GEOL 102 EXAM 2 Study
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Earth’s Structure
crust, mantle, outer core, inner core.
hyperthermophiles
Microorganisms that live in high-temperature environments; some of them are chemoautotrophs
Shield
A region uplifted and exposing crystalline basement of Precambrian age (> 2.5 billion years) and undeformed during the past 500 Ma
Platform
A region where flat layering sediments overlie platform basement rocks
Continental Basin
a region of prolonged subsidence where thick sediments have accumulated
Orogen
region where mountain building has been active
Extended Crust
region where recent deformation has involved large-scale extension
Large igneous province
large outpouring of basalt
Faults
are fractures in rocks created by tectonic processes where there has been relative movement of the rock on both sides of the fault
When doo we start seeing unconformities?
with regression
What are pieces of the mantle or lower crust brought up by volcanic eruptions called?
Xenoliths
Order of rock in Frenchman Mountins
Tapeats Sandstone → Bright Angel Shale → Muav Limestone
Scientists use ____ to study the layers of the Earth.
indirect methods
Density
mass/volume; the greater the density of the material, the slower the P-waves travel.
Rigidity
is how strongly the material resists being bent sideways and is able to straighten itself out once the shearing force has passed • The more rigid the material, the faster the P-waves • Solid rock is more rigid than loose soils
Compressibility
is how much the material can be compressed into a smaller volume and then recover once the compressing force has passed • The more compressible the material, the faster the P-waves.
Which part of the Earth does not transmit S-Waves?
Outer Core
Which response is good evidence that the Earth’s inner core is solid rather than liquid?
P waves move faster through the inner core than the outer core
What was the reason for the decline of stromatolites?
rise of other organisms, has to be in a shallow marine environment
How do we identify glaciers within the proterozoic era
striations, not fossils.
Greenville orogeny is related to the formation of what supercontinent?
Rodinia
What are redbeds regarded as
show oxidation of minerals, carbonates forming
Xenolith
foreign piece of rock, pieces of mantle brought up with volcanic intrusions/eruptions.
P Waves
primary waves, travel through solids and liquids (fastest).
S waves
Secondary Waves - only travel through solids.
Hypocenter (focus)
The location where fault slip occurs. it is usually on a fault surface.
Moho
The crust-mantle boundary
Where is the moho located?
lithosphere
Which wave travels the fastest?
P-wave
What is it called when an abrupt change in seismic wave velocity takes place at the base of the crust?
Moho Discontinuity
Which rock type is inferred to make up the mantle?
preidotite
Which of the following is not a type of plate boundary - transform, convergent, divergent, subduction
subduction
The San Andreas Fault in California is an example of which type of plate boundary?
transform, right -lateral strike slip fault
The Himalayas were formed as a result of which type of plate interaction?
Continental-Continental Convergence
In normal faults, the hanging wall moves __.
down
What is the main difference between diorite and andesite?
Texture
Many regionally metamorphosed rocks were once
roots of tall mountains
Thick sequence of sedimentary rocks can accumulate where?
a basin subsides with the accumulation of sediments
The location, thickness, and some properties of the Earth's internal zones may be determined studying.
