1.02 Bifocal lenses
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is the most common type of bifocal and how does it work
Solid plastic bifocals
The segment will be on the front surface
The rear surface will be powered to give the necessary prescription
Types of segment construction
Solid
Fused
Cemented (bonded)
Materials used for lenses
Glass
Plastic
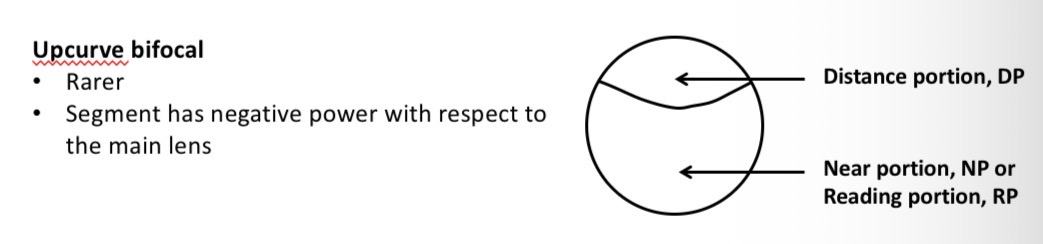
What is an Upcurve segment type
A small relatively negative segment is aded to a lens that corrects for near vision
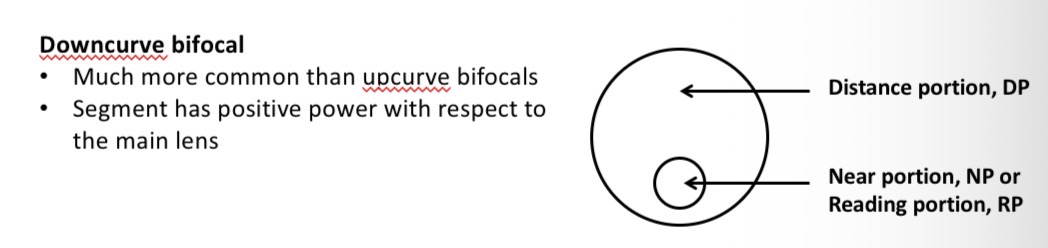
What is a downcurve segment type
A relatively positive segment is (usually) added to the lower part of a distance vision lens to correct for near vision
Most common
What are the different types of segment shapes
Round
Flat top/ straight top/ D segment
Curved top/ C segment
Ribbon segment/ B segment
Executive/ E style
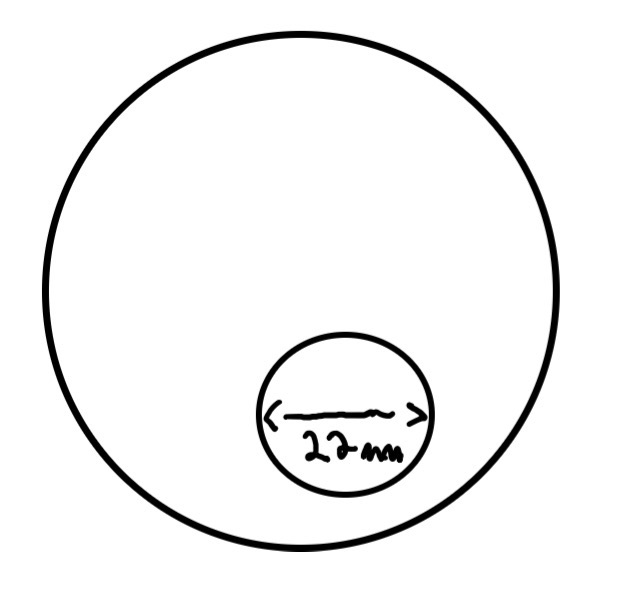
What does a round segment look like
22 refers to the diameter of the segment in mm
What does a D segment look like
The segment width in mm
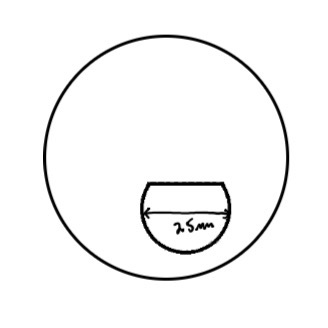
What does a C segment look like
Why is a C segment better than D segment bifocal
C segment provides a slightly better cosmetic result than D
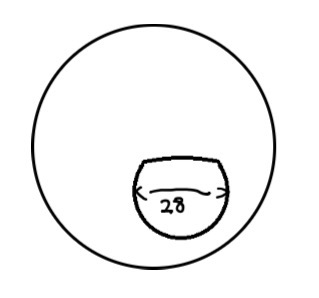
What does a B segment look like
