Resin bonded bridges - All
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
biggest threat to dentist profession (paper)

Botched: (of a task) carried out badly or carelessly “a botched attempt to steal a car”

the ‘daughter test’


RBB def


Classification- evoltution of RBB
Rochette bridge
maryland bridge
cast mesh FPD
Virginia bridge
adhesion bridge

ONLY DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THEM : the metal surface finishing technique employed

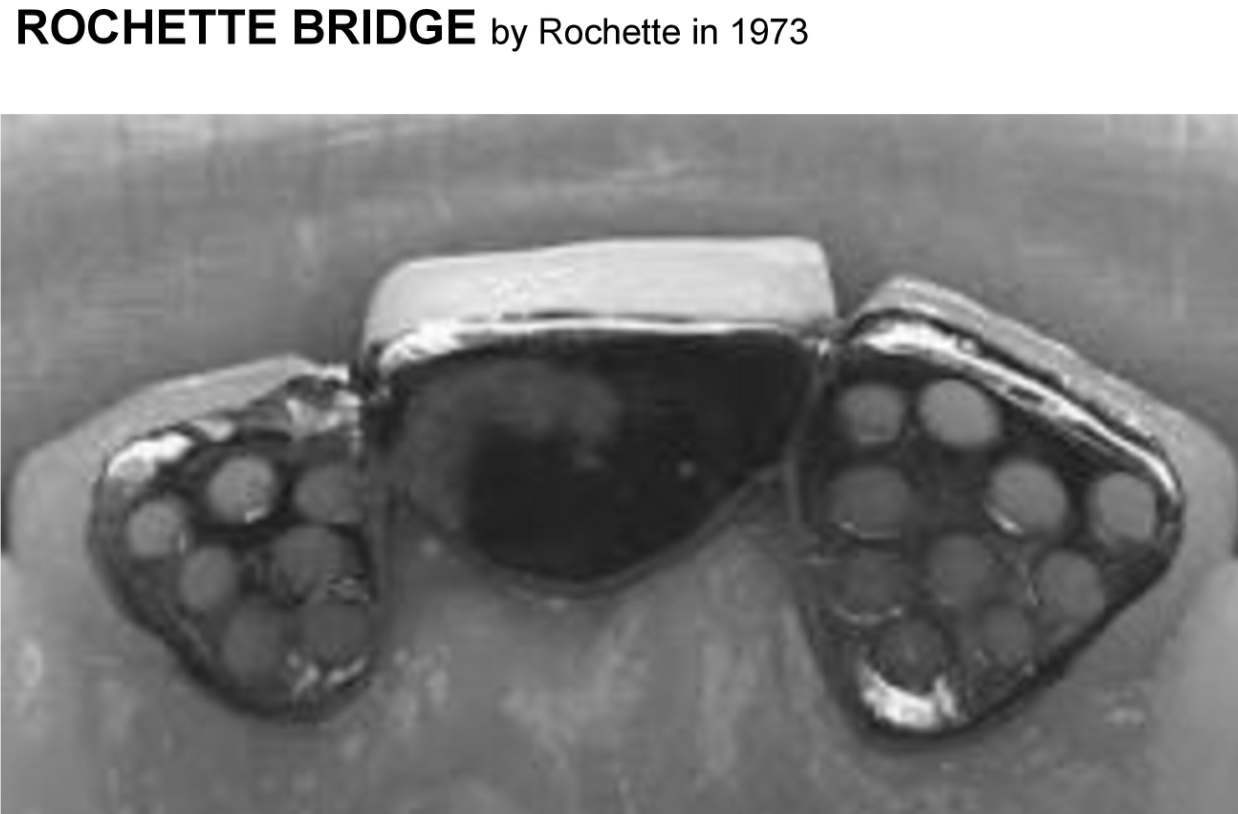
What is the ROCHETTE bridge (1973)?
A Rochette bridge is a fixed partial denture that uses metal wings (retainers) bonded to the lingual or palatal surfaces of adjacent teeth. These metal retainers are perforated and cemented using composite resin. The central pontic (false tooth) replaces the missing tooth.
