ACC2400
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Why is AIS important?
AIS looks at how businesses create sales to generate data that can be used for decision-making and improving operational efficiency. It provides a framework for collecting, processing, and analysing financial data, which aids in strategic planning and enhances overall business performance.
What is an information system?
An information system is a coordinated set of components for collecting, storing, and processing data, enabling the management and dissemination of information to support decision-making in an organisation.
List how data should be portrayed or stored.
Access restricted
Accurate
Available
Reputable
Complete
Concise
Consistent
current
objective
relevant
timely
useable
understandable
verifiable
What is the value of information?
The benefit produced by the information minus the cost of producing it.
What is a business process?
A set of activities and tasks that, once completed, will accomplish an organisational goal.
It involves the transformation of inputs into outputs to create value.
Involves various department working together
How does AIS add value to an organisation?
improving quality and reducing cost of goods/ services
sharing knowledge
improving effectiveness and efficiency of supply chain
improving internal control structure
How to improve data control for input data?
Using prenumbered source documents
Assign a sequential number to each new transaction = prevent misplacement and completeness
Approving or verifying a transaction = make sure inventory being sold is not out of stock
Checking the customer's credit before making a credit sales
List the type of coding for data storage
Systematic assignment of numbers or letters to items to classify and organise them
Sequence codes = numbered consecutively
Block code = blocks of numbers are reserved for specific categories of data (example product code)
Group codes = two or more subgroup of digits used to code an item
Mnemonic codes = derived from description of the item
List the type of data processing activities
Creating new data records
Reading, retrieving or viewing existing data
Updating previously stored data
Deleting data
What is batch processing?
Updating done periodically
Cheaper and more efficient
Only for applications that do not need frequent updates
time gap between when the transaction occurs and when it is recorded
What is real time processing?
Update as each transaction occurs
Information is always current = increase decision making usefulness
More accurate = data can be corrected in real time or refused
Provide significant competitive advantage
What is online batch?
The transaction occurs and is recorded in a temporary file
All data in temporary data is used to update master data later
How are information output used?
Reports are used by employees to control operational activities and by managers to make decision and to formulate business strategies
External users = evaluate company profitability, judge creditworthiness, or comply with regulatory requirements
What are the control objectives?
Safeguard assets = prevent or detect unauthorised acquisition, use or disposition
Provide accurate and reliable information
Prepare financial reports in accordance with established criteria
Promote and improve operational efficiency
Encourage adherence to managerial policies
Comply with applicable laws and regulations
What is master data?
permanent accounts that carry across time and are connected to transactions
provide detail to support transactions
What are the output type?
document = record of transaction
report = summary of data
query = uses data to answer specific questions
What is an ERP system?
Integrate all aspects of an organisation's activities
It is modularised which catered to company's specific needs
Collects, process and stores data and provides the information managers and external parties need to assess the company
Centralised database to share information across business processes and coordinate activities
data is captured once and available to the entire organisation
data can be shared across organisation
List the advantages and disadvantages of an ERP system
Advantages:
Provides an integrated, enterprise-wide, single view of the organisation's data and financial situation
Data input is captured or keyed once
Management gains greater visibility into every area of the enterprise
Better access control
Standardised across business units
Disadvantages:
Cost
Amount of time required = high risk of project failure due to the time taken to fully implement an ERP system
Changes to business processes
Complexity
define COBIT 2019
General model for how organisations can manage their technology and think about the risk of technology
Internationally used framework
Framework for the governance and management of IT
Allows management to achieve objectives
Managing information technology throughout the entire organisation
What are the function of application control?
Preventive controls deter problems before they arise
Detective controls discover problems that are not prevented
Corrective controls identify and correct problems
Define internal control
processes implemented to provide reasonable assurance that the control objectives will be achieved.
What is general control? list some examples.
make sure an organisation’s information system and control environment is well managed
Examples:
policies on hiring employees
password/ system access control
procedure to follow when acquiring / installing new software
restricting access to physical IT resources
What is application control?
prevent, detect, and correction transaction errors and fraud in application program
What are the focus of application control?
authorisation, accuracy, completeness, and validity of data inputs
processing data correctly and in a timely way
outputs are accurate and complete
audit trails to track data through input, process and output stage
What is the aim of time based model?
uses a combination of preventive, detective and corrective controls
mix of controls should last long enough for timely detection of attack and responses to the attack before information is compromised
P>D+R = larger the gaps = the more effective the control system
P = time needed to break through preventive control
D = time taken to DETECT an attack
R = time taken to response to attack and prevent it
What is system development?
Process of defining, designing, testing and implementing a new software application or program
What is goal congruence?