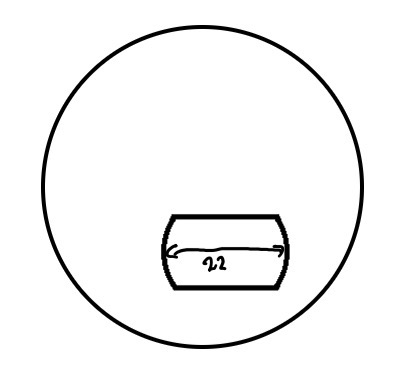
What does an E style look like
Problem with E style bifocals
Lens can be very thick
Even for low prescriptions
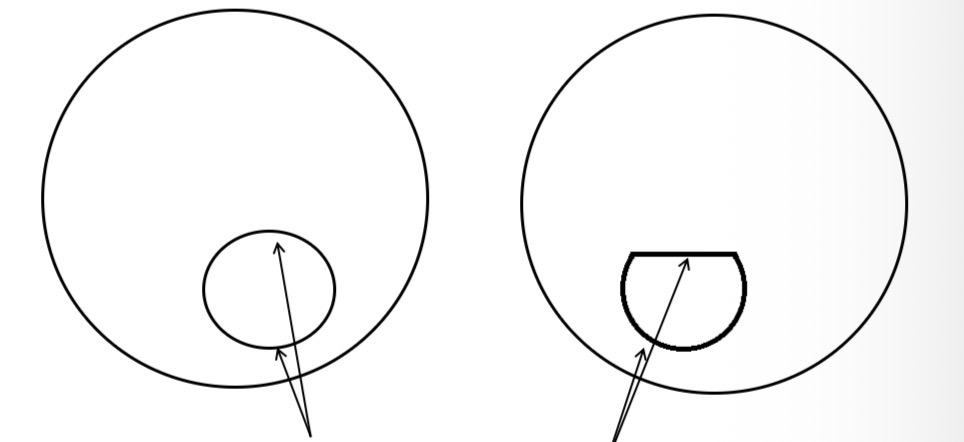
What is the boundary between 2 adjacent portions of a multifocal or lenticular lens called
Dividing line
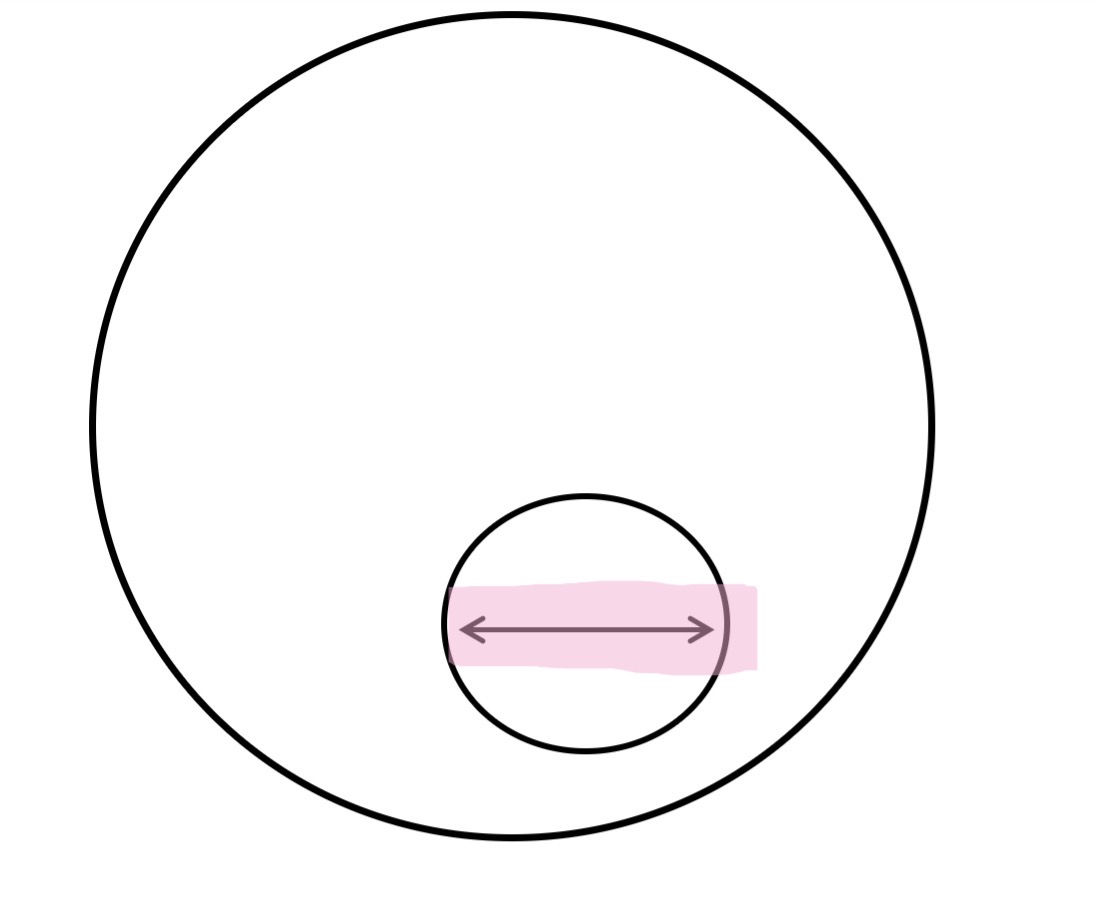
What is this
Segment diameter
For segments were the dividing line is circular - the diameter of the circle of which the boundary of the finished segment forms a part
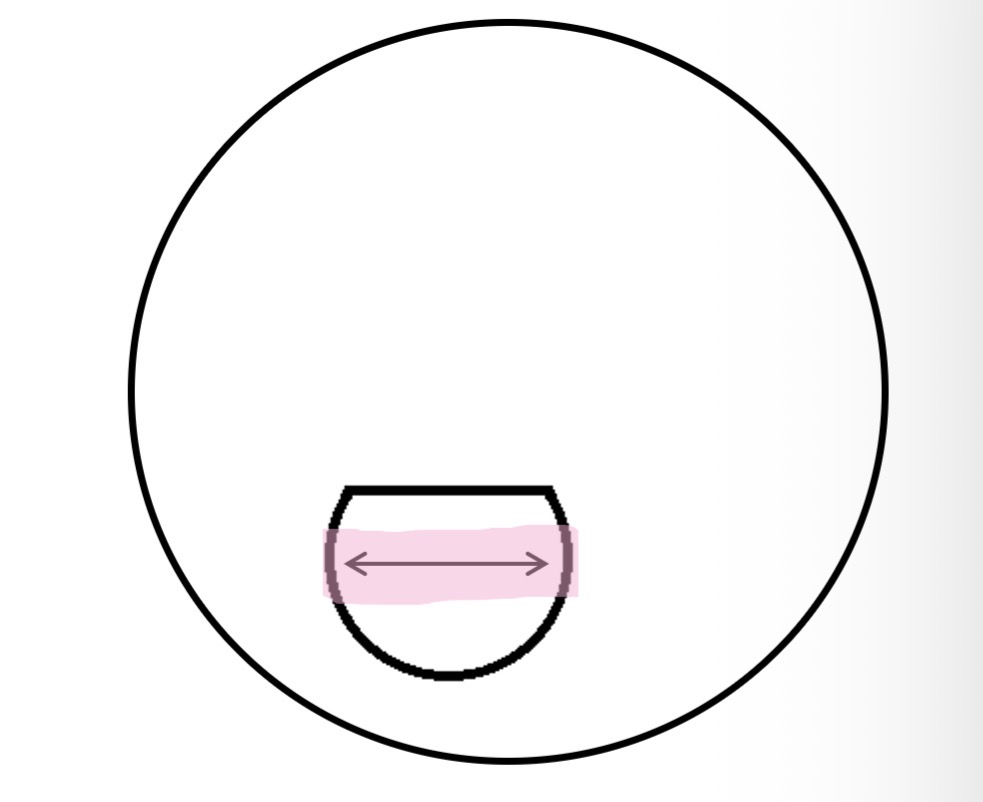
What is this
Segment width
For non circular segments - the maximum horizontal dimension of the segment
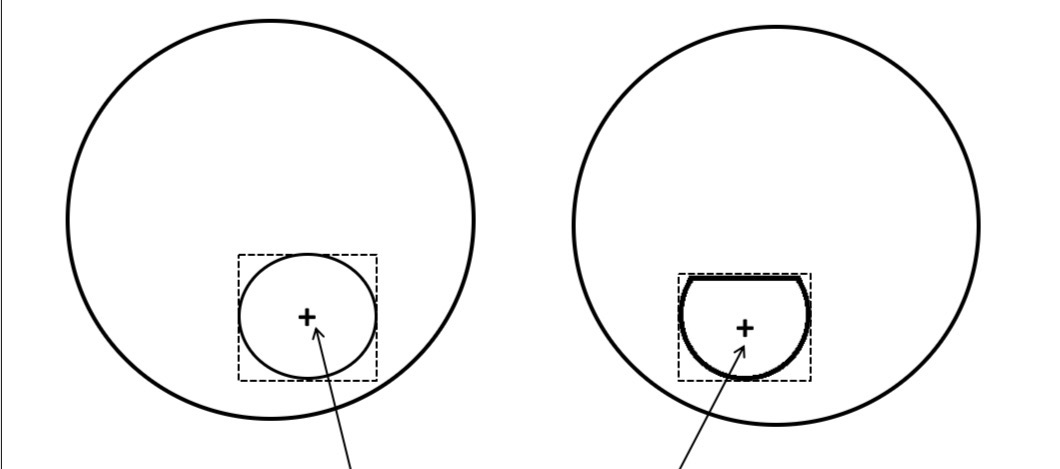
What is this
The segment centre, S
Boxed centre of the rectangle formed by the horizontal and vertical tangers to the segment dividing line, or the lens periphery if the segment extends to the lens edge
Note the segment centre and the near optical centre may be at different points
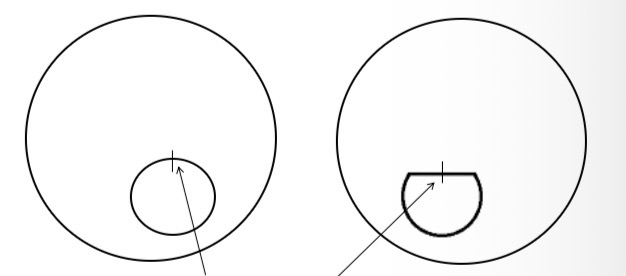
What is this
Segment extreme point, s

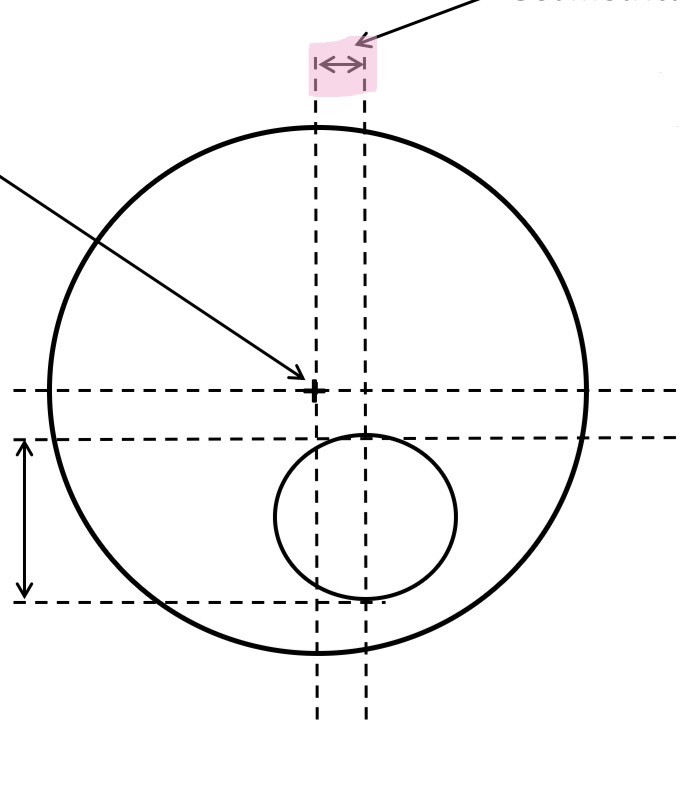
What is this
Geometrical inset
Distance between vertical lines through the distance centratikn point and the midpoint of kf the segment (segment extreme point)
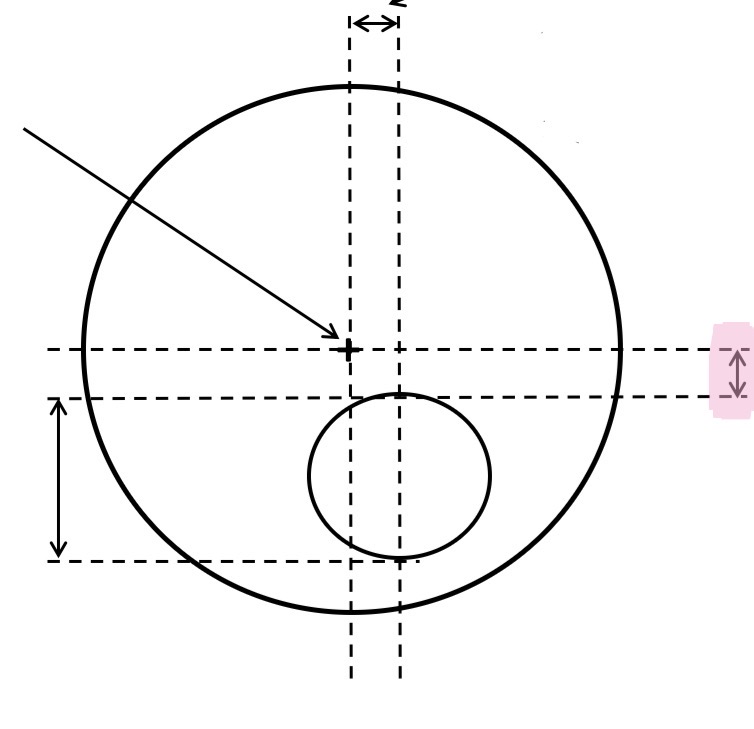
What is this
Vertical segment displacement. Segment drop.