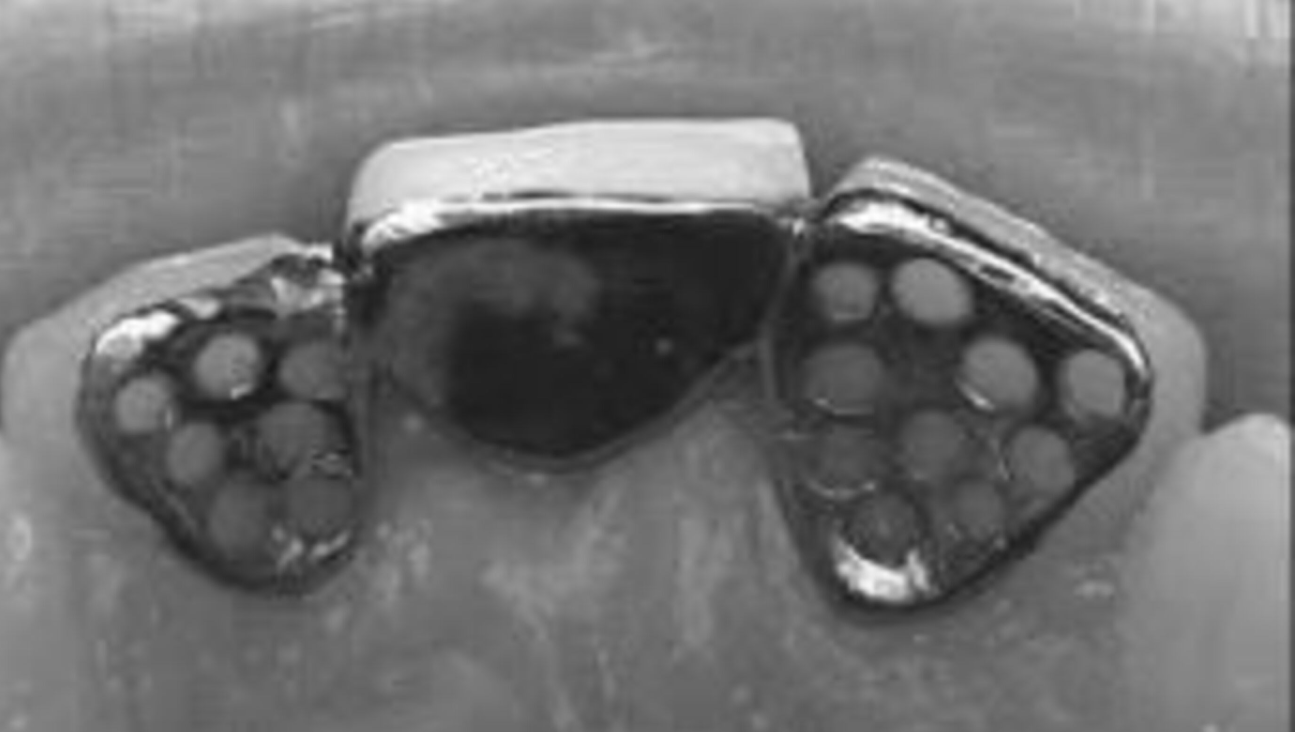

What is the Maryland bridge (1980)?
