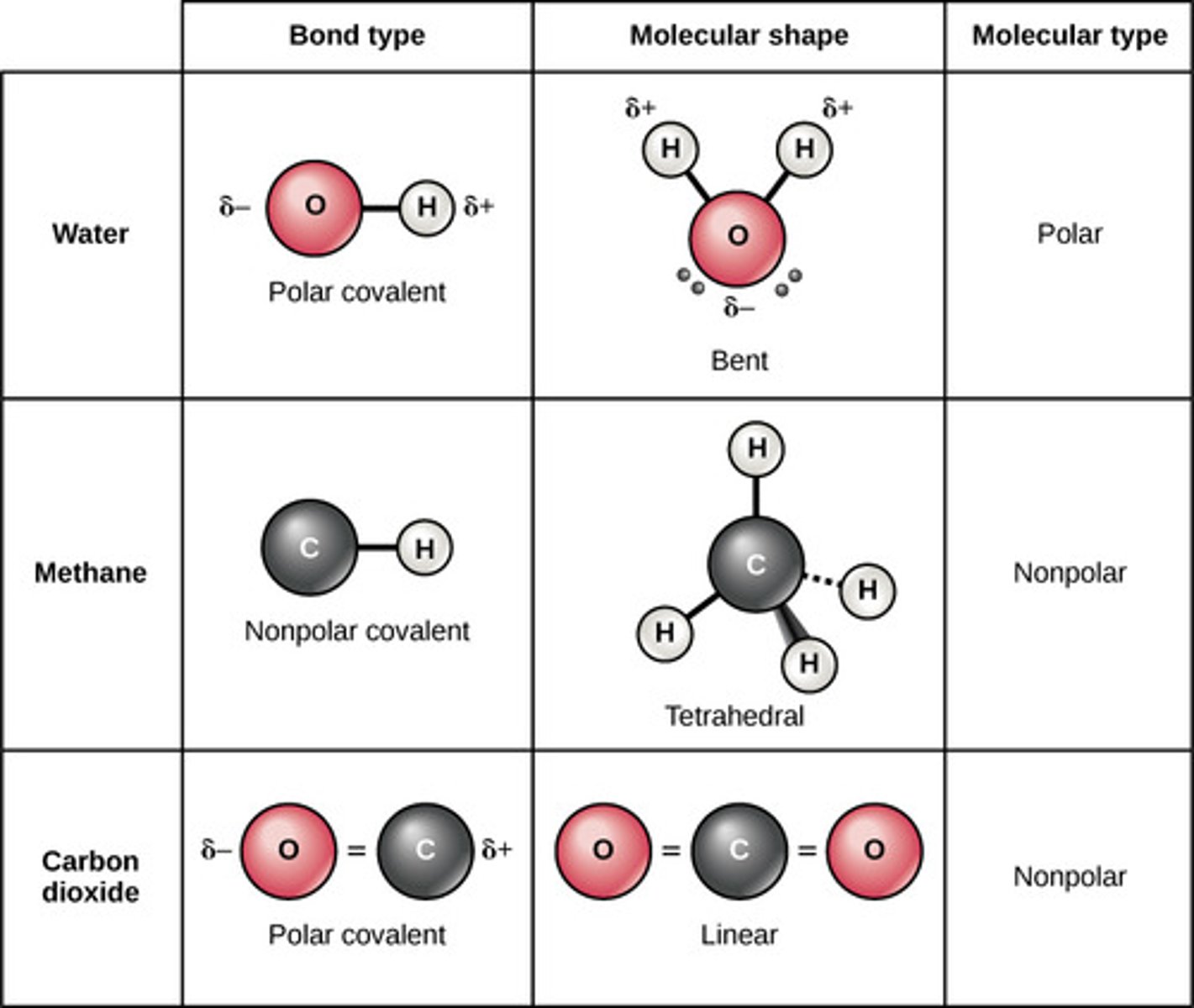
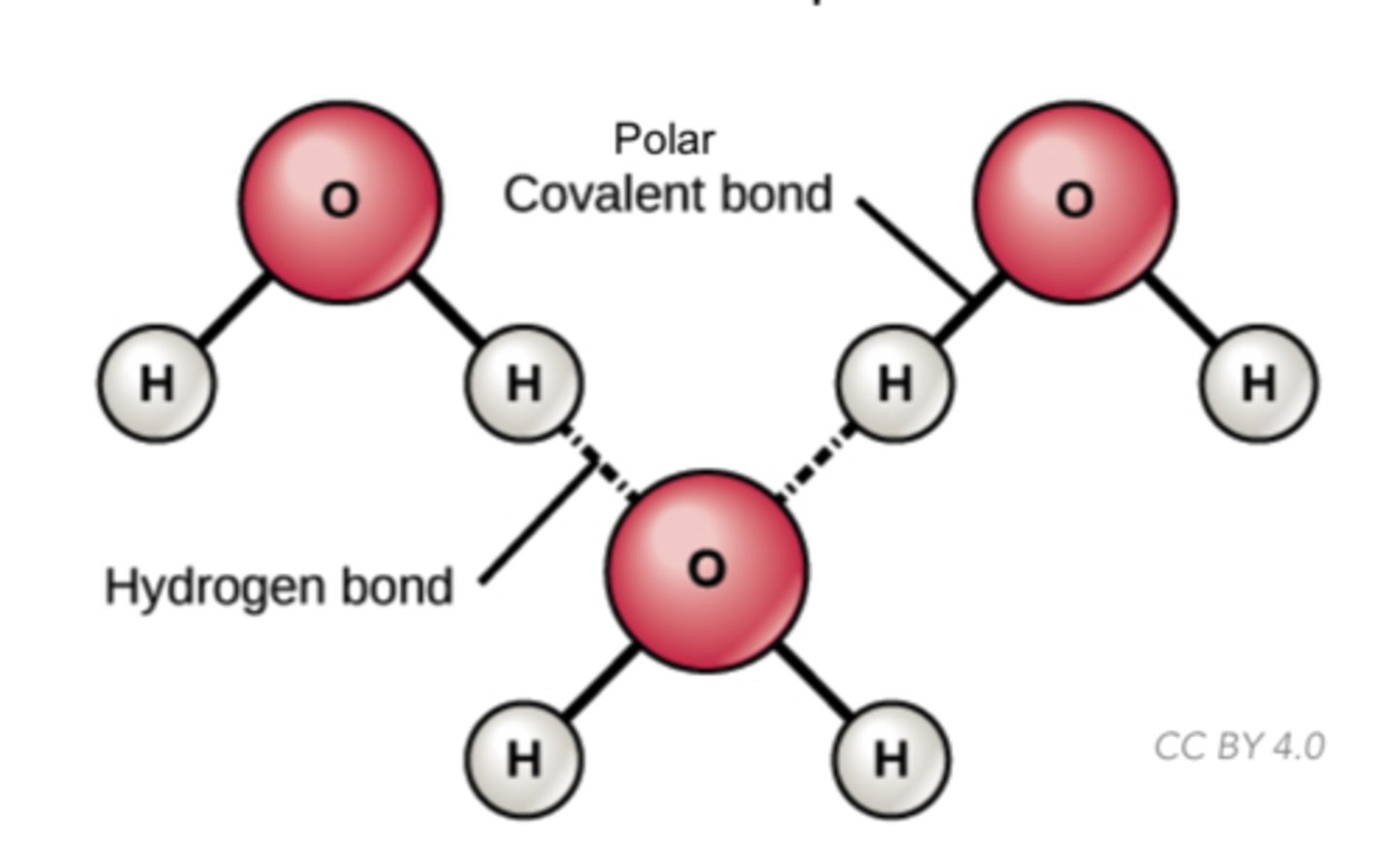
Which chemical bond involves a weak bond between molecules with a hydrogen attached to a highly electronegative atom and is attracted to a negative charge on another molecule (F, O, or N)?
hydrogen bond
Which property of water describes its ability to dissolve substances with its dipole?
excellent solvent
Which property of water describes its ability to absorb a large amount of energy before changing temperature?
high heat capacity
(Note: also explains water's high heat of vaporization)
Which property of water describes its expansion upon freezing to become less dense than its liquid form?
ice floats
(Note: H-bonds are maximum distance apart)
Which property of water describes its attraction to like substances and itself?
cohesion/surface
tension
(Note: attracted to
other substances
with H-bonds,
including itself!)

Which property of water describes its attraction to unlike substances?
adhesion
(Note: capillary
action is the flow
of water without
external force -
ex: against gravity)
What are molecules composed of carbon atoms?
organic molecules
What is the simplest unit of a macromolecule?
monomer (1 unit)
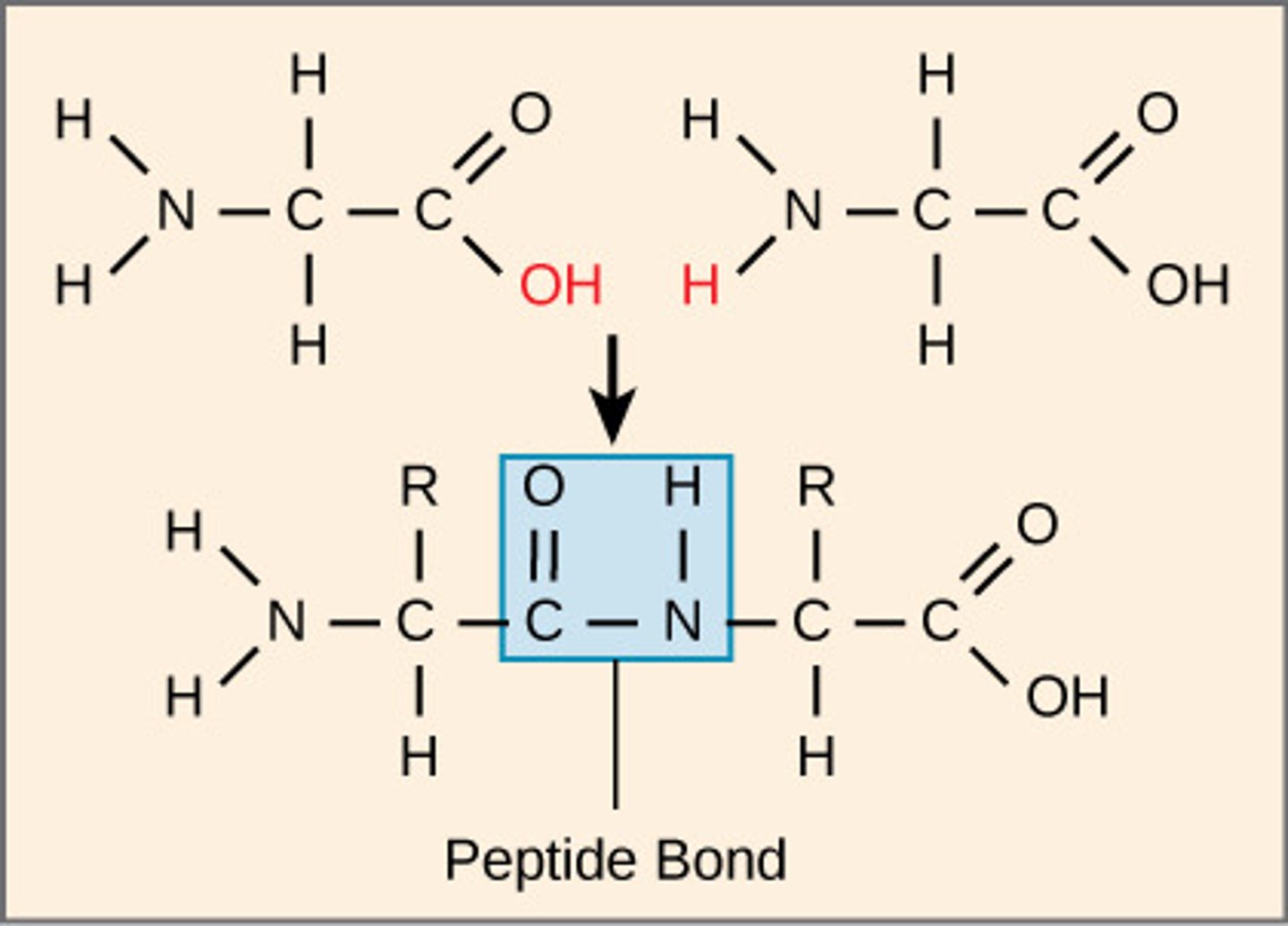
What is the term for the linking of monomers?
polymer
What are are particular clusters of atoms that give organic molecules their key properties?
functional groups
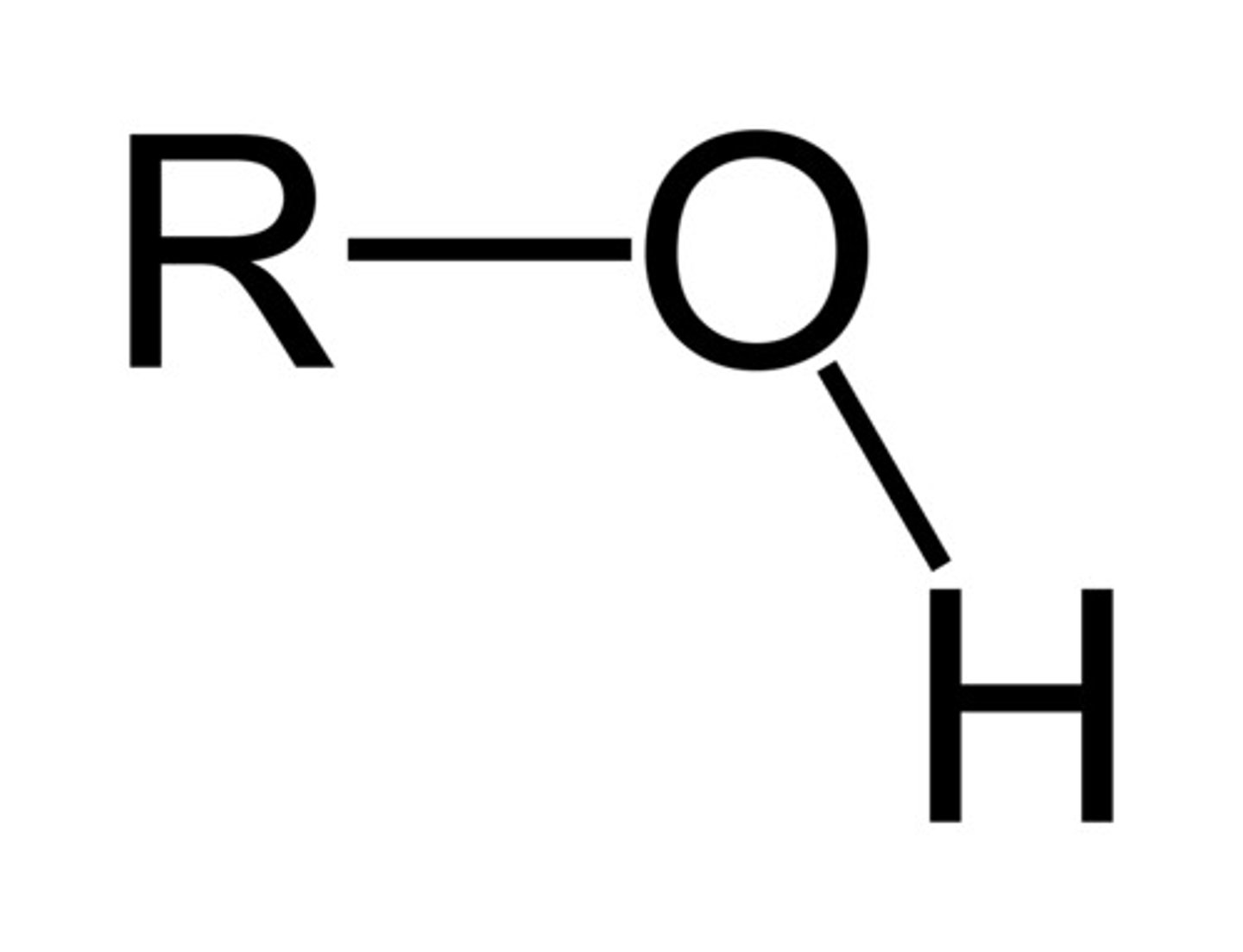
What is the chemical formula for the hydroxyl functional group?
OH
(Note: polar and hydrophilic)
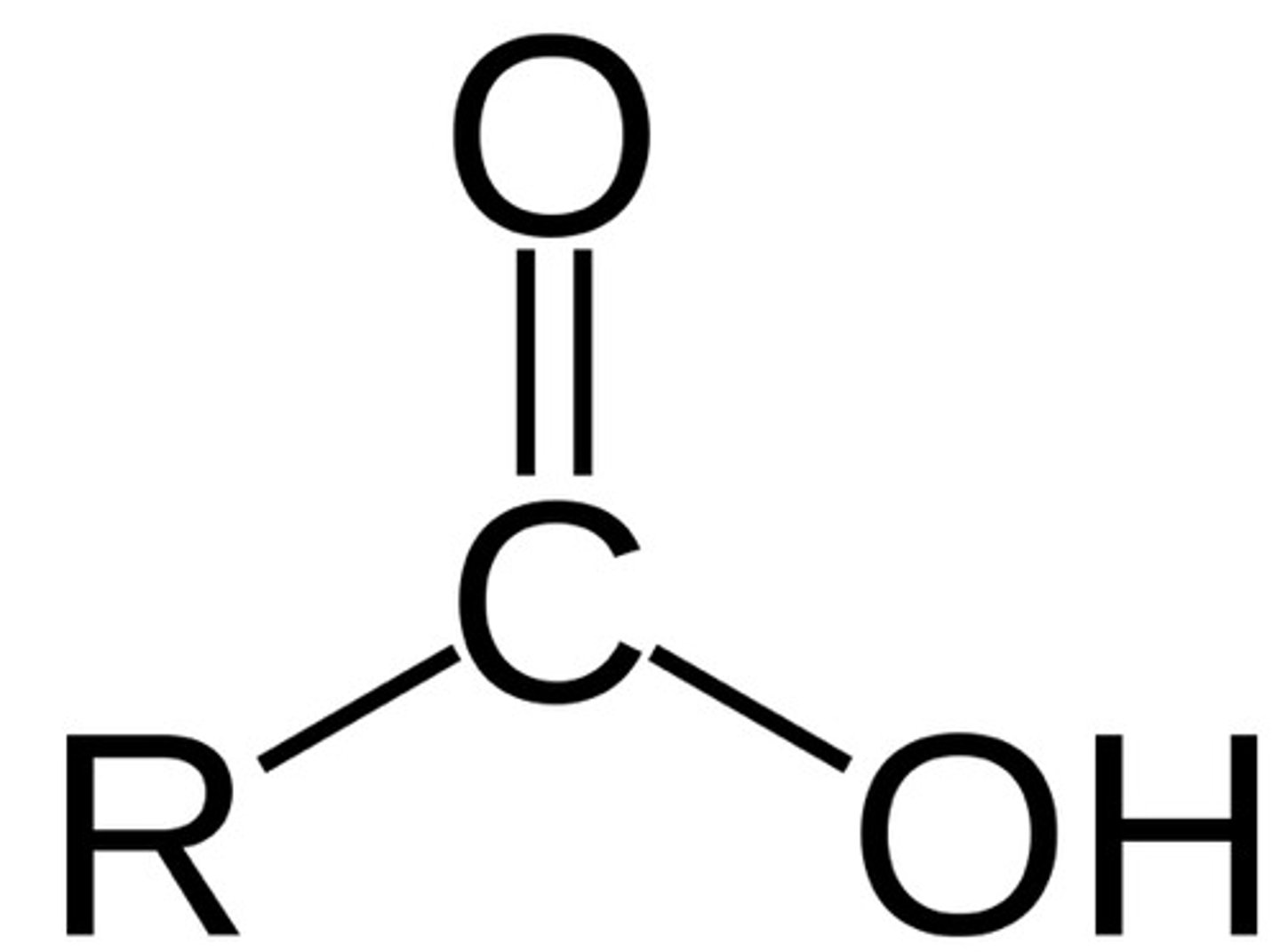
What is the chemical formula for the carboxyl functional group?
COOH
(Note: polar, hydrophilic, and a weak acid)
What is the chemical formula for the amino functional group?
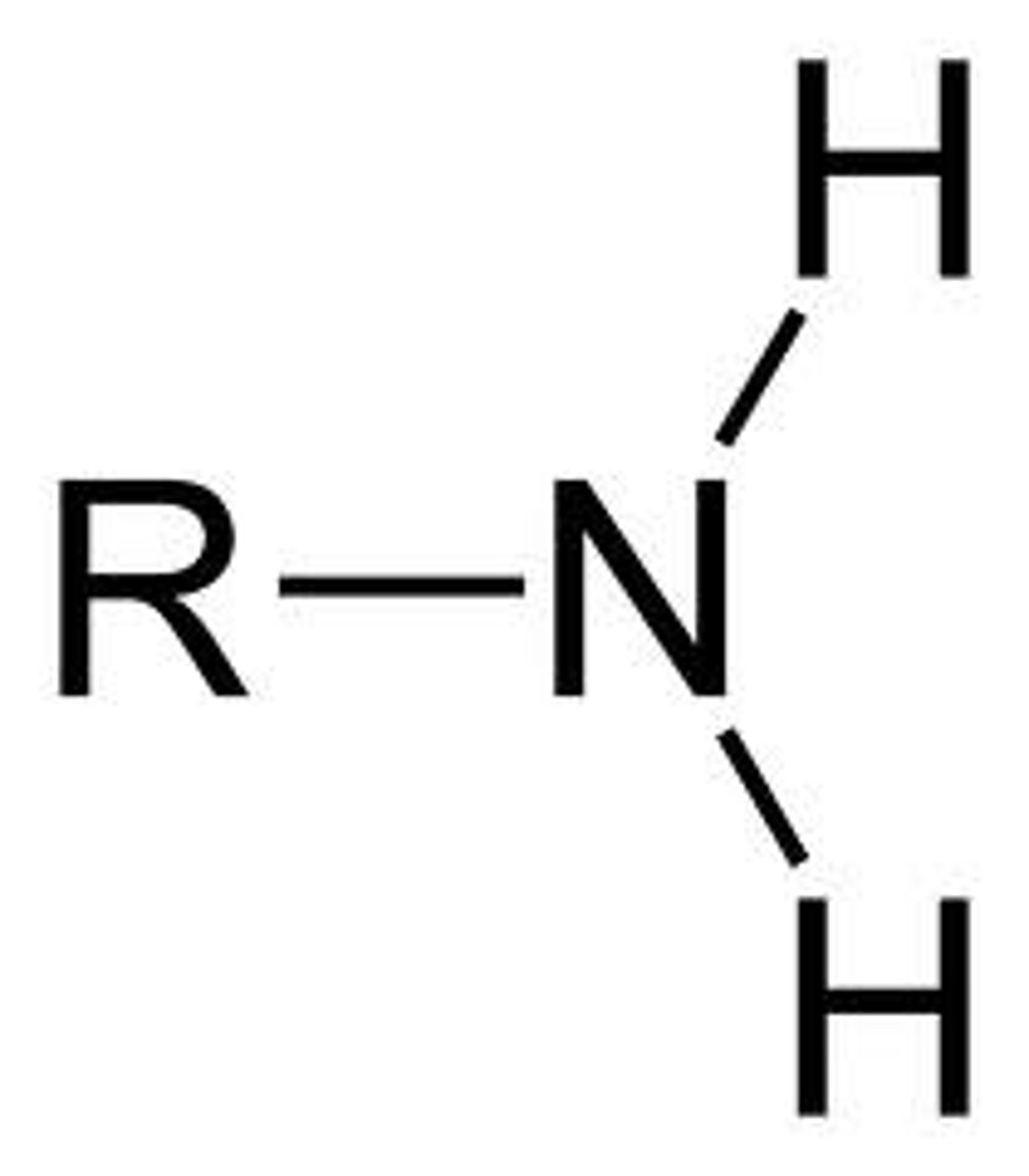
NH2
(Note: polar, hydrophilic, and a weak base)
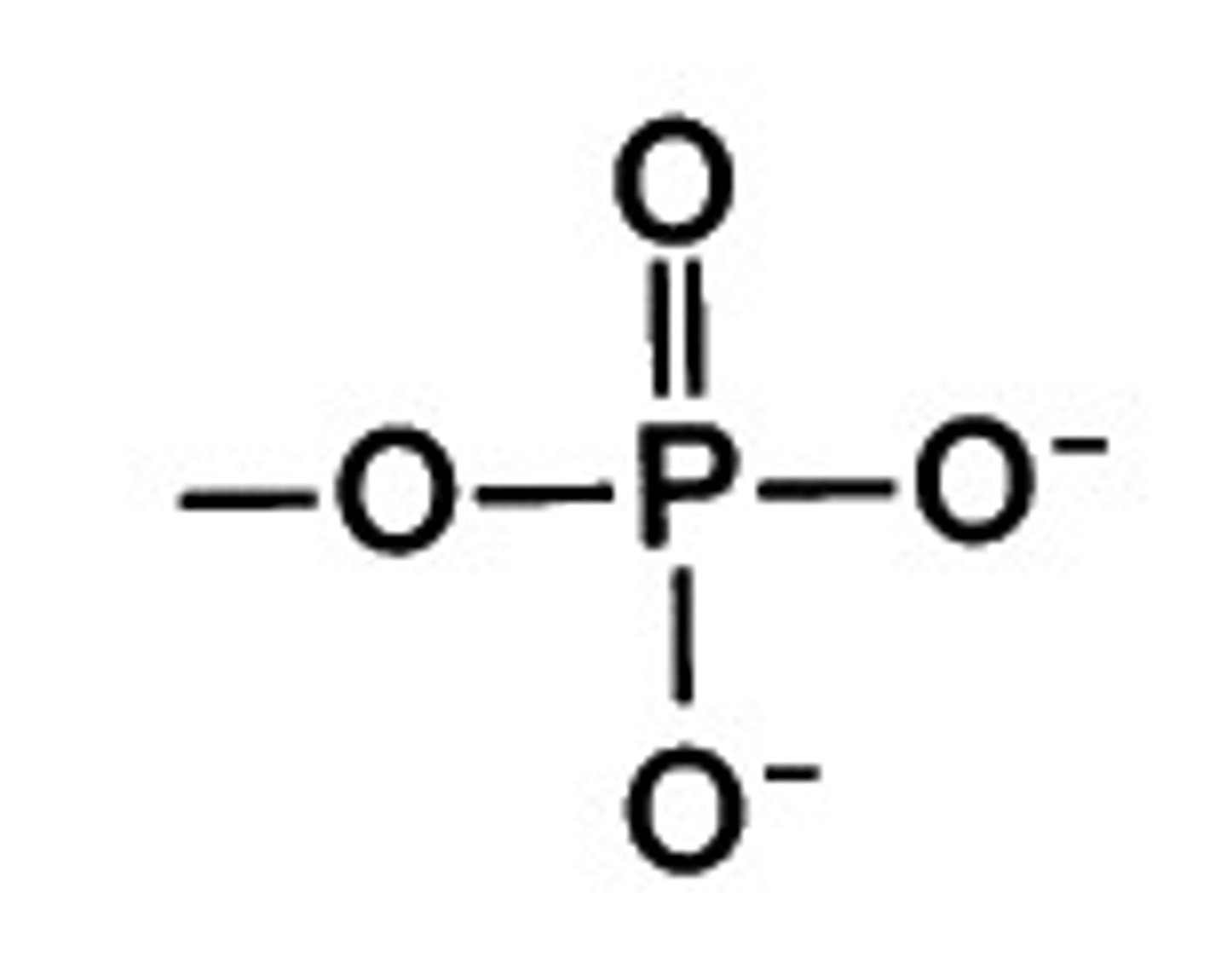
What is the chemical formula for the phosphate functional group?