Vertical distance between the distance optical centre and the segment extreme point
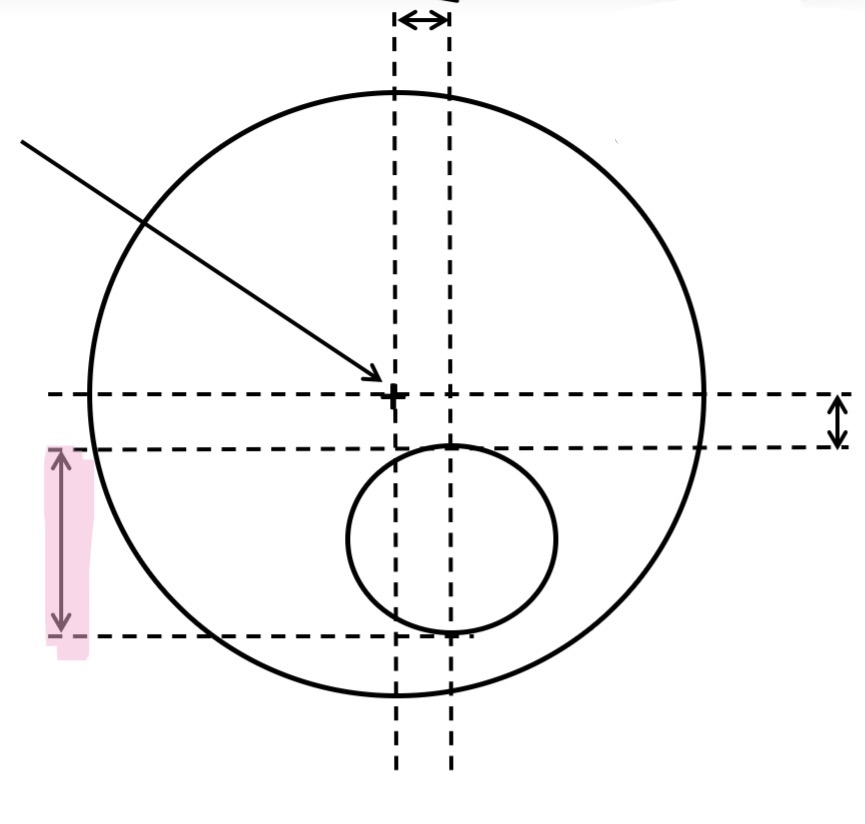
What is this
Segment depth
Maximum vertical dimension of the segment if a semi finished lens, measured through the segment extreme point
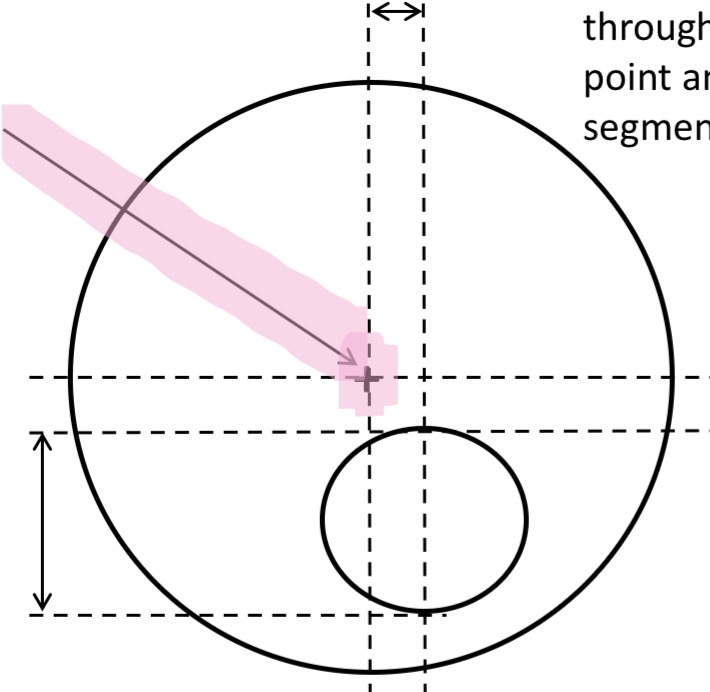
What is this
Distance centration point, P
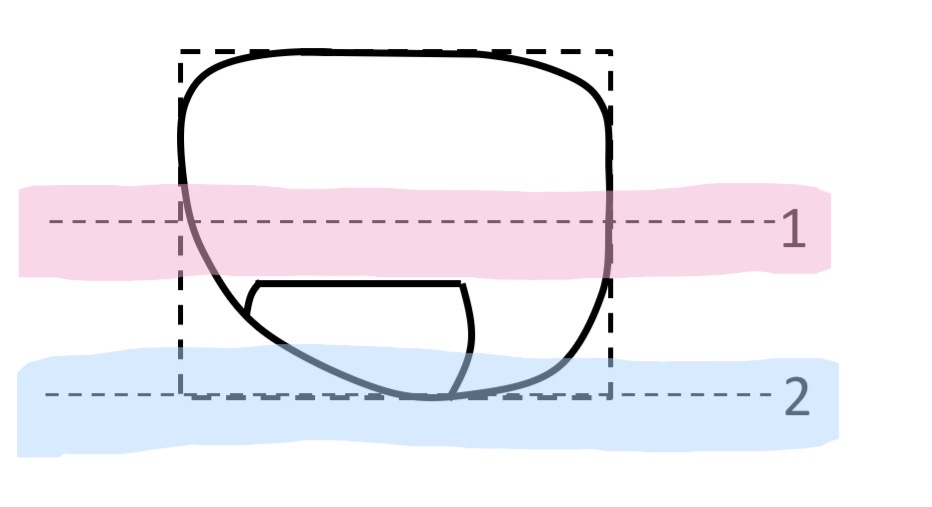
What are these
1 - horizontal centre line
2 - horizontal tangent to the peak of the bevel of the edge of the lens at its lowest point
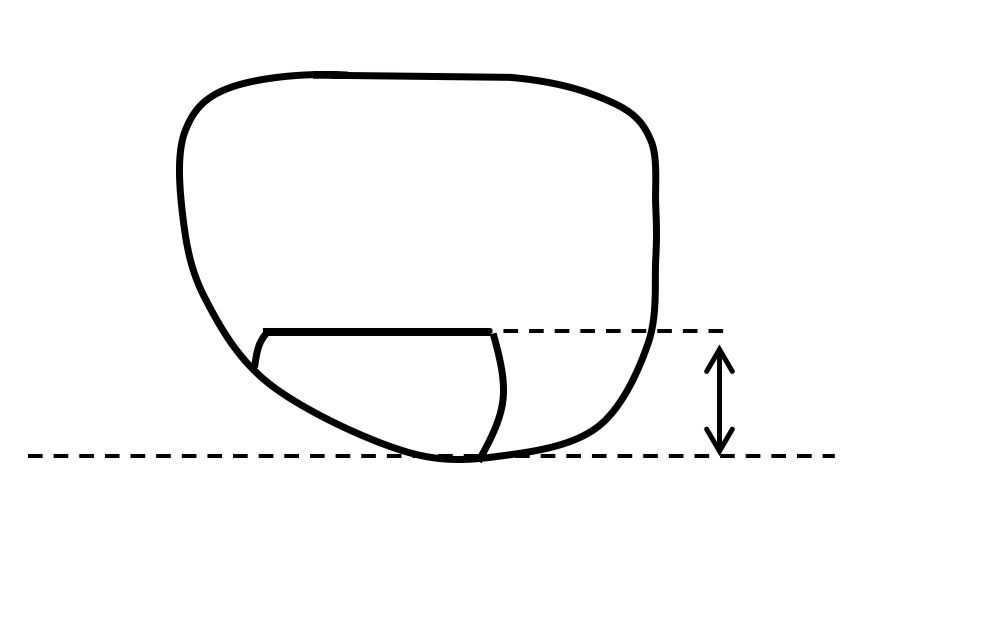
What is this
Segment extreme point height (seg height)
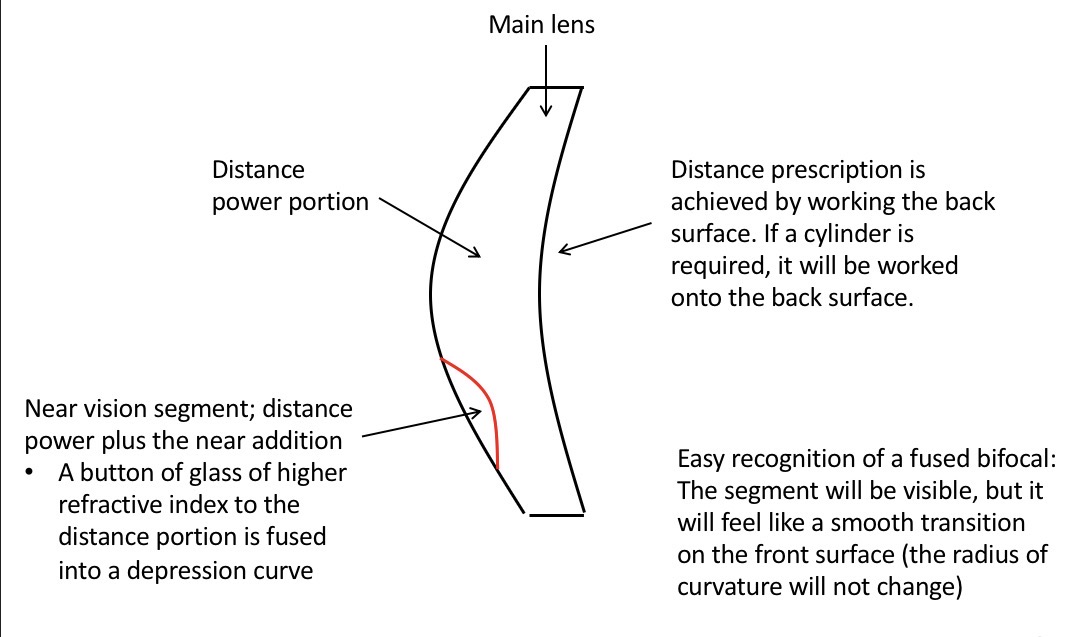
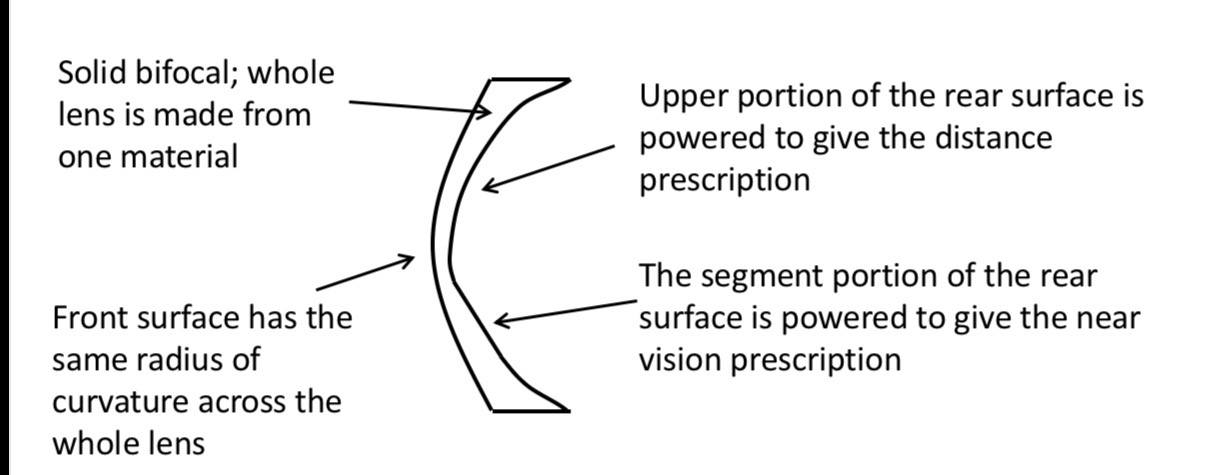
Bifocal basic structure -how is distance and near vision achieved
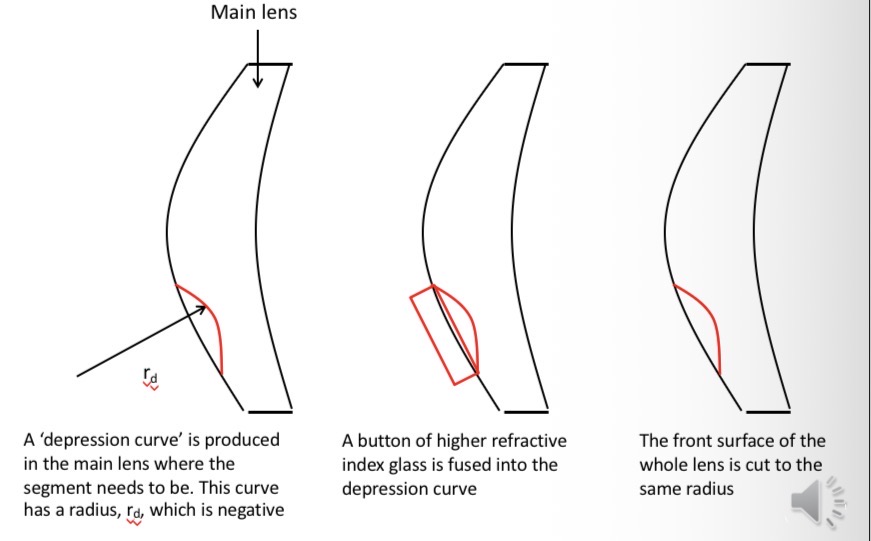
Distance Rx is worked into the back surface.