When subsystems achieve its goal while contributing the organisation’s goal
List control frameworks
Control objectives for Information and Related Technology (COBIT)
Committee of Sponsoring Organisation (COSO)
Internal control framework
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
What does COBIT do?
Allows management to benchmark security and control practices of IT environments.
Allows users to be assured that adequate IT security and control exist
Allows auditors to substantiate their internal control opinions and to advise on security control matters
What are the key principles of COBIT?
Meeting stakeholder needs = create information system that adds value to its stakeholders
Covering the enterprise end-to-end = integrates all IT functions and processes into companywide functions and processes
Applying a single, integrated framework = align at high level with other standards and framework
Enabling a holistic approach = result in effective governance and management of all IT functions
Separating governance from management
Define COSO
Defines internal control
provides guidance for evaluating and enhancing Internal Control systems
What are the components of COSO?
Control environment
Risk Assessment
Control activities
Information and Communication
Monitoring
What are the components of COSO ERM Cube?
Internal Environment
Objective settings
Event identification
Risk Assessment
Risk response
Control activities
Information and Communication
Monitoring
Explain Internal environment
Management philosophy, style, and risk appetite
Commitment to integrity, ethical values, and competence
Internal oversight by Board of Directors
Organisational structure
Assign authority and responsibility
HR attracts, develops, and retains competent people
External influences
It is the idea of:
Sending the messages
Getting the right people
Having the right procedures
Up to managers to put these in place
Explain Objective setting
The board sets objectives that support organisation strategies and missions
Are consistent with risk appetite --> how much risk are we willing to accept
Explain Event identification
What internal and external things could impact the achievement of objectives?
Consider operational risks inside the business and external factors
Explain Risk assessment and Risk response
Assess inherent risk, develop a response, assess residual risk
Estimate risk likelihood and assess impact
Identify potential control activities for the risk
Calculate the costs and benefits of the control activities
Decide on risk response – Accept, Avoid, Share, Reduce (implement control activity)
Controls are in place because we know it could go wrong
Expected loss = impact x likelihood
Explain Control activities
Policies, procedures and rules that provide reasonable assurance that control objectives are met and risk responses are carried out
Having segregation of accounting duties such as authorisation, recording and custody --> different system duties
Explain information and communication
Information required to do their job
Information available and accurate for management
People should know how transactions are performed and recorded
Internal and external communications
Employees need to understand their responsibilities
Explain monitoring
Continuous assessment of internal control system to assess performance and identify and deficiencies
Compare performances
Potential risks
Check if controls are working
What are some of the controls used to protect resources?
Physical security
Process controls
IT solutions
List the physical security that can be implemented
Entry points to buildings
Restrict access to computer equipment and monitor access attempts
Access to networks
Physical devices
What are some control user access?
Authentication control:
The process of verifying the identity of the person attempting to access the system
Types of credential:
Something the person knows
Something the person has
Some physical or behavioural characteristics
Authorisation control:
The process of restricting access of authenticated users to specific portions of the system and limit what actions they are permitted to perform.
Define user access control
Implement a sets of control that protect sensitive information from unauthorised use and access by employees
What are some IT solutions?
Anti-Malware controls
Network Access
Device and software Hardware controls
Encryption
List ways that can be used to detect attacks
Log analysis:
The process of examining logs to identify evidence of attack
Intrusion detecting system:
Comparing observed traffic to its rulebase
Produces warning alerts when it detects a suspicion pattern of network traffic
Honeypots:
A decoy system
Allow company to monitor and intervene when appropriate
Continuous monitoring:
Timely identify potential problems and identify opportunity to improve existing controls
What does penetration testing do?
Provides rigorous way to test the effectiveness of the organisation's information security
Provides data about the effectiveness of the organisation's ability to detect and response
What is an ethical dilemma?
A person must decide the best choice of action
Ethic is guided by morals, law and policies
How human should live or related to each other
Standards used by members to decide the right course of action
APESB code of ethics is mandatory for all members of the accounting profession
What are ethical theories?
help decide the best course of action
Derive into consequentialist and non-consequentialist theories
Define consequentialist theories
Focus on the outcome or result of a decision
Produces good outcome = can be seen as ethical
Utilitarianism = maximise the society as a whole rather than individuals
Define non-consequentialist theories
Focus on the means of generating the outcome rather than the outcome itself
Right in themselves rather than right in a consequence
On the process of achieving the outcome
Emphasis on duties, rules and obligations
What are the APES code of conduct?

