Heartworm Infection and Disease in Dogs - Lectures 16, 17, 18
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is the common name of Dirofilaria immitis?
canine heartworm
The following characteristics match which species:
large filamentous worms living in pulmonary artery and vasculature of dog, cats, and other mammals like pet ferrets
adult males, 12-20cm with coiled tails
femailed 25-31cm, non remarkable morphology
reproduction is viviparous
Dirofilaria immitis
What stage of reproduction is diagnostic for infection status of Dirofilaria immitis?
vermiform embryonic stage called microfilaria
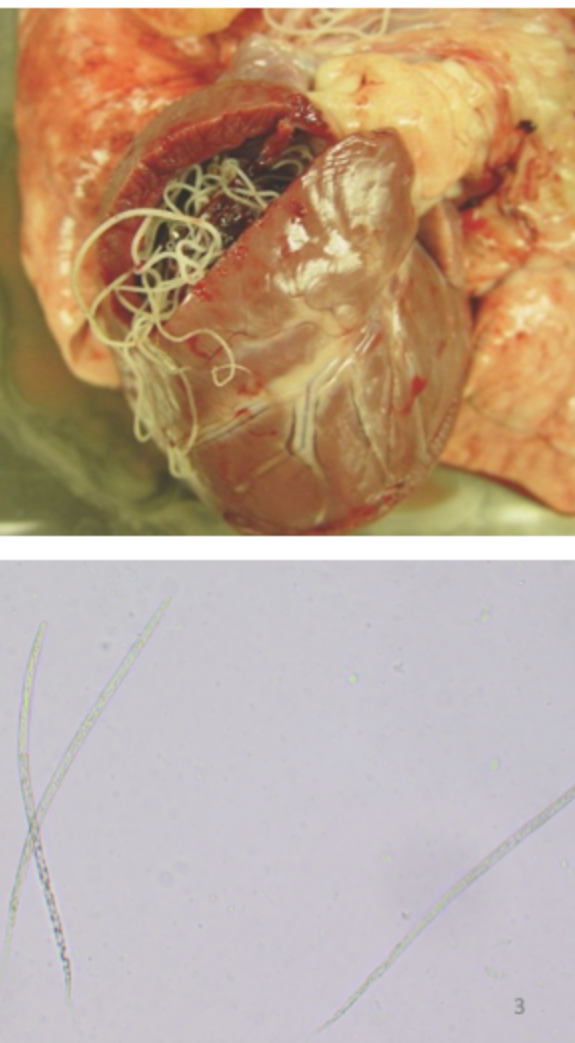
The image depicts what species?
Dirofilaria immitis
How are dogs infected with Dirofilaria immitis?
mosquiotes harboring infective stage larvae (microfilaria)
The following life cycle matches which species:
dogs infected by mosquito harboring infective stage larve
larvae migrate in SQ tissue and colonize the pulmonary artery 70-100 days post infection where they become reproducing adults
microfilaria begin circulating approximately 6 months post infection
female mosquitoes feeding on microfilaremic dogs complete life cycle
development to infective stage in mosquito takes approximately 14 days at >57F
Dirofilaria immitis
The lifecycle of canine heartworm is dependent on what for transmission of microfilaria to mosquito hosts?
infected animals
What factors affect transmission of canine heartworm?
vector efficiency
mosquito feeding activity
microfilarial activity in host
source and average number of blood meals taken
day/night time temperature variation
prevalence of microfilaremic hosts in area
Where do canine heartworms live in the host?
pulmonary arteries and right side of heart
What are the effects of canine heartworm infection?
obstructive fibrosis, pulmonary endothelial damage, and narrwing of vasculature bed with impaired blood flow
reduced cardiac output
What provides immune stimulation of the dog in cases of canine heartworm infection?
adult worms and their products
What can be seen on radiography in cases of canine heartworm infection?
reverse D radiographic profile
enlarged, thickened and tortuous pulmonary artery
pulmonary infiltrates in caudal lung lobes
Pulmonary hypertension due to canine heartworm induces what?
compensatory hypertrophy with enlargement of the right side of the heart
What is considered the most signfiicant veterinary health issue in companion animal medicine?