(PO4)3-
(Note: polar, hydrophilic, acid)
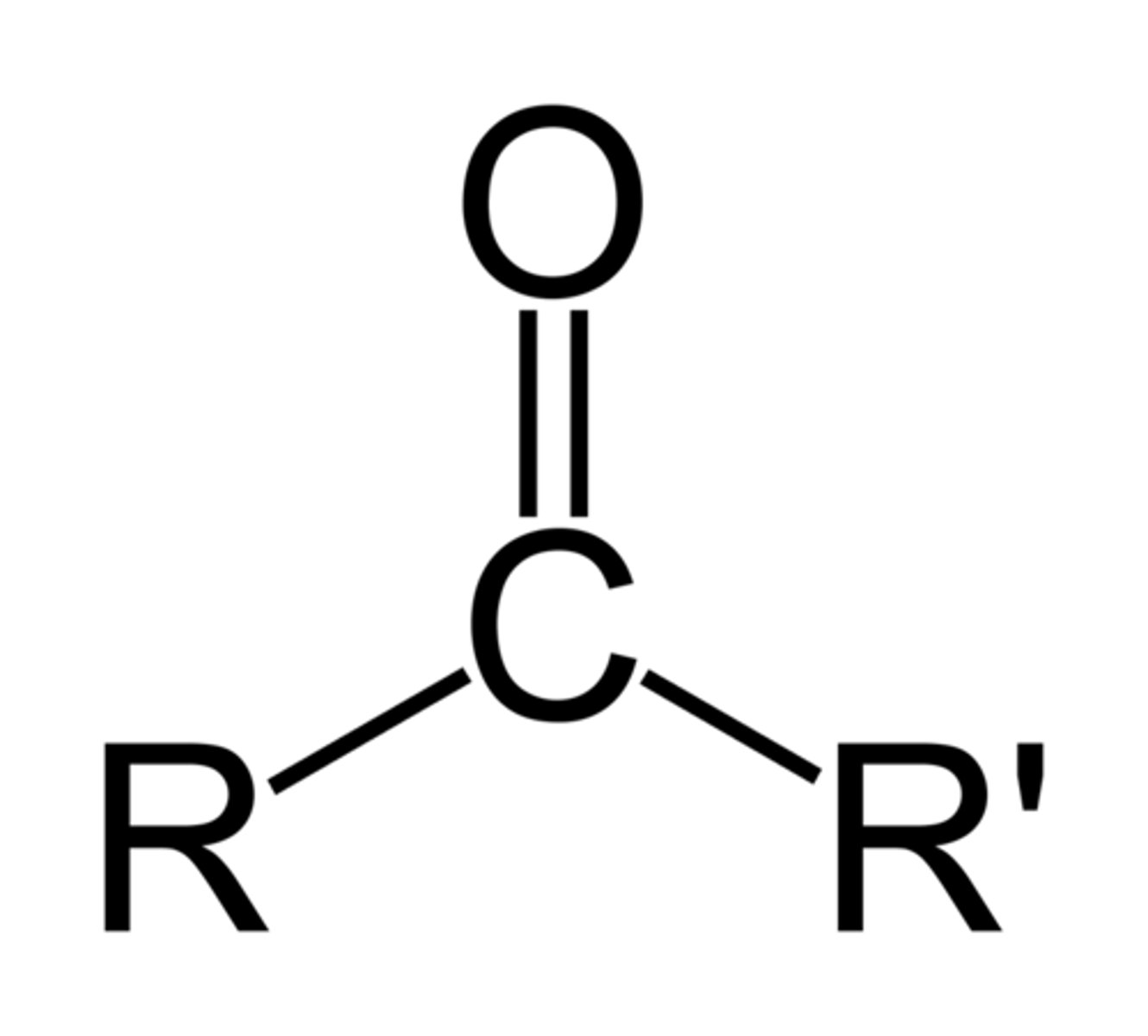
What is the chemical formula for the carbonyl functional group?
C=O
(Note: polar and hydrophilic)
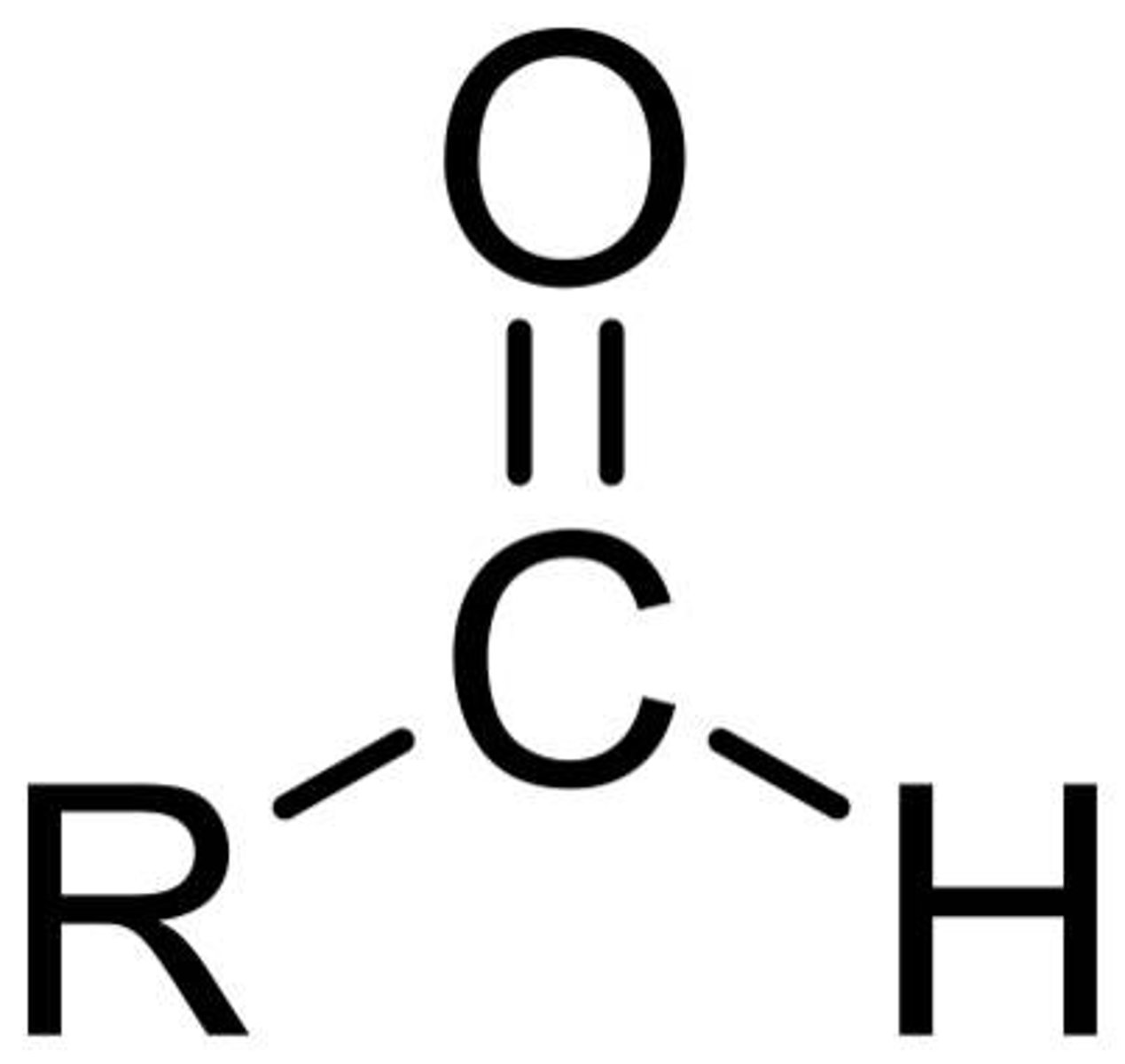
What is the chemical formula for the aldehyde functional group?
H-C=O
What is the chemical formula for the ketone functional group?
R-C=O
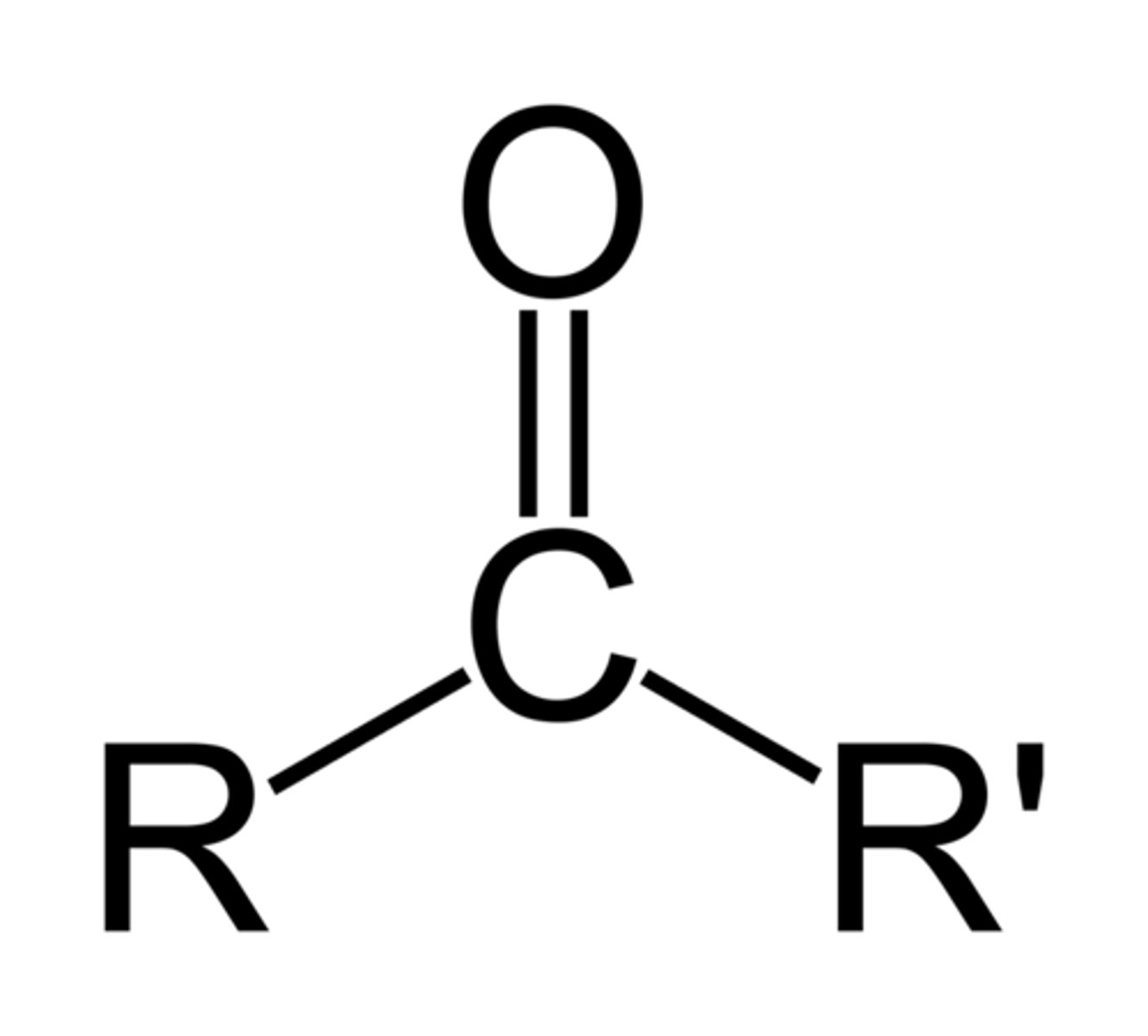
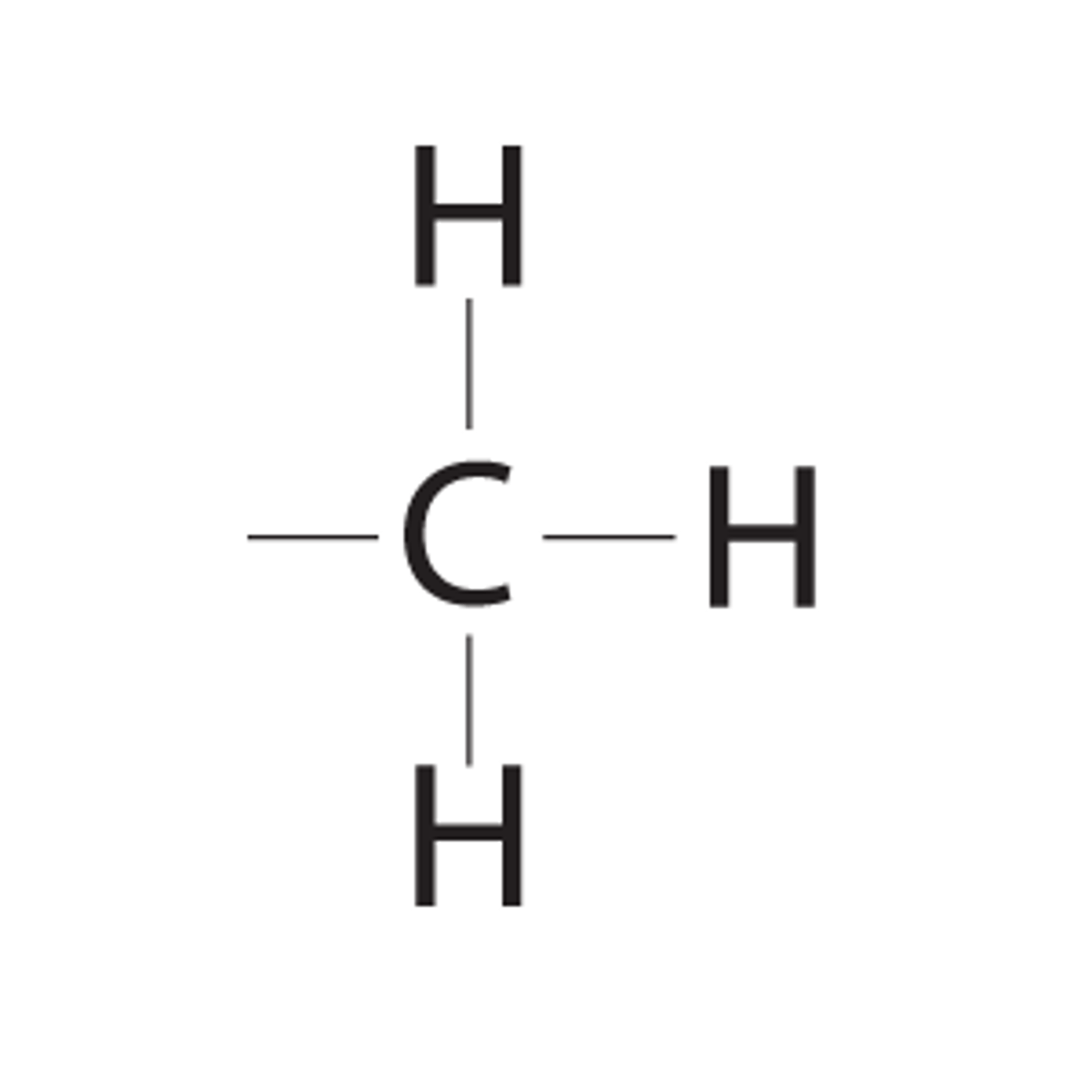
What is the chemical formula for the methyl functional group?
CH3
What is the term for a single sugar molecule?
monosaccharide
(ex: glucose or fructose)
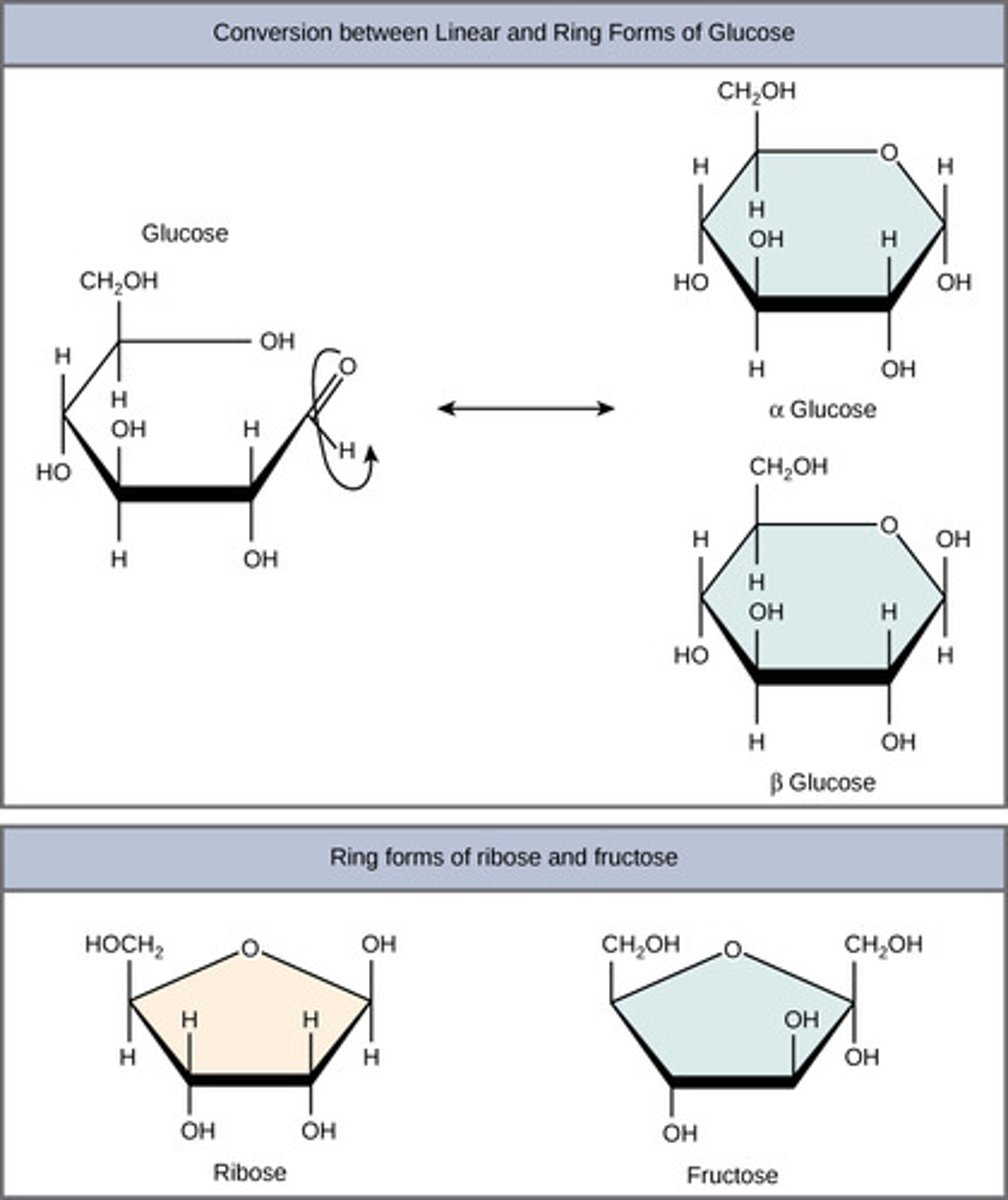
What structural component differentiates a monosaccharide as alpha or beta?