Near vision segment is the distance power plus the near addition- it is a button of glass of higher refracrive index to the distance portion which is fused into a depression curve
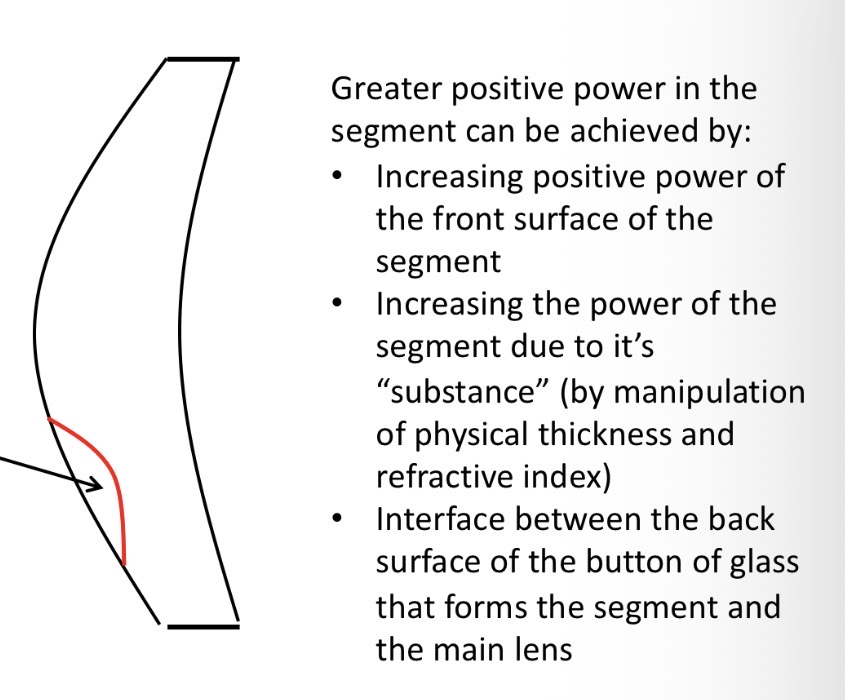
how can we get a greater positive power in the segment
Basic construction of a fused bifocal
What is a semi finished lens
A lens with the front surface prepared and the near addition determined, but the rear surface needs to be worked to get the distance prescription
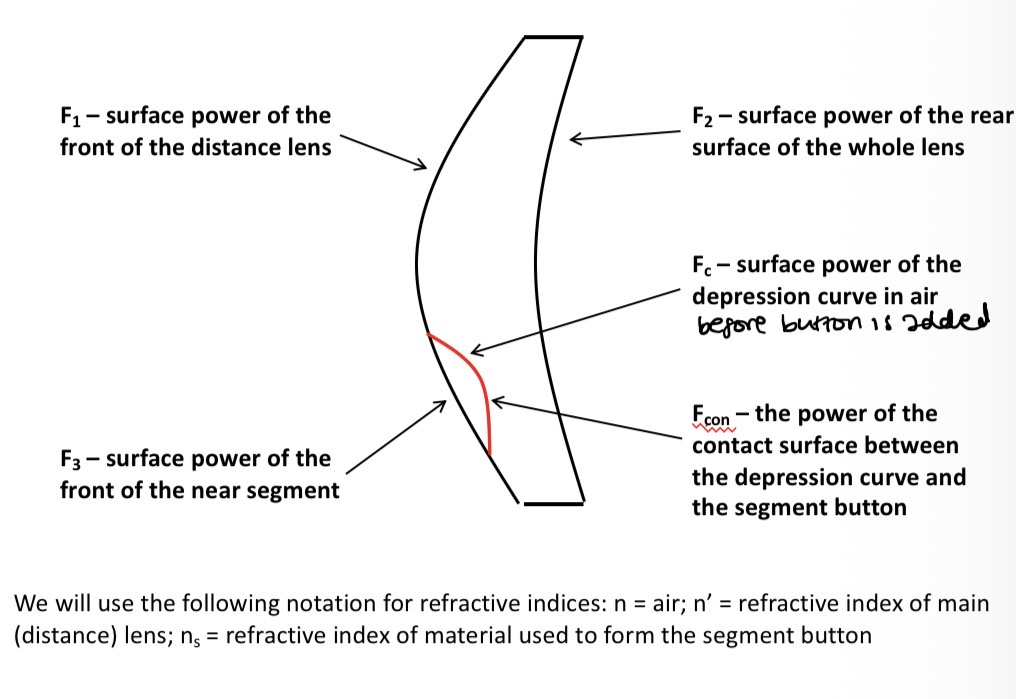
Bifocal surface notations (eg F1)
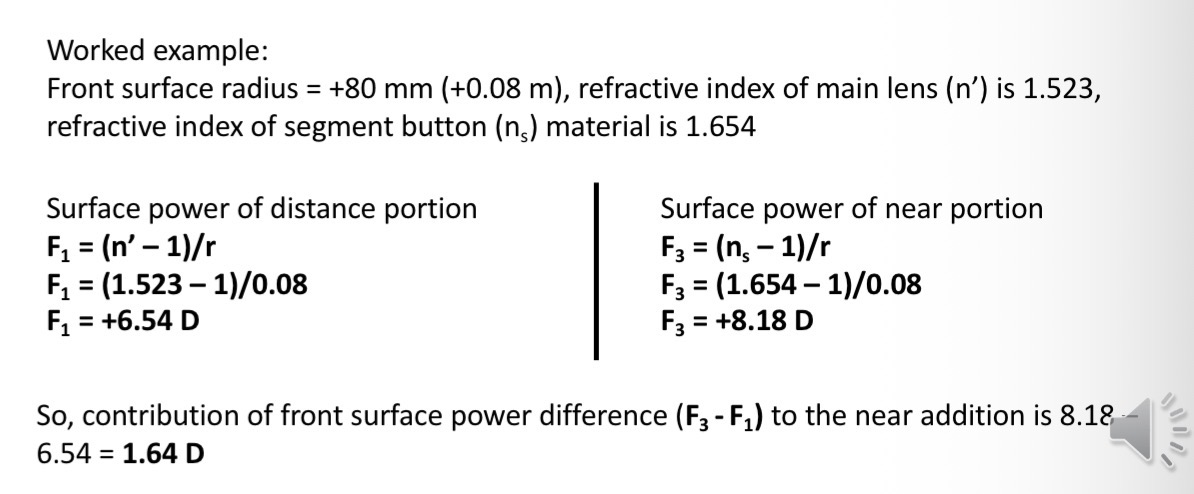
How is the near addition acheived
Increased positive power of the front surface due to the higher refracrive index of the segment
Radius of the front surface of the segment is the same as the distance portion
The button of glass is fused into the depression curve and surfaced
Front surface power formula
F = (n’ - 1)/r