Canine Heartworm
What portion of canine heartworm disease pathogenesis is related to the following:
recognized as an inciting factor in heartworm associated inflammatory disease
present in arthropod vectors
transmitted in utero from adult female worms to their microfilaria
currently thought to be an essential element to heartworm infection of mosquito host and survival of adult worms in definitive host
Endosymbiotic gram negative bacteria
What can occur due to obstruction of glomeruli in canine heartworm disease?
kidney disease
What syndrome caused by canine heartworm disease is described:
large numbers of adult worms are pushed through the right atrium into the vena cava
presenve obstructus blood flow and interferes with action of tricuspid valve
blood passing through the worm clot is hemolyzed
jaundice, hemoglobinemia, and hemoglobinuria
fatal course of disease if not attended to promptly
caval syndrome
What can occur in severe cases of canine heartworm disease and is known as the disorder associated with massive activiation and consumption of proteins involved in coagulation?
DIC (Disseminated intravscular coagulation)
What can be a facilitating factor of disseminated intravascular coagulation?
heartworm induced pulmonary thromboembolism
Heartworm prophylaxis was transformed with the discovery of what?
Ivermectin in 1983
Ivermectin used how?
monthly administration to target the infective L3/L4 larval stage
What is the mechanism of action for Ivermectin and Moxidectin on adult nematodes?
high affinity for glutamate gated chloride channels causing flaccid paralysis of somatic musculature, a paralytic effect on pharyngeal pump, and inhibition of female reproductive output
How do macrocyclic lactone drugs kill filarial nematodes?
high affinity for glutamate gated chloride binding sites associated with uterine wall of adult females and male reproductive tract and the tissues around the excretory secretory pore of juvenile larval stages and microfilaria
Heartworm preventative prevent canine heartworm disease but do not prevent canine heart worm infection. What does this mean?
prevents disease resulting from reproductively active adult worms
kills infective L3 and early L4 larvae acquired over the previous 30 days since last treatment
What are signs of ivermectin toxicity?
tremors
ataxia
blindness
signs of toxicosis
Animals with what mutant allele have ivermectin sensitivity?
mutant MDR1 allele
Why is it important to distinguish infection due to lack of effectiveness from geographic isolates and “gaps” in owner compliance?
pharmaceutical liability for treatment for lack of effectiveness
It is important to establish the heartworm status of all pets at least once a year, how?
antigen and microfilaria testing
What disease is facilitated largely as an immune mediated inflammatory response to worm presence in the pulmonary arteries?
canine heartworm disease
What is a significant etiologic factor for inciting host inflammatory repsonse in canine heartworm disease?
Wolbachia pipientis
Most cases of canine heartworm disease occurring in animals on prophylactic programs result from what?
owner compliance issues (not lack of effectiveness)
What is the typical clinical presentation of a dog with heartworm disease?
adult dog, >6 months of age
exercise intolerant
outdoor animal
no consistent history of HW prophylaxis
Explain heartworm diagnosis by blood examination using a filter test.
based on examination of fresh blood collected in EDTA (purple top)
blood lysed in 2% formalin solution
microfilaria are concentrated on membrane
membrane examined microscopically on glass slide
Explain heartworm diagnosis by blood examination using a Knott’s test.
based on examination of fresh blood collected in EDTA (purple top)
blood lysed in 2% formalin solution
microfilaria are concentration by centrifugation
wet mount examined on microscope slide
The Filter test and Knott’s test are how many times better than direct microscopic examination of blood drop?