The new design of the wing is perforation free, and the retention to the resin could obtained by producing microspaces in the wing (retainer) internal surface through various ways such as electrochemical pit corroding technique (metal etching)
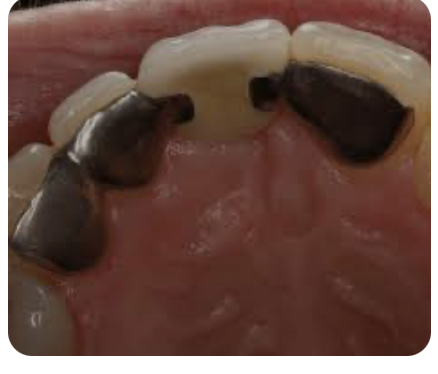
Cast mesh FPD
In this design, they use a non-etching method to produce metal surface roughness before the alloy is cast
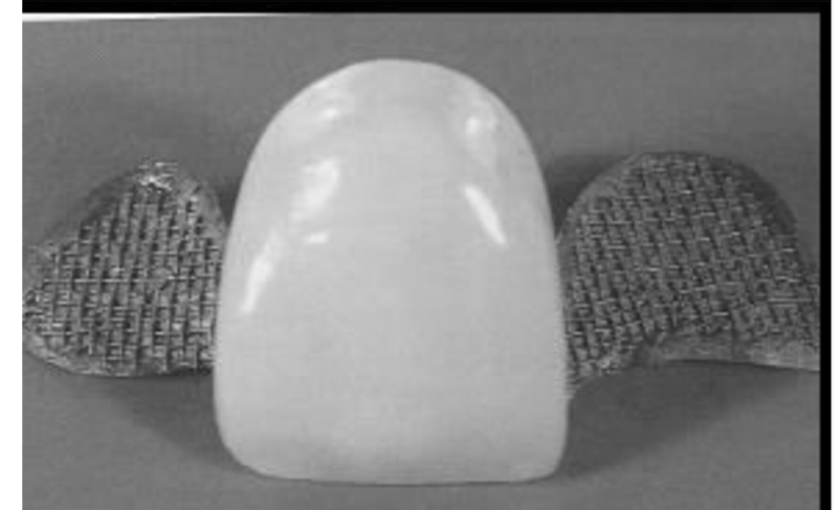
Virginia bridge
This design produced particle-roughened retainers by incorporing salt crystals into the retainer patterns to produce roughness on the inner surfaces; this methods is known as the lost salt technique for producing Virgina bridges
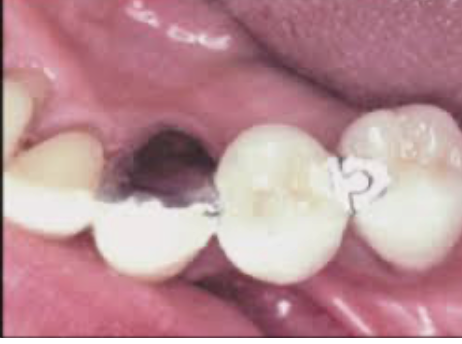
Adhesion bridge around 1990
In this design there is no need to make any surface modification before casting, after casting, we clean the surfaces with air abrasion, then prepare the retainer inner surface fro adhesion by various methods. The bond in this design depends on the inherent bond ability of the newer resin cement to the alloy.
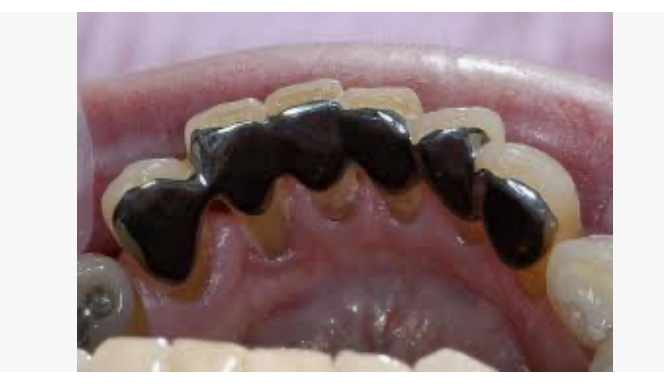
Advantages of Resin Retained Bridges
reduce cost and chair time by as much as 50 percent
conservative, minimum tooth structure needs to be removed; the preparation is confined to enamel only
anesthesia is not used during tooth preparation (aid to monitor the proximity of the preparation to the DEJ by the patient comfort’s level)
Supragingival margin is mandatory in resin-bonded fixed partial dentures
the restoration can be rebounded
Disadvantages of resin retained bridges
uncertain longevity?