seismic waves
Plate tectonic movement of the lithospheric plates may be based in part on large thermal convection cells in the Earth’s
asthenosphere
The igneous rock that makes up much of the oceanic crust is
basalt and gabbro
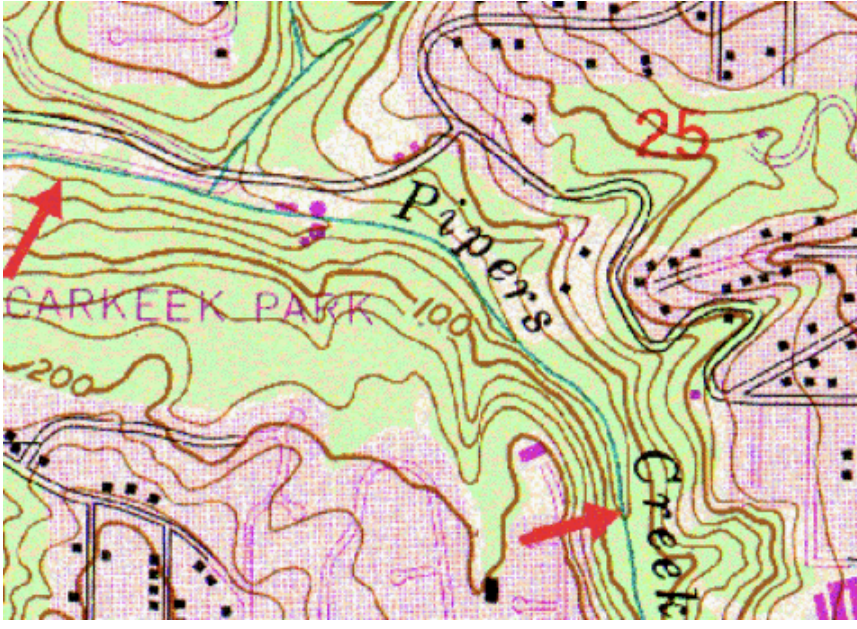
What is the contour interval of this map?
25 feet
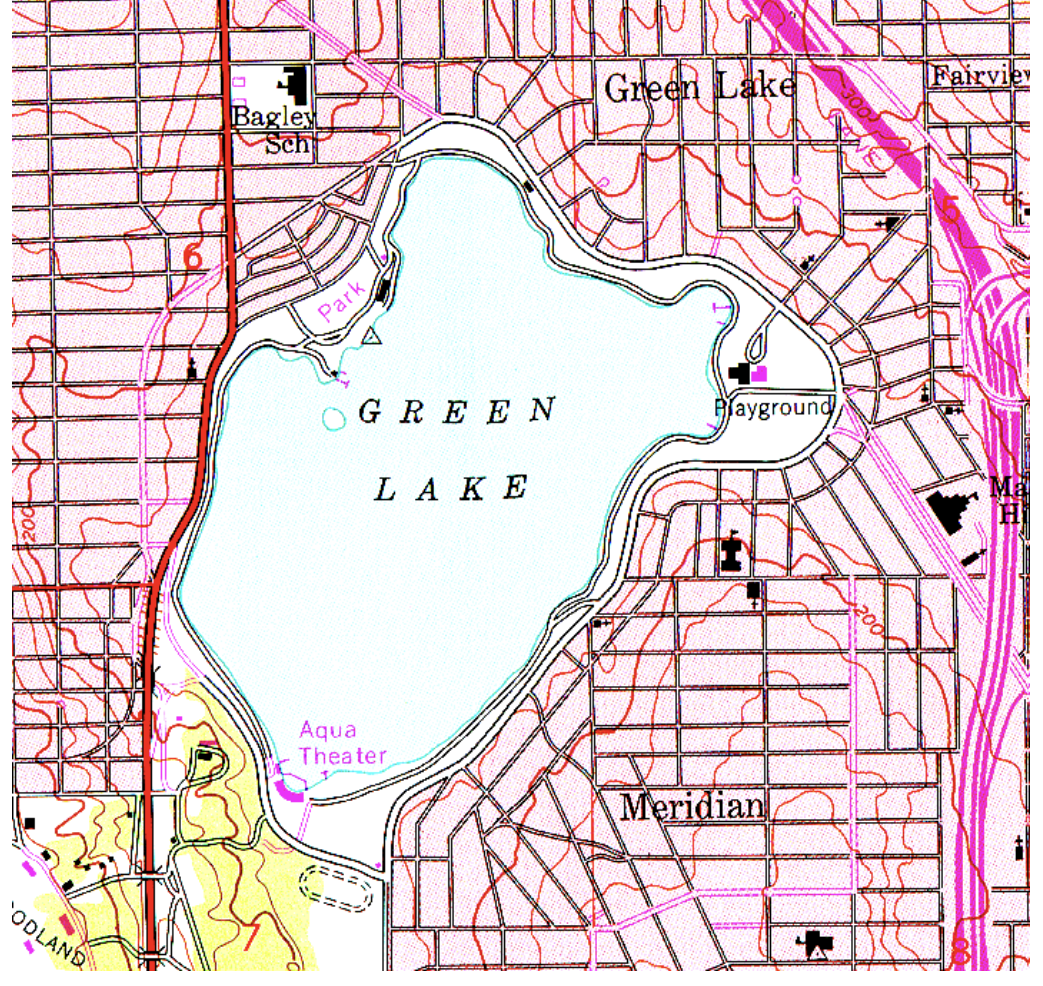
What is the approximate elevation of Green Lake?