What is corporate governance framework?
the framework of rules, relationships, systems and processes within and by which authority is exercised and controlled within corporations
What are they doing to achieve their goals
How do they manage risks
How do they promote ethical behaviour
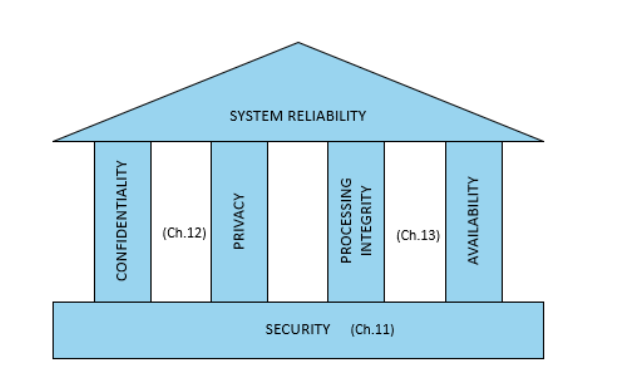
What makes up trust service framework?
It is made up of confidentiality, privacy, processing integrity and availability.
These pillars allow business data or information to be protected from unauthorised access. It also ensures that the data is accurate and complete, available to meet operation and contractual obligations
Information security is the foundation of system reliability
reliable systems are available to use whenever needed
What is the responsibility of auditor for fraud?
To identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial report due to the fraud
To obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding the assessed risks of misstatement due to fraud
To respond appropriately to fraud
What are the values of data?
Data is key to the business process and can generate value
The importance and social impact of personal data places obligations on organisations to protect data
Complying with regulations requires a cost-benefit approach
Recognise that data breaches impact people and their livelihood
Customers and other parties entrust their data to the business
There is an ethical and moral obligation to protect the data
What makes up trust services framework and information reliability?
Accurate: details of transactions and/or events that are recorded in system reflect what actually happened
Complete: All transactions and/or events that are recorded in the information system
Valid: Only transactions and/or events that actually happened / assets or liabilities that actually exist should be recorded in the information system
Authorised: Transactions and/or events are approved and carried out by people with suitable authority and information is accessed and used in approved ways
List some input controls
field check
sign check
limit check
range check
size check
completeness check
validity check
reasonableness check
check digit verification
List some processing controls
Data matching
File labels checking
recalculating batch totals
cross-footing balance test
zero balance test
write protection mechanisms
Concurrent update controls
List some output controls
User review of outputs
Reconciliation procedures
external data reconciliation
Data transmission control
What are the type of recovery plan of a business?
Disaster recovery plan = outlines procedure to restore an organisation’s IT capability in the event its data centre is destroyed
Business Continuity plan = specifies how to resume all business processes in the event of a major calamity
What are the four data analytic techniques?
Descriptive analytics
Diagnostic analytics
predictive analytics
prescriptive analytics
Define descriptive analytics
information that results from the examination of data to understand the past
It uses exploratory data anlysis techniques = explores data without testing formal models or hypothesis
Define Diagnostic analytics
Build on descriptive analytics
answer the question “why did this happen?”
Employ confirmatory data analysis techniques = test a hypothesis and provides statistical measures of the likelihood that the evidence refutes or supports a hypothesis
Define Predictive analytics
Information that results from analyse that focus on predicting the future
Analysing historical data to manifest themselves in the future
Define Prescriptive analytics
Information that results from analyses to provide a recommendation what should happen
“what should be done?”
Programmed actions a system can take based on predictive analytics results
What are the design principles for high quality visualisations?
Simplifying the representation of data
Emphasising what is important
Representing the data ethically = avoid data deception
What is the importance of documentation?
Depicting how the system works
Training users
Designing new system
Controlling system development and maintenance costs
Standardising communication with others
Auditing AIS
Documenting business process
Why do accountants need to understand documentation?
Understand how system works
Evaluate the strength and weakness of a company's internal control
To determine if a proposed system meets the needs of its users
Read documentation to follow audit trail
Auditing responsibilities
Demonstrate their understanding of a system internal controls
What is a flow chart?
Describe an information system:
Inputs and Outputs
Information activities (processing data)
Data storage
Data flows
Decision steps
What are the types of flow charts?
Document
System
program
Describe a document flow chart
Show the flow of documents and information between departments or areas of responsibility
Separation of duties between management
Describe a system flow chart
Depicts relationship among system inputs, processing and outputs (data processing cycle for a process)
Describe a program flow chart
Illustrates the sequence of logical operations performed by a computer in executing a program
What is a business process program?
Visual way to represent the steps or activities in a business process
Easily understood of what takes place in it
Interactions between entities and within an entity
What is a data flow diagram?