No space correction, if the edentulous space is wider than the mesiodistal width of the tooth that would normally occupy the space
no alignment correct, good alignement of the abutment teeth is required because the prosthesis’s path of insertion is limited by enamel thickness
black triangle
shade changes
try in period
difficult temporization
Indications for RRB
Mandibular incisor replacements: treatment of choice for replacing one or two missing mandibular incisors when the abutment teeth are undamaged
Maxillary incisor replacement in edge-to-edge or moderate overbite situation
periodontal splint (the splinting of periodontally compromised teeth was the first use of a RRB FPD, although significant differential mobility may be a contra-indication)
Single posterior tooth replacements
Where abutment teeth are minimally or un-restored, with sufficient enemel present for adhesion
patients unwilling or unsuitable for surgical treatment including implants, bone augmentation
fixed retention after orthodontic treatment
needle-phobic patients
Contraindications for RBB
Extensive caries, heavily restored, abutment teeth with reduced enamel available for adhesion
Deep vertical overbite. So much enamel must be removed from the lingual surface of a maxillary incur in this occlusal relationship, the retention would be drastically reduced because of the poor bonding strength afforded by the exposed dentin
small abutment teeth, eg peg laterals, microdot teeth with a reduced surface area for adhesion
Mal-aligned abutment teeth which will result in a poor path of insertion and poor aesthetics
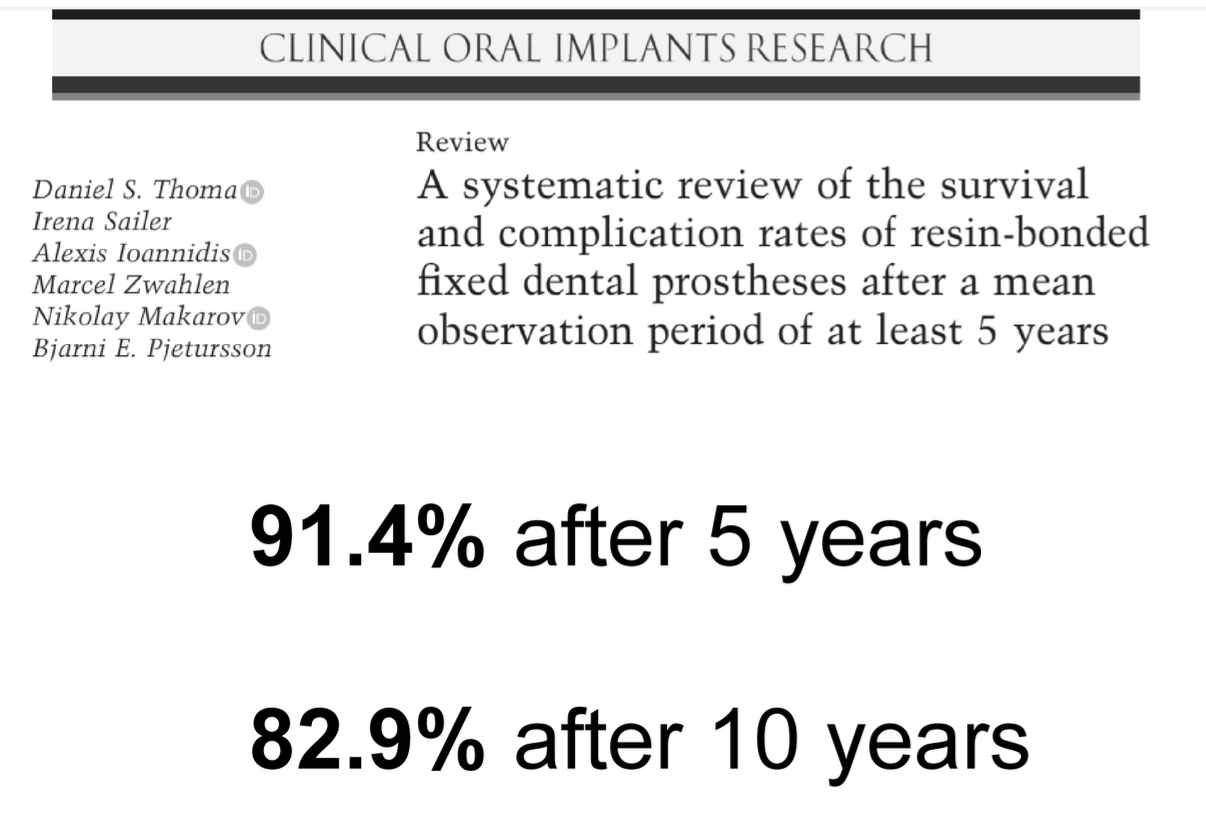