How does Front surface power formula prove near segment is more positive
F = (n’ - 1)/r
Near and distance have the same radius
Near has a higher refractive index
If the segment is thicker would this give a higher or lower positive power
The thicker the segment the higher the positive power
Rear surface power formula
F = ( 1 - n’ ) / r
Calculating the contact surface effect
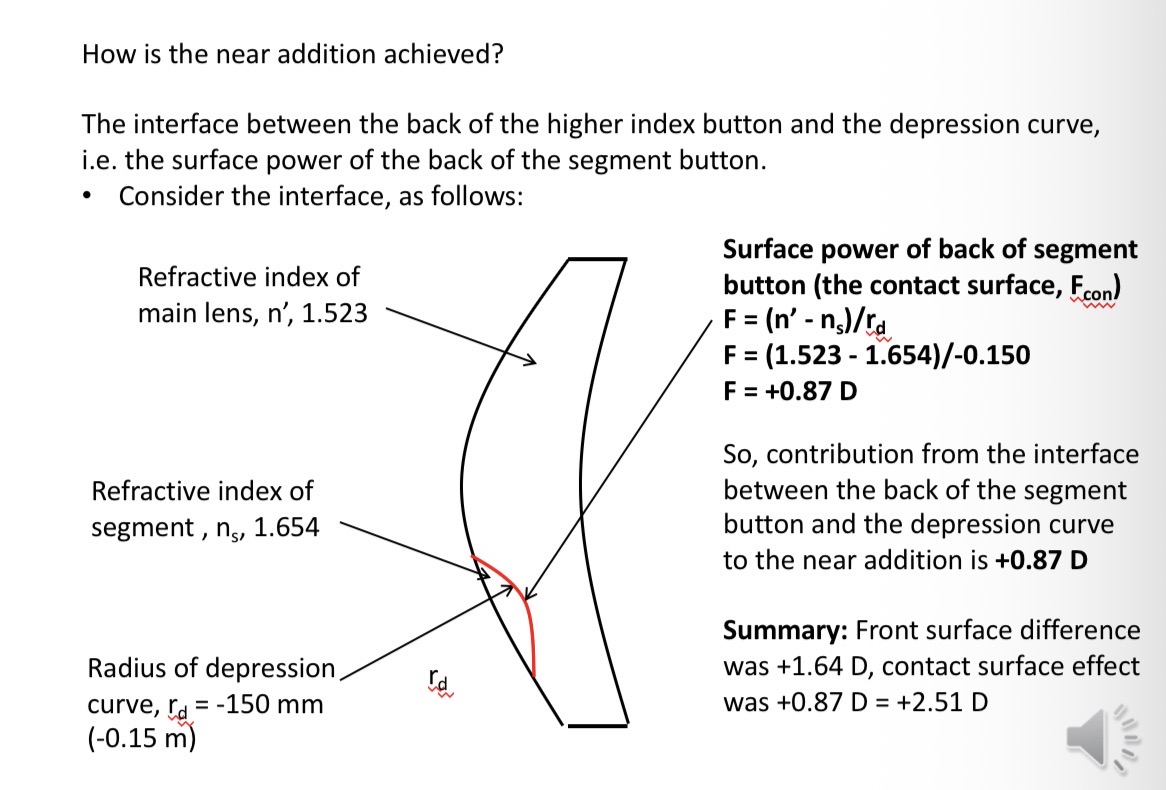
Near addition formula

What is the blank ratio (k) the relationship between
The relationship between:
The refractive index if the materials selected for the main lens and segment button
The power of the depression curve in air, Fc
The blank ratio formula

Formula to calculate the power of the depression curve inair from the blank ratio, add and front surface power

Formula to calculate the radius of the depression curve

How is addition achieved in solid bifocals
Different surface power between distance portion and near segment