125-150 feet
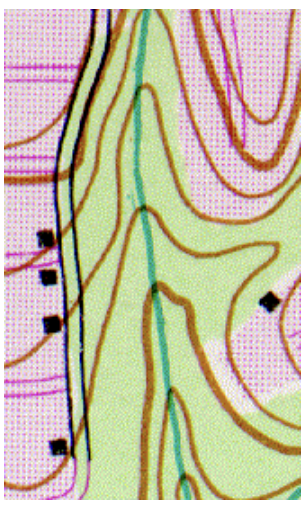
To the left is a small portion of a topographic map showing a road and a creek (blue-green line) in Carkeek Park in Seattle. North is always toward the top of topographic maps such as this |
Using the "Rule of V's" determine which way is the creek flowing.
north-to-south
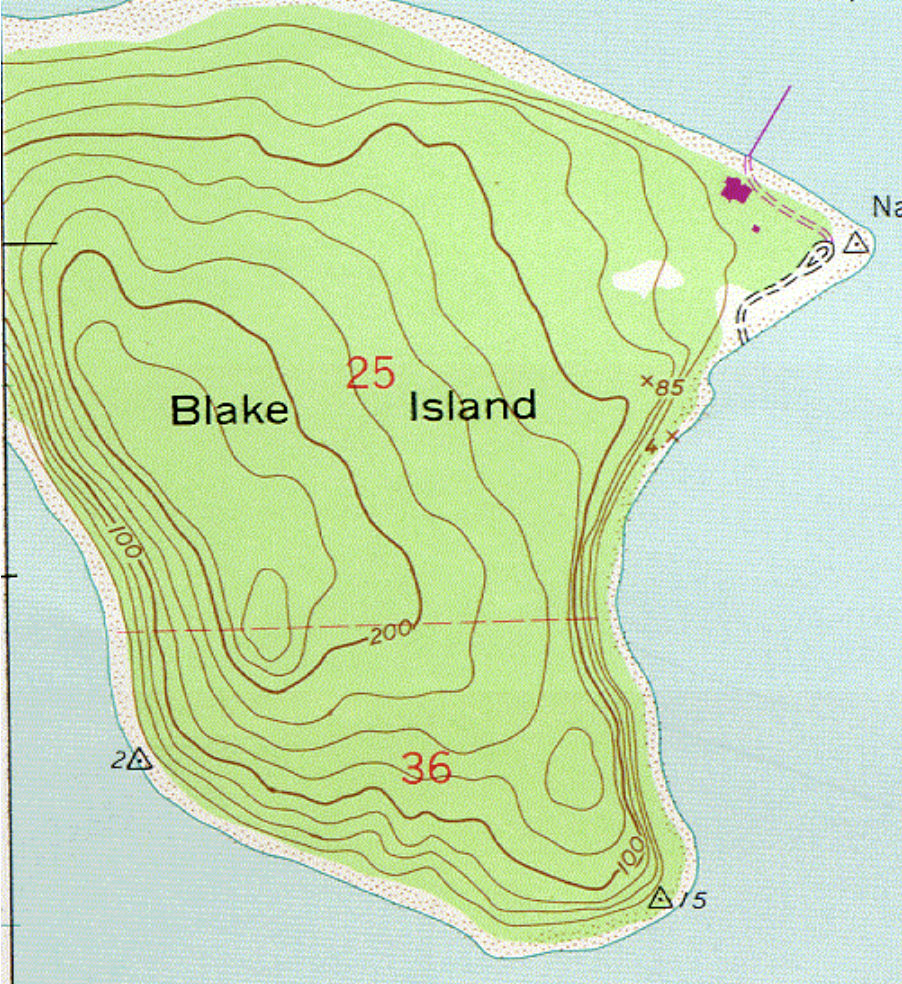
From which direction would it be easiest to climb from the shore to the top of Blake Island?