Survival and complication rates of RRB after an observation period of at least 5 years
87,7% after 5 years urgent need for studies with a follow-up time of 10 years or more, to evaluate the long-term outcomes

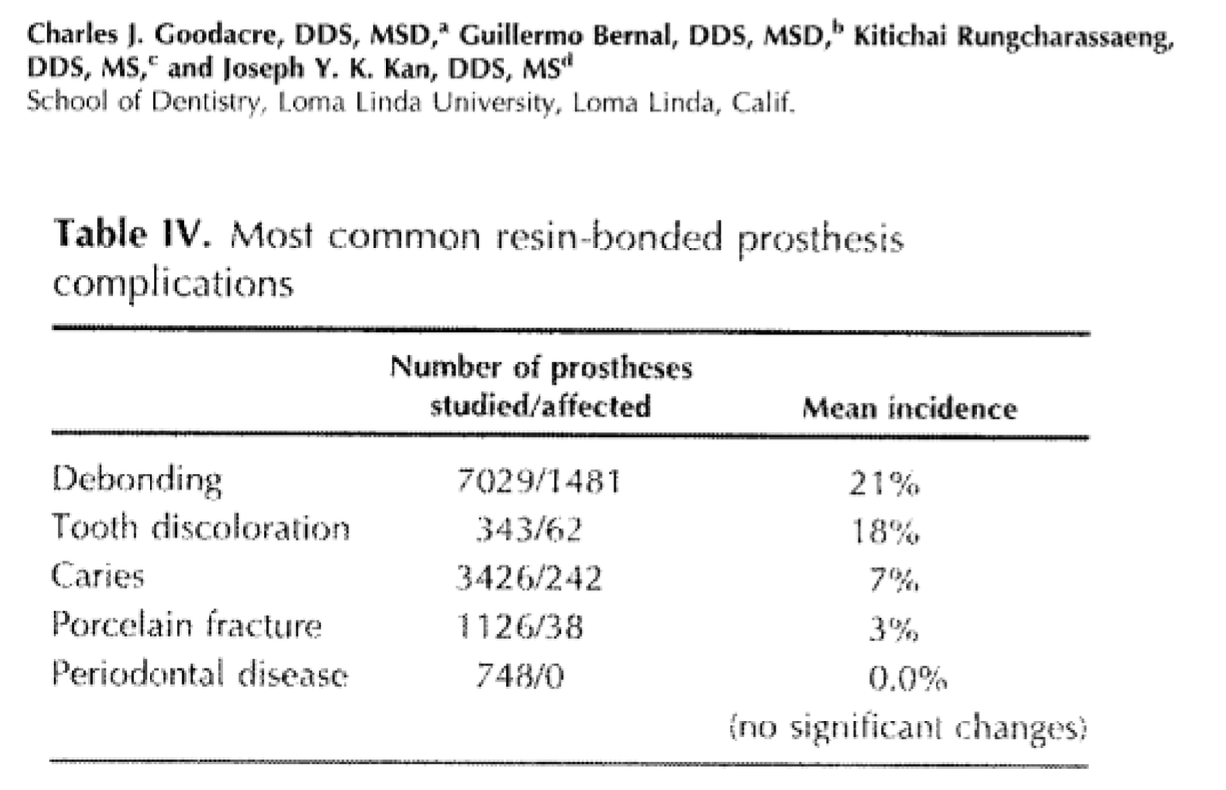
RBB- clinical complications in fixed prosthodontics
debonding
tooth discoloration
caries
porcelain fracture
periodontal disease
Longevity of implant crowns and 2-unit cantilevered resin-bonded bridges
78 subjects participated in this study (39 ISC and 39 cRBB cases)
Both had a mean observation time exceeding 100 months)
ISCs and cRBBs had similar survival rates
BUT there was a significant difference in “success”:
ISC (69,2%)
cRBBs (89,7%)
Causes of RBB de-bond
Bond failure → attempt rebond and overcome adhesive failure following a strict bonding protocol
moisture contamination at time of fit
incorrect seating with uneven cement layer
inadequate surface treatment of fit surface
cement manufacturer’s instructions not followed
occlusion → unfavorable loads on pontic in static and dynamic occlusion—→ minimal adjustment to correct RBB occlusion where appropriate, or consider new RBB with different design or alternative restoration to meet occlusal demands
Inadequate design: consider new RBB with different design or alternative restoration
insufficient coverage of abutment
rigidity: inadequate connector height and/or retainer thickness
fixed-fixed design used where a cantilever design may be favorable (e.g.significant differential mobility of abutments)
ambitious use of a cantilever design where fixed-fixed may be more favorable
