Communities
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Rarefaction Curves
Most species are rare; very few species are common
Ecological Niches
Every organism has a set of environmental parameters that they can live in
Ex. Temperature, humidity, color, etc.
Fundamental Niche
Full spectrum of all environmental conditions
Realized Niche
The actual environmental conditions they can live in
Barnacles
If two organisms have the same niche, they cannot live in the same place
Competitive Exclusion
Multiplicative growth, but they must hit carrying capacity. If they both have the same niche, only one can occur there, and the other goes extinct.
Ex. Neanderthals
Resources Partitioning
Species that all use the same habitat, but different parts of it
Character Displacement
Two sympatric species with broadly overlapping distributions of resource use
Community Composition
What enables species to coexist
Species evenness: Most species in most communities are rare
Ex. Salt Marshes - species-poor
Ex. Fens - species-rich
Competitive Exclusion vs Resource Partitioning
Competitive exclusion involves species that have the same niche, while resource partitioning refers to species that fill different niches in a habitat.
Body Size and Tropic Level
Most species are small - advantageous to have a large body mass because it’s lower metabolism per unit pass + large individuals eat larger prey and escape predation
Larger population densities → reduced extinction risk
Energy
Only 2% of the usable light that hits the planet is absorbed by plants, 98% gets frittered away
GPP: Gross Primary Productivity
All the light that is converted to biomass
NPP: Net Primary Productivity
Light that is passed from plants to herbivores and all other trophic levels of heterotrophs
1st Level: Respiration
2nd Level: Primary Consumer (Herbivores)