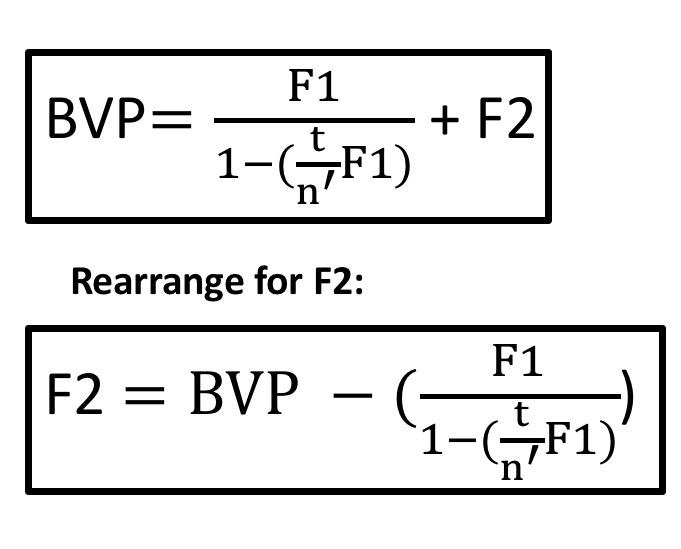
BVP formula
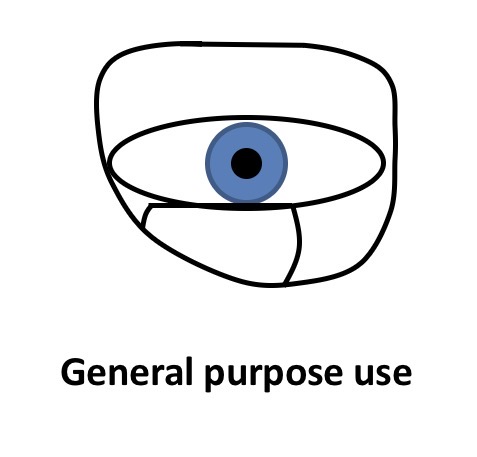
Where should the segment extreme point/top be positioned normally
Level with the lower limbus
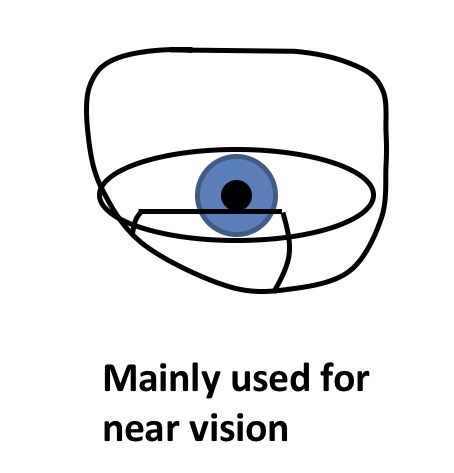
Where should the segment extreme point/top be positioned If specs are used mainly for near vision
Slightly above the lower limbus of the eye
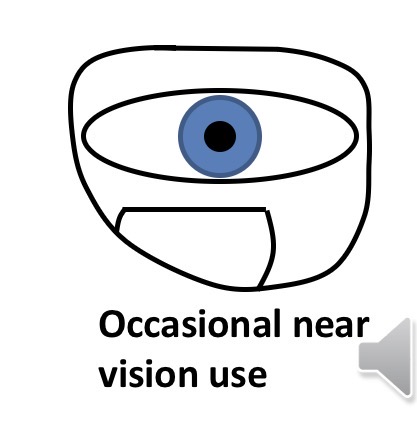
Where should the segment extreme point/top be positioned If specs are occasionally used for near vision
Lower than the lower limbus of the eye
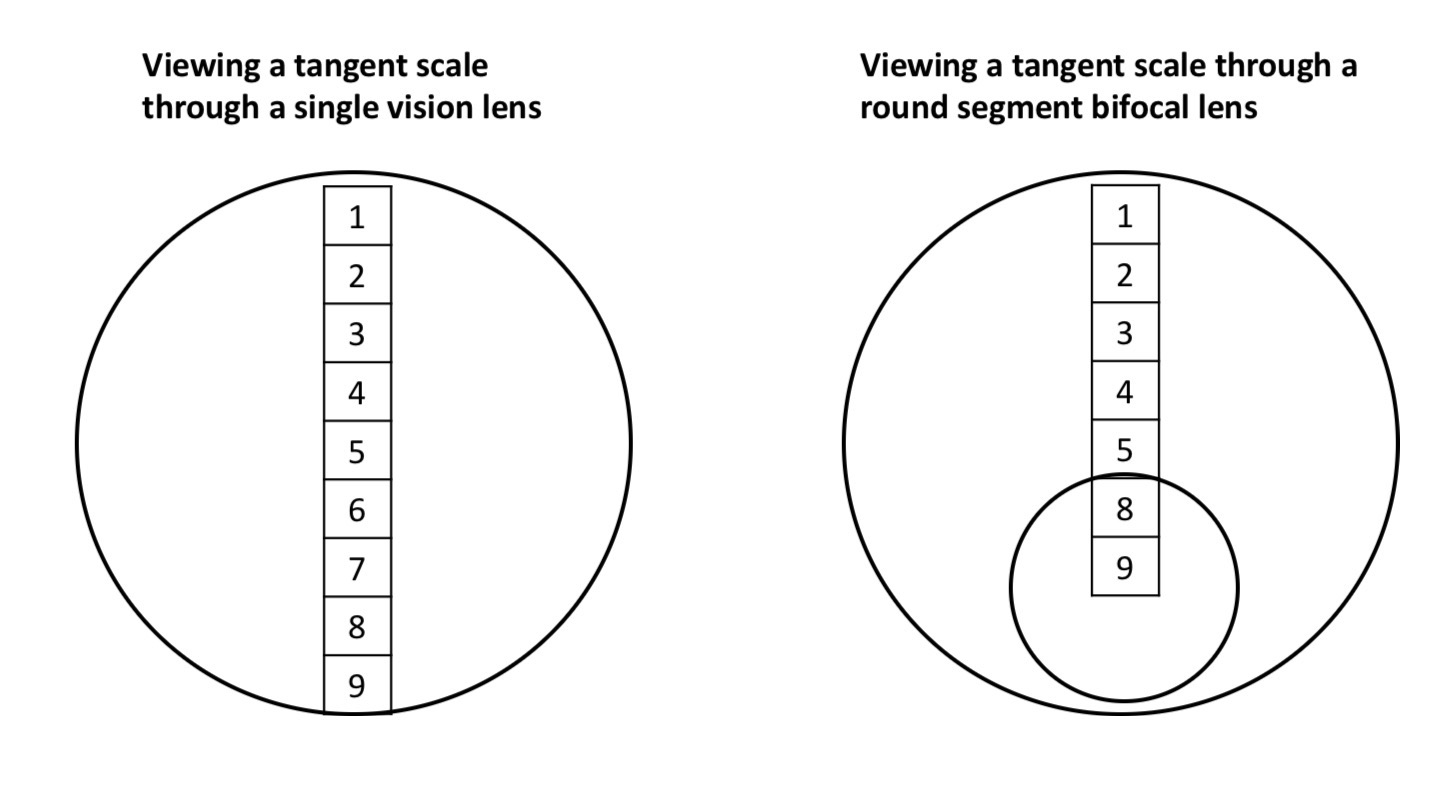
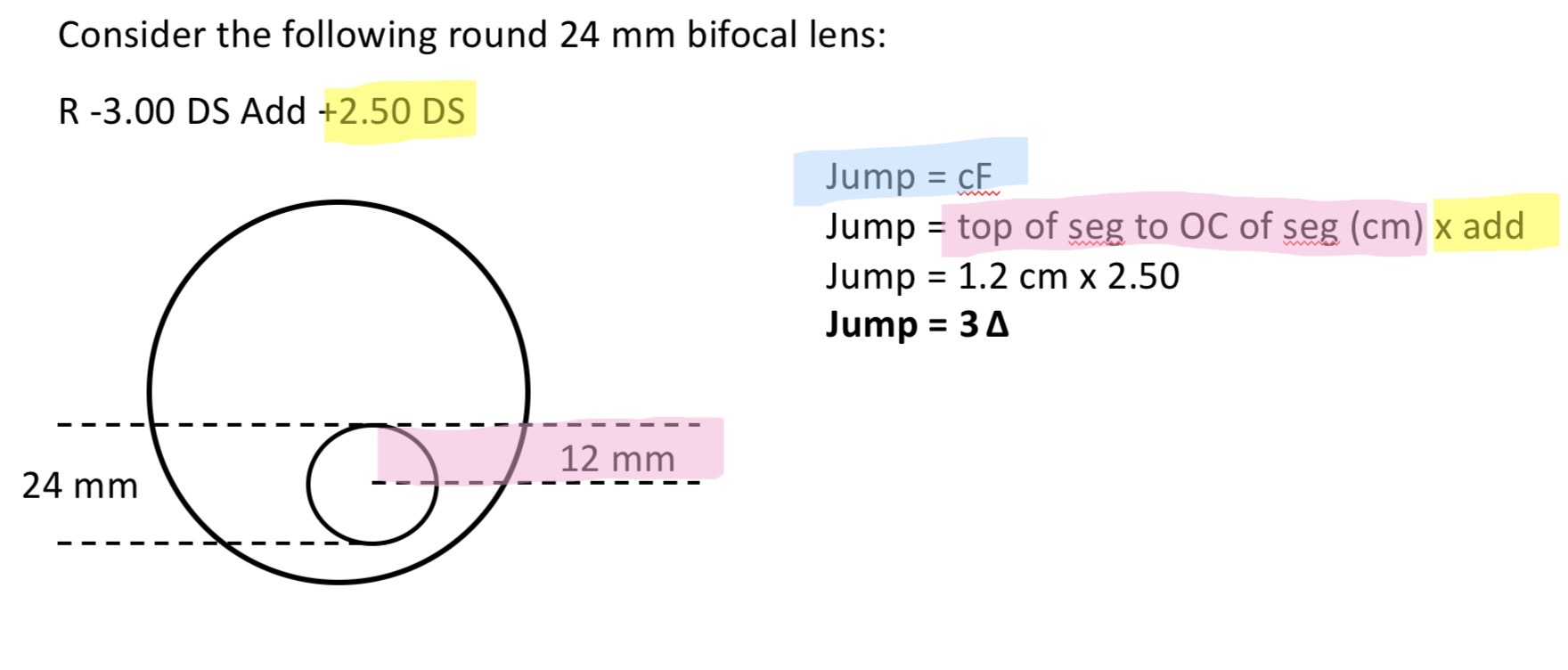
What is ‘jump’
Describe the sudden change in prismatic effect across the transition between the distance portion and the near segment of a bifocal
It can produce disturbing effects fir the pt where the image of an object moves suddenly as it crosses into or out the segment
Segment gives base down prism causing image to move upwards to top of segment
