NURS 125 Eyes, ears, and mouth
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
CN I-olfactory
sensory nerve responsible for smell and plays a key role in the sense of taste
assessment: through identification of odours presented to each nostril while the other nostril is occluded
CN II-Optic
sensory nerve that controls vision, visual acuity, field of vision
involved in the pupillary light response
→ assessment:
visual acuity tested using the Snellen chart for distance vision
colour perception using pseudoisochromatic plates(colour blindness twst)
fundoscopic exam(ophthalmoscope)
CN III-Oculomotor
motor nerve controls movements of the eyeball (up, down, medial) and upper eyelid
Assessment:
Pupil response→ Shine a light into each eye (check for direct and consensual response).
Accommodation→ Ask the patient to focus on a near object (check for pupil constriction).
Eye movement→ Have the patient follow your finger in 6 cardinal directions( draw an H with your finger)
CN IV-trochlear
motor nerve that controls eye movement (downward and inward)
Assessment: Ask the patient to follow your finger as you move it toward their nose (testing downward and inward eye movement).
CN V-trigeminal
sensory: general sensation in face, scalp, corneas, nasal and oral cavities
assessment→ Lightly touch(cotton swap) the forehead, cheeks, and chin on both sides of the face and ask if the sensation is the same on both sides aka “dull/sharp test”
pain and temperature- use cool end of tuning fork
motor function: chewing
assessment→ Ask the patient to clench their teeth while palpating the masseter and temporalis muscles to check for strength
move jaw side to side as examiner attempts to push midline in each direction
CN VI-abducens
motor nerve involves movement of the eye(lateral, outward)
assessment→ Ask the patient to follow your finger as you move it laterally (test for the ability to move the eye outward).
CN VII-facial
motor: facial expressions
raise eyebrows, show teeth
puff cheeks/close lips tight
close eyes tight→ 7 hook(closes the eye)
secretion of saliva
parasympathetic:
lacrimal glands→ ask about dry eyes
salivary glands→ ask about dry mouth
sensory: taste anterior 2/3 of the tongue
external ear sensation→ contracts the stapedius muscle
CN VIII-Vestibulocochlear(auditory)
sensory nerve controlling hearing and balance
observe eyes for nystagmus(rapid, uncontrolled eye movements)
Assessment: Hearing: Perform Rinne and Weber tests with a tuning fork.
perform Romberg test(measures a person’s sense of balance)→ needs proprioception, vision, and vestibular function
whisper test
Balance: Ask if the patient feels any dizziness or unsteadiness.
CN IX-glossopharyngeal
sensory→ taste and sensation from back of tongue
motor→ swallowing and speech
parasympathetic→ saliva secretion
assessment→ Taste on the back 1/3 of the tongue, swallowing, salivation, gag reflex
CN X-vagus
sensory: taste and sensation from epiglottis and pharynx
motor: swallowing and speech
Ask the patient to say "ah" and observe the uvula. It should remain midline
assess palatal arches- damaged side cannot counteract(look for lowered and flattened palatal arch)
parasympathetic→ muscle contraction of thoracic and abdominal organs and secretion of digestive fluids
CN XI-accessory
motor→ head shoulder movement(larger muscle control) e.g. sternocleidomastoid
Shoulder shrug and head turn
Ask the patient to shrug both shoulders against resistance. Also, ask them to turn their head against resistance on each side.
CN XII-hypoglossal
motor→ movements of the tongue, cheek, and jaw
Ask the patient to stick out their tongue. Check for asymmetry, atrophy, or tremors. Ask the patient to move the tongue from side to side.
general survey of eyes and ears
look at the overall impression
observe the skin→ colour, rashes/tags, other
anatomy→ as expected, symmetry
movement→ expected
look at the presence of eyebrows, lashes
look at the skin around the eyes and ears
behaviour→
myopia
a common vision condition where close objects are seen clearly, but distant objects appear blurry, also known as nearsightedness
hyperopia
a vision condition where distant objects are seen clearly, but close objects appear blurry, also known as farsightedness
presbyopia
vision deteriorates with age, making it difficult to focus on close objects.