1. anomeric carbon -OH down = alpha
2. anomeric carbon -OH up = beta
(Note: to remember, think alpha means away)
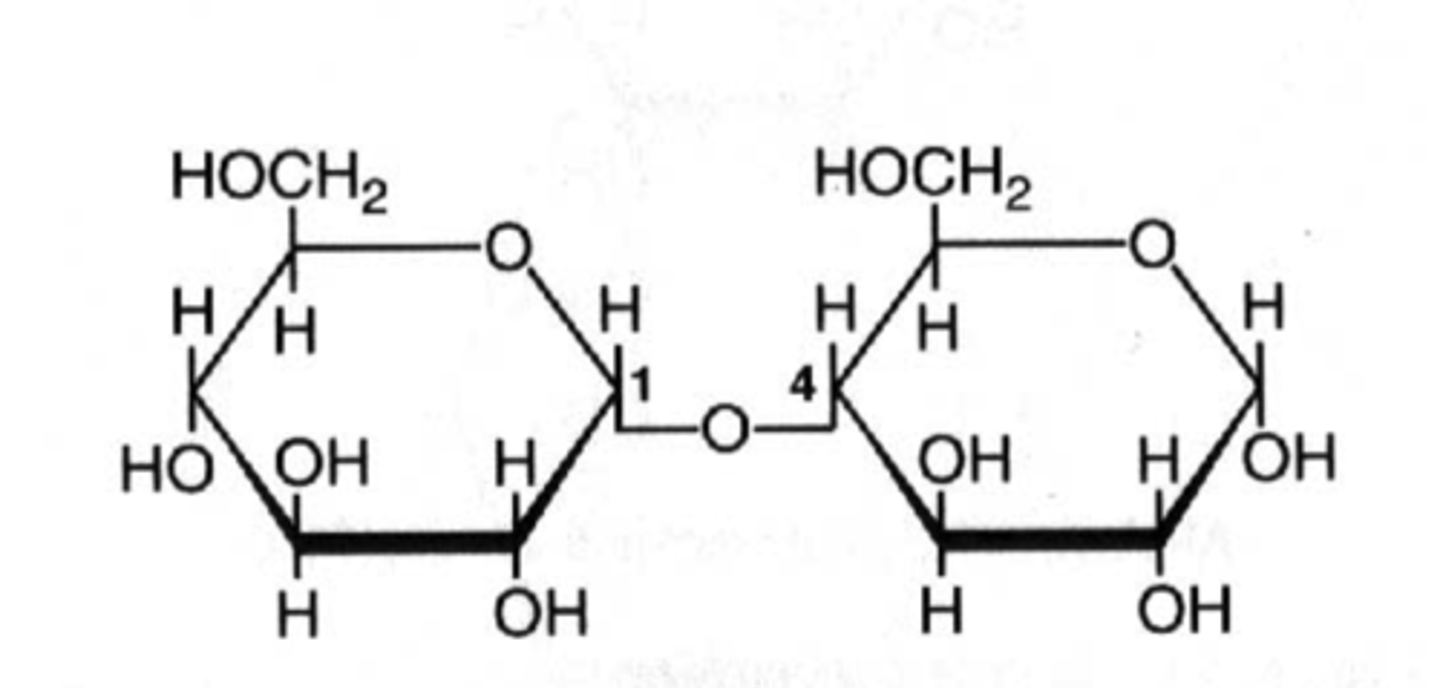
What is a two-sugar molecule joined by a glycosidic linkage?
disaccharide
(Note: sucrose, lactose, and maltose)
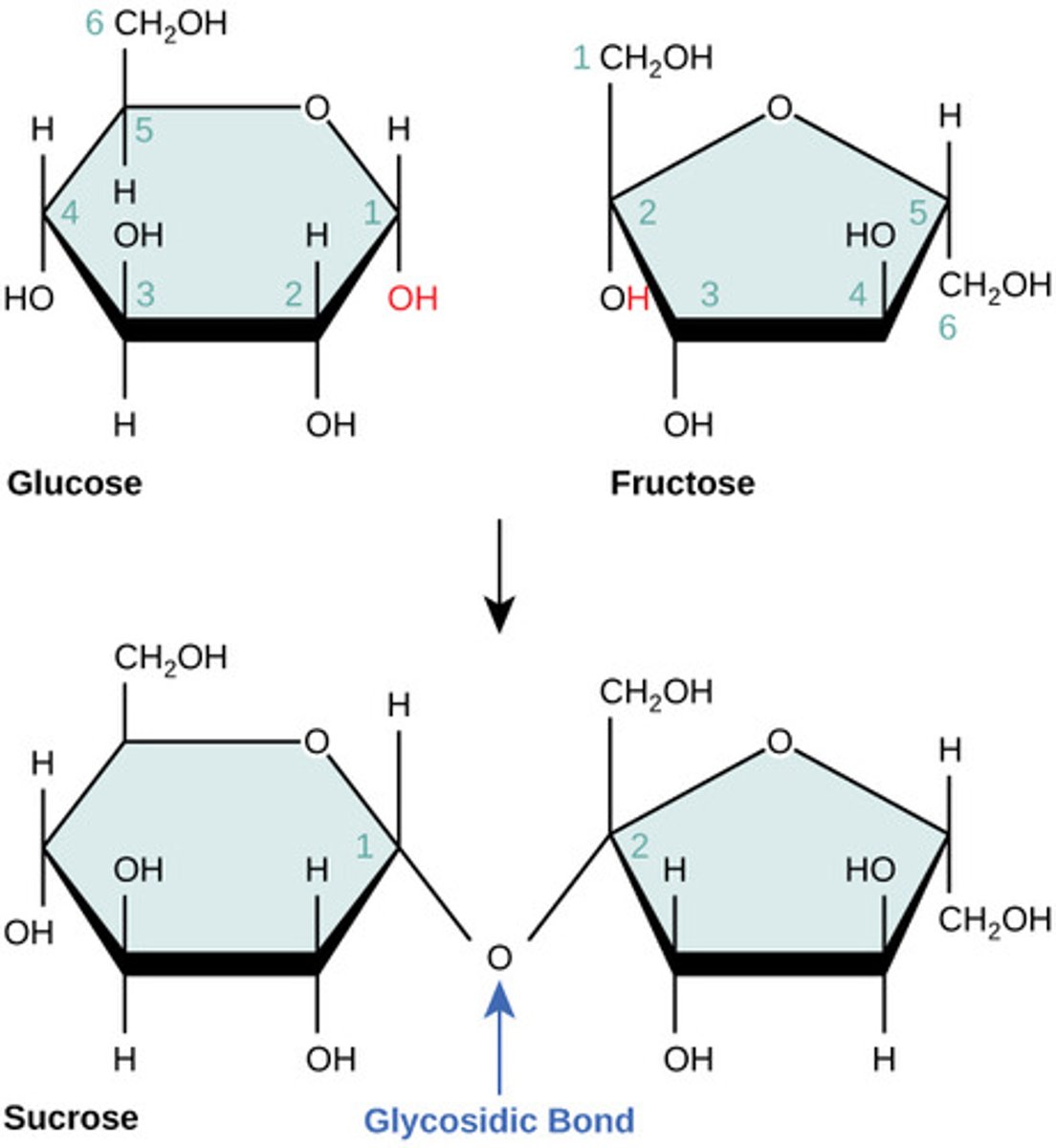
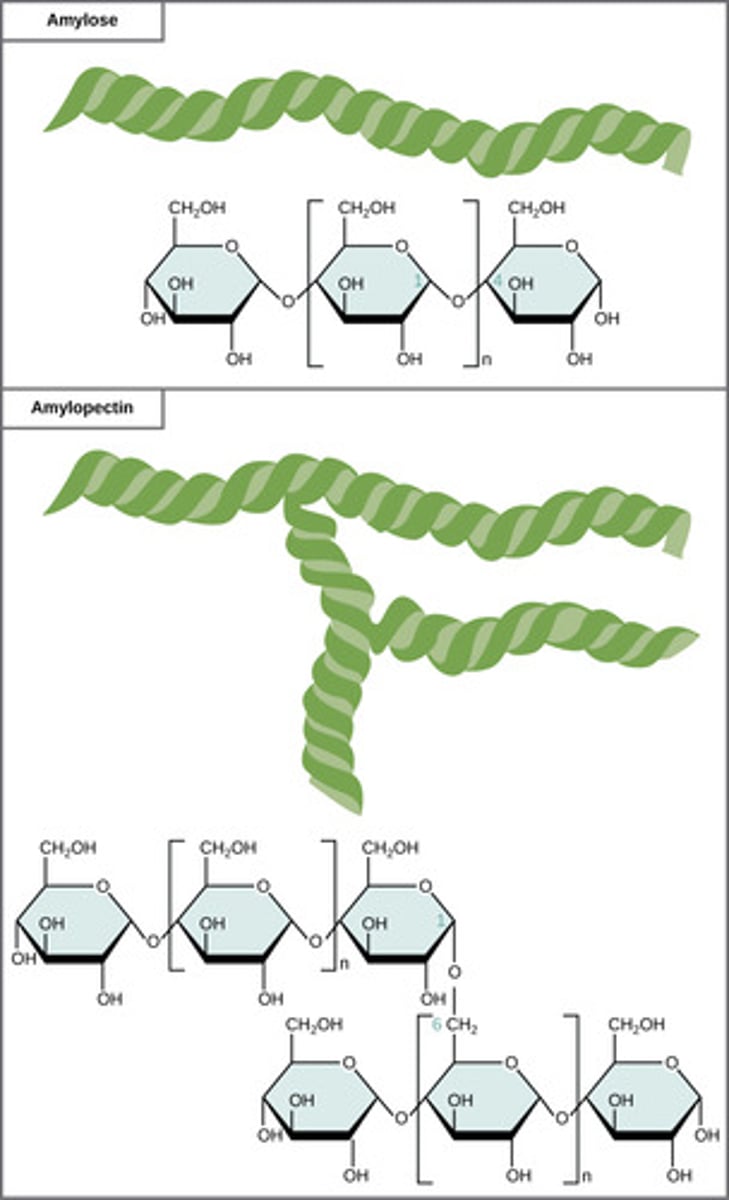
What is a series of connected monosaccharides?
polysaccharide
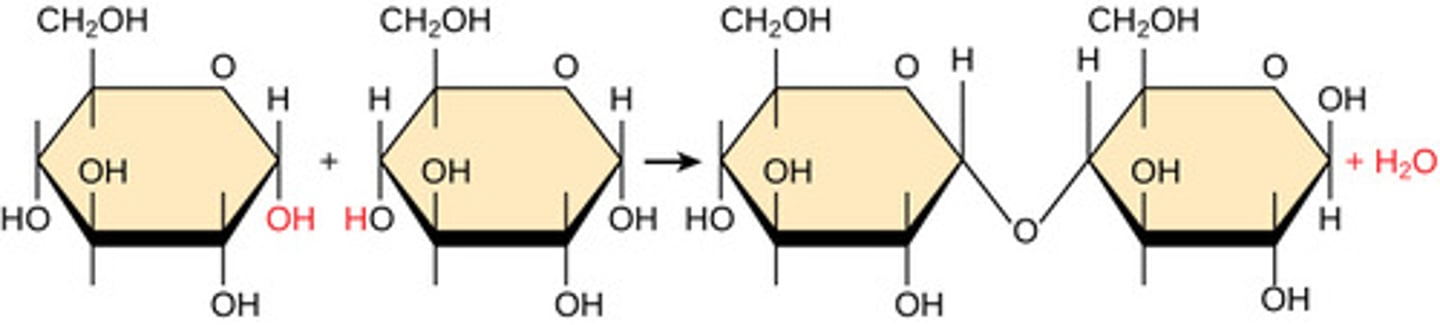
By what mechanism do polymers bonds form?
dehydration synthesis
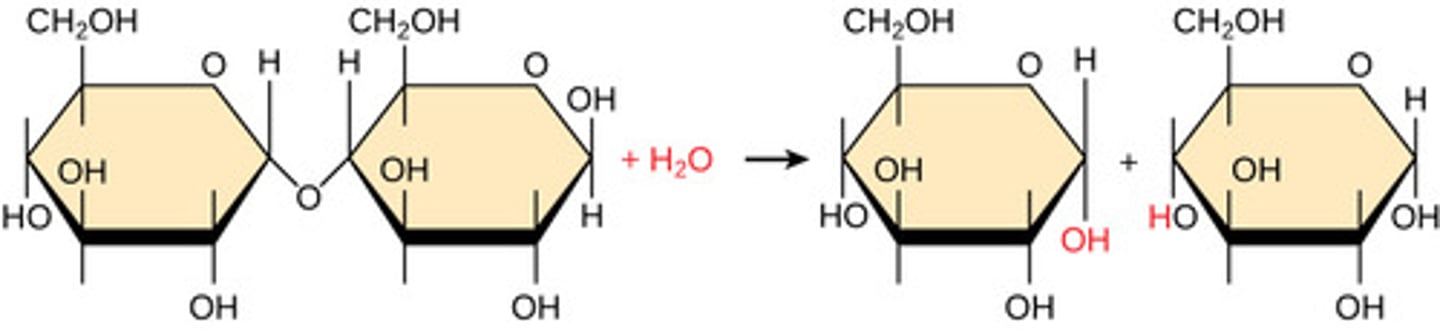
By what mechanism do polymers bonds break?
hydrolysis
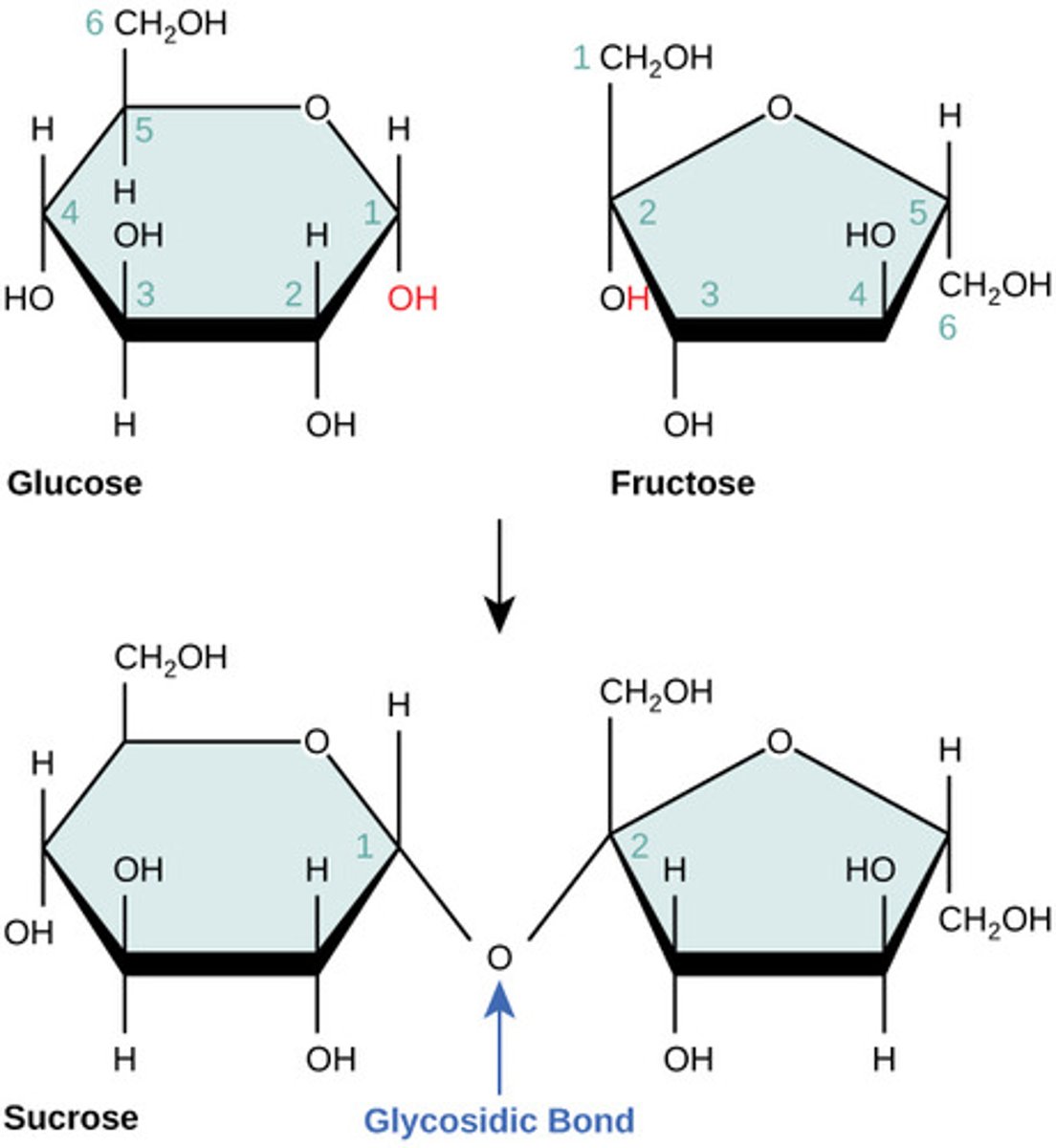
Which monomers compose sucrose?
glucose + fructose
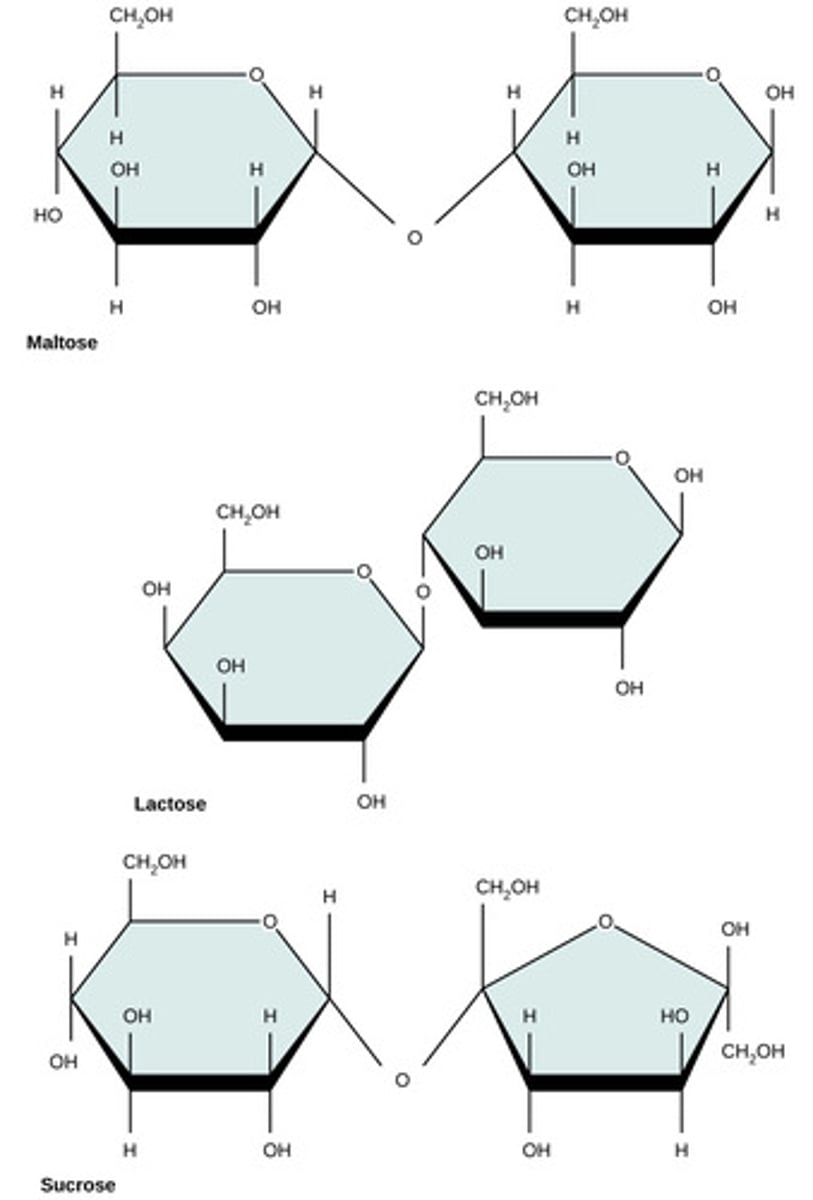
Which monomers compose lactose?
glucose + galactose
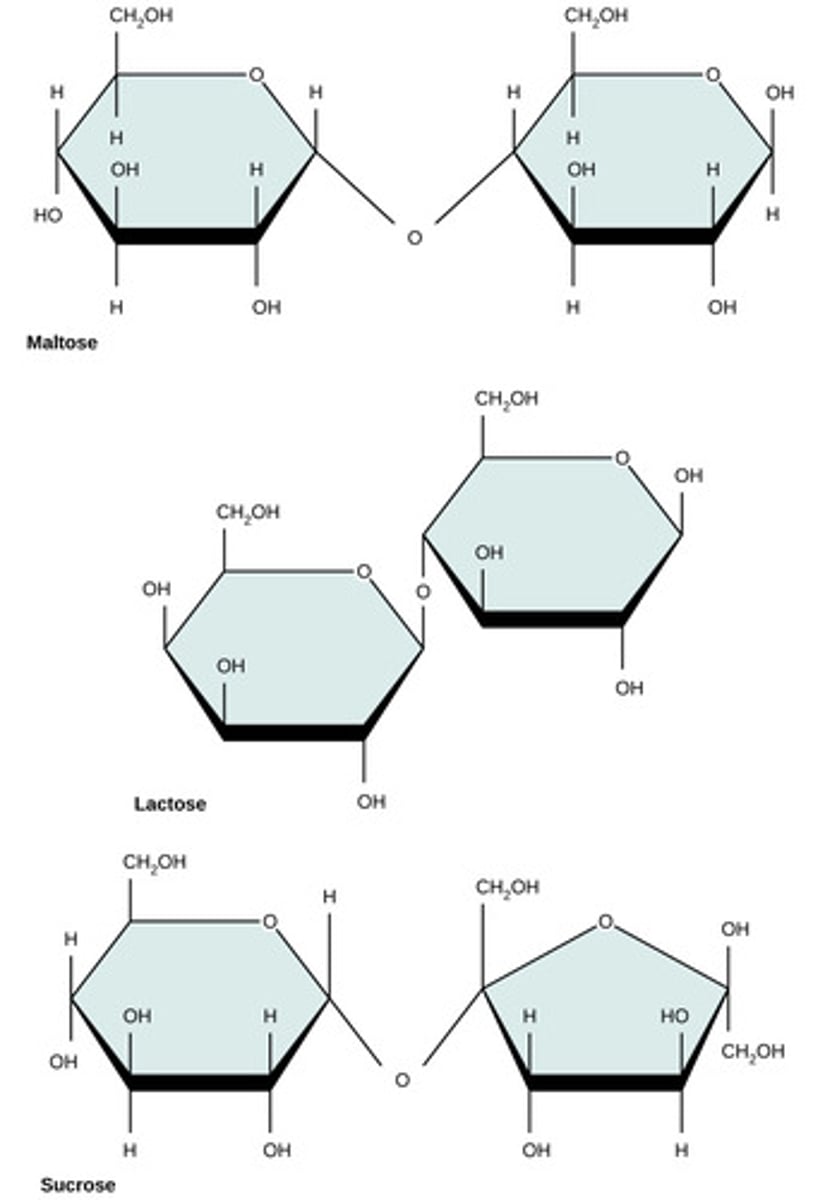
Which monomers compose maltose?
glucose + glucose
What is a polymer of alpha-glucose molecules; store energy in plant cells?
starch
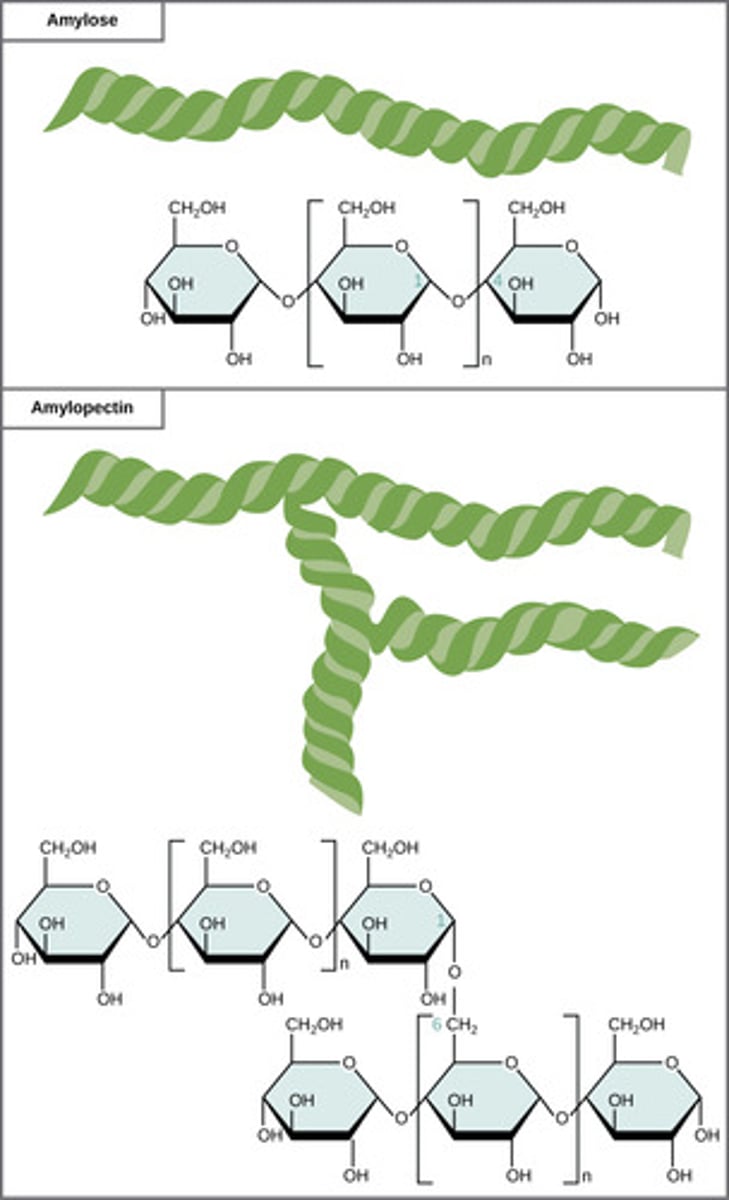
What is a polymer of alpha-glucose molecules; store energy in animal cells?