Abutment selection: consider new RBB with different design or alternative restoration
inappropriate size of abutment
restored teeth with insufficient surface area of enamel for bonding
KEY POINTS FOR RBB SUCCESS - How should the retainer wing extend?
Retention success relies on bond strength and the cement lute, therefore:
Extend the retainer wing over maximum available enamel (including occlusal)
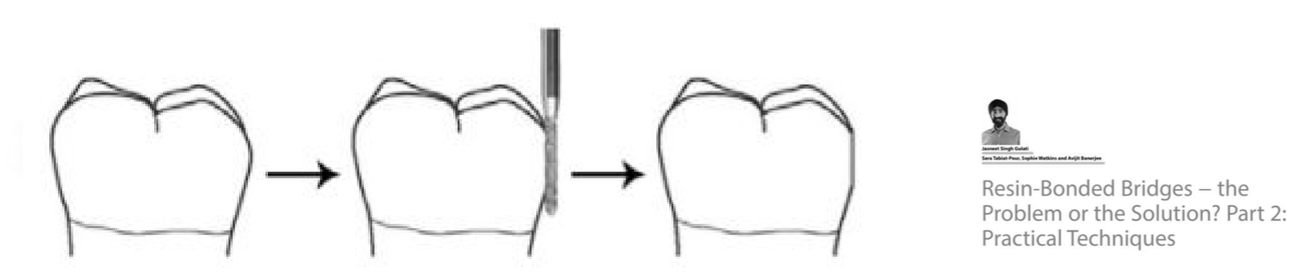
KEY POINTS FOR RBB SUCCESS - Why is the bond to enamel strongest and essential for success?
Bond to enamel is strongest and therefore essential for success:
Abutments should be minimally restored with resin composite or un-restored
Prepare tooth within enamel only to optimize bond and protect from recurrent caries
avoid complex preparations such as rest seats and slots which complicate the procedure and risk dentine exposure
avoid occlusal preparation - cement high in occlusion if necessary
KEY POINTS FOR RBB SUCCESS - How can we reduce stress on the cement lute?
Reduce stress on the cement lute by:
Rigid framework
Maximum connector height (proximal preparation within enamel)
Extend framework occlusal and onto incisal edges for added rigidity and results in loading cement lute in compression
Cement high if necessary (Dahl concept)
limiting path of insertion via proximal guide planes
extend over maximum available enamel for bonding so that occlusal forces are spread over larger area decreasing stress on lute
→ An intra-oral air-abrasion unit is an extremely useful part of the armamentarium when using adhesive bridgework, both for initial bonding and re-bonding
KEY POINTS FOR RBB SUCCESS - How can we optimize aesthetics?