A consequence of this is a loss of visual field at the top of the segment
Formual to calculate the amount of jump
Jump = cF
c = top of segment to OC of seg (cm)
F = add
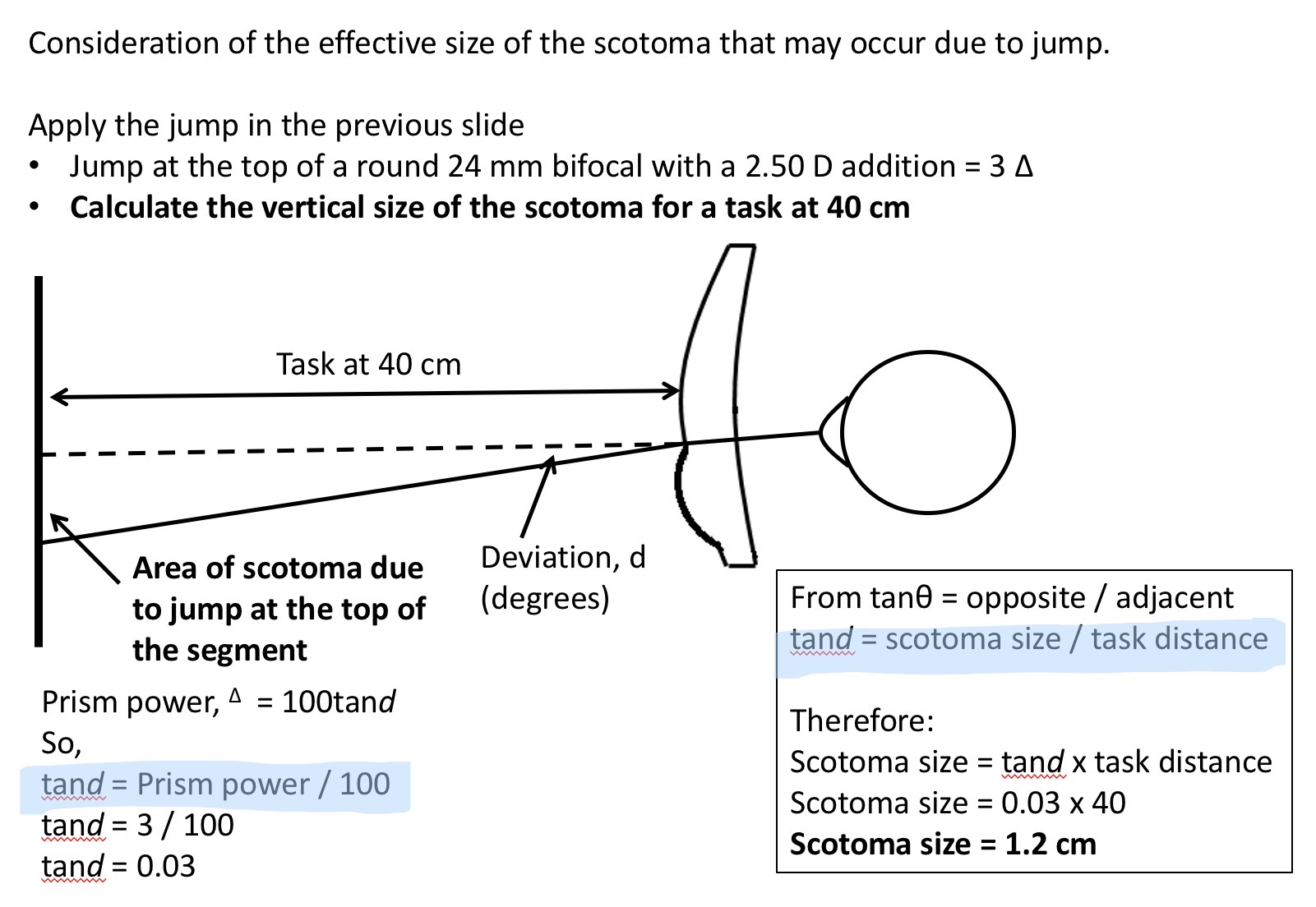
How to calculate the vertical size of the scotoma (vf loss in a jump)
calculate prism power
Prism power = 100 x tan (deviation angle)
Rearrange to work out tan (d)
scotoma size = tan (d) x task distance
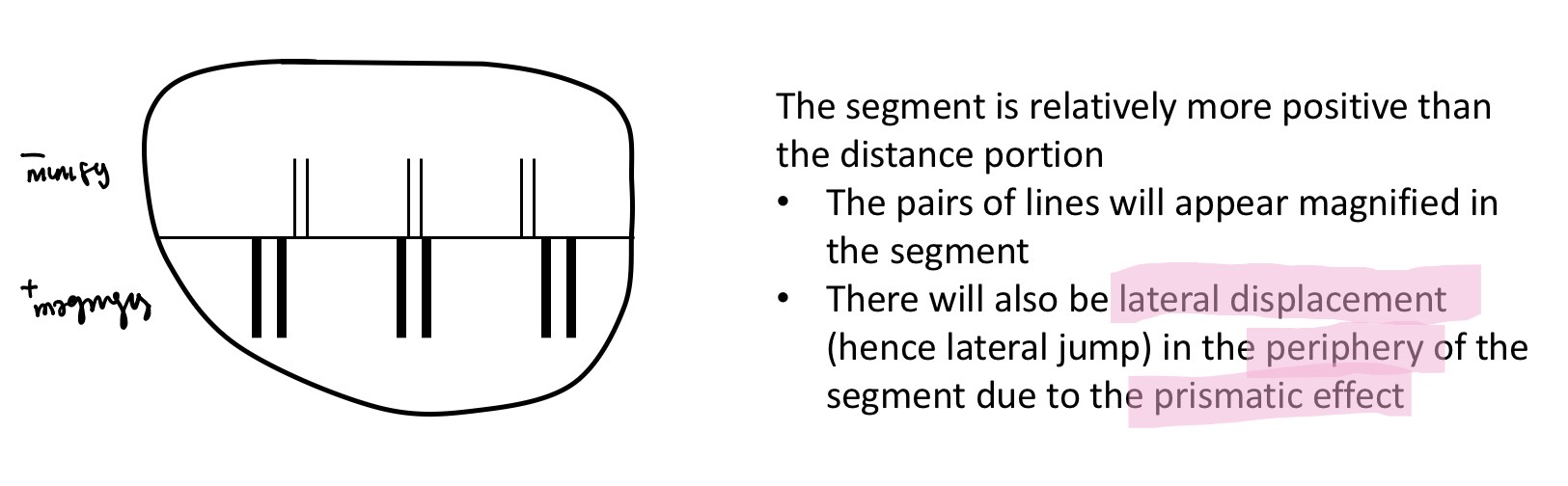
What is Lateral jump
Horizontal displacement of the image when moving between the distance portion and near segment
Most apparent with a high add and a large segmenr
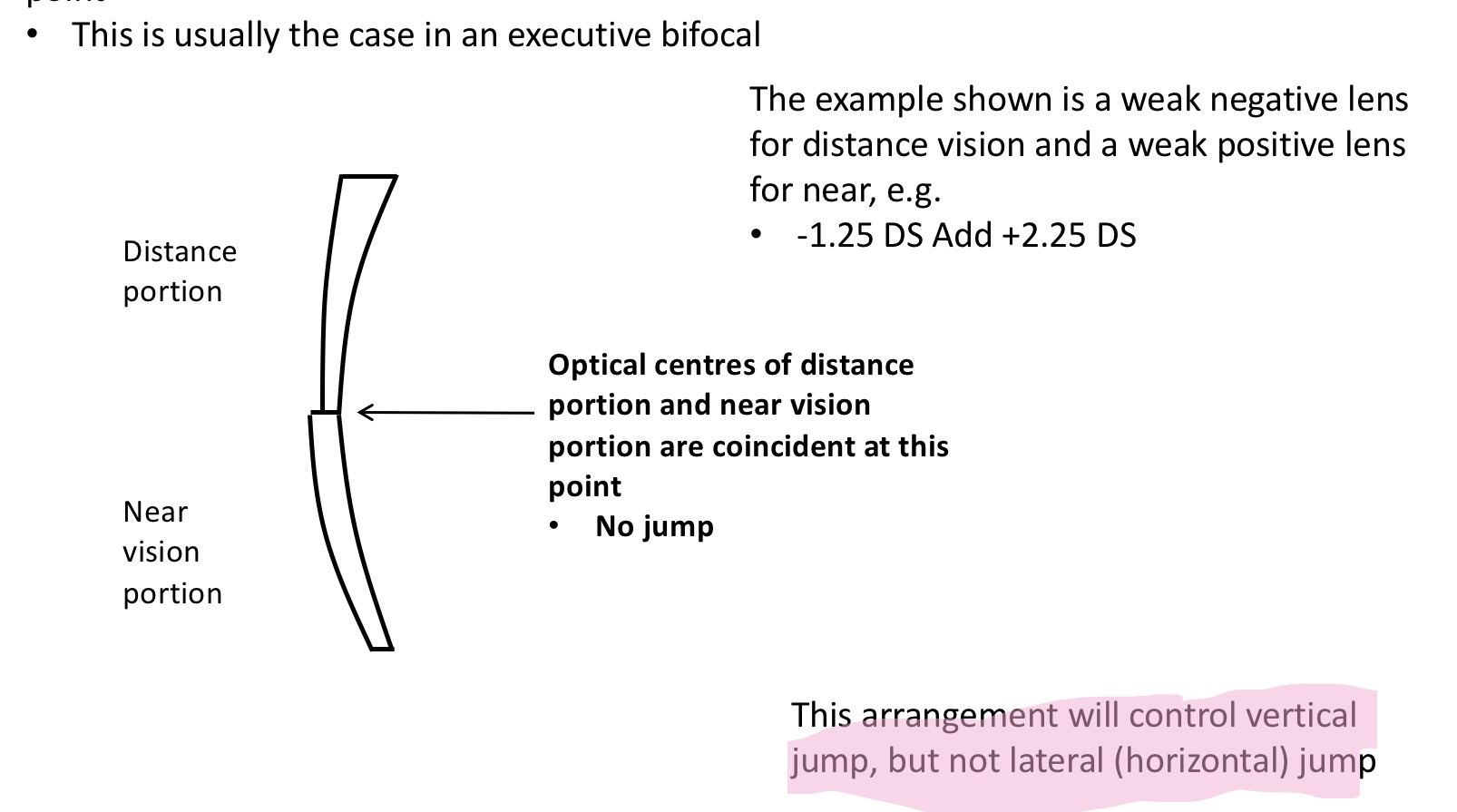
How to reduce vertical jump
By placing the optical centre of the distanc portion and the OC of the near segment at the same point
This is usually the case in an executive bifocal
Problem with anisometropes and bifocal lenses
