4.3 Carbon cycling
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
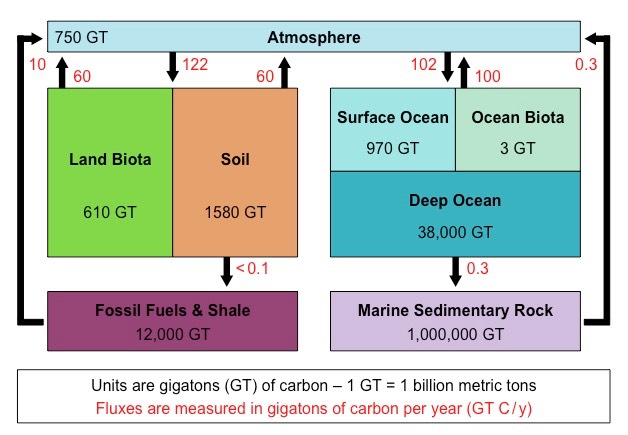
Carbon cycle
A biogeochemical cycle where carbon is exchanged between 4 spheres of earth.
Things carbon is exchanged in
Atmospheric gases – mainly carbon dioxide (CO2), but also methane (CH4)
Oceanic carbonates – including bicarbonates dissolved in the water and calcium carbonate in corals and shells
As organic materials – including the carbohydrates, lipids and proteins found in all living things
As non-living remains – such as detritus and fossil fuels
Carbon concentration gradient
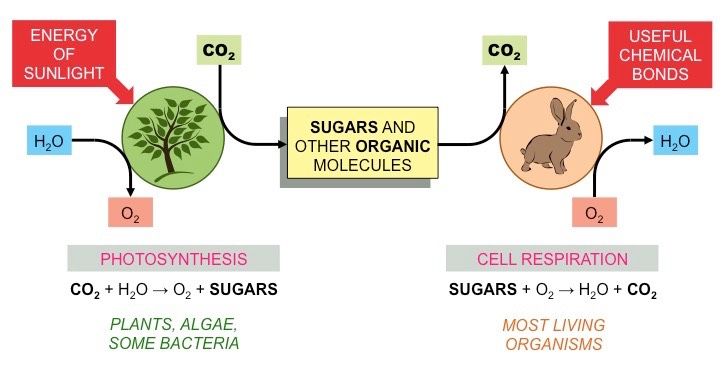
The process by which the concentration of carbon dioxide is greater outside the cells of plants which allows for passive diffusion into the plant.
Compensation point
The point that the net carbon dioxide is 0 due to an offset between cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
Carbonic acid
A product of when atmospheric carbon dioxide dissolves in water, creating carbonic acid. Creates hydrogen ions causing ocean acidification.
Created carbonate ions (H2CO3 ⇄ HCO3– + H+) which acquires metal ions
Calcium carbonate
Formed by the combination of hydrogen carbonate ions from with calcium which allows for shelled organisms to create their exoskeletons.

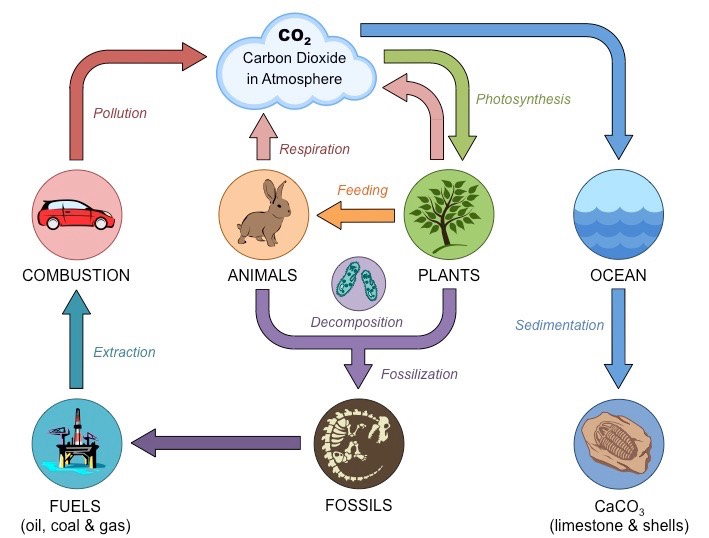
Methane
A gas formed typically in the digestive tract of animals, wetlands, and marine sediments.
Coal formation
When peat is compressed under sediment, the heat and pressure produces coal which can be burned to release heat and carbon dioxide.
Combustion
The burning of organic compounds in the presence of oxygen.
Produces exergonic reaction
Carbon sink
A forest, ocean, or other natural environment viewed in terms of its ability to absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Gigaton
1 billion metric tons. Typically used to talk about carbon