5.4: supply energy sustainably
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
it is widely recognised that there is a need to.
optimise efficiency of energy conversions
reduce fuel consumption & pollutant emissions
what can be used as an alternative energy source to fossil fuels?
biofuels (fuels from plant or organic waste)
produces less greenhouse gas emissions
limitations of biofuels
manufactured from crops - using land that would otherwise be used for food production for people & animals
fossil fuels are likely to be only partially replaced by bioethanol & biodiesel
biomass used as solid biofuel is inedible & doesnt contribute to food shortages & higher food prices BUT the fuel produced is of low quality that doesn’t produce much energy when burned (methane content significantly lower)
energy supplies need to be:
sustainable
minimise CO2 emissions
efficiency of:
fuel cell
thermal power stations
car engines
fuel cell: 85%
thermal power stations: 30-40%
car engines: 25-30%
why are fuel cells more efficient and how is it better?
single energy transformation (chemical energy → electrical energy), whereas multiple transformations in power stations and internal combustion engines
substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions
fuel cells can be designed to use which fuels & which fuel is the most popular
natural gas
methanol
ethanol
ammonia
HYDROGEN - most popular
hydrogen economy
fuel cells as replacement for internal combustion engine
hydrogen economy plans
currently → hydrogen produced by fossil fuels
if → source of hydrogen were renewable, energy supplies would be more sustainable, drastic reduction in greenhouse gas production and other pollutants without affecting quality of life
development of hydrogen-based fuel cell technologies
commercial products powered by fuel cells are more widely available and utilised
increased global resolve to limit climate change
how is hydrogen fuel cell ‘zero emission’
water is almost the only product apart from electricity and heat
BUT unless hydrogen fuel is produced with renewable energy, this can result in significant levels of greenhouse gases and otther pollutants
process of hydrogen production from fossil fuels + steam reformming
ex) natural gas, oil, coal
process of steam reforming → steam reacts with fossil fuel at high temperatures in presence of nickel catalyst
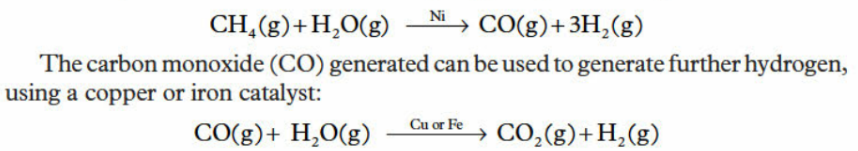
disadvantages of steam reforming
hydrogen produced has lower energy content than original fuel
original chemical energy of these exothermic reacttions is lost as waste heat during producttion
leads to CO2 emissions
advantages of steam reforming
as CO2 is produced at site of process, greenhouse gas could be captured and stored, preventing release to atmosphere
lower cost
2 methods of generating hydrogen susttainably
using electricty to convert water to hydrogen:
electricity generatted from renewable sources such as solar-power farms and wind farms
collecting biogas from landfill sites & converting methane in the gas to hydrogen by stteam reforming
green hydrogen costs
hydrogen sources from renewable sources is the most desirable method of production
energy produced from hydrogen would be sustainable
costs twice as much as hydrogen from coal and natural gas
hydrogen supply storage
hydrogen has a very high energy content by mass compared to fuels like petrol
gas at room temperature
established methods for storage in cars is as liquid/compressed hydrogen
energy per litre of liquid is much less than that of a petrol → hydrogen vehicle needs larger fuel tank
hydrogen safety
poses safety challenges
highly flammable and potenially explosive
hydrogen sensors to detect leaks
fuel cells likely to have criticalrole in:
renewable energy
energy storage
energy management
greenhouse gas reduction
elements of fuel cells that need to be developed and optimised
electrode materials
electrolytes
cost
energy storage
safety
lifetime
performance
renewable energy sources such as…
solar and wind will play an increasing role in the supplly of energy
development of new battery and fuel cell technologies is
part of move from linear to circular economy
microbial fuel cell (MFC)
converts organic material to electrical energy by the action of microorganisms
microorganisms form a film on the surface of the anode and oxidise organic material (producing CO2, protons and electrons)
microorganisms then transfer electrons to the anode of the fuel cell
cathode reaction use a variety of oxidants (often O2)
MFC anode cathode reactions

MFC advantages
operate at or near room temperature
can use low-grade waste materials
soil
sediment
wastewater
agricultural waste
used for sustainable wastewater treatment and contaminant removal & generating low-power electricity