They have a large difference (2DS) in refractive error between their eyes which creates issues with binocular vision
Pts could experience vertical dipopia in bifocals due to differential vertical prism between the two eyes
(Look at calcs)
How to reduce differential prism in anisometropes
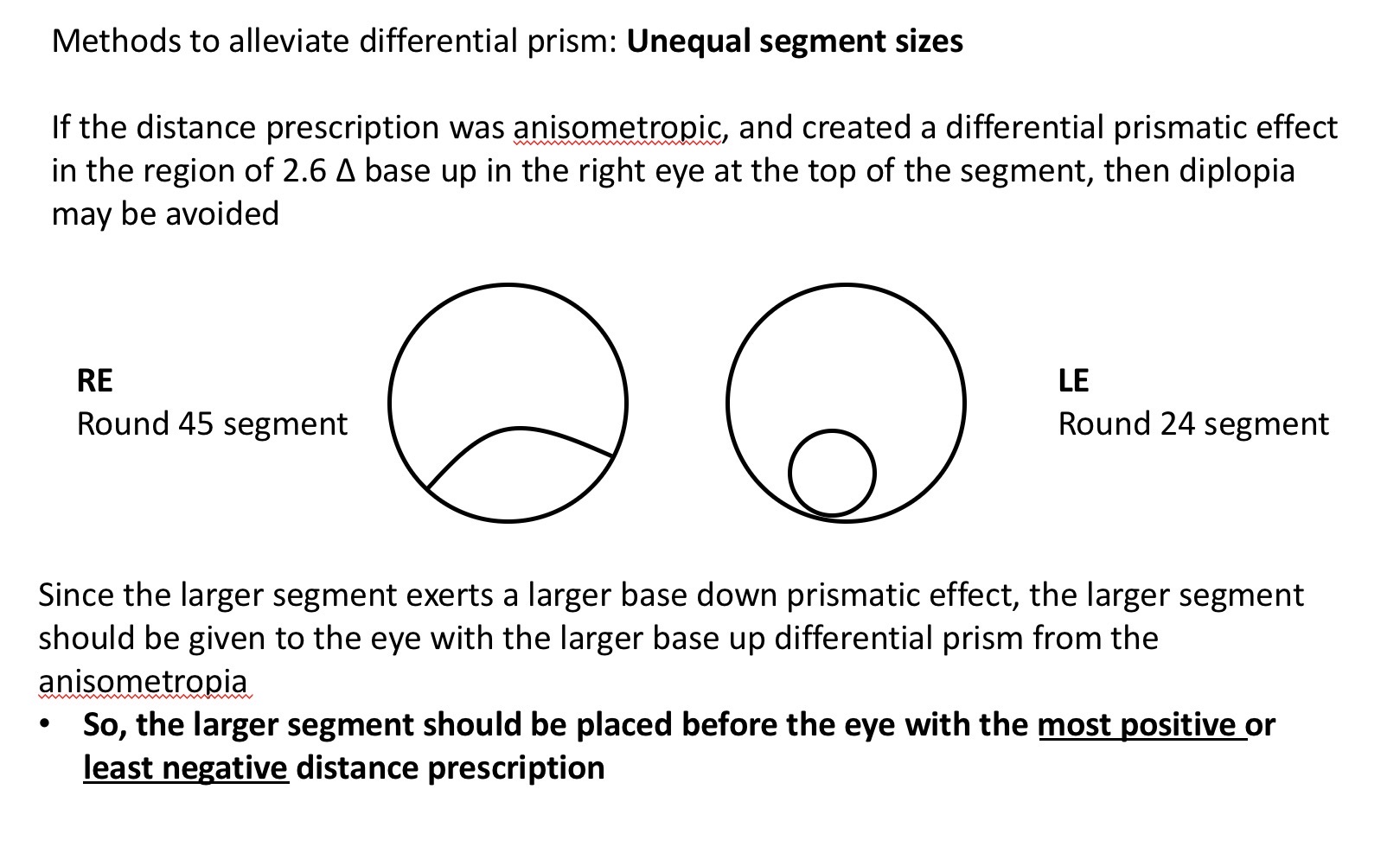
Unequal segment sizes
Since rhe amount if vertical prism is related to the diameter of the segement, placing a different segment size before esch eye might help reduce prism
The RE 45mm seg gives more base down prism than LE 24mm diameter
If near add was +2.25 at the top of RE there would be 2.50 × 2.25 = 5.6 prism dioptres base down
LE 2.50 × 1.2 = 3 prism dioptres base down
Giving a differential effect of 2.6 base down in RE at the top of seg …
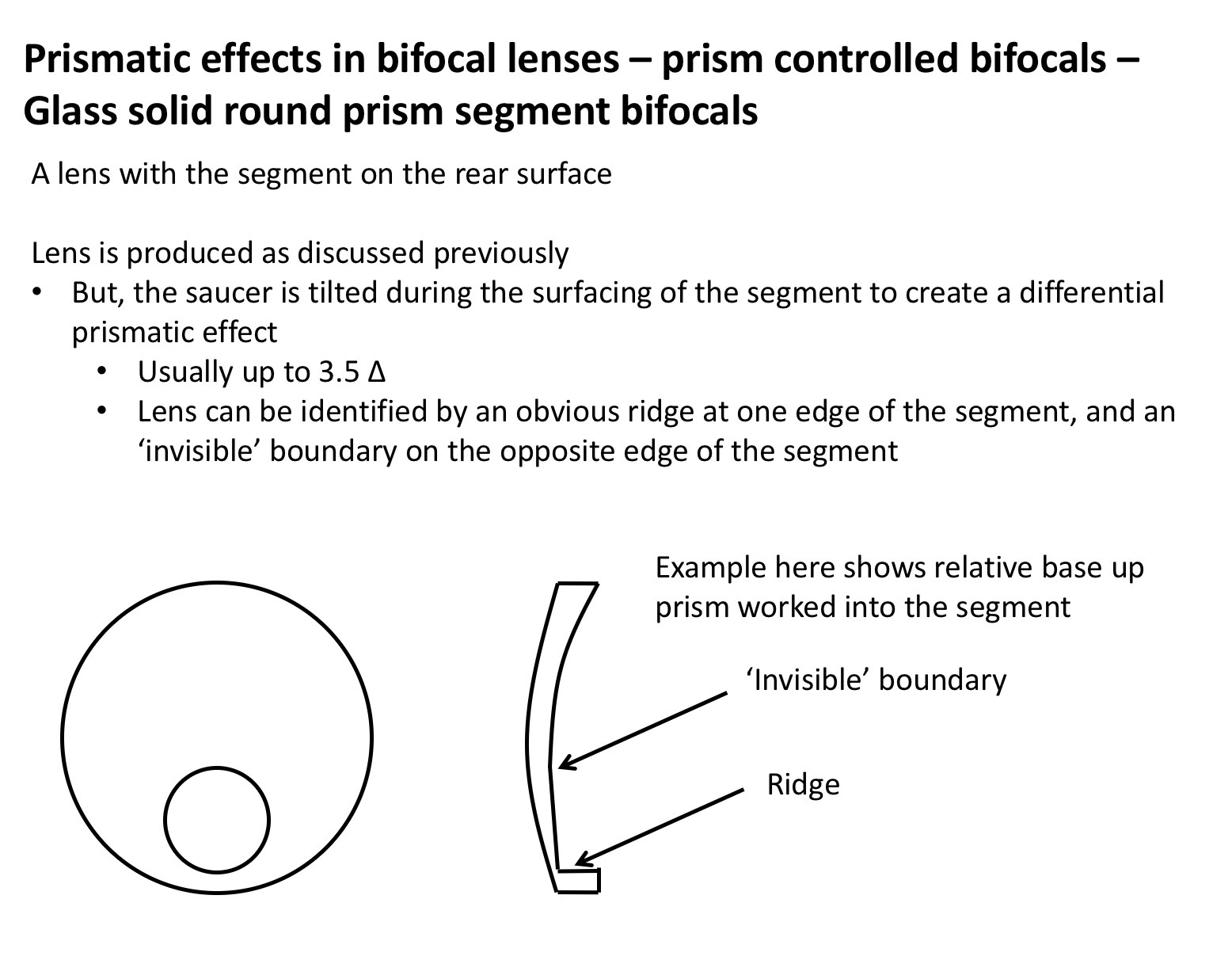
Prism controlled bifocals
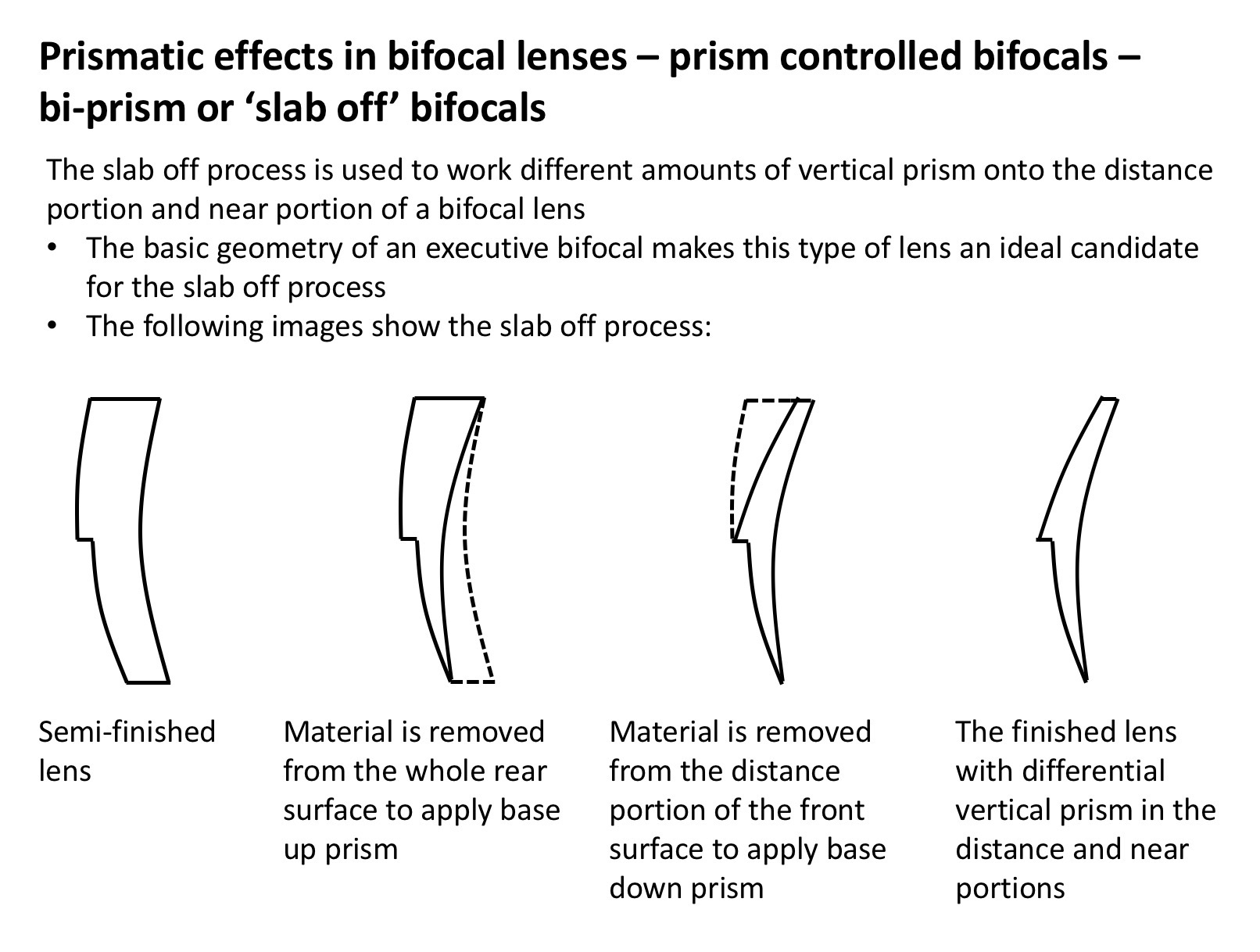
Slab off bifocals
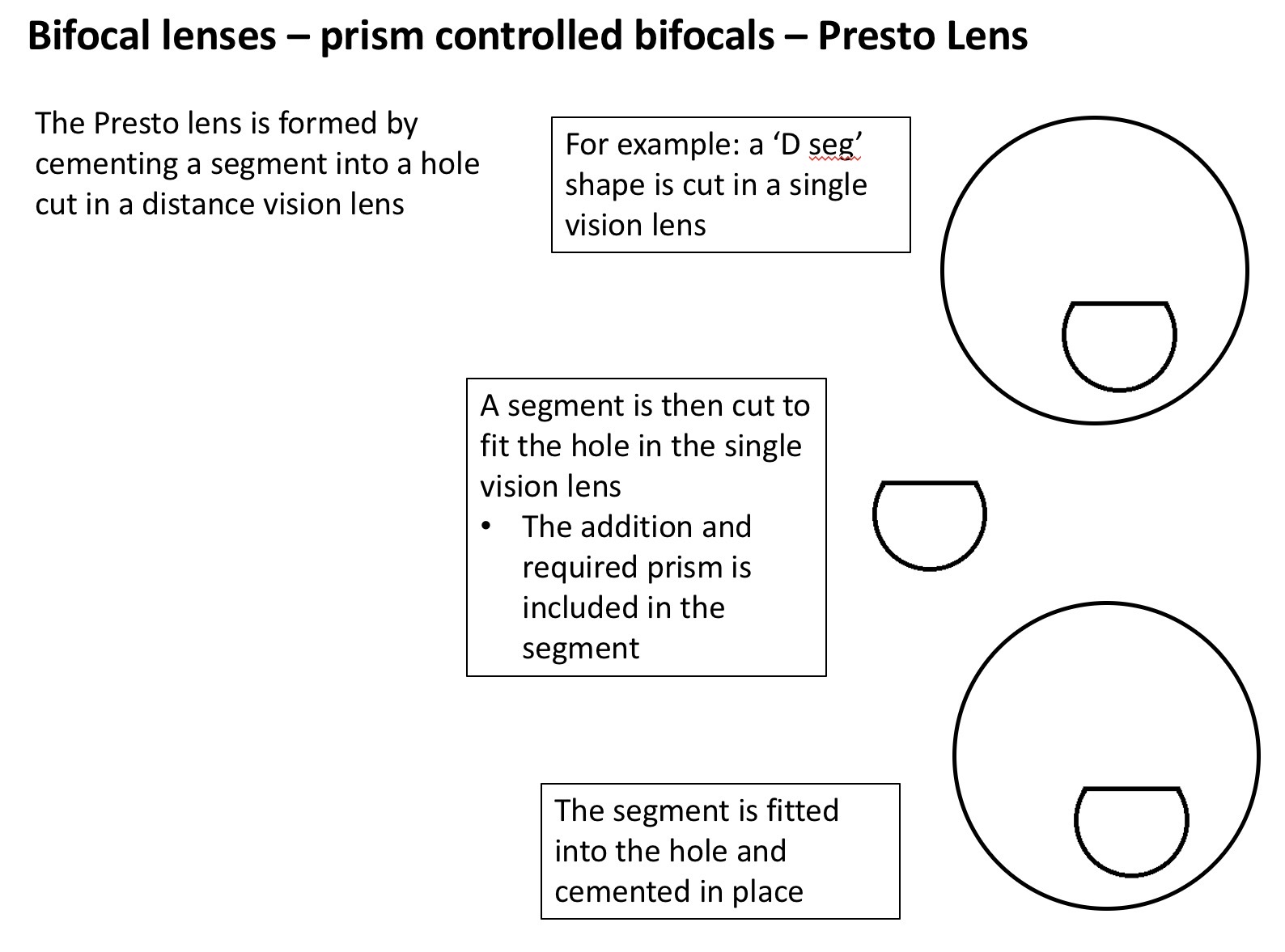
What is a presto lens