glycogen
(Note: differ in polymer branching from starch)
What is a polymer of beta-glucose; structural molecules for walls of plant cells and wood
cellulose
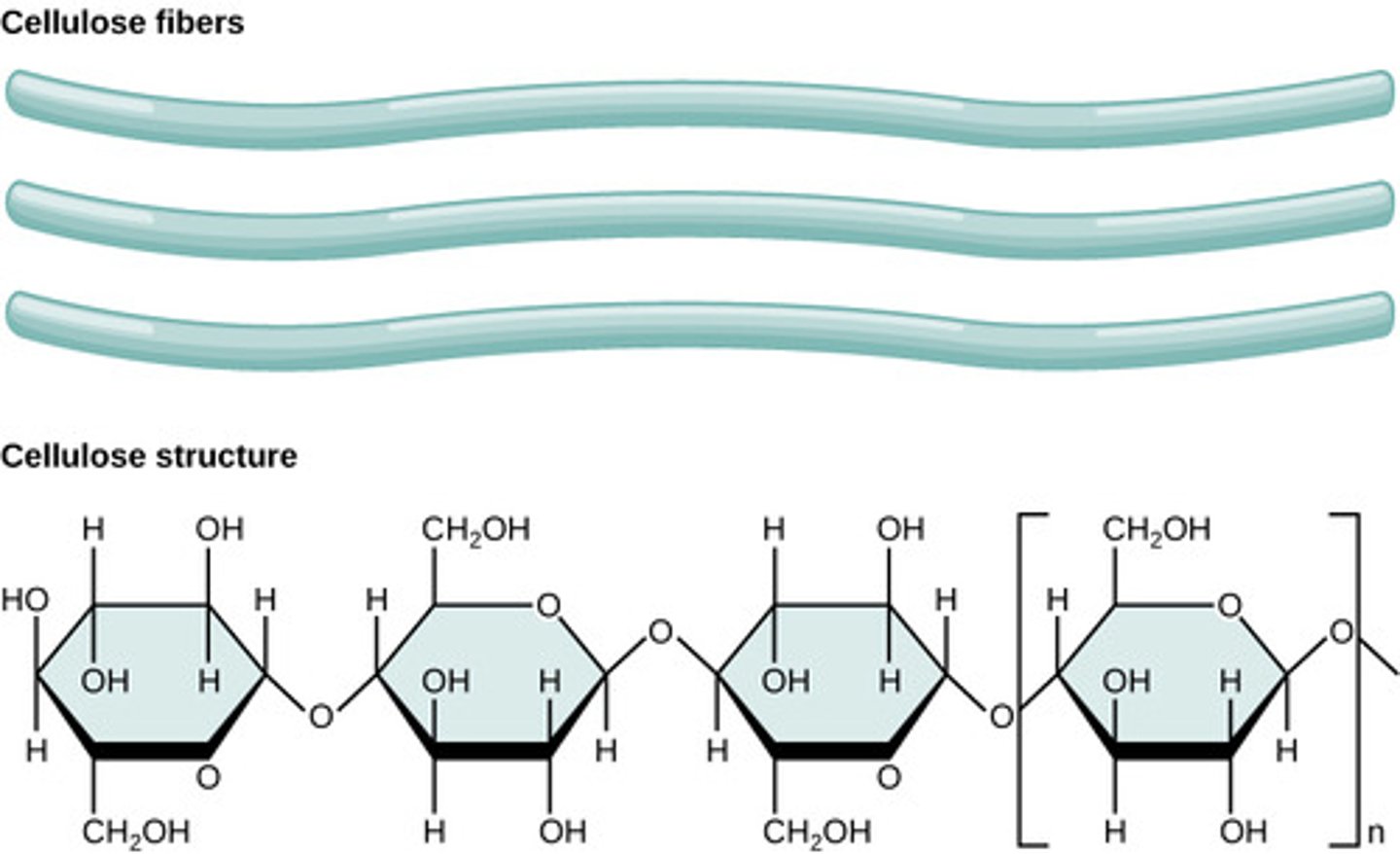
What is a polymer similar to cellulose, except each beta-glucose group has a nitrogen-containing group (n-acetylglucosamine) attached to the ring?
chitin
(Note: structural molecule in insect exoskeletons and fungal cell walls)
What are hydrophobic molecules that function in insulation, energy storage?
lipids

What are lipids consisting of three fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol backbone?
triglycerides
(AKA: triacylglycerols)
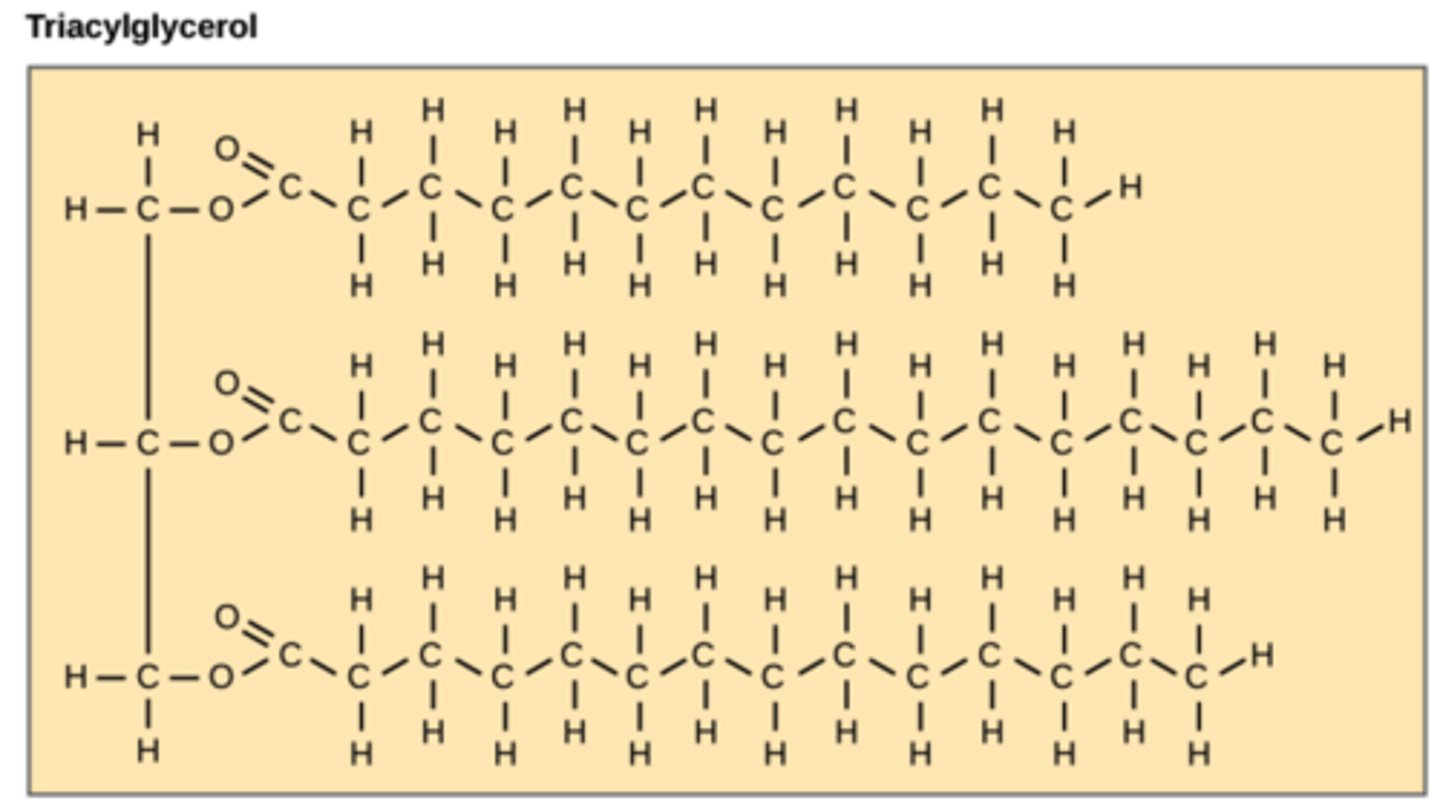
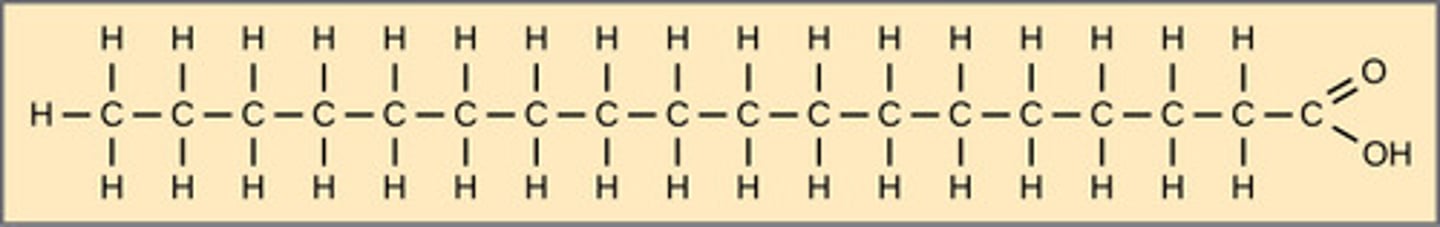
Which triglyceride contains no double bonds and has straight chains?
saturated
(Note: are bad for
health since the straight
chains stack densely and
form fat plaques)
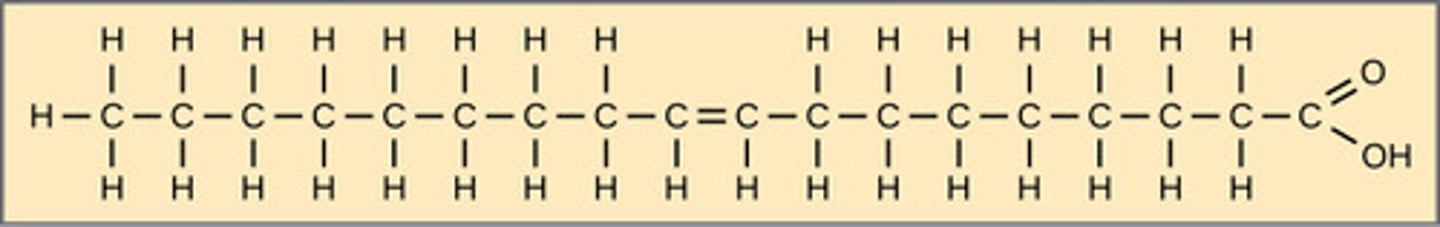
Which triglyceride contains double bonds that cause kinks in chains?
unsaturated
(Note: are better for
health since chains
stack less densely;
can be cis or trans)
What are lipids comprised of two fatty acids and a phosphate group (+R) attached to a glycerol backbone?
phospholipids
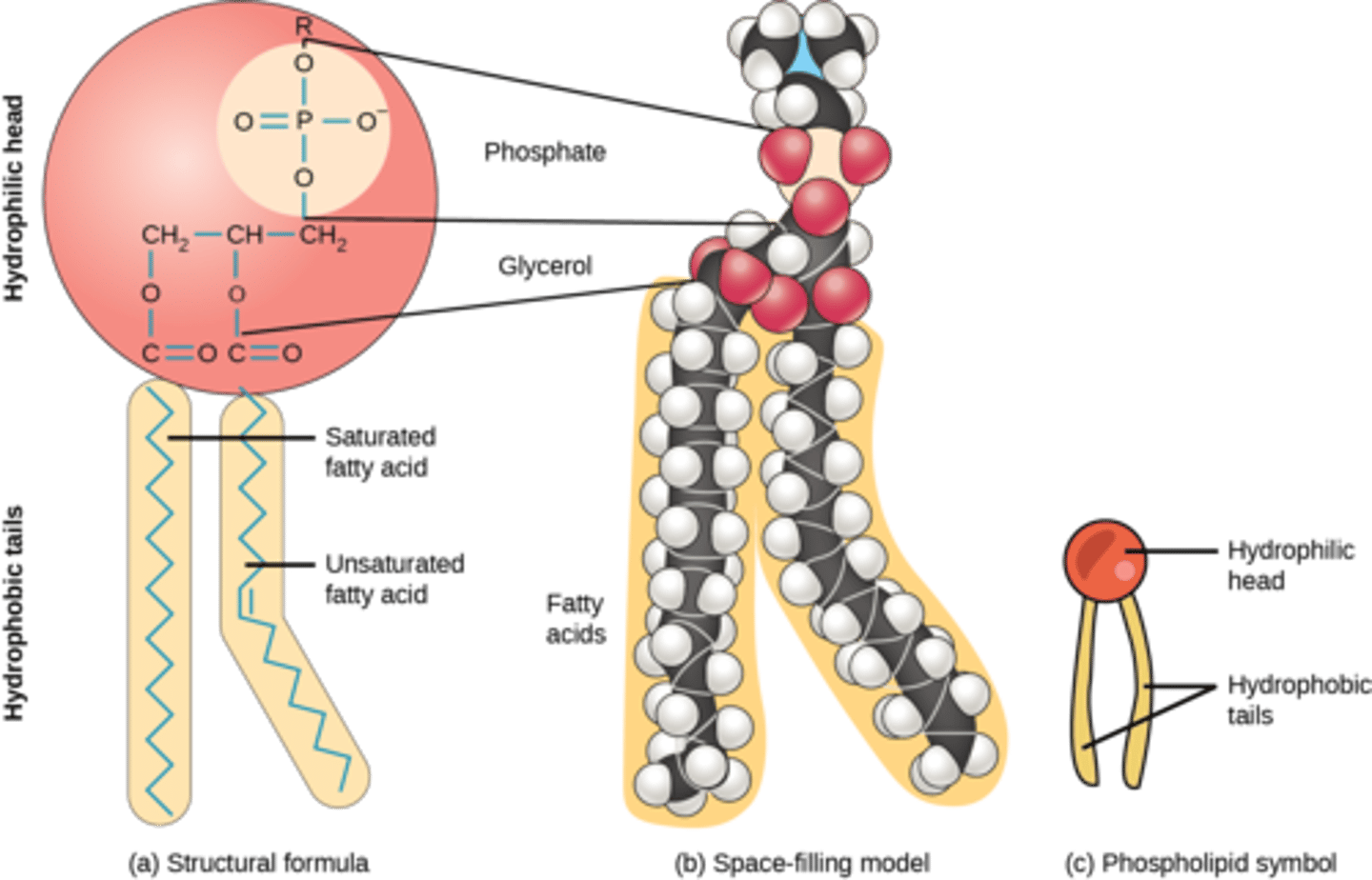
What is the term for a phospholipid exhibiting both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties?
amphipathic
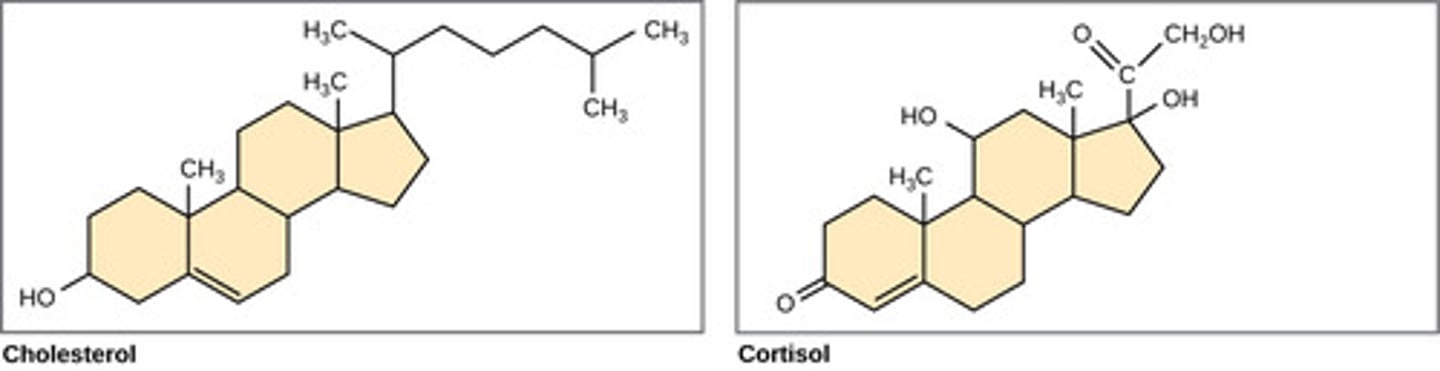
Which lipid derivates contain three 6 membered rings and one 5 membered ring?
steroids
(Note: sex hormones,
cholesterol,
corticosteroids)
Which lipid derivatives are esters of fatty acids and monohydroxylic alcohols, used as protective coating or exoskeletons (lanolin)?
waxes

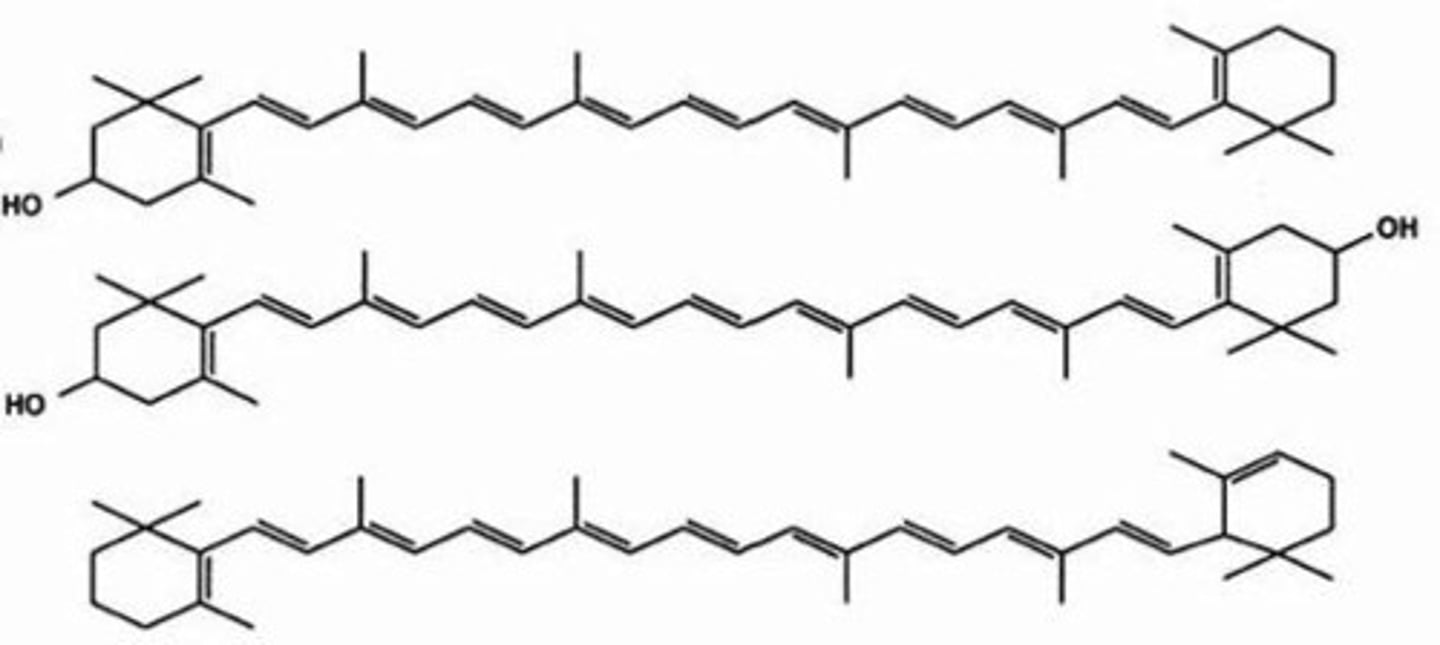
Which lipid derivatives are fatty acid carbon chains with conjugated double bonds and six-membered C-rings at each end?
carotenoids
(Note: includes
pigments which
produce colors in
plants and animals.
Subgroups are
carotenes and xanthophylls)
Which lipid derivatives are a 4 joined pyrrole ring that often complexes with a metal?
porphyrins
(AKA: tetrapyrroles)
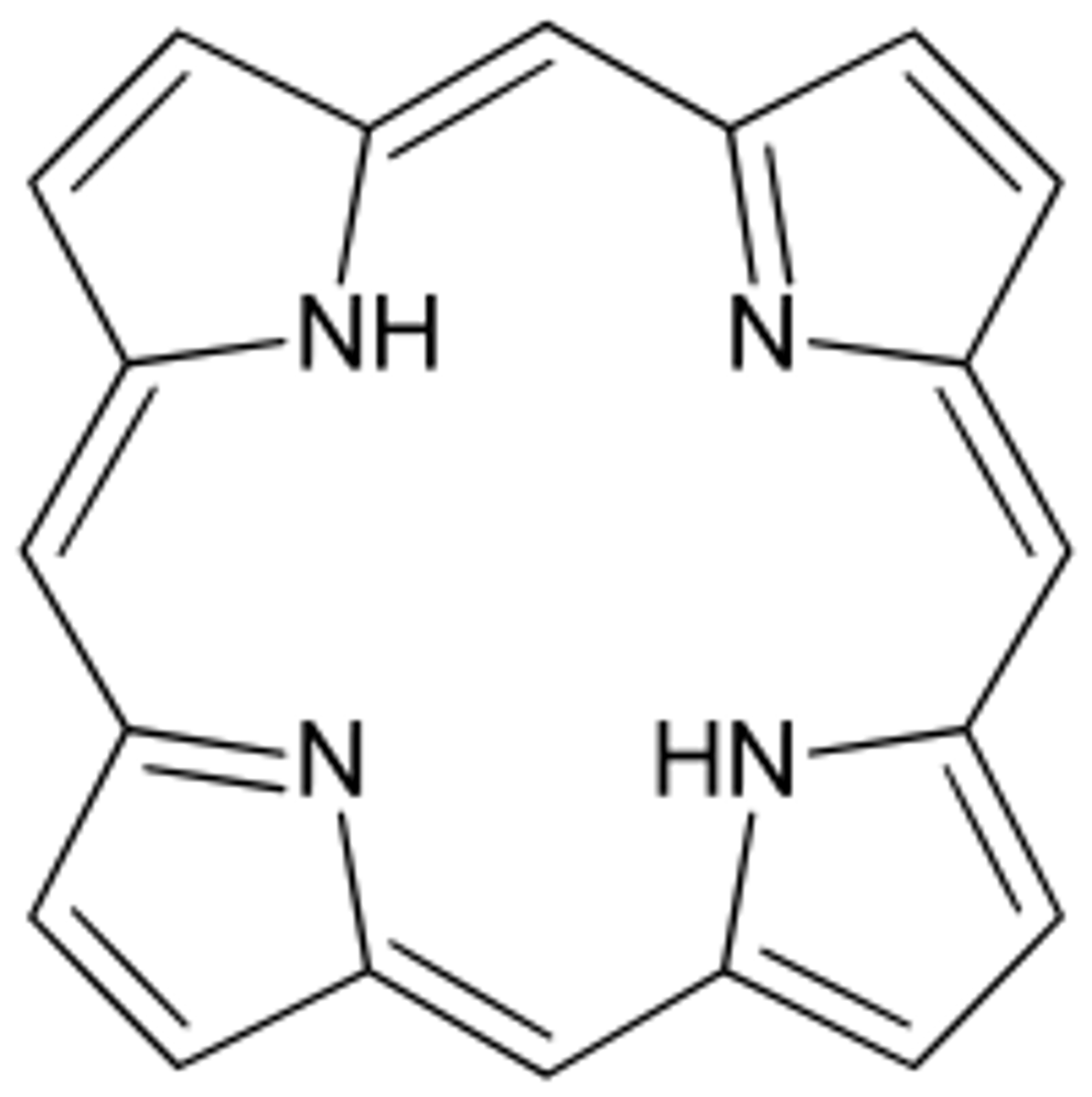
Which lipid derivatives are specialized fat cells?
adipocytes
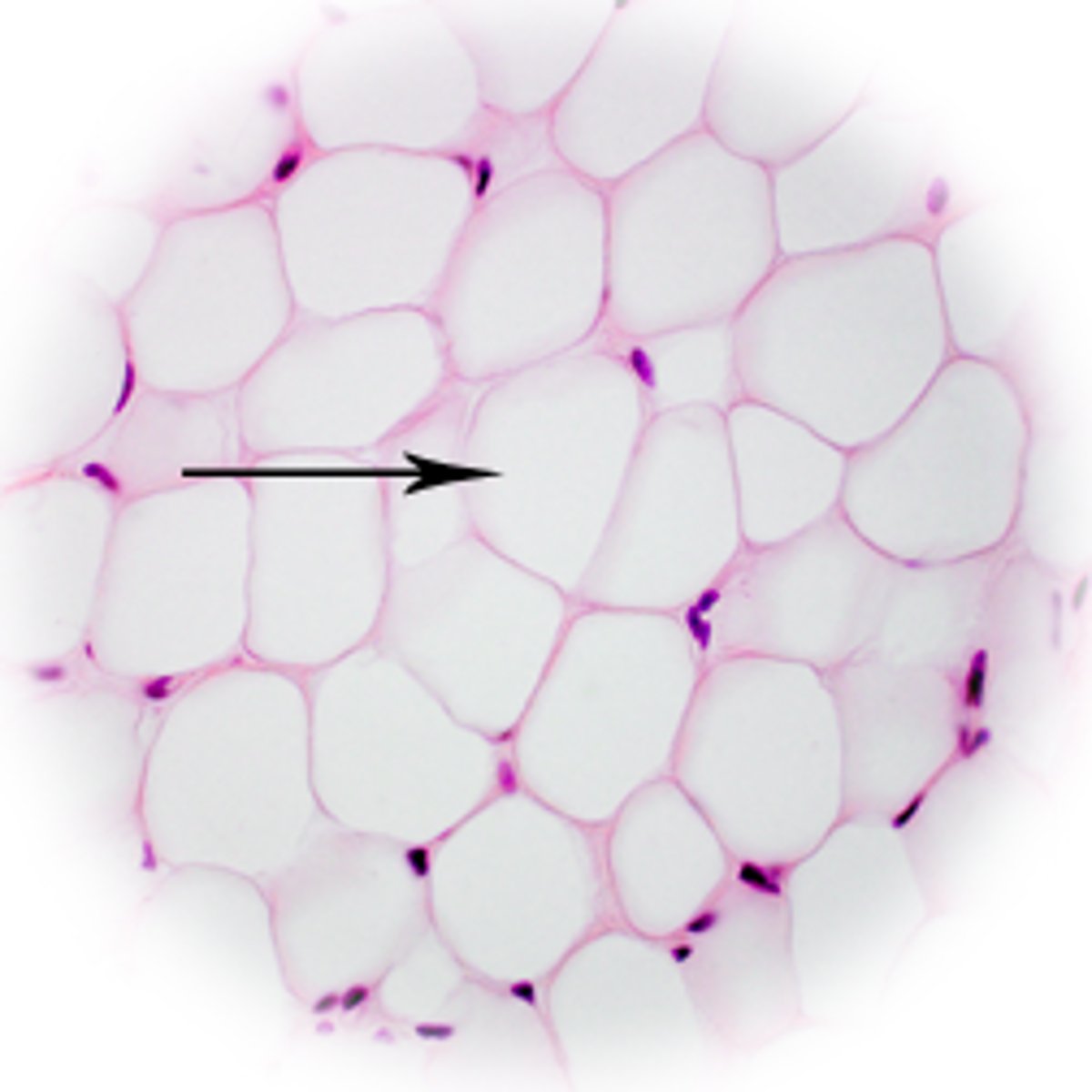
Which adipocyte is composed primarily of triglycerides with a small layer of cytoplasm around it?