astigmatism
a common refractive error caused by an irregular shape of the cornea or lens, leading to blurred or distorted vision at all distances
photophobia
sensitivity to light, causing discomfort or pain in bright environments
strabismus
a condition in which the eyes do not properly align with each other, often resulting in double vision or the inability to focus on a single object
diplopia
the perception of two images of a single object, commonly known as double vision
Health History
PERMAFRost
Past medical history
Examination
Radiographs
Medications
Allergies
Family history
Review of systems
Oral conditions
Social history
Treatment history
physical assessment of the eyes
inspection and palpation(only)
inspection: looking into all part of the anatomy from the eyebrow to the pupil
can be uncomfortable so wear a mask
take note of differences in anatomy due to aging e.g. no eyebrows in elderly
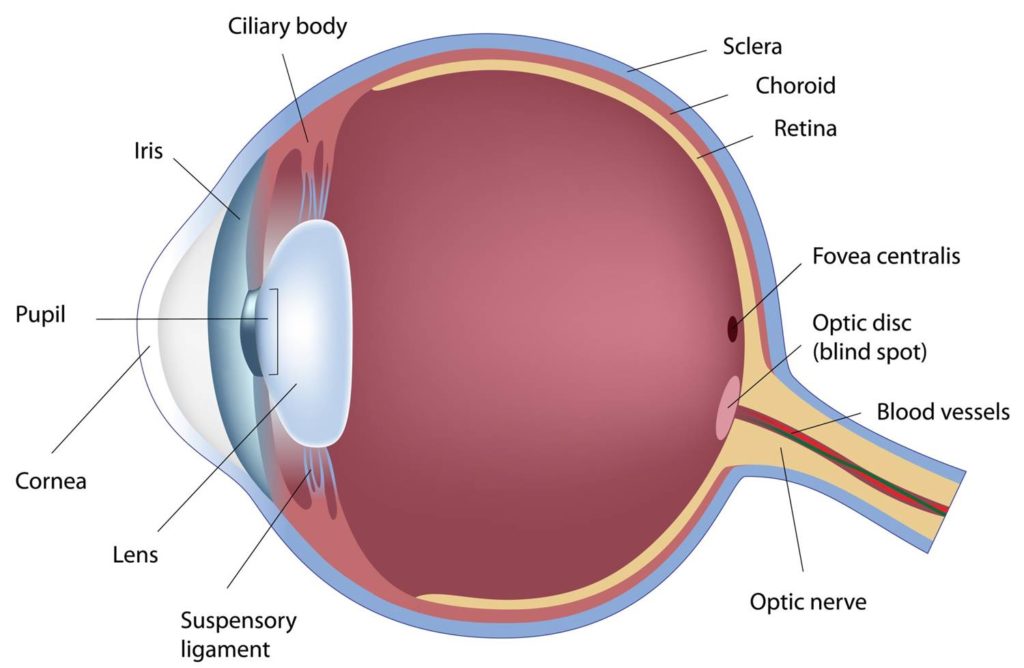
conjunctiva and sclera assessment
conjunctiva→ thin, transparent membrane lining the inner eyelids and covering the sclera
expected: clear, some small blood vessels
Sclera→ white part of the eye
expected- white
Assessment: gently pull down underneath the eyelid with finger pads to inspect sclera and conjunctiva
anisocoria
unequal pupil sizes that can indicate neurological issues or trauma(can be harmless)
miosis
small constricted pupils, eyes are asymmetric, different looking eyelids that can indicate trauma
mydriasis
dilated pupils that can be normal if given eye drops but can also indicate brain injury
arcus senalis
discolouration around the cornea that represents cholesterol deposits that have affected the eye
common in older adults
greater concern in young people
pupillary light response
pupils should respond symmetrically and expected when a light source is introduced
look for direct and consensual response
look at the pupil the light is shinning on as well as opposite eye pupillary response(to make sure pupils are responding as they should)
this test is done with every eye related appointment and on all newborns
visual acuity
tests body and eye anatomy ability to accommodate to see far and near
Snellen test→ measures distance visual acuity
Jaegar test→ measures near vision
Snellen’s test
distance visual acuity that is considered the gold standard
distance from the chart(always 20 feet)
20/20= normal vision
legal blindness is best corrected vision 20/200
The numerator (20) refers to the distance at which the test is conducted (usually 20 feet).
The denominator (20) represents the distance at which a person with normal vision can read the same line of letters.
Jaegar test
measures near vision
chart with letters are placed 14 inches from the eyes
read to smallest letter(i.e. 14/14)
macula
small, central part of the retina in the eye
responsible for sharp, detailed vision needed for activities like reading, driving, and recognizing faces
contains a high concentration of photoreceptor cells (rods and cones), especially cones, which help with color vision and fine details.
Damage to the macula can lead to macular degeneration, affecting central vision.
static and kinetic confrontation
Static confrontation:
examiner holds up a static (non-moving) number of fingers in different areas of the patient’s visual field while one eye is covered
The patient identifies the number to check for blind spots or peripheral vision loss.