3rd Level: Secondary Consumers
4th Level: Apex Predators
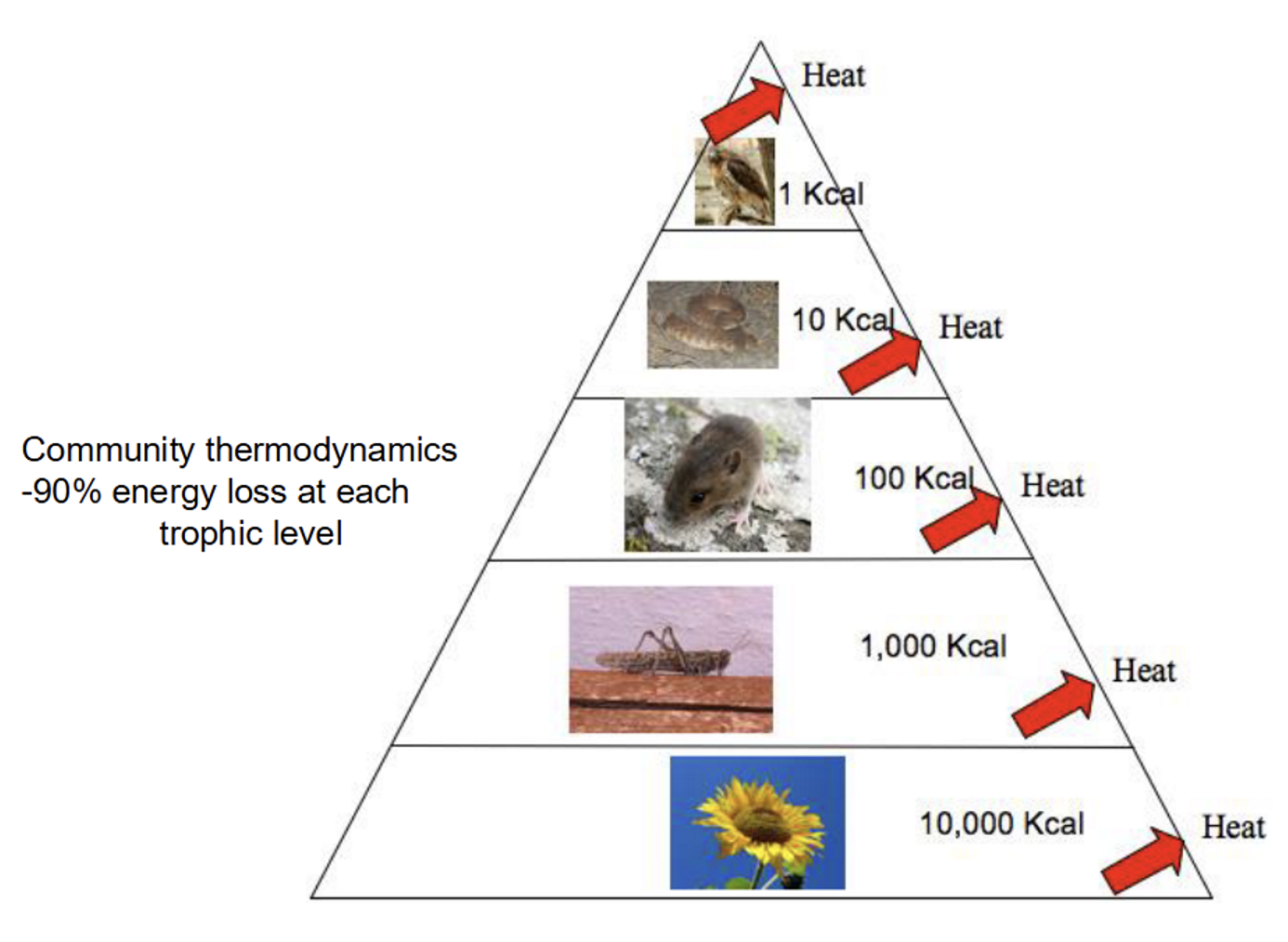
Trophic Pyramid
90% energy loss at each trophic level
Big animals are rare because there’s barely any energy at that level
Free-living herbivores are more abundant, predators of herbivores, and then predators of predators
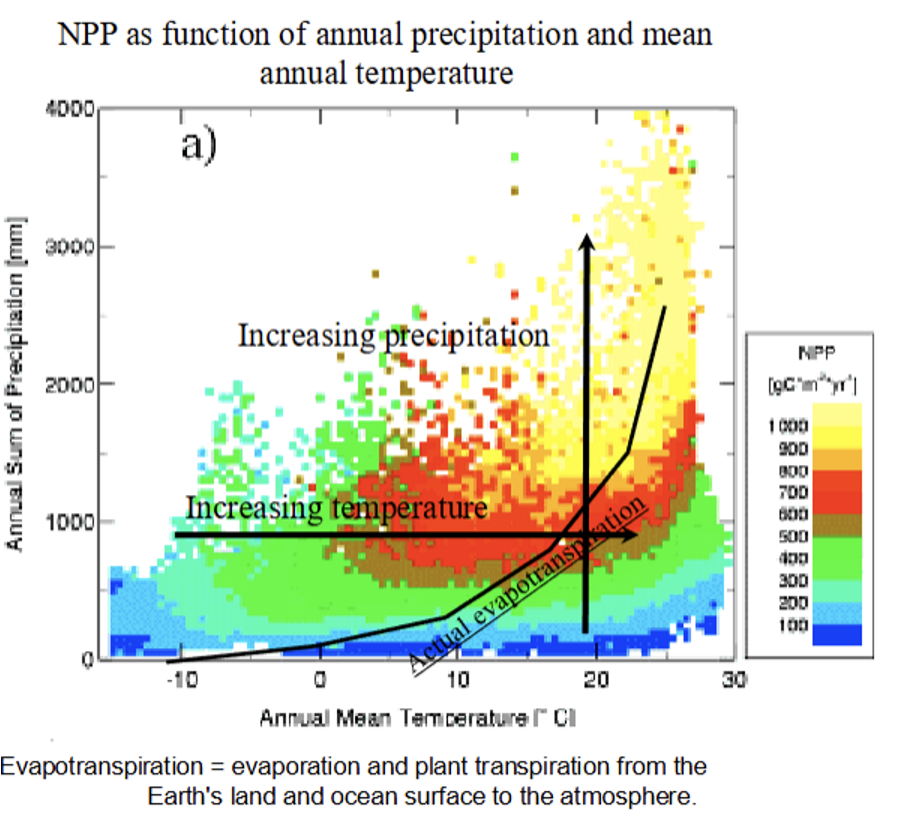
Tropics: Evaporation + Transpiration
The Hotter it is, it gets too hot for productivity to occur. However, if there's an increase in water, there's a latitudinal gradient that tells us about where species occur and where species diversity changes on the plant
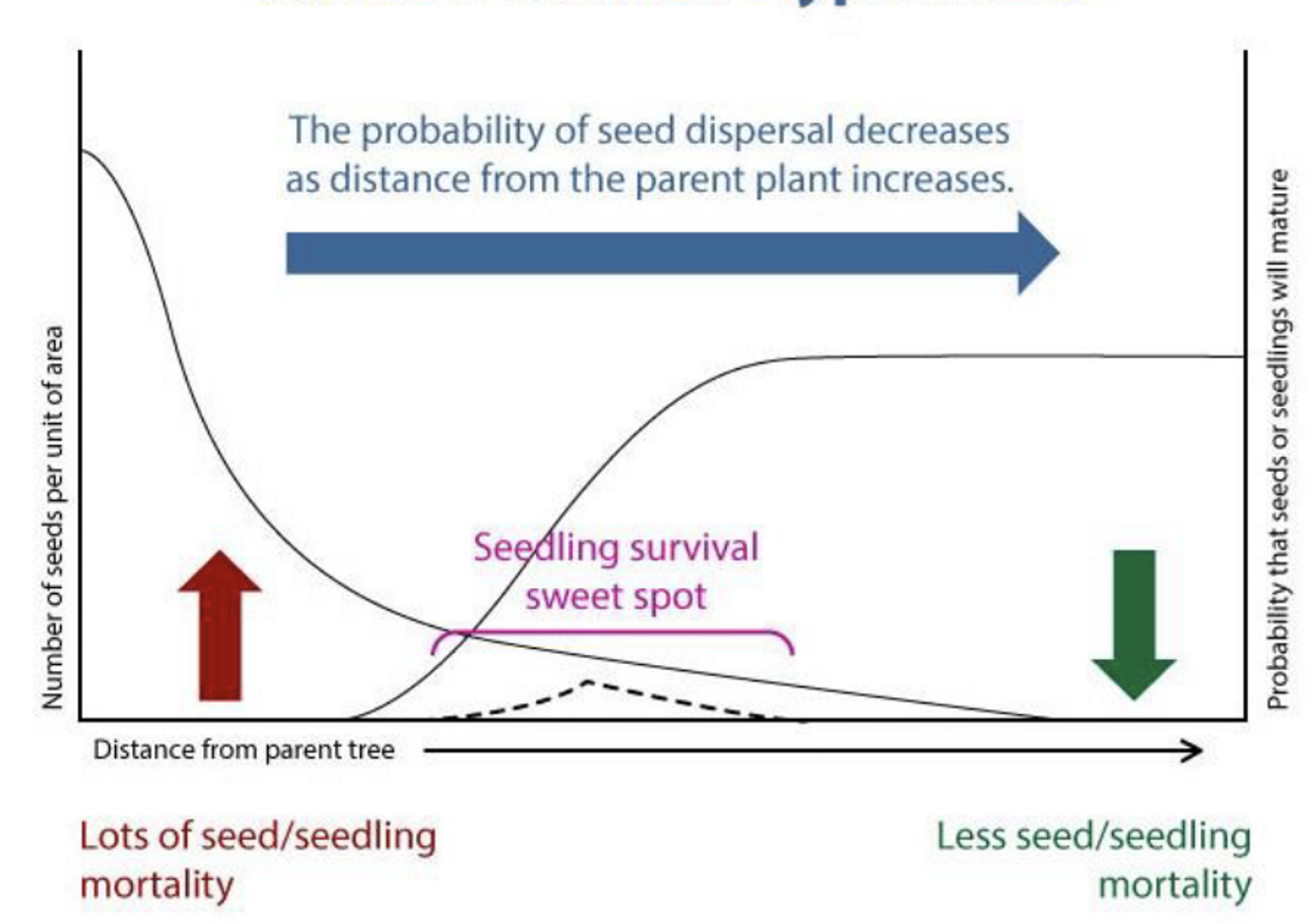
Janzen-Connel Hypothesis
The probability of seed dispersal decreases as distance from the parent plant increases
Insect herbivores only ate seeds of specific trees
High predation rates in areas w/ high seed fall
High Equilibrium Diversity in Tropics