white fat cell
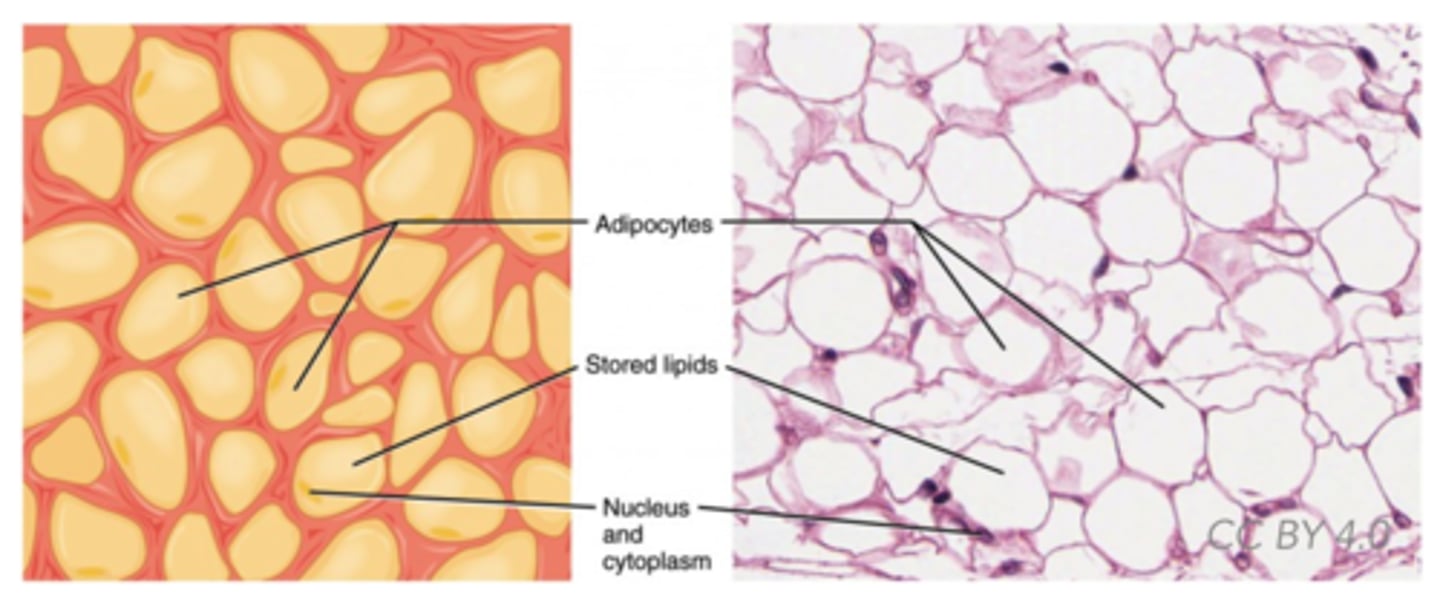
Which adipocyte has considerable cytoplasm, lipid droplets scattered throughout, and lots of mitochondria?
brown fat cell
Which lipid derivatives are similar to phospholipids but have a carbohydrate group instead of a phosphate group?
glycolipids
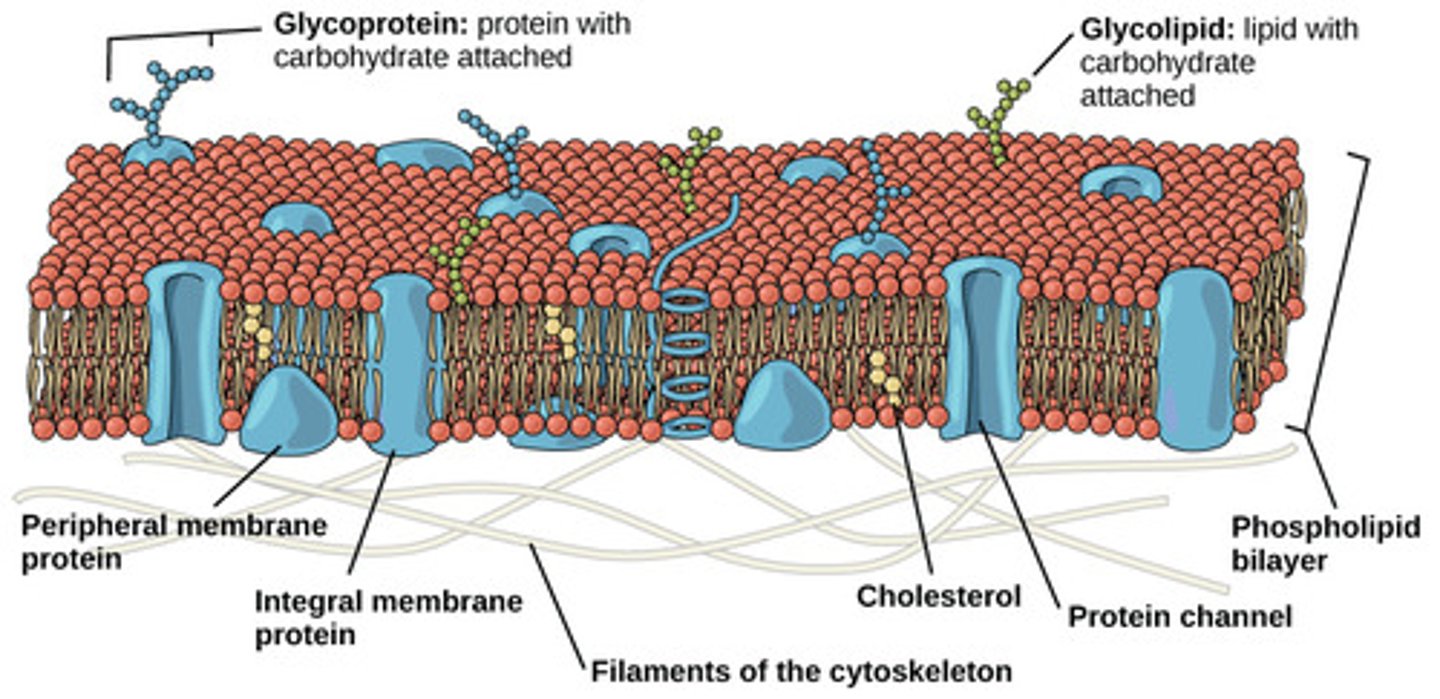
Which lipid derivatives contain lipid cores surrounded by phospholipids and apolipoproteins to transport fats in the blood?
lipoproteins
What membrane components might cells modify to maintain their cell membrane's fluidity?
fatty acids
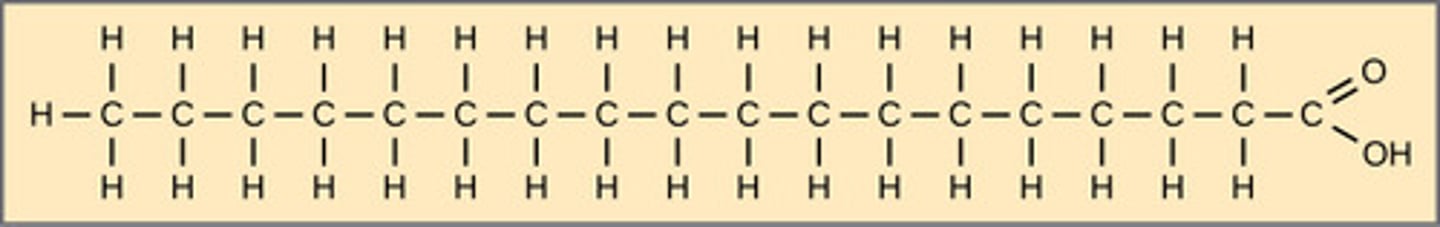
In cold weather, what naturally happens to cell membranes?
become rigid
In warm weather, what naturally happens to cell membranes?
become more fluid
In cold weather, how does a cell compensate to prevent cell membrane rigidity?
incorporate cholesterol
and mono and polyunsaturated
fatty acids into the membrane
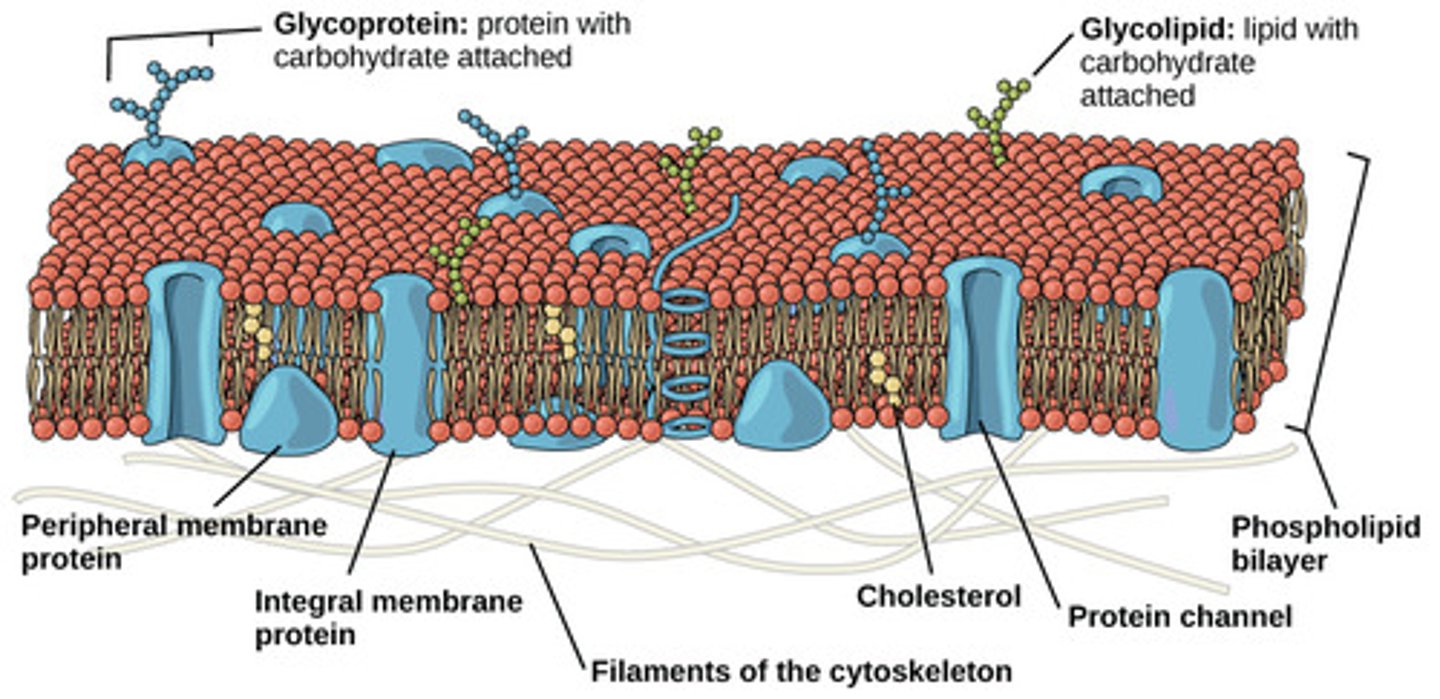
In warm weather, how does a cell compensate to prevent cell membrane collapse?
incorporate cholesterol
into the membrane
(Note: the fatty acid
tails are saturated so
they become straight
and pack tightly, thus
decreasing fluidity)
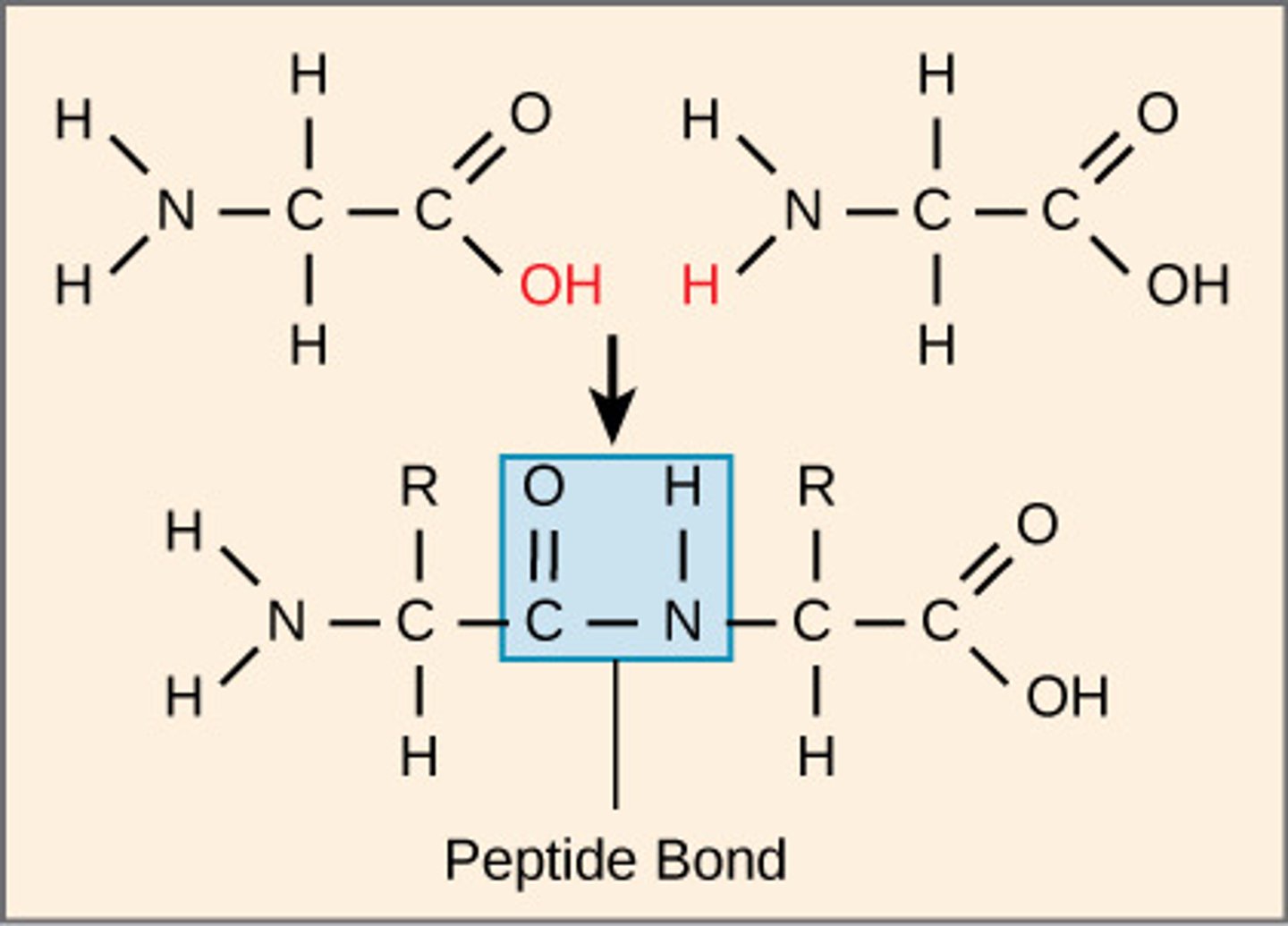
What are polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds?
proteins
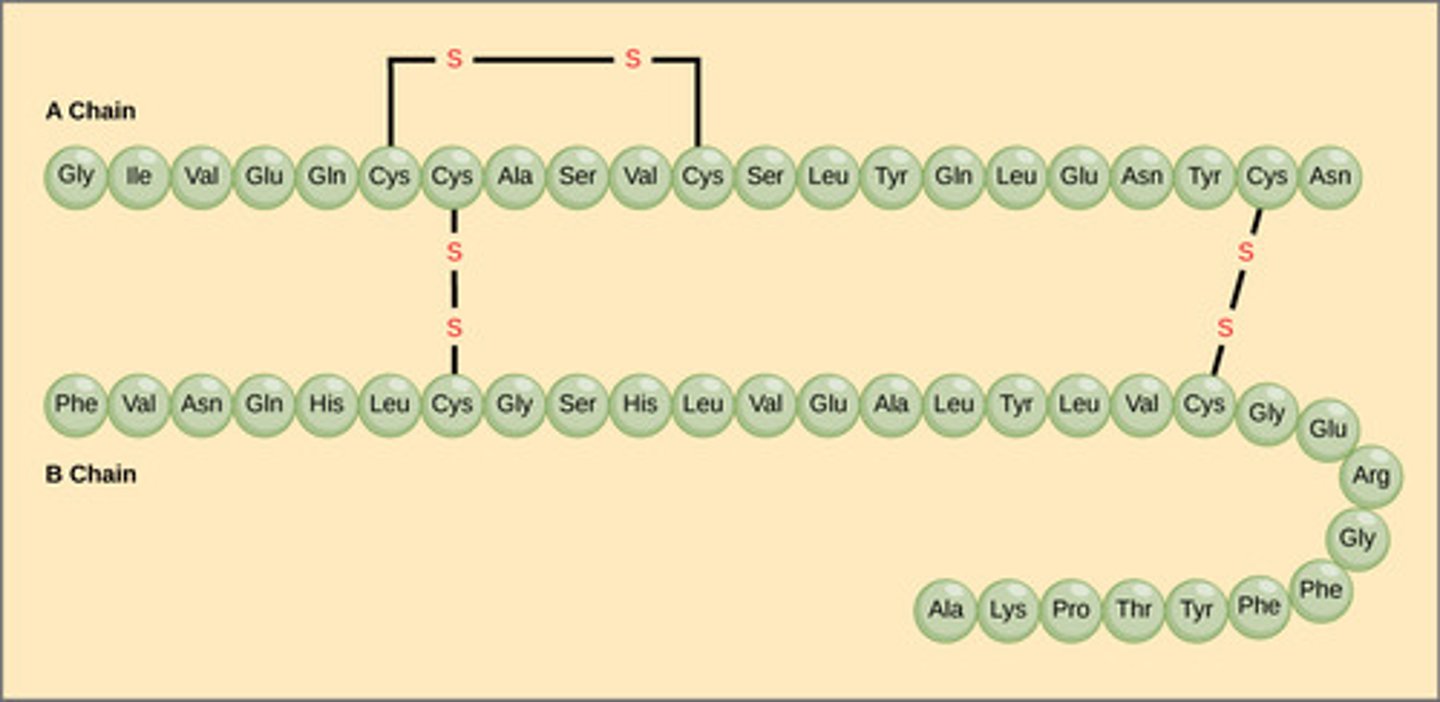
Casein in milk, ovalbumin in egg whites, and zein in corn seeds are examples of which type of proteins?
storage proteins
hemoglobin and cytochromes are examples of which type of proteins?
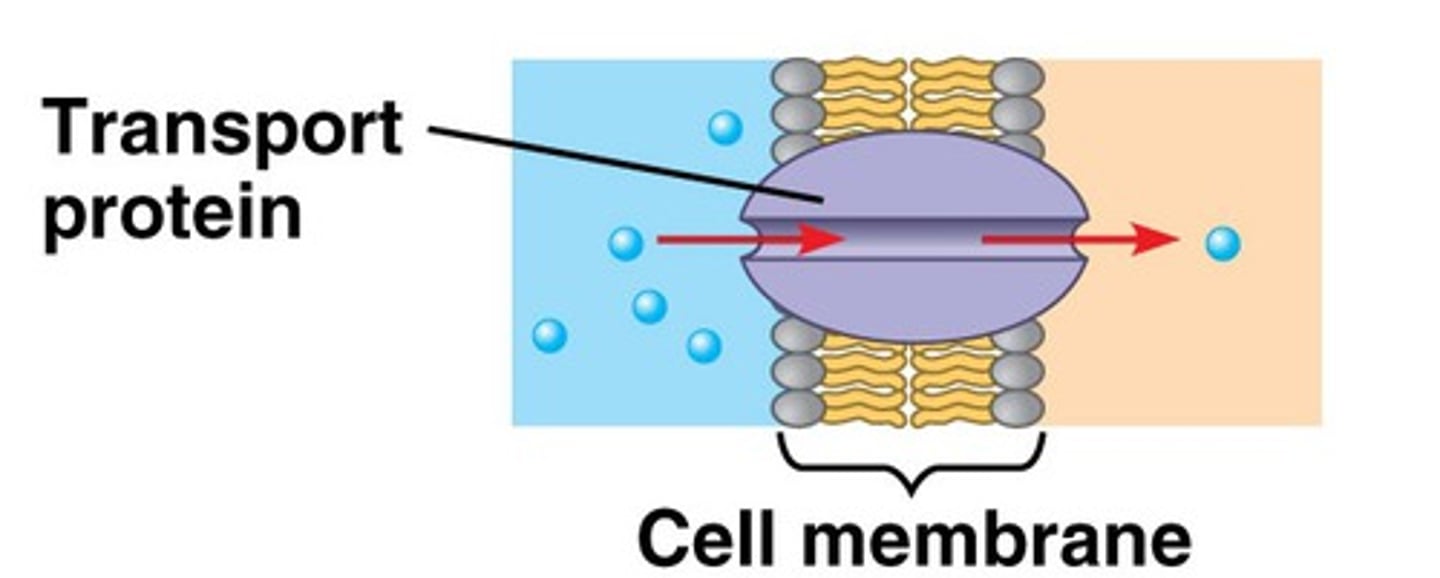
transport proteins
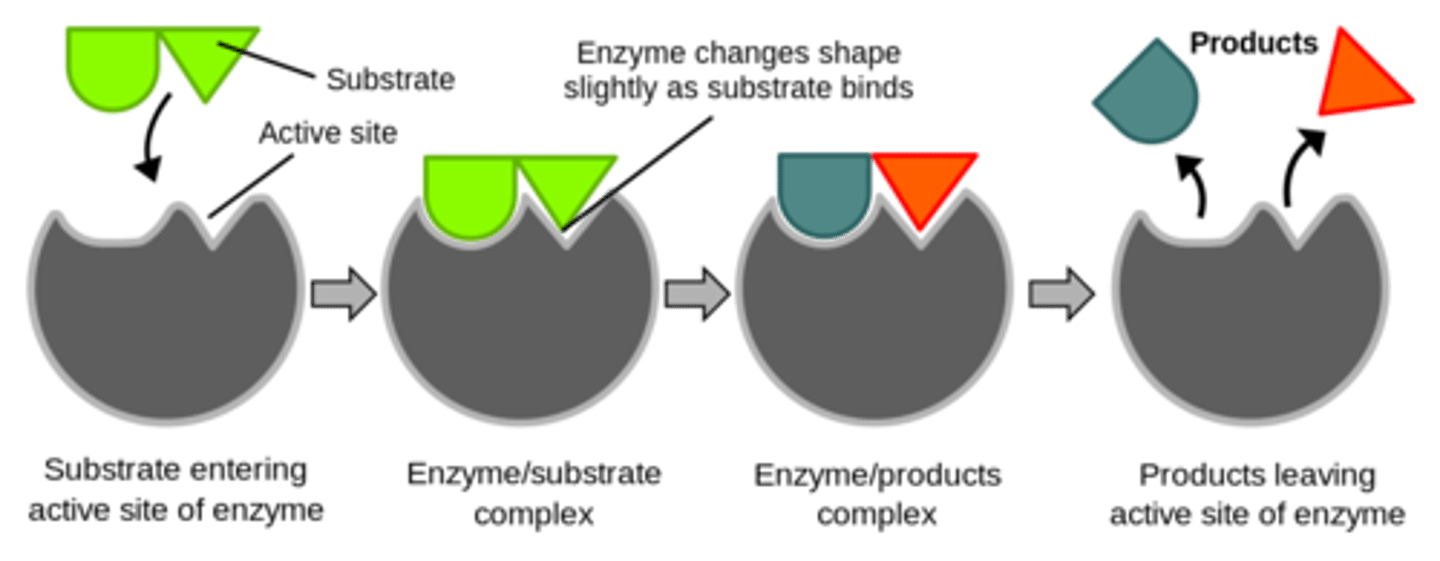
Which proteins catalyze reactions in both forward and reverse directions based on the substrate concentration?