Optimize aesthetics by:
Using opaque ciment to prevent greying of incisor abutment teeth
mimic presence of retainer wing (loss of translucency) by placing cotton roll behind anterior abutment during shade-taking
shade-taking before impression stage to avoid dehydration affecting tooth colour
consider use of electrosurgery in pontic area for improved pontic emergence profile
Article
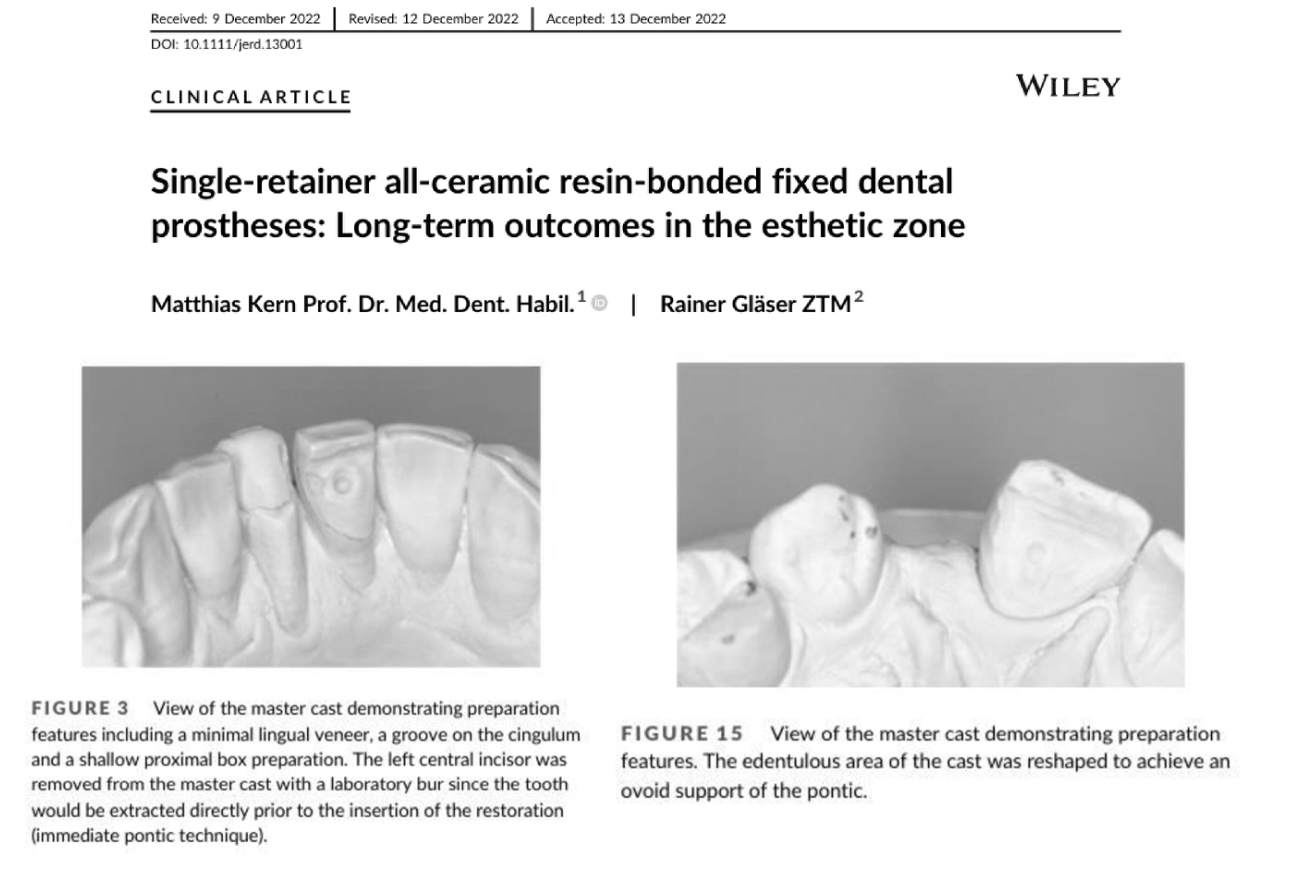
Accoring to Kern, what are the contraindications for RBFDPs?