6 to 8 times
The following description matches which parasite:
length 280-300 micrometers
width 6.1-7.2 micrometers
head is tapered
tail is straight
Dirofilaria immitis
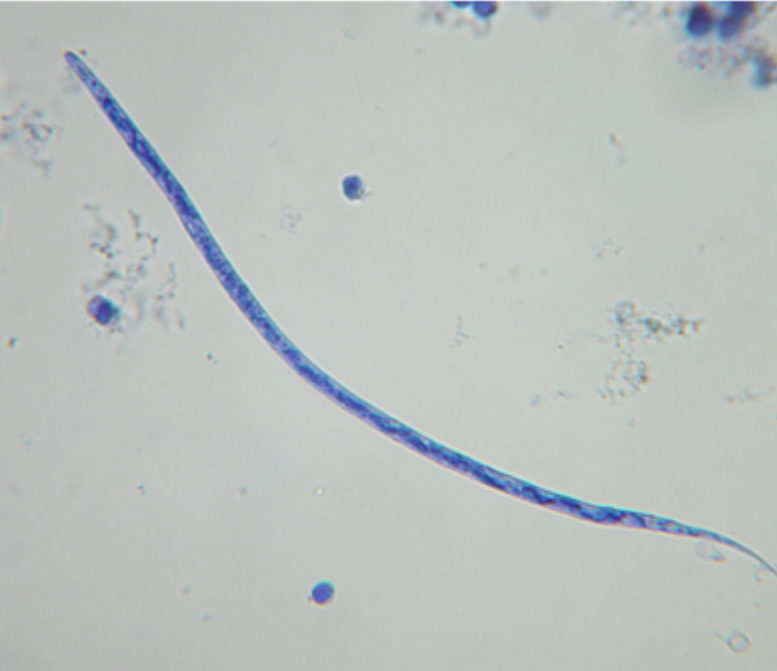
The image depicts what species?
Dirofilaria immitis
The following description matches which species:
nonpathogenic filarial worm that lives in SQ tissue
flea is obligate intermediate host
length 215-270 micrometers
width 4.7-5.8 micrometers
head is blunt
tail often hooked
Acanthocheilonema reconditum (aka Dipetalonema)
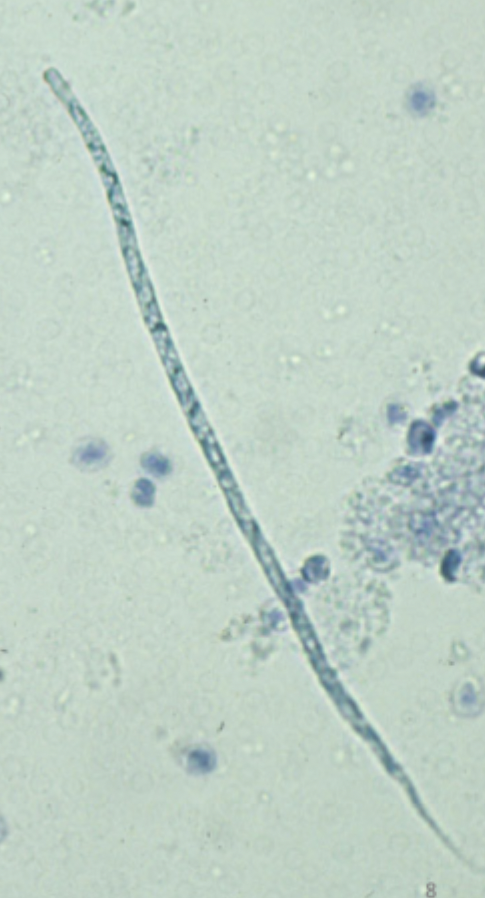
The image depicts what species?
Acanthocheilonema reconditum (aka Dipetalonema)
What diagnostic issues do we face for canine heartworm?
testing in companion animal practice to detect infection geared towards symptomatic animals and they are screening patient in relation to prophylactic programs
technology shift over last 30 years away from microfilaria detection and reliance on antigen testing
there is a renewed interest in microfilaria detection with recognition of drug resistant isolates
Describe serologic testing for heartworm.
commerically available test kits validated for use in dogs and cats
ELISA based formated directed at female uterine antigen
inexpensive and easy to use
positive test indicated by color change or develpoment of dot/line on reactiond evice
inherent test accuracy defined by sensitivity and specificity
Tests with poor sensitivity are susceptible to what test results?