enzymes
(Note: almost all
are proteins, but
RNA can also act
as an enzyme)
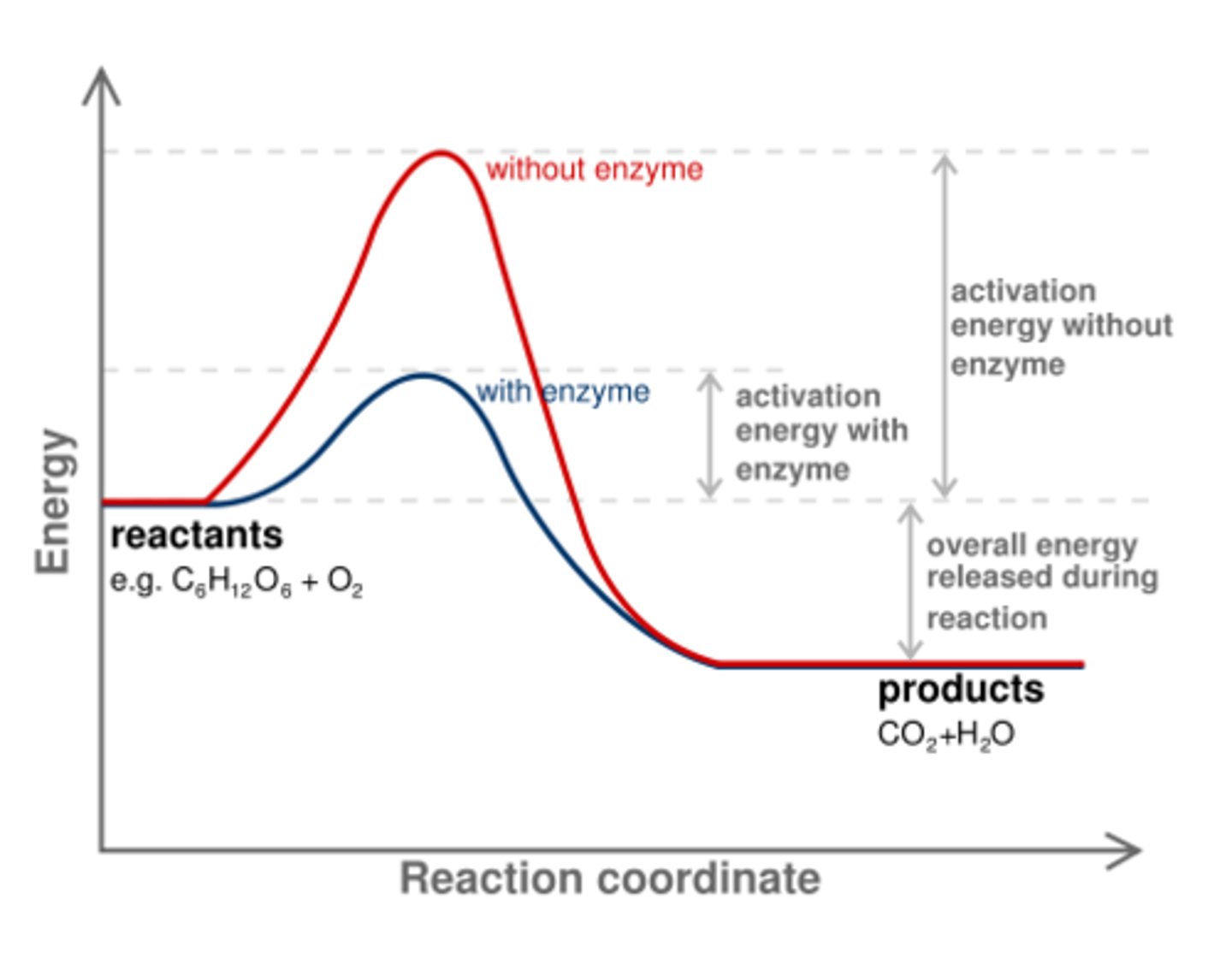
How does an enzyme change the spontaneity of a reaction?
they do not
(Note: they only change
the rate at which the
reaction occurs,
not it's equilibrium point)
By what factors is enzyme efficiency determined?
temperature and pH
Amylase catalyzes the breaking of which bonds in starch?
alpha-glycosidic
What are non-protein molecules that assist enzymes?
cofactors
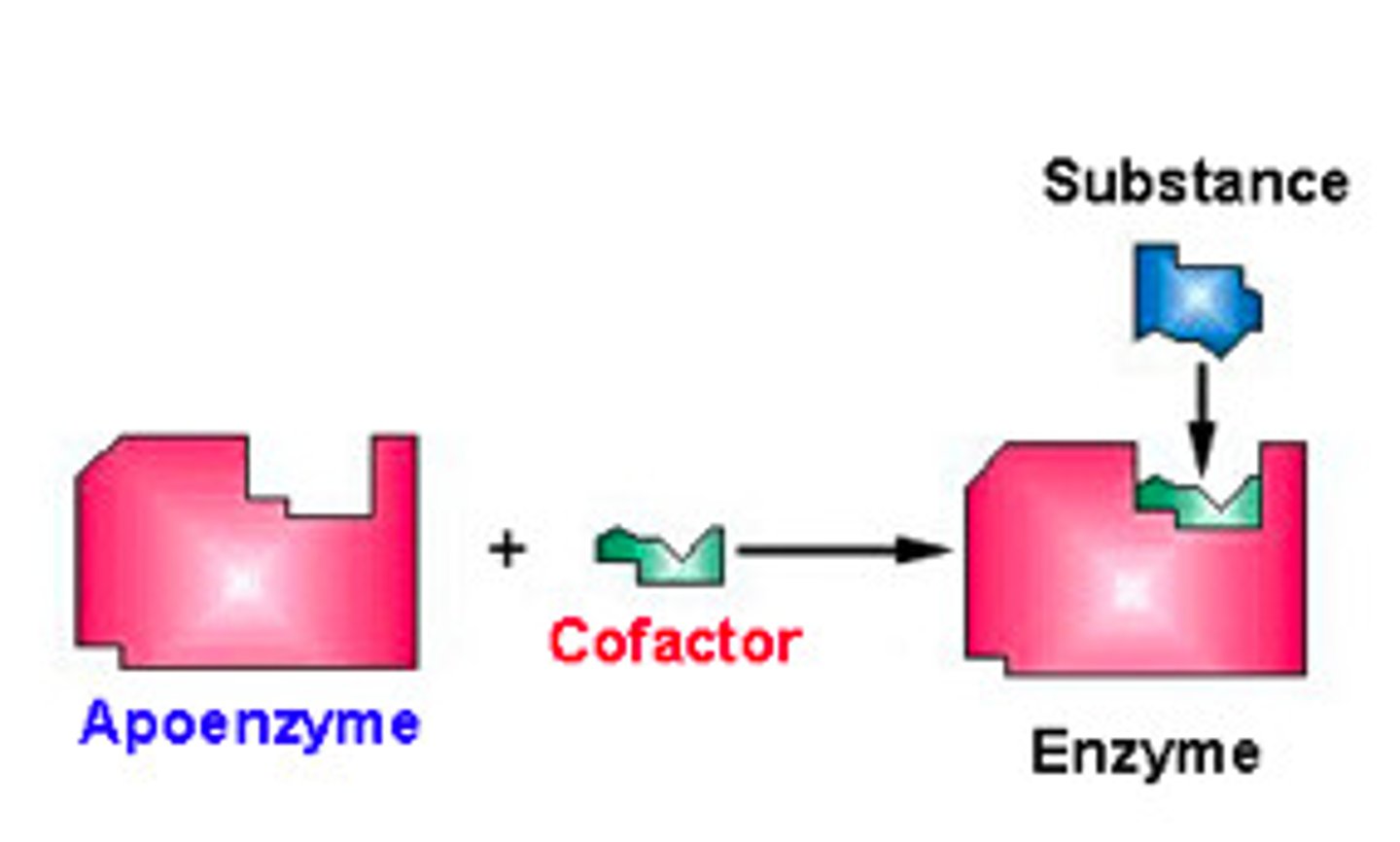
What is an enzyme called that is not combined with its cofactor?
apoenzyme/apoprotein
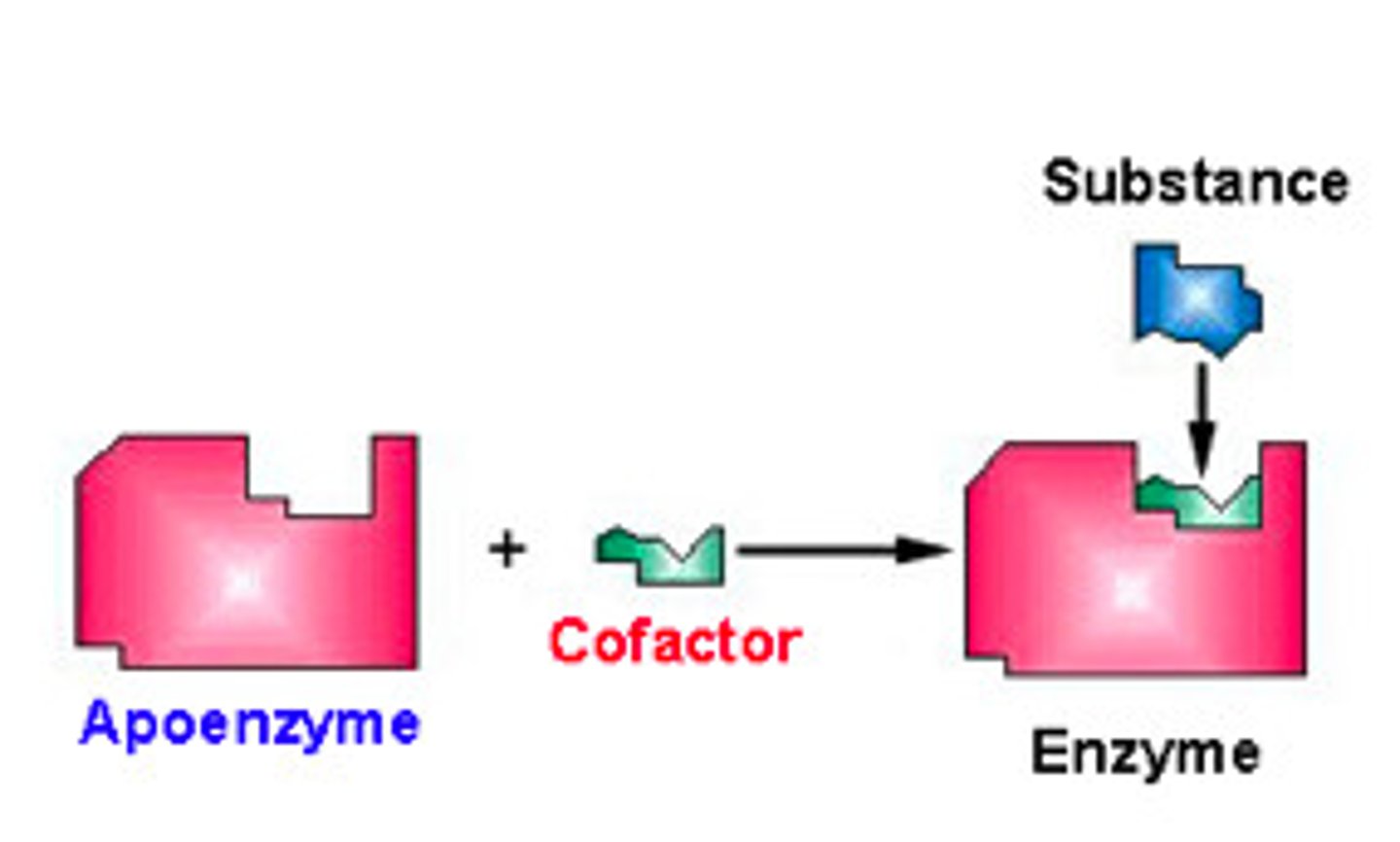
What is an enzyme called that is combined with its cofactor?
holoenzyme
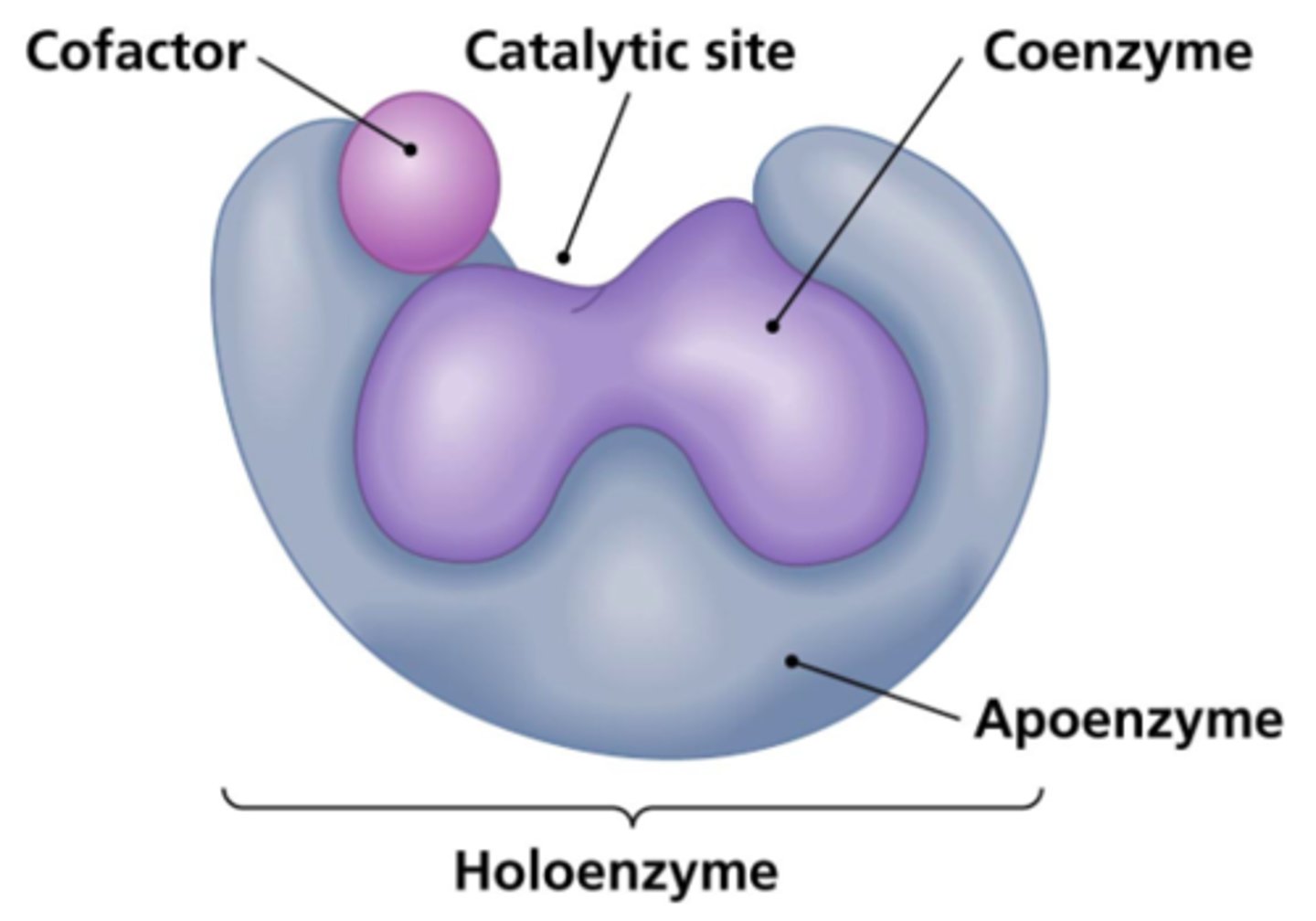
What is a cofactor that is organic?
coenzyme
(ex: vitamins)
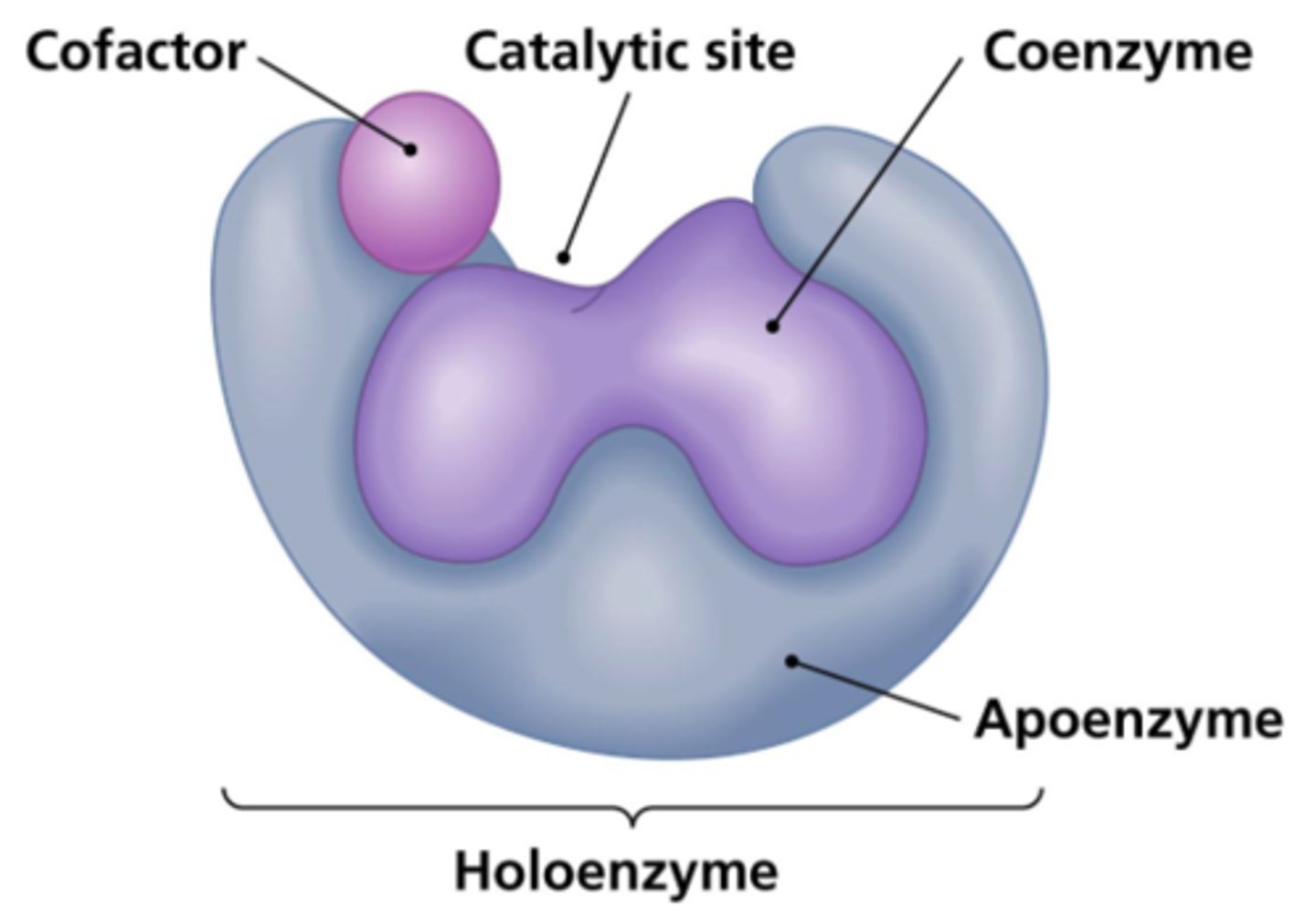
What is a cofactor that is covalently bound to its enzyme?
prosthetic group
What is the classification of proteins that are formed entirely of amino acids?
simple
What is the classification of functional proteins that act as carriers or enzymes?
albumins and globulins
What is the classification of fibrous proteins that have
structural function (ex: collagen)?
scleroproteins
What is the classification of a simple protein and a non-
protein?
conjugated
What is the classification of a protein bound to a lipid?
lipoprotein
What is the classification of a protein bound to a
carbohydrate?
mucoprotein
What is the classification of a protein bound to a pigmented molecule?
chromoprotein
What is the classification of a protein complexed
around a metal ion?
metalloprotein
What is the classification of a protein that contains histone or
protamine, bound to nucleic acid?
nucleoprotein
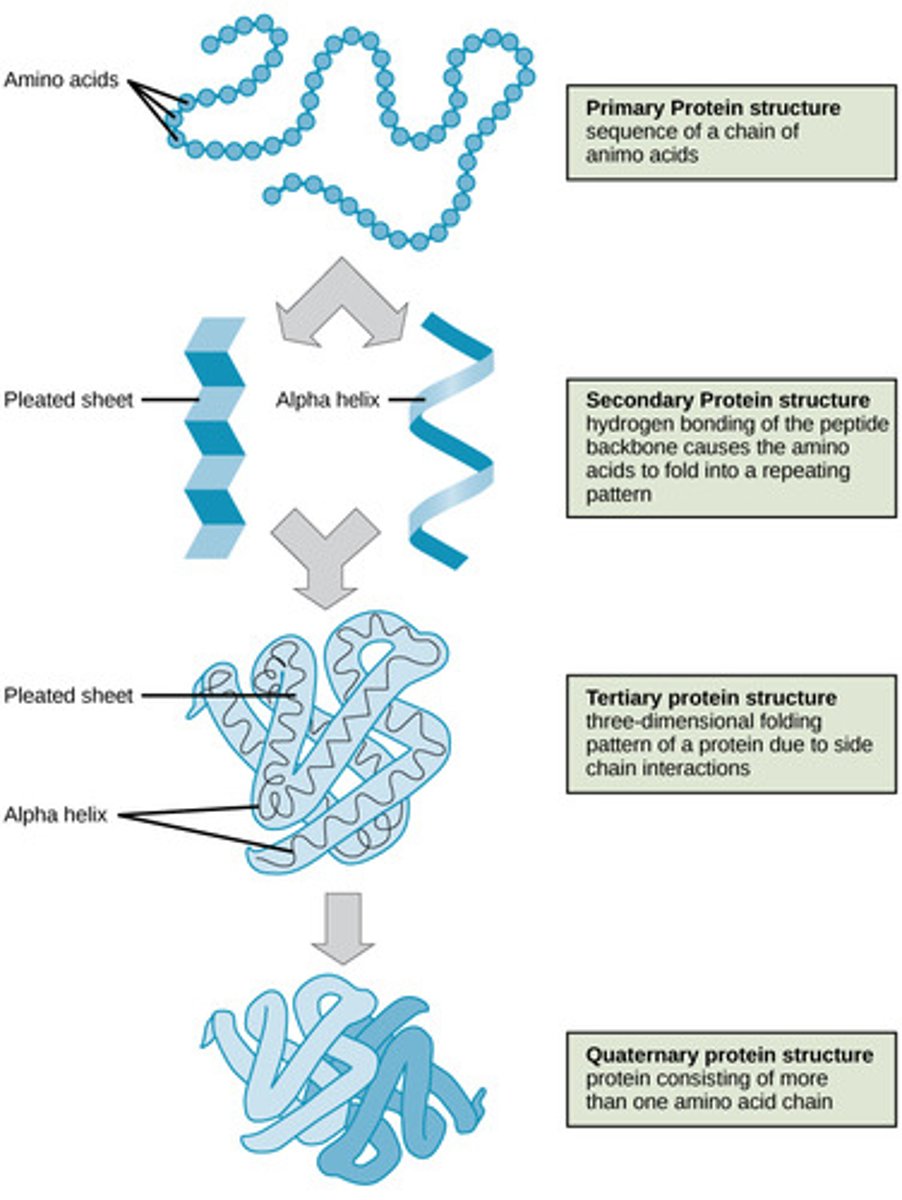
Which protein structure involves the sequence of amino acids connected by peptide bonds?