Kinetic confrontation:
examiner moves a small object or wiggling fingers from the periphery toward the center while the patient states when they first see movement
This tests the patient’s ability to detect motion and peripheral vision range
red light reflex
the reddish-orange reflection seen in the pupil when light from an ophthalmoscope shines into the eye
It helps check for eye health and detect conditions like cataracts, retinal detachment, or tumors.
A normal red reflex means there are no major blockages in the ey
important screening tool for children(retinoblastoma)
how to perform the red light reflex
Darken the room to make the reflex more visible.
Use an ophthalmoscope and set it to 0 diopters.
Stand about 2 feet away and shine the light into the patient's eyes.
Look for a red or orange glow in both pupils.
If the reflex is white, dim, or absent, further evaluation is needed.
air conduction
how sound travels through the air, entering the ear canal, passing through the eardrum and middle ear, and reaching the inner ear (cochlea) to be processed by the brain
It is the normal way we hear sounds, like voices or music.
most efficient and usual pathway for sound to travel to the inner ear
measured using Rhinne’s test→ place tunning fork on the mastoid process(bone conduction), when patient stops hearing it move the tunning fork towards the ear(air conduction)
Bone conduction(BC)
bypasses the external ear and delivers sound ways/vibrations directly to the inner ear via the skull
conductive hearing loss
caused by blockage in the ear canal or middle ear(wax or fluid)
wax blockage can easily be removed
fluid buildup needs further testing
Conductive Hearing Loss: Bone conduction (BC) is greater than or equal to air conduction (BC ≥ AC).
sensorineural hearing loss
caused by damage to the inner ear, nerve, or brain
common causes→ aging, loud, ototoxic drugs
presbycusis= age related hearing loss
hypertension linked to hearing loss
tinnitus
ringing or noises in the ears
vertigo
type of dizziness related to the inner ear or something else(more detailed assessment)
otalgia
earaches/ ear pain
infections/discharge
otorrhea
Inspection and palpation
inspection: know the anatomy of the ear
notice if something looks different
Palpation:
palpate the lobe for lesions, cysts, etc
triangle fossa, helix→ assess how they bend to ensure cartilage is there(especially young kids)
how to use otoscope in the ear
adult: pull the pinna up and back
infant/child under 3: pull pinna straight down→ pull cartilaginous structure away
bracing technique
used to stabilize the otoscope and prevent injury while examining a patient’s ear.
How to Perform It:
Hold the otoscope like a pencil, using your dominant hand.
Rest the side of your hand or fingers against the patient’s cheek or head to steady your hand.
Gently pull the ear (up and back for adults, down and back for children) to straighten the ear canal.
Insert the otoscope slowly while keeping your hand braced to prevent sudden movement if the patient shifts.
left hand to left ear, opposite hand supporting
whisper test
evaluates for loss of high-frequency sounds and shows the highest specificity for identifying hearing loss
60 cm away from the person, one ear is closed(press gently on tragus), one is open
whisper something(numbers and letters) person should be able to hear clearly in both ears
it is the 1st assessment of hearing, if it fails move onto Weber and Rhine’s test
weber test
tunning fork either 512 or 1024hz vibrated on forehead
normal findings: no lateralization
Conduction hearing loss(CHL)= lateralization to diseased ear
Sensorineural(SNHL)→ lateralization to healthy ear
rinne test
measures better bone conduction vs air conduction
air conduction should be better than bone conduction
tunning fork(512 or 1024 hz) vibrated first in front of ear on the mastoid process
normal finding: better air conduction
CHL→ better bone conduction
SNHL→ cannot be teste
cataract
lens fills up with fluid and plaques
becomes opaque making it difficult to see
can cause blindness
gingivitis
inflammation and infection of the gums
cavities
very small hole that forms on the surface of a tooth
oral cancer
disease resulting from abnormal cell growth in the mouth, lips, tongue or throat
general survey of the mouth
uniform colouring of lips, mouth, and area around the mouth
are there rashes, tags, and tags?
observe tongue movement and teeth
history of present illness
Location
Associated signs and symptoms
Timing
Exposure/environmental factors
Reliving factors
Severity
Nature/quality
Aggravating factors
Patient perspective
significance to the patient
Physical assessment
inspection of the lips, mouth, tongue, ulva, teeth
use tongue depressor to move the cheeks away
look at the inside of the cheeks for lesions, colourations, etc
Expected findings:
ulva should be present
complete upper and lower palate
palpation of the lips(not a lot of palpation is done) with gloved hand
red flags
trauma to the eyes or ears→ e.g. Battle’s sign or raccoon eyes
sudden changes in vision of hearing
fluid leaking from the ears flowing head trauma→ could potentially be Cerebrospinal fluid leaking out