Topic 5: Composition of matter
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
anything that occupies space and has mass
what is matter
defined volume
defined shape
volume of solids is virtually independent of pressure and temperature
what are the key properties of solids
fixed volume
shape depends on the container
volume of liquid is virtually independent of pressure and temperature
what are the key properties of liquids
no fixed volume
no fixed shape
expands to completely fill container
volume of gas is dependent on pressure and temperature
what are the key properties of gases
matter that has a constant composition - all samples of a pure substance have exactly the same makeup and properties
what is a pure substance
composed of two or more types of matter that can be present in varying amounts and be separated by physical changes
what is a mixture
a mixture with uniform composition and properties and appears the same visually throughout
what is a homogenous mixture (solution)
mixture that varies in composition or properties from point to point
what is a heterogenous mixture
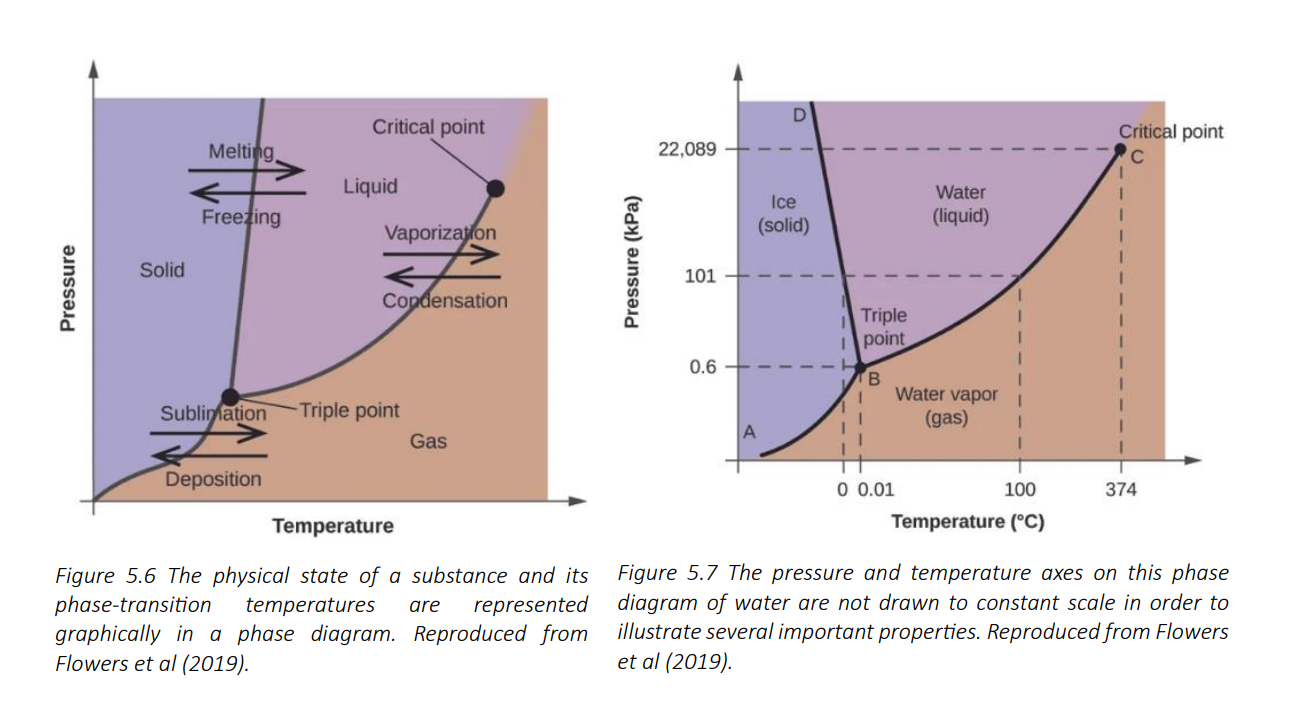
liquid-vapour curve
separates the liquid and gaseous regions of the phase diagram and provides the boiling point at any pressure
solid-vapour curve
indicates the temperatures and pressures at which ice and water vapour are in equilibrium (as shown in fig 5.7)
corresponds to the sublimation/deposition points for water
solid-liquid curve
shows the temperatures and pressures at which ice and liquid water are at equilibrium
represents the melting/freezing point of water
critical point
this is the point of intersection of all three curves
at this point all three phases coexist in equilibrium
at pressures lower than the triple point, water cannot exist as a liquid, regardless of the temperature
describe the different points on a phase diagram
matter is made of elements
elements consist of only one type of tiny particles (atoms) with a characteristic mass
a compound is a mixture of different elements bonded together in a specific mass ratio
what are the observations of Dalton’s atomic theory
the characteristics of an element depend on its type of the smallest unit (atoms)