primary
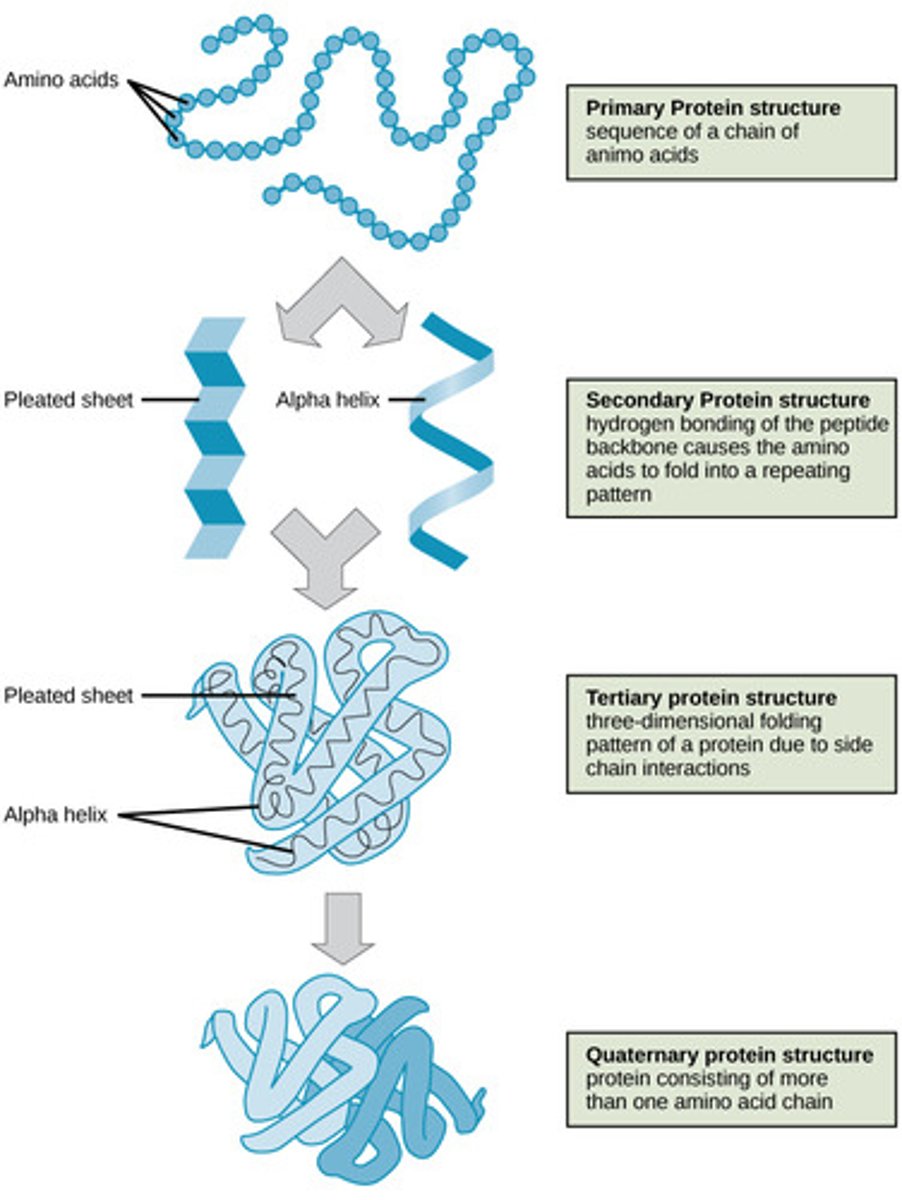
Which protein structure involves the 3D shape resulting from hydrogen bonding between amino and carboxyl groups of adjacent amino acids?
secondary
(Note: alpha helices and beta sheets)
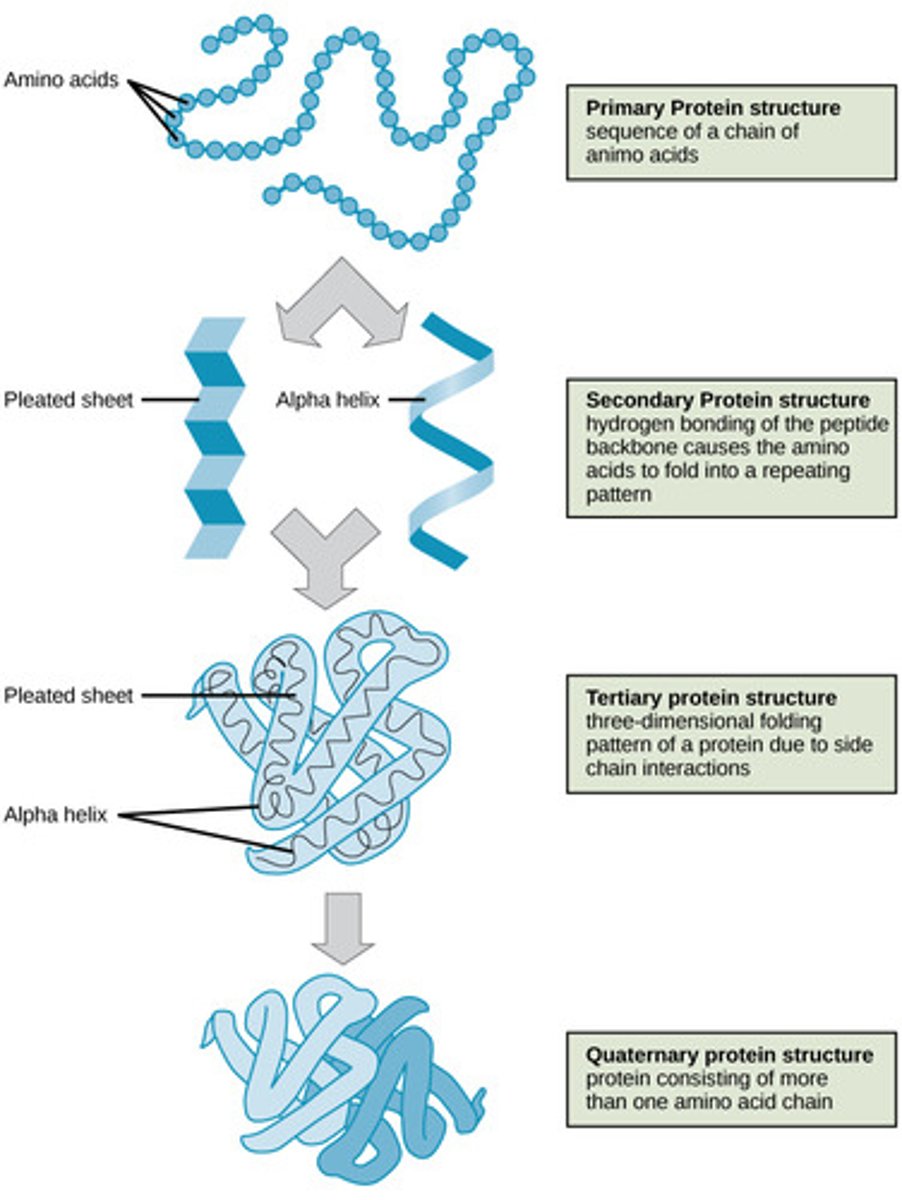
Which protein structure involves the 3D structure that forms due to non-covalent interactions between amino acid R groups (subunit interaction)?
tertiary
What are the non-covalent interactions found in tertiary structure?
1. H-bonds
2. ionic bonds
3. hydrophobic effect
4. disulfide bonds
5. Van Der Waals forces
Which protein structure involves the 3D shape of a protein that is a grouping of two or more separate peptide chains?
quaternary structure
Which proteins are somewhat water-soluble, dominated by tertiary structure, and have a diverse range of functions?
globular proteins
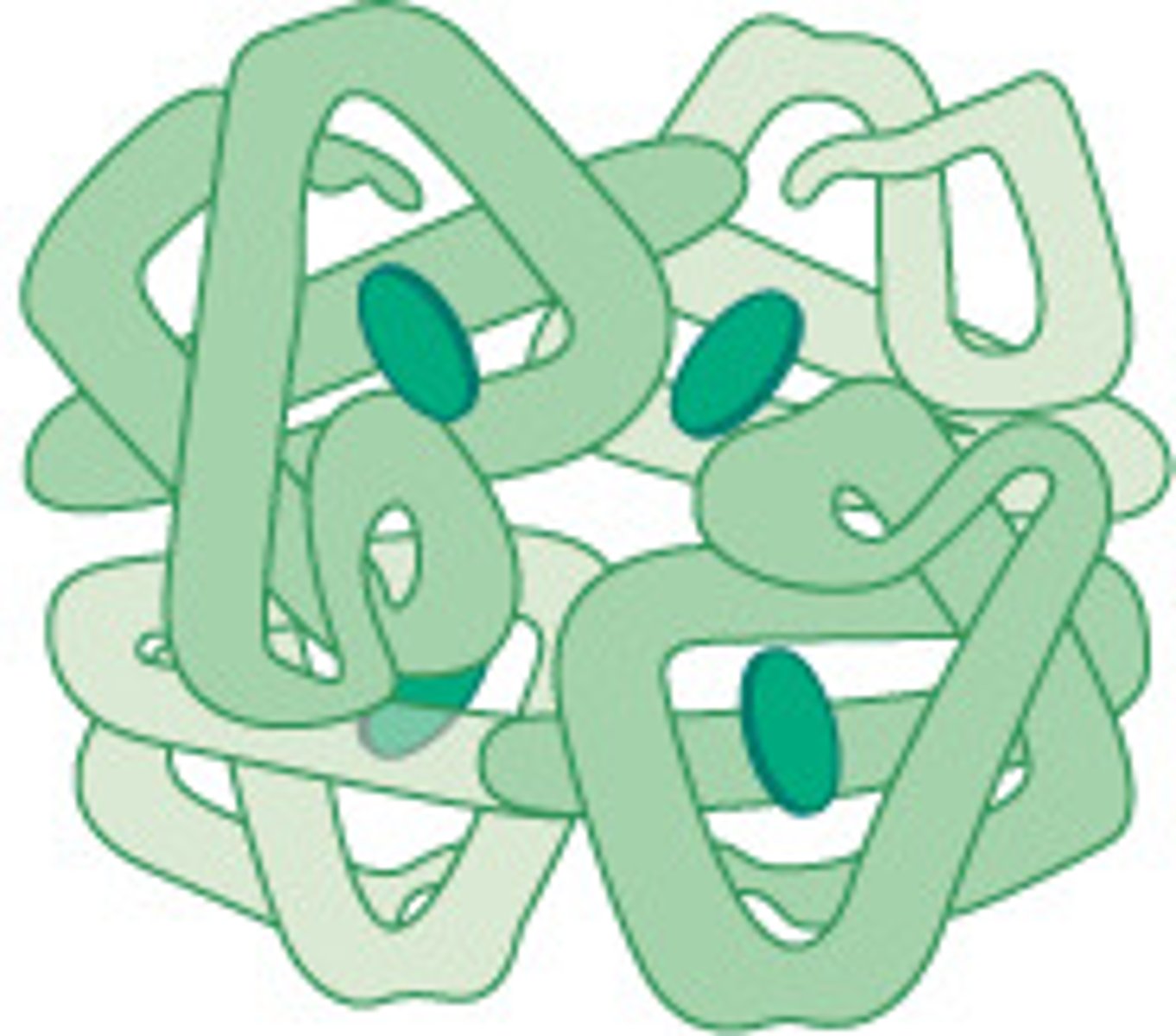
What are the functions of globular proteins?
1. enzymatic
2. hormonal
3. inter/intracellular storage and transport
4. osmotic regulation
5. immune response
Which proteins are not water soluble, dominated by secondary structure, are long polymers, and add strength to cells?
fibrous/structural proteins
(Note: collagen and keratin)

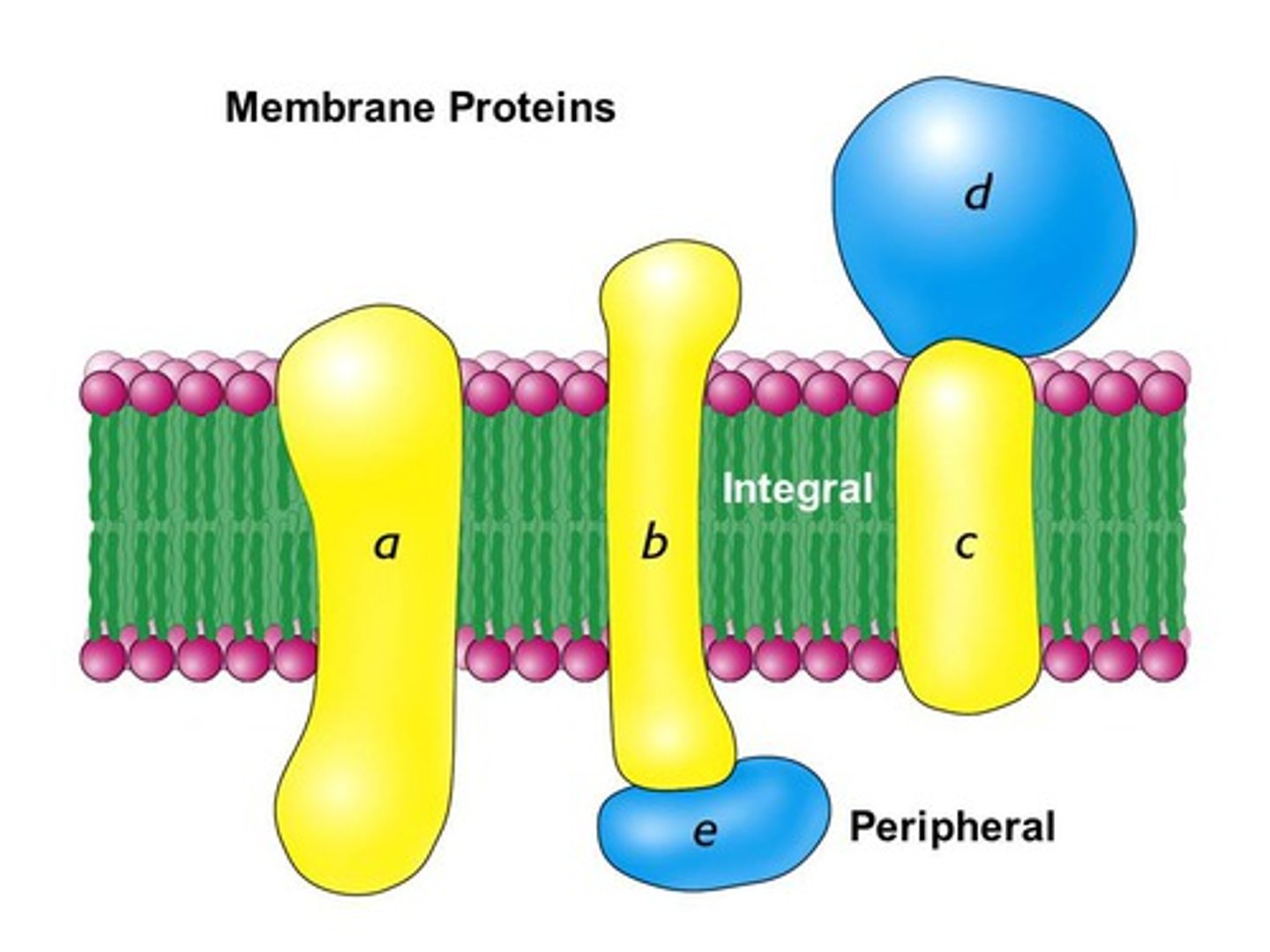
Which proteins function as membrane pumps, channels, or receptors?
membrane proteins
What process can occur when proteins are taken out of their ideal temperature, pH range, or solvent?
denaturation
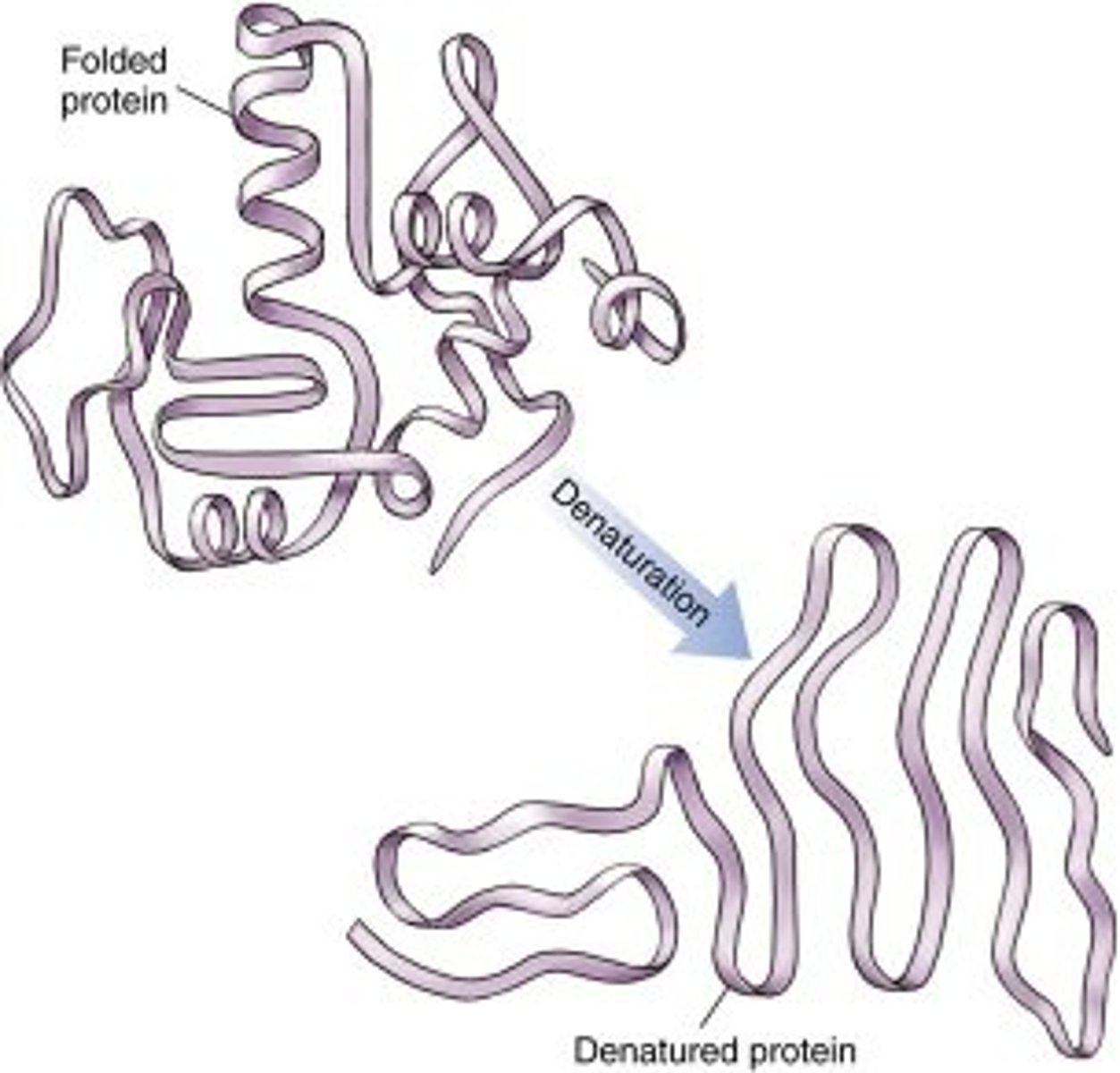
What happens to the structure of the protein following denaturation?
reversed back to primary structure
Is protein denaturation permanent?
usually irreversible, but in some cases, it can be reversed with the removal of the denaturing agent
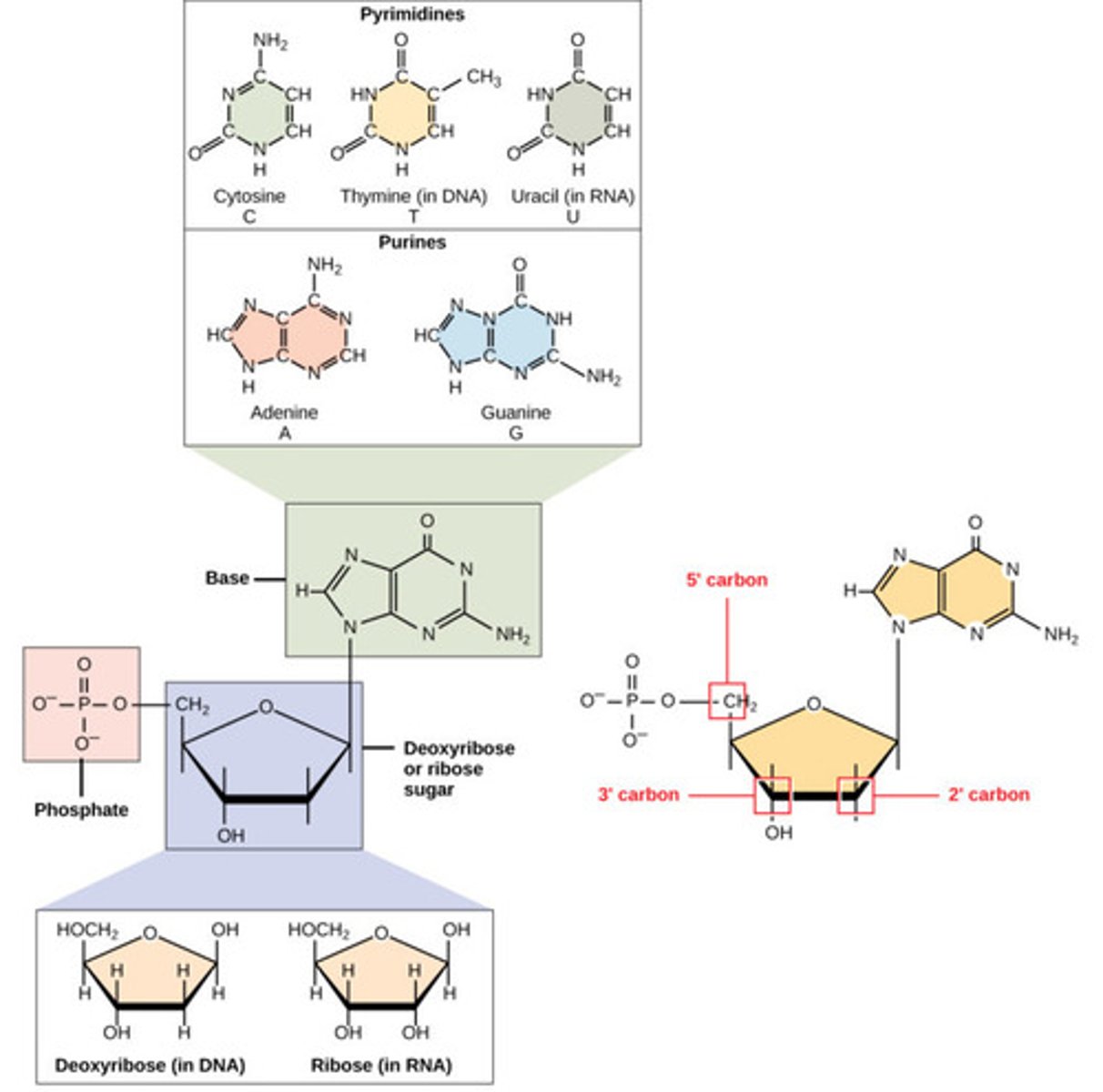
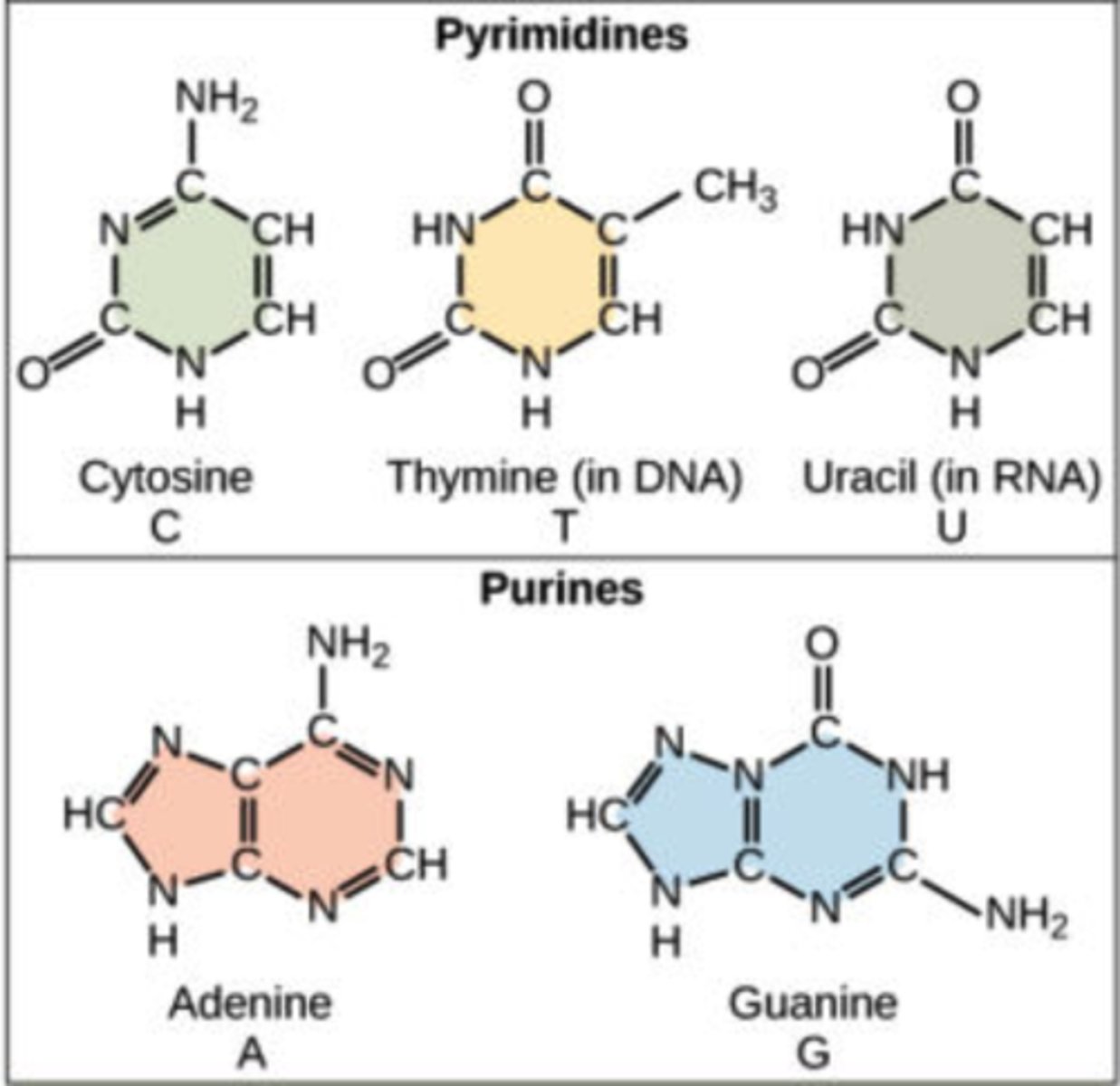
What are monomers that make up nucleic acids?