false negatives
Sensitivity is affected by what?
amount of antigen available for detection (number of worms, sex ratio of worm infection, maturity of worms)
Define sensitivity.
the ability of the test to detect subjects with infection
Define specificity.
the ability of the test to detect those without infection
Specificity is affected by what?
false color development
poor ability to discriminate color/non color
poor washing techinque
cross reaction with other parasitic species due to shared immunodominant proteins
Poor specificity leads to what test results?
false positives
What is predictive value?
the probability that the test correctly discriminates between subjects with and without infection
Predictive value is a function of what?
sensitivity, specificity, and prevalence of infection in the population
Low prevalence is correlated with what?
poor positive predictive value (excessive false positives)
High prevalence of disease is correlated with what?
greater positive predictive value
How do we interpret positive canine heartworm test result?
first ask “which population characteristics best describe this client’s pet”
interpret test with appropriate PPV, confirm with radiographs, etc and treat accordingly
remember predictive value is greater with disease prevalence
What do we do when symptomatic animals test canine heartworm negative?
some clinically ill animals are known to mount a significant antibody response with effect of binding HW antigen in blood so not available for detection
sometimes these cases may be micofilaremic so Knott’s test ot DiFil test can assist diagnosis
radiogaphs and cross testing with another heartworm serology kit is also indicated
What do we do when healthy dogs on canine heartworm prophylaxis test postiive?
chances are this animal was probably infected during the last visit, but the test was false negative because it was conducted during prepatent period (susceptibility gap)
if owner compliance reliable, then animal may only have a couple worms and can be manage without problems
What are the objectives for treatment of canine heartworm infection?
to mitigate the clinical condition of the affected animal
to arrest the disease process by elimination of adult worms and their migrating stages
to elimiate microfilaria that are infectious to mosquitos and susceptible hosts that constitute a reservoir for maintenance of the parasite and further transmission
What are the 3 phases of treatment for canine heartworm?
pre-adulticide clinical evaluation and treatment
adulticide treatment
post-adulticide evaluation and treatment to eliminate microfilaria if necessary
What is included in the preadulticide clinical evaluation and treatment phase?
clinical evaluation
removal of heartworm larvae and Wolbachia
What is included in the adulticide treatment phase?
Melarsomine dyhydrochloide to kill adult worms greater than or equal to 100 days post infection in pulmonary artery (2 or 3 injection protocols available)
“slow kill” alternatives (not endorsed by AHS, CAPC, or FDA labeled)
What is included in the post-adulticide evaluation and treatment to eliminate microfilaria if necessary?
antigen testing to verify treatment effectiveness
microfilaria testing and treatment
What does early treatment (diagnosis to day 30) involve?
pre adulticide clinical evaluation at diagnosis: classify patient as symptomatic or asymptomatic, blood chemistry panel, radiographic evaluation, blood exam for microfilaria
1st treatment to remove migrating heartworm larvae acquired within last 30-45 days prior to diagnosis using Ivermectin, Selamectin, Milbemycin, or Moxidectin
Treatment to remove Wolbachia using doxycycline at 10mg/kg BID x4 weeks to reduce risk of thromboembolic complications, enhance killing activity of adulticide, and render microfilaria uninfective to mosquitoes
2nd monthly prohylactic treatment at day 30
What does adulticidal treatment (day 60 to Day 90) involve?
removal of adult worms in pulmonary artery/right ventricle using immiticide or diroban (melarsomine dihydrochloride)
treated animal on cage rest and leash walk for 6-8 weeks
What immiticide treatment regimens are there for day 60 to day 90?
classic FDA labeled (2 injection) for stabilized class 1 and class 2 at 2.5mg/kg, IM deep epaxial lumbar, SID, 24 hours apart
AHS/CAPC recommended 3 total injections without regard to heartworm disease class at 2.5mg/kg, deep epaxial lumber, SID, once at day 60 following initial diagnosis and repeat twice at 24 hour intervals on day 90 and 91 post diagnosis
Why do we use Diroban (melarsomine dihydrochloride) as our preferred immiticide in adulticidal treatment?