Focuses on data flow for processes, sources and destination of the data, and data storage
Describe the logical nature of a system —> what tasks the system are doing
What are the pros and cons of a data flow diagram?
Pros:
Promote quick and relatively easy project code development
Method is easy to learn
Easy to read
Cons:
DFDs for large systems can become cumbersome difficult to translate and read, and time consuming to construc
What are the types of data flow diagram levels?
Context diagram:
Highest level (most general)
purpose: show inputs and outputs of the system
Level-0:
purpose: shows all major activity steps of a system
Characteristics: processes are labeled 1.0,2.0 and so on
Level-1:
purpose: show one major activity divided into sub-activities
characteristics: processes are labeled 1.1, 1.2 and so on
Possible errors with data flow diagram
Black hole: only input flows
Miracle: only output flows
gray hole: insufficient inputs to produce what is needed
Tardis: number process is wrong
Magic: a file that moves by itself from one data store to another
Break and enter: no direct data flow between 2 sources of destination
Use correct symbols and terminologies
What are the typical logical process?
Capture: exists if processing needed to record transaction in a format suitable for internal processing
validate: verifying, checking
Execute: goods shipped, generate output
Why is the revenue cycle important?
Maintain and keep a check on the cash flow of the organisation
Useful to maintain a steady stream of income for the business
What is a revenue cycle?
A set of exchange transaction contracts between the firm and its customer
Providing goods or services
Collecting cash payments
To provide the right product in the right place at the right time for the right price
How can the objective of revenue cycle be achieved?
Effectively conduct, record and monitor sales of goods and services
To arrange the prompt supply of goods and services
To ensure payments for goods and services are correctly received, recorded and banked
What are the key decision in a revenue cycle?
Operational levels:
Respond to customer's request and inquires
Calculate inventory availability
Select good delivery method
Strategy-level:
Price setting
Sales return and warranty policies
Provision of customer credit facilities
Cash collection policies and procedures
What are the business activities in a revenue cycle?
sales order entry
shipping
billing and accounts receivable
cash collection
What are the general threats and controls for revenue cycle?
Inaccurate or invalid master data
Data processing integrity controls
Restrict access to master data
Review of all changes to master data
2. Unauthorised disclosure of sensitive information
Access controls
Encryption
Tokenization
Loss or destruction of master data
Backup and disaster recovery procedure
Poor performance
Managerial reports
What is the primary objective of the expenditure cycle?
Minimise the total cost of acquiring and maintaining inventory, supplies and various of services the organisation needs to function
What kind of business decisions could be made in an expenditure cycle?
Strategic level decision:
Made by senior management
Include creation of policies about purchasing supplies
Operational level decision:
Determining the optimal level of inventory and supplies to carry
Which supplier provide the best quality and service at the best price
Evaluate the performance of suppliers
What are four basic business activities performed in an expenditure cycle?
Ordering
Receiving
approving supplier invoices
cash disbursements
What are the general EC threats?
Inaccurate or invalid master data
Unauthorised disclosure of sensitive information
loss or destruction of data
poor performance
What are some controls for EC threats?
Data processing integrity control
Restriction of access to master data
Reviewing of all changes to master data
Access control
Encryption
Backup and disaster recovery procedure
Managerial reports
What are the key activities of the ordering process?
Identify a need for items/ services to be purchased
Prepare a request for purchase
Select the supplier
Send purchase order to supplier
Purchase requisition (PR) sent to Purchasing department (PD)
PD raises purchase order (PO) (legal contract)
Evaluate suppliers and process the purchase order
List some of the threats in ordering process
stockout/excess inventory
purchasing items not needed
purchasing items at inflated price
purchasing goods of inferior quality
unreliable suppliers
purchasing from unauthorised suppliers
List some of the controls in ordering process
Use barcode/ RFID tags
Review and approve the purchase requisition
Review purchase orders
Track and monitor product quality
Maintain a list of approved suppliers
What are the key activities of a receiving process?
Delivery arrives
Verify the delivery
Record details of the delivery
Prepare receiving report
Send goods to warehouse
What are the key activities in approving supplier invoice?
Supplier invoice arrives
Verify invoice is valid
Update accounts payable
What are the key activities in cash disbursement?
Identifying accounts payable that are due to be paid
Prepare payment details
Approve payment
Make payment
Record payment details
What is program evaluation and review technique (PERT)?
Depicts all project activities that require time and resource with completion estimates
What is a Gantt chart?
bar chart that organises activities on the left hand side and project time schedule with a bar drawn to show the progress to date for a particular activity
What are the types of system testing?
Walk-throughs : step by step review
Processing test data : test all valid transactions and error conditions
Acceptance tests: use copies of real data