From the Northeast
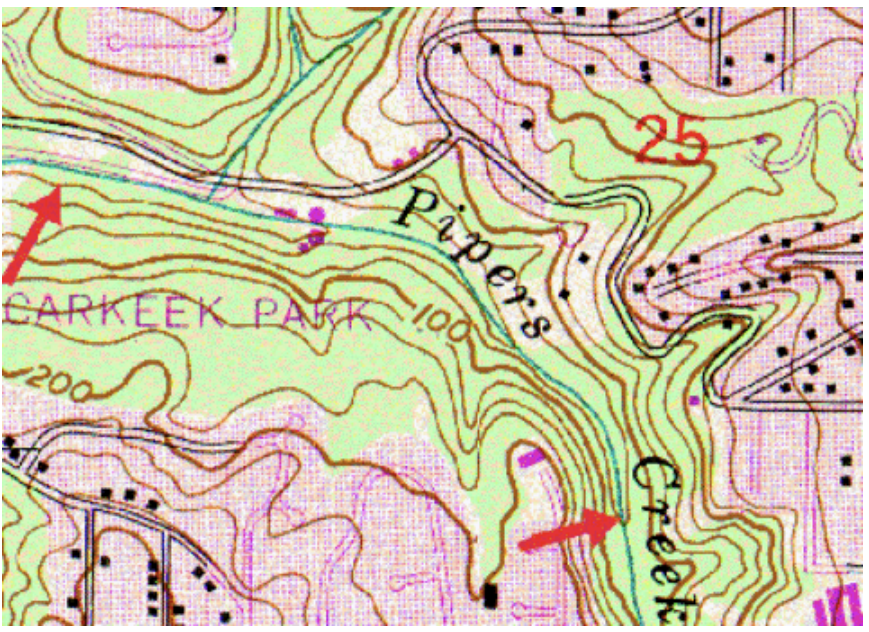
What is the elevation difference between the two red arrows?
25 feet.
Which of the following lists of planets are in correct order, from the sun to space.
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
What is a Wilson Cycle?
Opening and closing of ocean basins
Which of the following is false regarding BIFs?
Occurred during a time when photosynthesis did not occur.
Evidence of an iron core generating a magnetic field dates back to __________.
3.4 billion years ago
The Moon is thought to be __.
formed by a collision of the Earth with and object of Mars size
The Earth’s initial crust is composed of
komatiites
Proterozoic was a time of continent building. Which of the following was the Earth’s first known large continent?
Nuna
The Wopmay Orogen recorded what type of event?
Wilson Cycle
Red Beds are regarded as evidence for __.
sustained free oxygen in the atmosphere
Where did much of the initial oxygen produced by photosynthesis end up?
bonded to iron.
LVZ
lower velocity zone in the upper mantle
Asthenosphere
located below the lithosphere and is weak, hot, and ductile. Flows plastically.
Lithosphere
strong, rigid and cold, includes the crust and part of the upper mantle.
Continental Drift
proposed by Alfred Wegener, suggests that continents were once joined together in a single supercontinent called Pangea.