a compound has unique properties due to its type of atoms and their fixed ratio
chemical changes rearrange atoms but neither create nor destroy them
what are Dalton’s postulates on the atomic theory
All samples of a pure compound contain the same elements in the same proportion by mass
what is the law of fixed proportions
protons (p+)
neutrons (n)
protons and neutrons make up the nucleus
electrons (e-)
what subatomic particles make up atoms
due to the mass of p+ and n in the nucleus
why do atoms have gravitational potential energy
due to the speed of the electrons that orbit the nucleus
why do atoms have kinetic energy
innermost shell - up to 2e-
outermost shell - up to 8e-
what are the occupancy limits of electron shells
all atoms are energetically most stable when they have 8 valence electrons as 4 pairs
what is the octet rule
shiny
conduct heat and electricity
exist in different oxidations states
what are some properties of metals
alkali metals
what type of elements exist in group 1
alkaline earth metals
what type of elements exist in group 2
pnictogens
what type of elements exist in group 15
chalcogens
what type of elements exist in group 16
halogens
what type of elements exist in group 17
noble gases
what type of elements exist in group 18
highest energy level shell containing electrons
what is a valence shell/band
unoccupied energy levels
what is a conduction shell/band
the energy level of the valence shell and the number of valence electrons
what determines the characteristics of a material
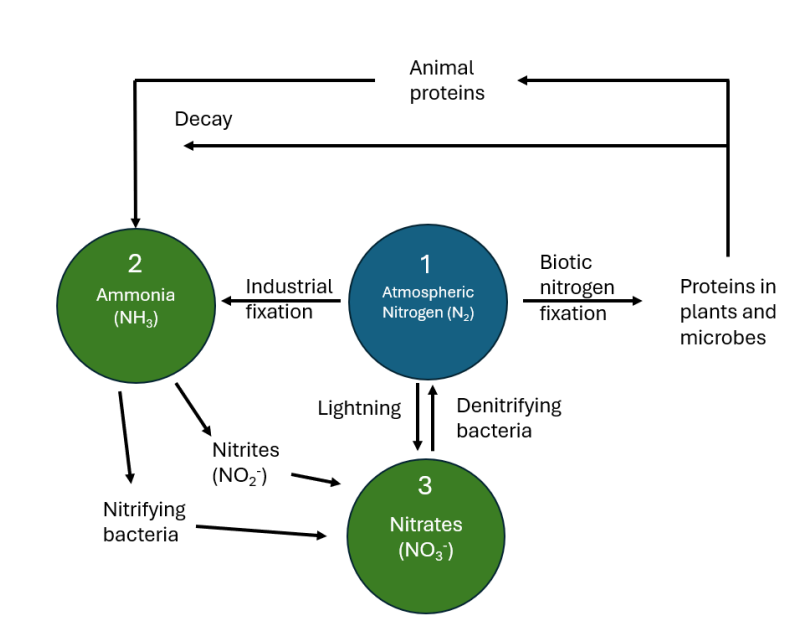
N2 gas from the atmosphere is ‘fixed’ either by industrial processes to ammonia (NH3) directly or nitrogen fixing bacteria for uptake by plants or microbes or through lightning to nitrates
plants source nitrogen as either nitrate ions, ammonium ions, or urea, then animals source their nitrogen from plants or other animals
proteins made by animals or plants are either metabolised or excreted and ultimately experience decay which then leads them to be further metabolised into ammonia, NH3
under atmospheric conditions, ammonia is converted into nitrates, NO3-, they are then available to the root systems of plants
describe the nitrogen cycle