nucleotides
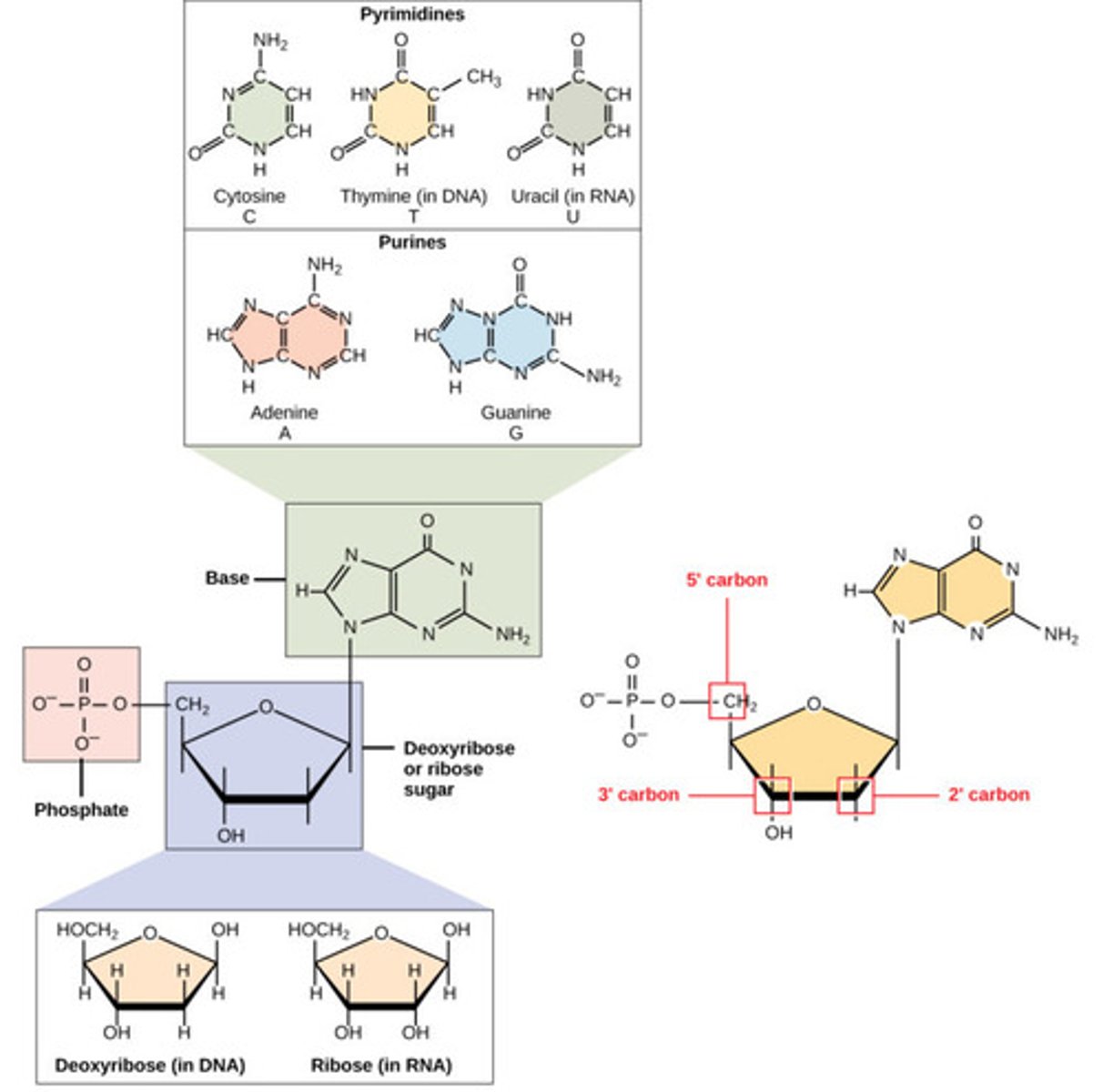
What are the components of nucleotides?
1. nitrogenous base
2. five carbon deoxyribose sugar
3. phosphate group
What unit consists of a sugar and nitrogenous base?
nucleoside
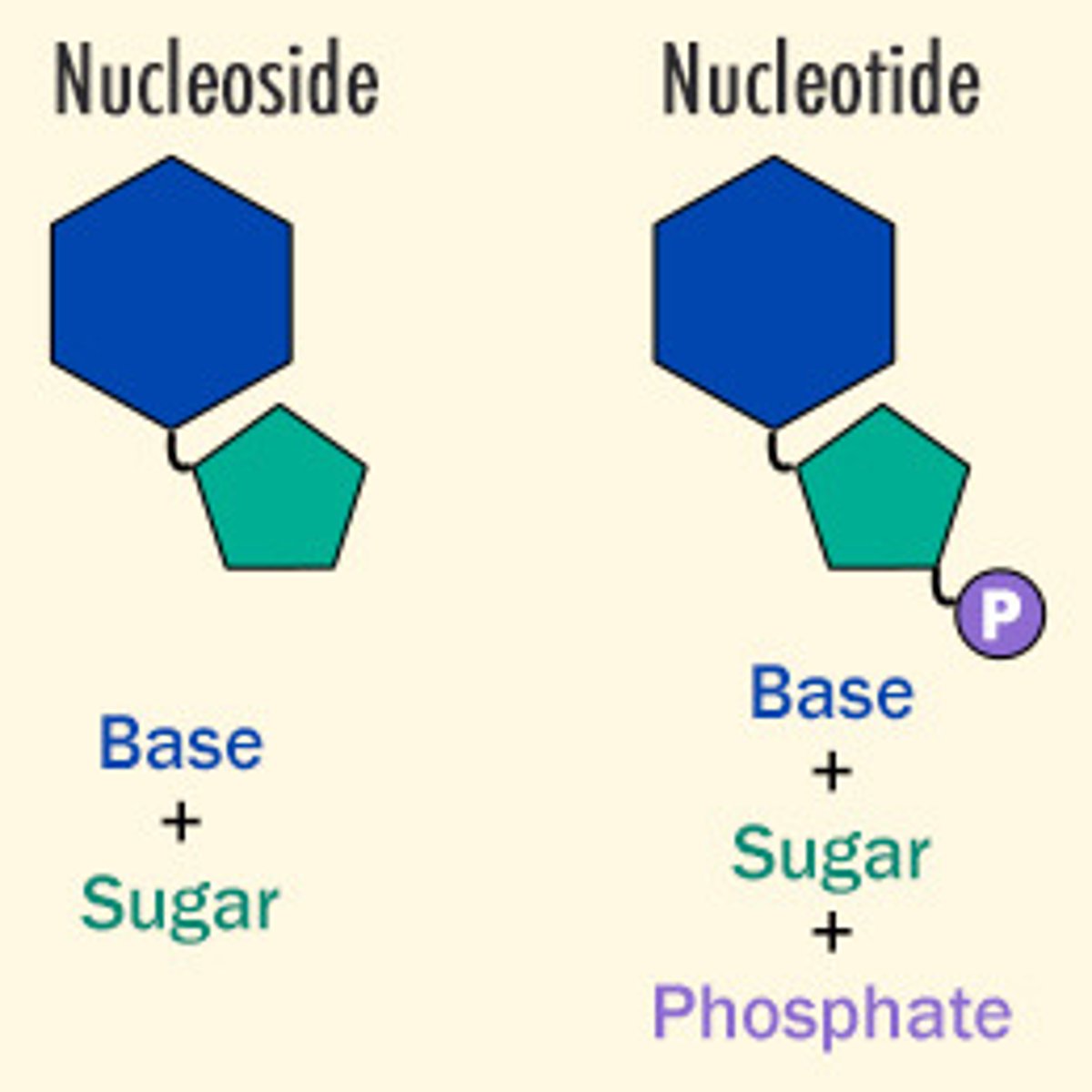
What is a nitrogen-containing compound that makes up a nucleotide?
nitrogenous base
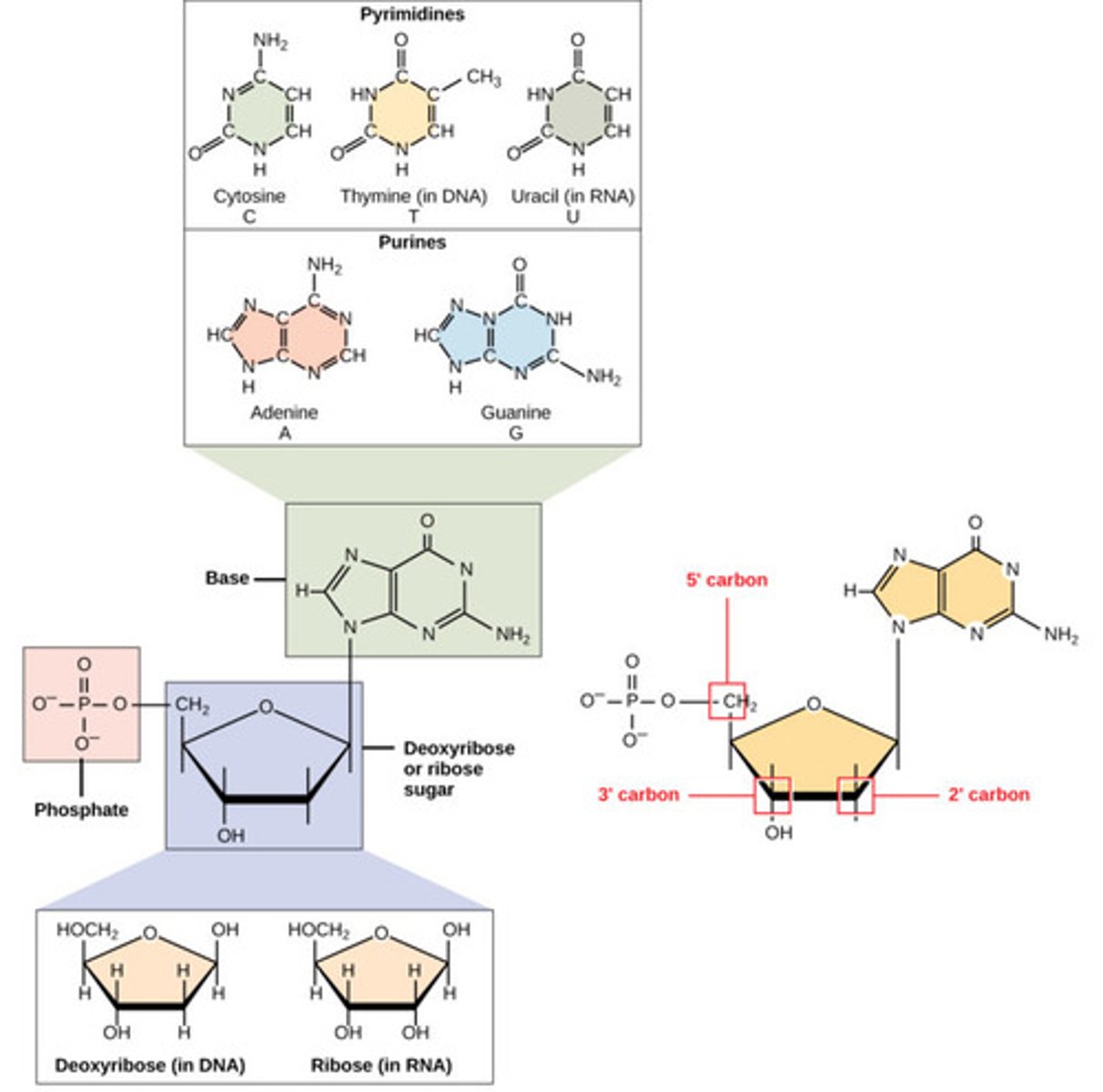
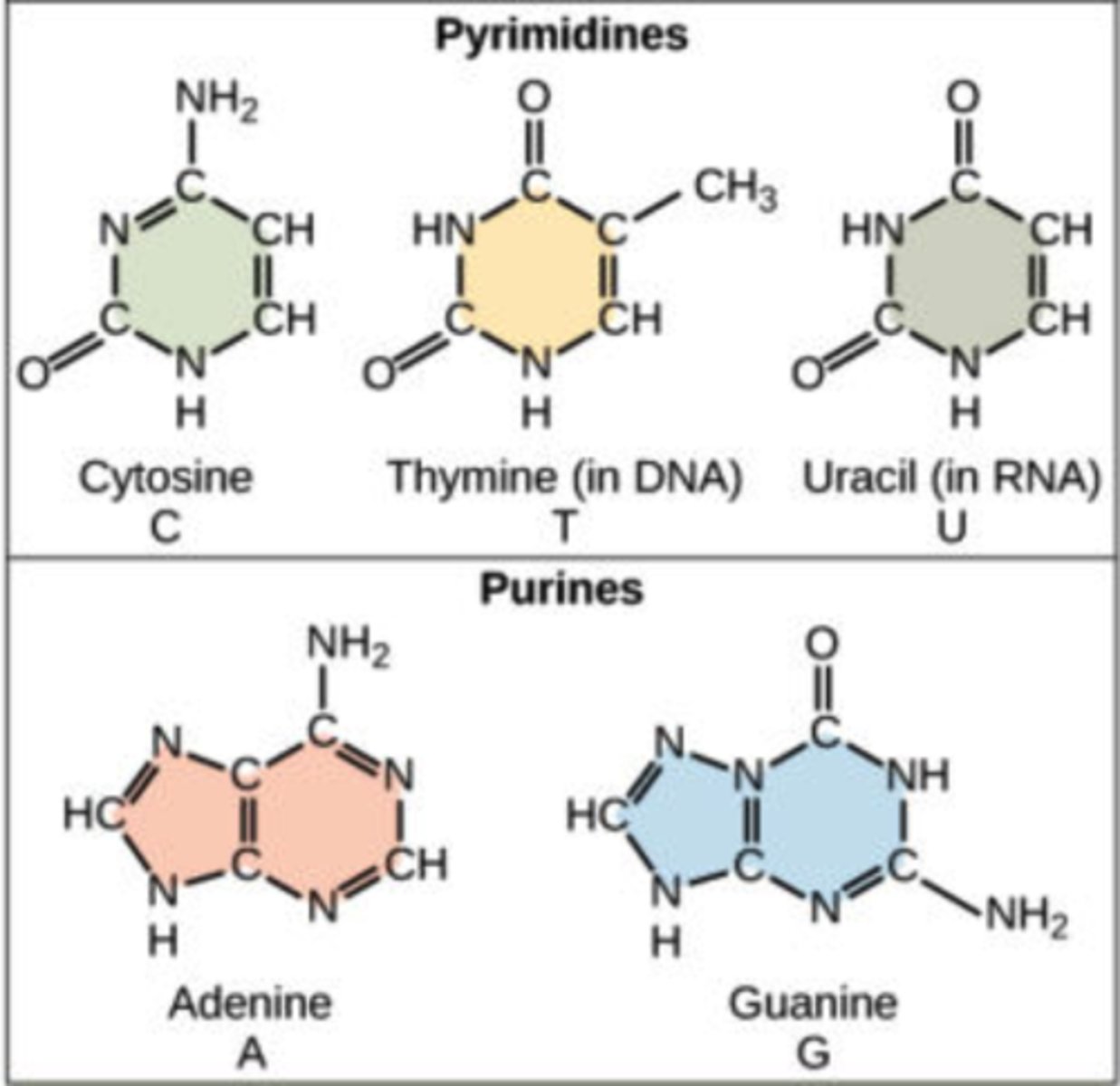
What are the nitrogenous bases found in DNA?
1. adenine (A)
2. thymine (T)
3. cytosine (C)
4. guanine (G)
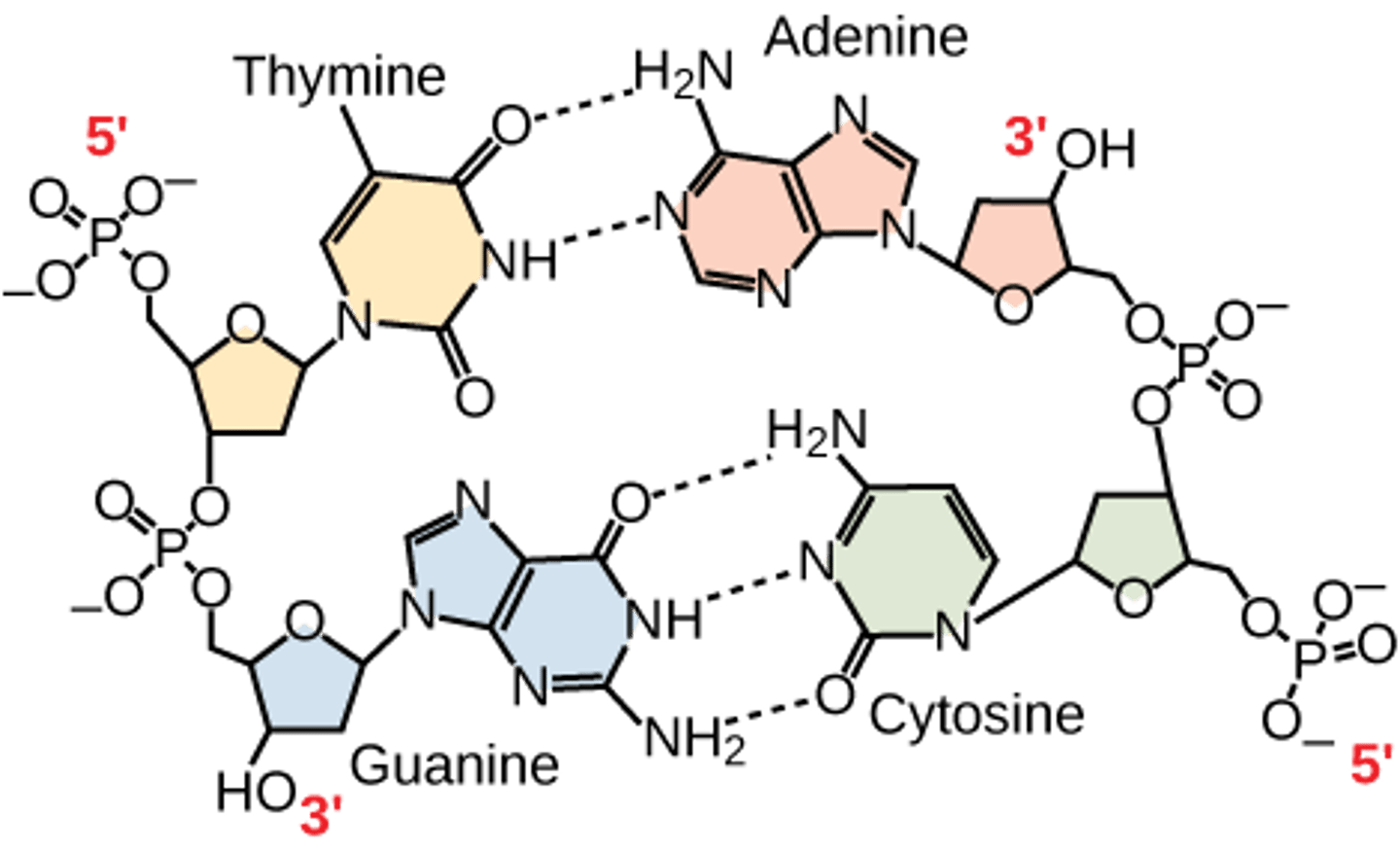
How many hydrogen bonds connect A and T?
2
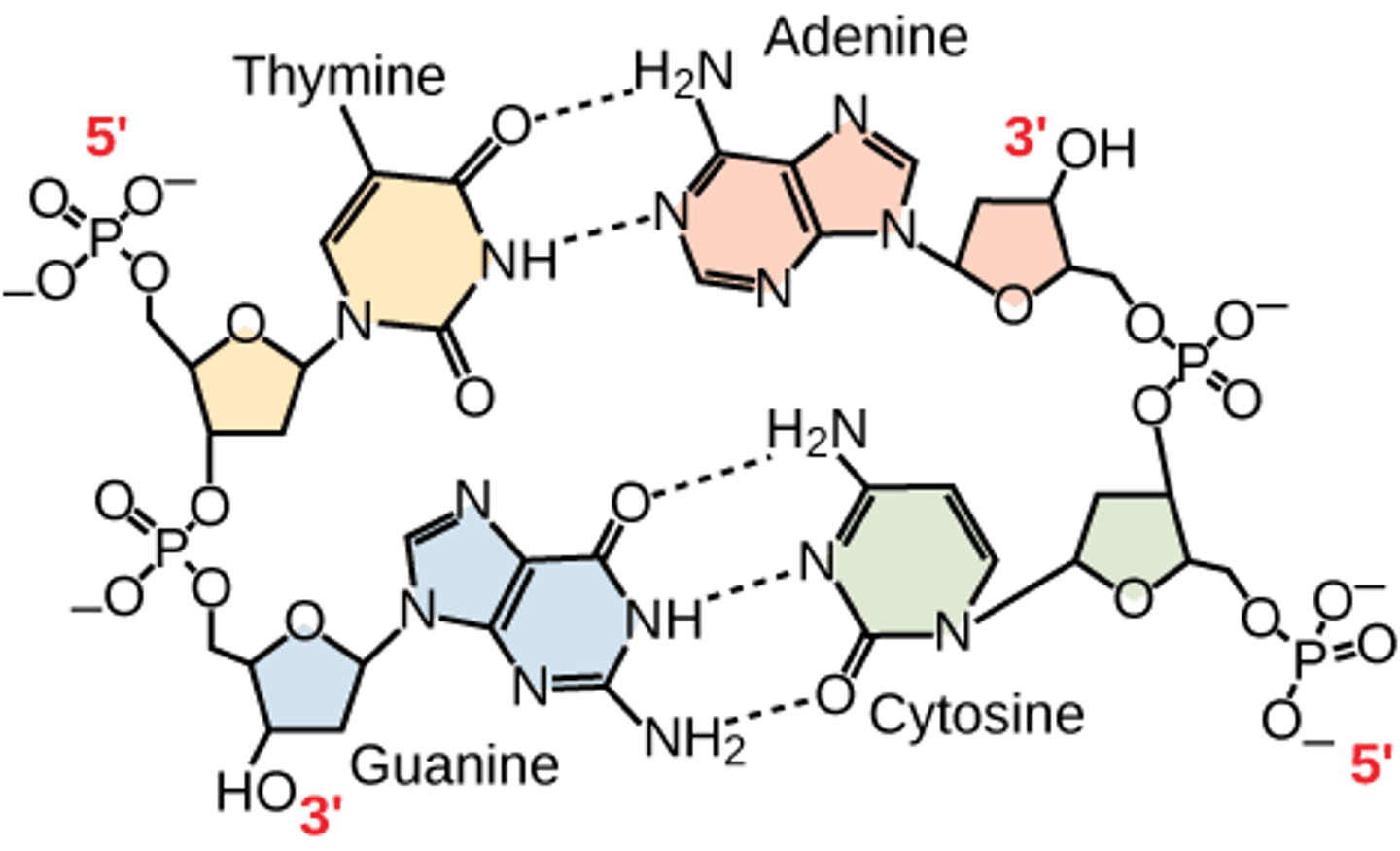
How many hydrogen bonds connect C and G?
3
What are the nitrogenous bases found in RNA?
1. adenine (A)
2. uracil (U)
3. cytosine (C)
4. guanine (G)