insufficient bonding surface area (<30 mm² of enamel)
inadequate occlusal space (<0,7 mm)
insufficient connector height (<3 mm)
inappropriate occlusal guidance (which should not be on the pontic)
the presence of bruxism without a night guard
Article by King
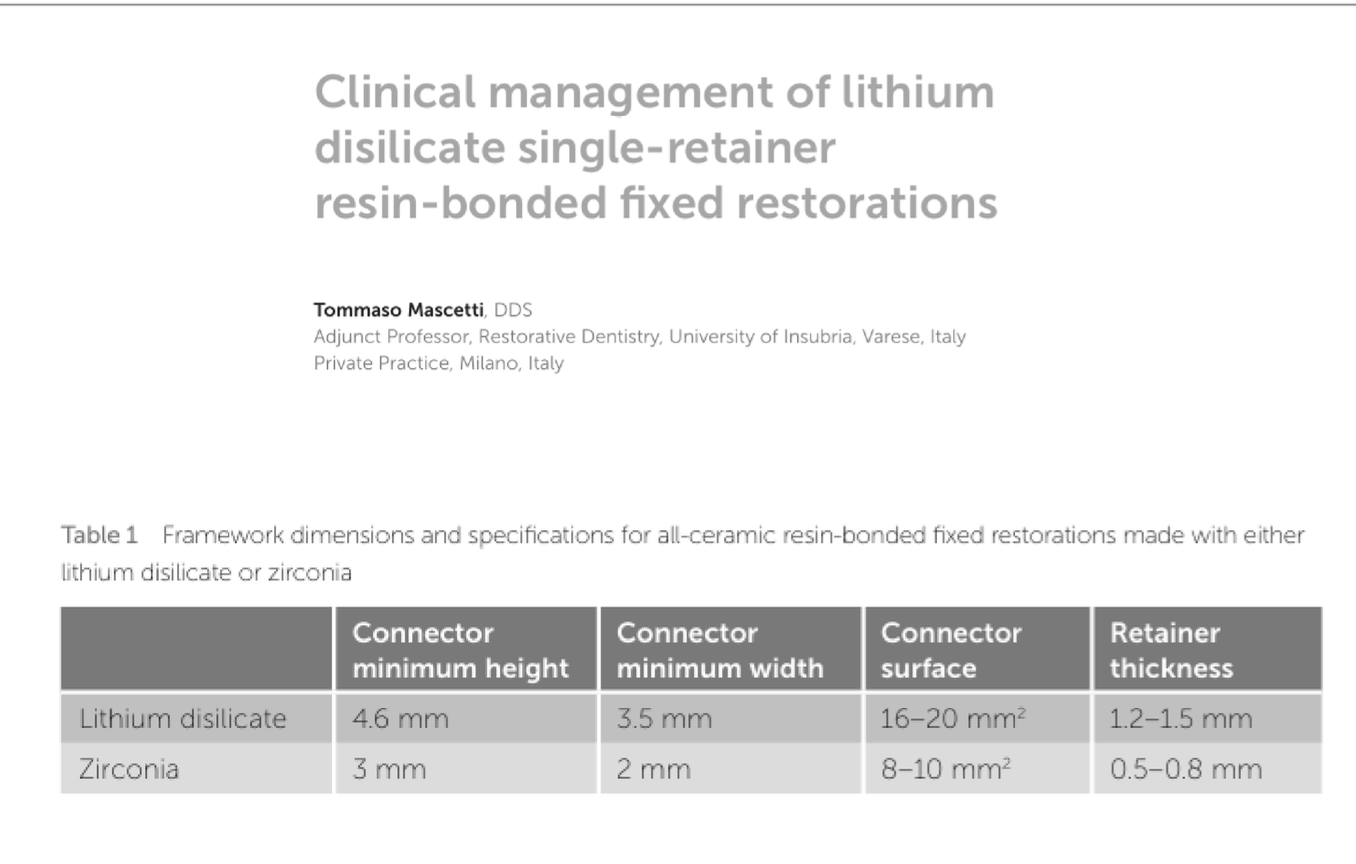
Article by Alquitaibi

Framework dimensions and specifications for all-ceramic resin-bonded fixed restorations made with either lithium disilicate or zirconia
Article by Mainjot