safe, highly effecacious (90-98%)
only effective against adult worms in pulmonary artery at 100 days post infection
expedient, full course treatment in 60-90 days
low risk of hepatotoxicity
What risk do you run when using Diroban (Melarsomine Dihydrochloride) as an immiticide?
pulmonary thromboembolism risk
Describe the Moxy-Doxy “slow kill” adulticidal treatment.
advantage multi (Imidicloprid + Moxidectin) monthly for 10 months
Doxycyline 10mg/kg BID for 30 days
efficacy 95.9% elimination of adult heartworms
killed microfilaria by 21 days
Describe the original “slow kill” ivermectin adulticidal treatment.
efficacious over extended period of time (71% when given over 24 months, 95% at 29 months)
pulmonary thromboembolism risk
heartworm associated inflammatory disease stilll ongoing
Describe the new “slow kill” regimen of ivermectin.
ivermectin 6-8 micrograms/kg, SID at 15 days intervals for 6 months
doxycycline 10mg/kg SID for 30 days
efficacy 78% at 36 weeks post intiial treatment
killed microfilaria by 12 weeks
How do we mitigate the post-adulticidal risk of thromboembolism?
exercise restriction
treatment of Wolbachia with doxycycline
Although corticosteroids are recommended to suppress the inflammatory response of host in adulticidal treatment, why should we not give them?
dogs receiving prednisone appeared to have higher risk of thromboembolism
aggravation of intimal disease, act as pro-coagulants, and reduce pulmonary blood flow necessary to clear deteriorating worms and debris
What is the only FDA approved adulticidal treatment for heartworm?
Melarsomine
Is Moxy-Doxy endorsed by AHS and CAPC?
No
Why do we add doxycycline to our treatment regiments?
because all treatment effects are enhances with its use
reduction of inflammatory biomarkers
mitigate pathological changes
renders microfilaria non-infective to mosquitos
What is your first responsibility when considering heartworm disease?
to address the health of your patient (clinical condition and prep for successful tx outcome)

You are given the case study attached. What caused the patient’s adverse reaction?
Patient being started on Milbemycin oxime caused this reaction. This makes us think patient had a large presence of microfilaria in its system as Milbemycin oxime is known for killing all present microfilaria within 24 hours. Thus, if this patient had a large presence of microfilaria, then a kill that fast would have thrown the patient into shock.

You are given the case study attached. What diagnostic measures and treatment options should have been employed to prevent this outcome?
Should have checked for microfilaria prior to starting Milbemycin oxime. If they had check for microfilaria prior to starting that drug, then they would have known of the large microfilaria presence and never started Milbemycin oxime in the first place. Instead, they would have used a slower kill method to avoid throwing the patient into shock like ivermectin and doxycycline.
What is the most important factor driving transmission of Canine Heartworm Disease?
the occurrence of microfilaremic hosts in the area
Canine heartworm disease is prevented by the monthly administration of prohylactic drugs classified as macrocyclic lactone (Ivermectin, Milbemycine, Moxidectin). What is the best explanation for how these drugs prevent CHWD?
The drugs kill all infective larvae acquired in the 30 day period prior to the monthly treatment
A patient is identified as CHW positive with a reputable antigen detection assay. Which population tested is associated with the highest positive predictive value?
dogs receiving prophylaxis but showing clinical signs suggestive of CHWD
What role do microfilariae play in the heartworm lifecycle?
they are embryonic stage larvae and must develop in mosquitoes before becoming infective to canine hosts
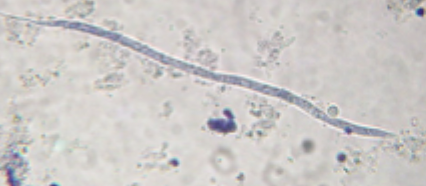
Microfilariae that look like these (300 micrometers long) were found in the blood of an adult beagle. What is their clinical signfiicance?
they are embryonic stage larvae and must develop in mosquitos before they are infective to canine hosts