Paradigm Shift to Plate Tectonics
occurred with developments with bathymetry, paleomagnetism, seafloor spread, and earthquake and volcanic activity.
Convergent Boundaries
plates move towards each other, features mountain building, deep earthquakes, volcanism.
Slab pull
the mechanism driving subduction.
Divergent Plate Boundaries
plates move away from each other, features seafloor spreading at mid ocean ridges, shallow earthquakes, volcanism, rift valleys
Transform Boundaries
plates slide past each other horizontally, results in strike-slip faults, shallow earthquakes.
Mantle Plumes
narrow, rising columns of hot, buoyant rock originating from deep within the Earth’s mantle.
Contour Lines
joining point of equal height above or below sea level
Contour interval
The amount of elevation change between adjacent contours
Strike
compass direction of a rock layer as it interacts with a horizontal surface
Dip
acute angle between the rock layer and the horizontal surface measured perpendicular to strike.
Solar Nebula Theory
formation of our solar system; process began with cold cloud of gas and dust which contracted rotated and flattened into a disk like shape.
Terrestrial Planets
are in the inner part of our solar system
Gas planets
outer part of our solar system
Early Atmosphere
formed through processes related to the planet’s accretion and early geological activity; primitive atmosphere derived from gases associated with the comets and meteorites that accreted to form the Earth. Composed of Hydrogen, helium.
Boring Billion
very little change in the atmospheric evolution.
Prokaryotes
lack a nucleus, unicellular, reproduce asexually by simple cell division. shown little evolutionary change for more than 2 billion years
Eukaryotes
reproduce sexually through the union of an egg and sperm; bigger, more complex, and larger than prokaryotes.
BIFs (Banded iron Formations)
units of sedimentary rock with alternating layers of iron-rich material and chert; photosynthesis was vigorous operation at the time they were deposited. Suggest an oxygen poor atmosphere.
Red Beds
sedimentary rocks with iron oxide cements, including shales, siltstones, and sandstones. Considered evidence for free oxygen in the proterozoic atmosphere.
Rock Record
provides information about earth’s past environments
Stromatolites
organo-sedimentary structures built by photosynthetic cyanobacteria in shallow warm water. Among earliest evidence of life. Indicate aquatic environments.
Ooids
round carbonate concretions form in agitated shallow seawater where back-and-forth wave action causes precipitation of carbonate around a nucleus. Indicate high-energy, shallow marine environments with strong currents and wave activity.
Glacier evidence and deposits
indicate periods of significantly colder global or regional climates; ice ages; deposits show striations, poorly sorted deposits containing a mixture of boulders in a mud matrix.Striations and polish on bedrock, formed by the movement of glaciers over the rock surface(evidence of ice flow)
Sauk Sequences
Neoproterozoic-Early Ordovician; represents major transgression
Tippecanoe Sequences
Formation during Ordovician - major transgression
Kaskaskia Sequences
Devonian-Early Carboniferous
Abasroka Sequences
Mid Carboniferous-Triassic
Wopmay Orogeny
NW Canadian Shield; 2.3-2.1 Ga
Greenville Orogeny
Eastern N. America and Canada; ~1.1 Ga; formation of supercontinent rodina
Taconic Orogeny
Mid Ordovician formation; Eastern margin of N.America
Caledonian Orogeny
Silurian-Devonian formation; NW border of Europe
Antler Orogeny
Late Devonian- Pennsylvanian formation; Western N. America
Nuna Supercontinent
~1.8-1.4Ga; break up in Mesoproterozoic; Wilson Cycle
Rodinia Supercontinent
~900 Ma Broke up ~750Ma; Occurred during the Tippecanoe sequence
Pannotia Supercontinent
~650 Formation; broke up during the cambrian; Wilson Cycle
Pangea Supercontinent
~Late Carboniferous-Early Permian formation; Laurussia and Gondwana collide
Which part of the Earth does not transmit s-waves?
outer core