a) Climatic stability
i. allows specialization, tighter niche packing
ii. new niches
b) Biotic Interaction: Stable climate → more predators and pathogens → numerical dominance of best competitors
c) Productivity: Increases toward equator; allows more specialization
Swallowtail Diversity
Increasing levels of specialization towards the tropics that allows more species to co-occur
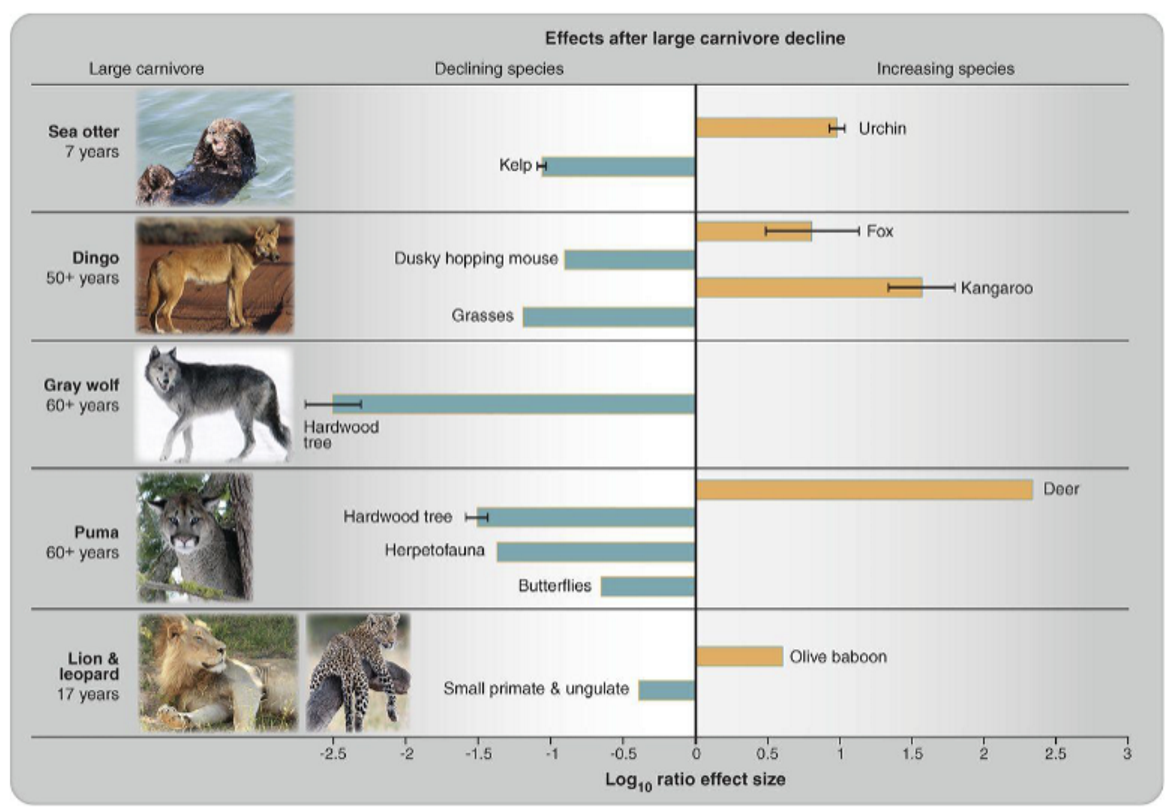
Carnivore Loss Around the World
Habitat loss, human interactions, no prey to hit on
Predators don’t mix with livestock
Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis
At low levels of disturbance, you get a few species b/c the best competitors take over
At high levels of disturbance, there aren’t many species b/c the species that are there are really good at colonizing disturbed habitats
Highly disturbed: Small boulders, Low Disturbance: Big Boulders, Medium Disturbance: Medium Boulders